structure and properties of graphite
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
graphite is an allotrope of carbon - what is an allotrope?
Allotropes are structures that have the same chemical properties but different physical properties due to differences in structure and bonding.
how many covalent bonds should carbon form to gain a full outer shell?
because carbon is in group 4, it will need to make four covalent bonds to gain a full outer shell
how many covalent bonds does carbon form in graphite?
3 - this leaves one delocalised electron for every carbon atom
how are the carbon atoms structured in graphite?
they form layers
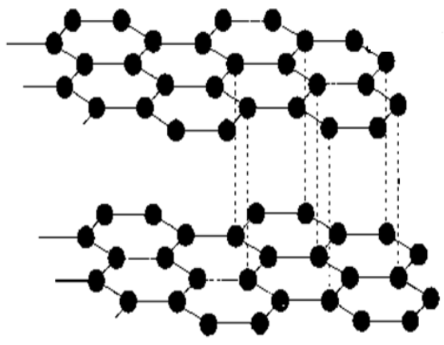
what is the difference between graphite and graphene?
graphene is just one layer of graphite
what is true about graphite’s hardness and why?
graphite is not very hard, but soft and slippery instead
there are forces of attraction between the multiple layers but they are very weak, meaning that when a force is applied they can slide over each other
what is true about graphite’s ability to conduct electricity and why?
unlike most other giant covalent structures, graphite is able to conduct electricity
because carbon forms 3 covalent bonds instead of 4, there is one delocalised electron for every carbon atom
this electron can carry a charge through the layers of graphite, meaning it can conduct electricity