MLAB 173 Midterm practice
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
3 functions of skin?
protection (UV + Pathogens), sensation, temperature regulation
2 any lab tests for a skin disorder?
Biopsy - melanoma, blood test - allergies
what muscle cells have centrally located nuclei?
cardiac, smooth
what muscle cell has peripherally (branching away from the centre) located nuclei?
skeletal
what muscle cells have striated appearance?
skeletal, cardiac
what vitamin is for calcium absorption?
D
during growth, what is it called when connective tissue transforms into cartilage or bone?
ossification
what bone is located inside the bone and contains cavities for bone marrow?
cancellous
What bone surrounds spongy bone and provides support?
compact
functions of skeletal system in terms of storage and production?
calcium, blood cells
bone cell that destroy bone?
osteoclast
bone cell that builds new bone?
osteoblast
what connects bone to muscle?
tendon
where are intercalated discs found?
cardiac muscle
energy source needed for muscle contraction?
ATP
3 main parts of a neuron?
cell body (soma), dendrites, axon
what cells provide protection and support for PNS and CNS?
neuroglia
neuroglia of PNS?
schwann and satellite cells
neuroglia of CNS?
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglial cells
autonomic nervous system control voluntary or involuntary functions?
involuntary
somatic nervous system controls voluntary or involuntary functions?
voluntary
glucose is stored in?
liver and muscles
how is liver responsible for hematological regulation?
produces blood clotting proteins, processing and storing iron
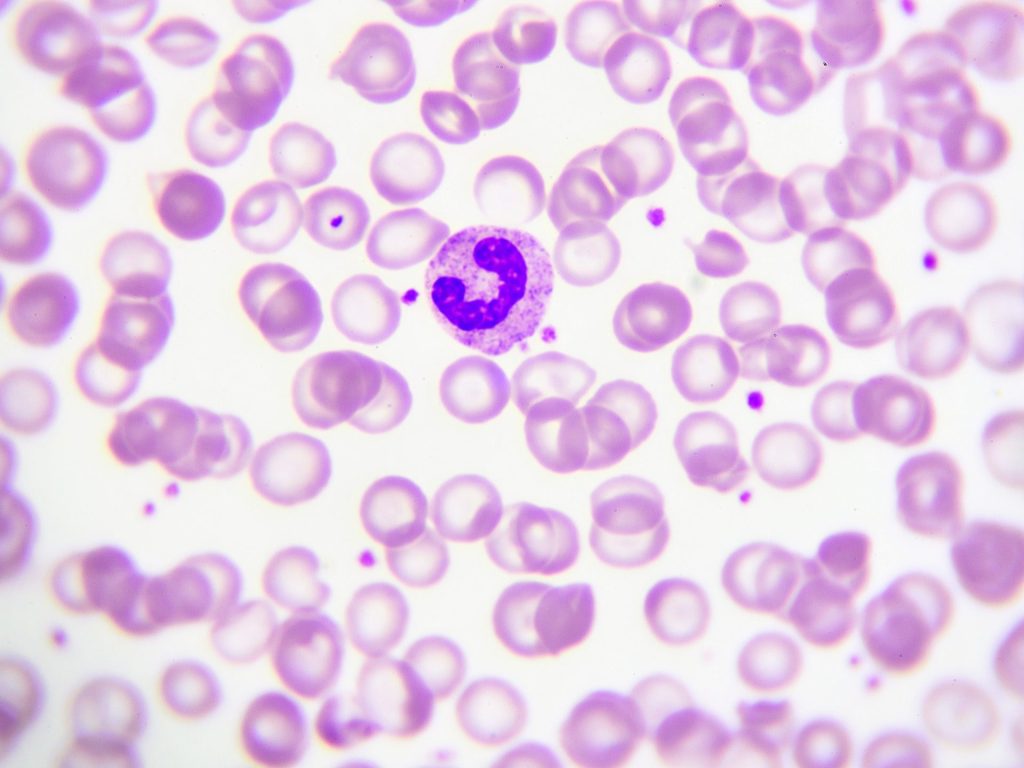
what WBC is the big one (multi nuclei)? what is its cell type? functions?
neutrophil, granulocyte, phagocytosis
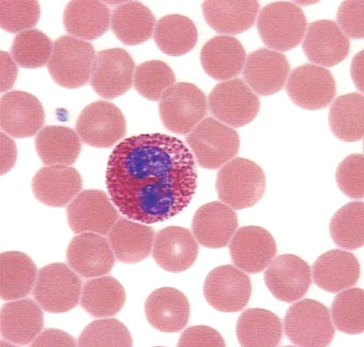
what WBC is the big one? what is its cell type? functions?
lymphocyte (T or B), agranulocyte, T cell attacks directly, B cell produces antibodies
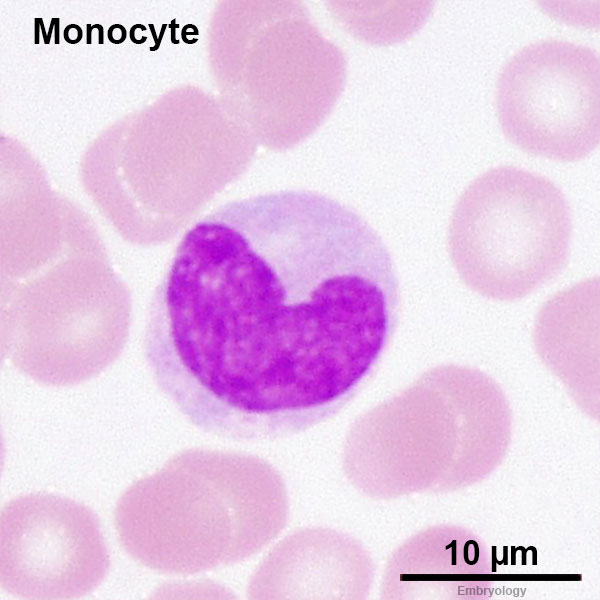
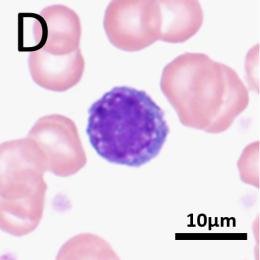
what WBC is the big one? what is its cell type? functions?
monocyte (Macrophage when active), agranulocyte, phagocytosis
what WBC is the big one? what is its cell type? functions?
eosinophil, granulocyte, ingest + detoxify foreign protein
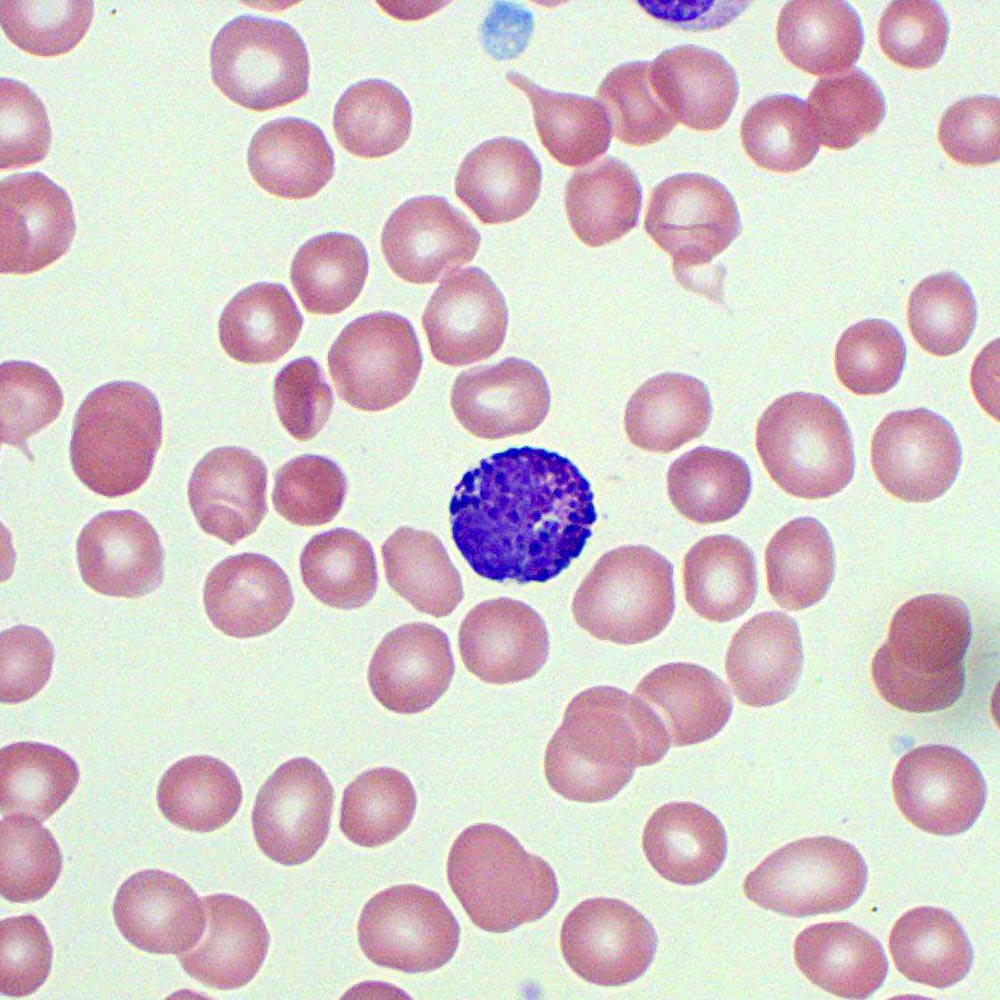
what WBC is the big one? what is its cell type? functions?
basophil, granulocyte, release histamine and heparin
granulocyte vs agranulocyte?
granulocytes have visible granules, agranules dont
3 steps for hemostasis?
vascular spasm, platelet plug formation, coagulation
process of breaking down a blood clot?
Fibrinolysis
substance that keeps alveoli from collapsing?
surfactant
carbondioxide is carried by?
bicarbonate ions
another name for natural immunity?
innate immunity
another name for adaptive immunity
acquired immunity
specificity (how does it recognize pathogens) of innate immunity?
non-specific
specificity of adaptive immunity?
specific
speed of innate immunity reaction?
rapid - immediate to several hours
speed of adaptive immunity reaction?
slower - several days
chemicals involved in innate immunity?
Complement proteins, interferons, cytokines
memory is the ability of what type of immunity?
adaptive
chemicals involved in adaptive immunity?
Antibodies, other signalling chemicals including cytokines
cells of innate immunity?
phagocytic
cells of adaptive immunity?
lymphocytes (B + T cells)
5 portions of the nephron in order?
glomerulus, proximal tubule, loop of henle, distal tube, collecting duct
glomerulus is found in the renal____?
cortex
type of epithelium found in the bladder?
transitional epithelium
3 waste products eliminated in urine?
water, urea, creatinine
2 treatments for chronic kidney disease?
dialysis, kidney transplant
B and T cells are produced in the _____, but T cells mature in the _____
bone marrow, thymus gland
what do lymphatic vessels have to control their flow?
valves
structure in the head of a sperm that contains an enzyme which helps the sperm penetrate the ovum is called the______?
acrosome
progesterone is produced in the ovaries by the________?
corpus luteum
where does the zygote attach to?
endometrium
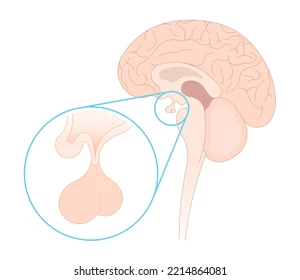
what glands is the front “ball”?
anterior pituitary gland
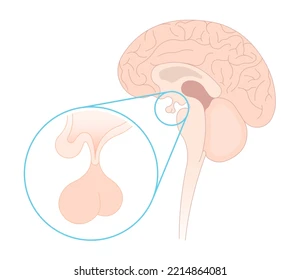
what gland is the back “ball”?
posterior pituitary gland
what glands reside on top of the kidneys?
adrenal glands
what happens during the ovarian cycle?
ovulation
2 reproductive hormones found in both men and women?
FSH, LH
what happens during the uterine cycle?
menstruation
Expanded name of TSH + function + gland?
thyroid stimulating hormone, stimulates thyroid to produce T3 and T4, anterior pituitary
Expanded name of ACTH + function + gland?
adrenocorticotropic hormone, controls production of cortisol, anterior pituitary
Expanded name of GH + function + gland?
growth hormone, stimulates growth of tissues, anterior pituitary
Expanded name of ADH + function + location?
antidiuretic hormone, re-absorption of water, posterior pituitary
hCG full name + function + gland?
humanchorionic gonadotropin, builds up uterine lining and placenta, placenta
hormone produced in the pancreas? its role?
insulin, regulates blood sugar levels
full name of T3? its role?
triiodothyronine, regulates basal metabolism
full name of T4 and its role?
thyroxine, regulates basal metabolism
what is estrogen?
female sex hormone
what is progesterone and its role?
female sex hormone, prepares body for pregnancy and maintains pregnancy
what is testosterone?
male sex hormone
roles of cortisol?
stress response, BP
Full name of PTH? its role? Gland?
parathyroid hormone, regulates calcium levels, parathyroid
The type of epithelium that lines capillaries is_____?
simple squamous
The normal range for pH in the human body is____?
7.35-7.45
how to recognize monocytes?
single nucleus
how to recognize neutrophils?
3 nuclei
how to recognize lymphocytes?
giant nuclei