Carbohydrates
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/214
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:04 PM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
215 Terms
1
New cards
Polyhydroxy compounds
aldehydes, ketones, alcohols,, acids and amines
2
New cards
Simply carbohydrates
* used for cellular foods
* either aldehydes or ketones
* either aldehydes or ketones
3
New cards
Simple formula for carbohydrate
Cn(H2O)n
4
New cards
What are the 3 forms of carbohydrates
1. Fischer
2. Haworth
3. Conformational
5
New cards
Haworth structure
* commonly followed
* best option because its between fischer and conformational
* best option because its between fischer and conformational
6
New cards
Carbohydrates
capable of isomerization on their own of by the action of cellular enzymes
7
New cards
pyran ring
6 membered ring
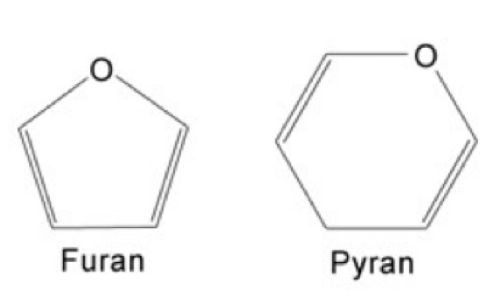
8
New cards
furan ring
5 membered ring
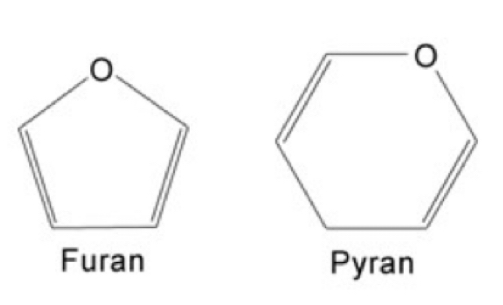
9
New cards
Probability of simple carbohydrates forming rings in solution
99%
10
New cards
Anomeric carbon
* C1 in a six-membered ring
* Center of the 2 configurational isomers (alpha and beta)
* Is reactive
* Also known are reducing carbon since it donates electrons
* Center of the 2 configurational isomers (alpha and beta)
* Is reactive
* Also known are reducing carbon since it donates electrons
11
New cards
Why is the reactive property of a anomeric carbon useful?
determination of glucose concentration in blood and urine
12
New cards
what does the aldehyde of C1 and o-toluidine react to form?
colored covalent complex
13
New cards
What does the reaction between anomeric carbon and proteins form?
forms a permanent bond with the proteins
14
New cards
what is special about mannose?
it can exist as a 5 or six membered ring
15
New cards
For monosachharides, how does the sugar exist?
single ring
16
New cards
For disaccharides, how does the sugar exist?
two sugar units
17
New cards
what are the 3 most common disaccharides?
1. maltose
2. sucrose
3. lactose
18
New cards
Maltose
found in germinating cereals and grains, 2 glucose units held together by an oxygen bridge
19
New cards
Sucrose
fund in cane, beets and carrots, one glucose and one fructose joined by an oxygen bridge
20
New cards
Lactose
found in milk, galactose and glucose joined by an oxygen bridge
21
New cards
are the oxygen bridges the same for each disaccharide?
no, it varies
22
New cards
What type of linkage does maltose have?
alpha(1-4) linkage
23
New cards
What type of linkage does sucrose have?
alpha(1-2) linkage
24
New cards
What type of linkage does lactose have?
beta(1-4) linkage
25
New cards
Where is the anomeric carbon in disaccharides?
present ONLY in the right-hand 6 membered ring
26
New cards
Oligosaccharide
carbs with more than one units
27
New cards
Glycan
number of saccharide rings greater than 10
28
New cards
Polysaccharides
carbs with many sugar units
29
New cards
What are the 2 main functions of polysaccharides/
* storage
* structure
* structure
30
New cards
Glycogen
storage form of polysaccharide in animals, very compact molecule due to extensive branching which is desirable for storage
31
New cards
Where is glycogen found in the eye?
corneal epithelial cells and retinal Muller cells
32
New cards
Corneal endothelial cells and photoreceptors and their relationship to glycogen
* utilize glucose at a higher rate
* cannot store glycogen
\
Storing is done by epithelial/Muller cells, usage is by endothelial and photoreceptor cells
* cannot store glycogen
\
Storing is done by epithelial/Muller cells, usage is by endothelial and photoreceptor cells
33
New cards
In metabolism, what is a carbohydrate’s role?
act as fuels for metabolism, constitutes of biological structures
34
New cards
Cellular metabolism
energy within glucose converted into a useful form (ATP)
35
New cards
What are the two types of chemical reactions
* catabolic processes (energy produced)
* anabolic processes (energy consumed)
* anabolic processes (energy consumed)
36
New cards
Are anabolic and catabolic reactions linked?
Yes, anabolic reactions NEED catabolic reactions to happen prior
37
New cards
Anabolic processes
reactions that synthesize cellular components and maintain its functions
38
New cards
ATP
adenosine triphosphate
39
New cards
What is important about phosphoenolpyruvate?
used in catabolic reaction that converts ATP to ADP
40
New cards
What 2 things does ATP connect?
anabolic and catabolic reactions
41
New cards
What are the 3 components of ATP?
adenine, ribose, and 3 phosphate groups
42
New cards
Function of the ribose and adenine components of ATP
* acts as handles to position the molecule at enzyme or protein reactive sites
* facilitates release of its potential energy by breaking outermost phosphate (ADP + Pi)
* facilitates release of its potential energy by breaking outermost phosphate (ADP + Pi)
43
New cards
What can lipids and proteins create by general metabolism?
ATP
44
New cards
What is the most common and immediate source of acetyl-CoA and ATP?
carbohydrates
45
New cards
Why is the use of proteins/lipids to make ATP “bad”?
destructive to tissues when usage becomes excessive
46
New cards
What are examples of the body using proteins/lipids for ATP production?
diabetes mellitus or starvation
47
New cards
what is important about the electron transfer step in kreb’s cycle
an important source for **efficient** ATP production
48
New cards
What part of Krebs cycle occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell?
Up to generation of Acetyl-coA
49
New cards
What part of Kreb’s cycle occurs in the mitochondria?
Beyond Acetyl-coA stage
50
New cards
What enters as glucose 6-phosphate?
glucose and galactose
51
New cards
what enters as fructose 6-phosphate
fructose and mannose
52
New cards
Glycolysis
small amount of ATP is produced in the formation of pyruvate
53
New cards
Oxidative phosphorylation
* involves shuttling of electron-bearing compounds along the mitochondrial, inner membrane
* involves production of substantial quantities of ATP
* involves production of substantial quantities of ATP
54
New cards
Electron shuttle
ends at the formation of water (by combining hydrogen and oxygen)
55
New cards
Anaerobic phase of glycolysis
begins when pyruvate is converted to lactate
56
New cards
Glucose-6-phosphate
* converted to glycogen for storage
* converted to pentoses for other metabolic requirements of the cell
* converted to pentoses for other metabolic requirements of the cell
57
New cards
what is important about Glucose-6-phosphate
metabolic junction for the continuation of glycolysis, storage or the pentose shunt
58
New cards
What does glucose-6-p undergo to create fructose-6-p?
isomerization
59
New cards
What does fructose-6-p undergo to create fructose 1,6-biphosphate? what mediates this sequence?
phosphorylation, phosphofructokinase
60
New cards
phosphofructokinase
a dominating enzyme that controls the rate of the whole pathway
61
New cards
what does fructose 1,6-biphosphate break down into?
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxy acetone phosphate
62
New cards
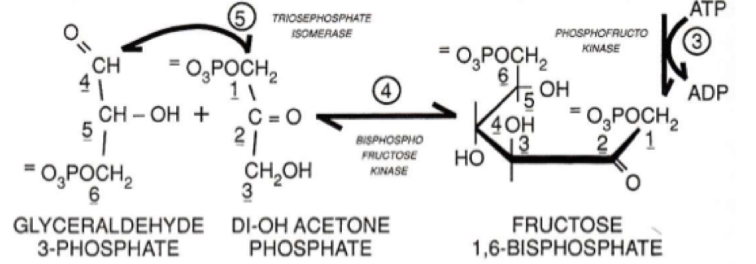
why is the presence of a phosphate group on each fragment (see picture) important?
fragments assure that they will remain in the cytoplasm
63
New cards
Where does glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate acquire its 2nd phosphate group from? What does this process require?
inorganic phosphate, requires NAD+ (coenzyme)
64
New cards
What is the result after glycolysis is completed?
* 2 molecules of ATP consumed
* 4 molecules of ATP formed
* NET GAIN: 2 ATP MOLECULES
* 4 molecules of ATP formed
* NET GAIN: 2 ATP MOLECULES
65
New cards
Pyruvate
last intermediate of the E-M pathway
66
New cards
Anaerobic metabolism
* only on single reaction beyond E-M pathway involving formation of lactate
* quick means for cells to obtain ATP without O2
* Small yield
* quick means for cells to obtain ATP without O2
* Small yield
67
New cards
Breakdown of stored glycogen
* gain of 3 ATPs anaerobically
* no ATP is required to form glucose-6-phosphate from glycogen
* no ATP is required to form glucose-6-phosphate from glycogen
68
New cards
Anaerobic glycolysis
* simple
* can run at a faster rate
* cell can obtain a high-energy supply in a short period of time
* can run at a faster rate
* cell can obtain a high-energy supply in a short period of time
69
New cards
What pathway do ocular tissues process glycogen?
anaerobic glycolysis
70
New cards
Problems with hard contact lenses
* metabolic strain on the epithelial cells
* 80% of available glycogen used in just over 8hrs of wear
* significant swelling
* due to increase of lactate
* osmotic strain and constant swelling
* 80% of available glycogen used in just over 8hrs of wear
* significant swelling
* due to increase of lactate
* osmotic strain and constant swelling
71
New cards
What happens to the cornea when oxygen falls below 54mmHg?
corneal swelling could be as much as 20% of the tissue volume
72
New cards
How much corneal swelling can happen overnight?
3% swelling, partial pressure of O2 drops from 155 to 60mmHg
73
New cards
Pyruvate diffuses into mitochondria to do what?
begin the aerobic phase of ATP production
74
New cards
Mitochondria function
* manufacture ATP aerobically
* enzymatic processing of reactions, both of which require a separate inner compartment
* enzymatic processing of reactions, both of which require a separate inner compartment
75
New cards
Structure of mitochondria
oblong shape and double membrane
76
New cards
structural significance of mitochondria INNER membrane
* impermeable to molecules and ions
* has a large surface area due to cristae
* insoluble electron transferring proteins and ATP synthase
* has a large surface area due to cristae
* insoluble electron transferring proteins and ATP synthase
77
New cards
Structural significance of the mitochondrial MATRIX
* contains numerous soluble enzymes
* site for conversion of pyruvate to acetylcholine-coA
* pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
* site for conversion of pyruvate to acetylcholine-coA
* pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
78
New cards
During acetylcholine-coA formation, how many electrons are transferred overall?
2 electrons, from pyruvate → NAD+ → NADH
79
New cards
What are important about the 2 electrons during acetylcholine-coA formation?
electrons are the first source of ATP synthesis in the aerobic pathway
80
New cards
Purpose of Krebs cycle
* to supply electrons for the synthesis of ATP
* help in energy production
* help in energy production
81
New cards
How many steps are there in krebs cycle?
9 enzyme catalyzed reactions
82
New cards
Where does krebs cycle occur?
in the mitochondrial matrix
83
New cards
what happens after 1 kreb cycle
* two carbons are lost as CO2
* Carbons are regained as acetyl-coA
* Carbons are regained as acetyl-coA
84
New cards
What are the most important steps of krebs cycle for deriving energy?
4, 5, 6, 7, and 9
85
New cards
In krebs cycle, what is GTP converted into?
ATP
\
(GTP + ADP → ADP + ATP)
\
(GTP + ADP → ADP + ATP)
86
New cards
Where does NADH and FADH2 travel during kreb’s cycle? what do they do when they reach their destination?
diffuses from the matrix to the inner mitochondrial membrane, they donate their electrons to the electron transferring proteins
87
New cards
Coenzyme Q
shuttles electrons between protein complex I and III, and also between complex I and II
88
New cards
Cytochrome C
shuttles electrons between protein complex III and IV
89
New cards
NADH
carries electrons to protein complex I
90
New cards
FADH2
carries electron to complex II
91
New cards
in oxidative phosphorylation, where do the hydrogen ions flow back through? what does this flow cause?
pores of fifth protein complex, AKA ATP synthase
\
release of ATP from ATP synthase
\
release of ATP from ATP synthase
92
New cards
What is the total amount of ATP produced by the aerobic exit of glycolysis
36-38 ATP molecules
93
New cards
what does the pentose shunt pathway do?
* generation of pentoses
* production of fatty acids
* cell detoxification
* production of fatty acids
* cell detoxification
94
New cards
Why are fatty acids important?
membrane synthesis
95
New cards
Why are pentoses important?
used for synthesis of nucleic acids and nucleotides such as adenosine
96
New cards
why is cell detoxification important?
removal of destructive forms of oxygen such as hydrogen peroxide
97
New cards
In the pentose shunt pathway, can some of the intermediates be recycled?
Yes
98
New cards
What are the functions of the electrons that are inserted into the coenzyme NADP+?
* reductive synthesis of fatty acids
* removal of hydrogen peroxide by a linked redox system
* removal of hydrogen peroxide by a linked redox system
99
New cards
Redox system
help in detoxification, present in ocular tissues
100
New cards
Gluconolactone
hydrolysis to open the ring structure and produce a sugar acid