Genetics Lab- Gene Mapping and Linkage Analysis
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What was the main goal of this lab?
To map distances between genes and distances between a gene and the centromere.
What does not occur across the centromere?
Crossing-over.
What can be used to determine the distance between a gene and the centromere?
The frequency of crossing over events.
Why do we use Sordaria fimicola?
ascomycete fungus (produces asci)
sexual reproduction occurs when two haploid (n) nuclei come together to form a diploid nucleus. next, this nucleus undergoes meiosis followed by mitosis to generate 8 spores within an ascus.
we can easily determine the distance between the spore color gene and the centromere by examining the spore organization.
the organization of the spores within the ascus enables us to determine crossing-over frequency.
Describe the Sordaria life cycle.
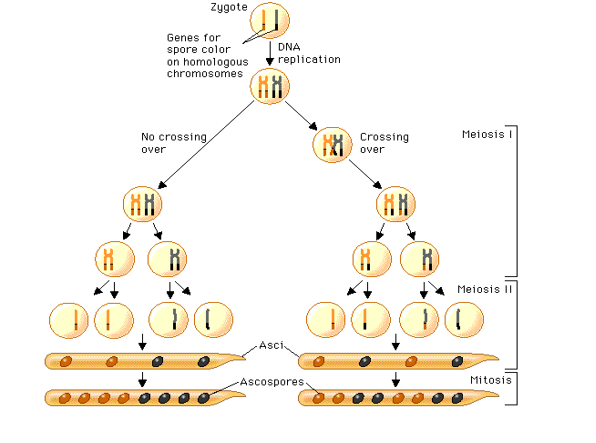
A diploid zygote containing genes for spore color on homologous chromosomes forms from two haploid strains.
DNA replication occurs, and the new cell contains two chromosomes.
From the cell with two chromosomes, crossing over occurs and produces a cell with two chromosomes of intertwined DNA. In another cell, crossing over does not occur.
The cells undergo Meiosis I, Meiosis II, and one round of Mitosis (8 haploid cells).
The cells are distributed linearly in an ascus and about 20 asci are assembled together in a perithecium.
In the cell where crossing over did not occur, there is even distribution of color in the ascospores. In the cell where crossing over did occur, there is an uneven distribution of color in the ascospores.
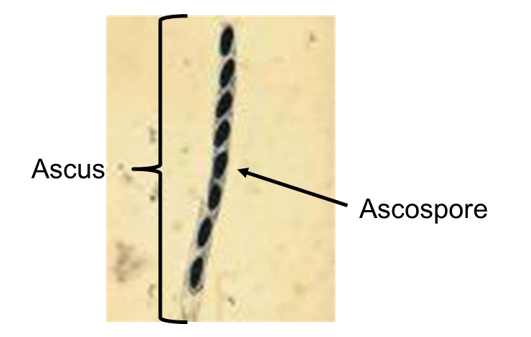
What is an ascus?
A sac containing the 8 cells which are the end result of meiosis and one round of mitosis.
What is a perithecium?
A round or flask-shaped fruiting body with a pore through which the spores are discharged.
What is an ascospore?
Each individual spore within an asci.
What is the significance of each ascospore within the ascus being haploid?
Whichever allele is present will get expressed, and that the genotype directly matches the phenotype.
How can the allele of the spore color gene be determined?
By simply looking at the color of each ascospore.
What strains of Sordaria were crossed in our experiments?
One with a tan spore color and one with a dark spore color.
What happens when crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes during Meiosis I?
The phenotypic sequence of spore color changes.
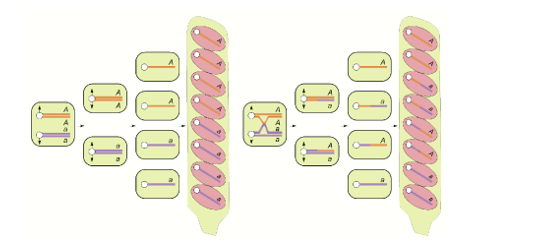
Describe this image.
The left part of the figure demonstrates meiosis and mitosis of a zygote (2n). Without crossing over, four ascospore on one side will be the same color.
The right part illustrates a crossing over between the gene and the centromere. The recombination alters the genotype sequence in an ascus, which will be observed as an altered color sequence.
What are the different combinations of crossing over?
T= tan
B= black
TTBBTTBB
TTBBBBTT
BBTTTTBB
BBTTBBTT
What is the formula for determining the distance of the gene from the centromere?
d=1/2 (# of recombinants/# of recombinants + # of non-recombinants) *100