Carina Foundations
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
is the situation in which available resources (factors of production) are finite but our wants/needs are infinite
what is the definition of scarcity?
- has a high price/value
- if the demand > supply
- if you can't find it (unavailable)
- the resources are allocated in certain ways (rational, lottery)
how do you know when something is scarce?
makes us make choices
what does scarcity make you do?
studies the behaviour of individual decision making in the economy (such as producers and consumers)
microeconomics definition
consumers (households) and firms (businesses)
what are the two main decision makers studied in microeconomics?
The study of the economy as a whole, is concerned with the aggregate or sum of behaviour
macroeconomics definition
Combination of many individual markets into one overall market
meaning of aggregate
using our scarce resources in the least wasteful way
what is one thing the study of economics is about?
refers to the long-term maintenance or viability of any particular activity of policies. and in economics refers to the ability of the present generation to satisfy its needs by the use of resources and non-renewable resources, without limiting the future-generations ability to satisfy their own needs
sustainability definition
land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
what are the 4 factors of production?
all natural resources or ' gifts of nature'
what does the land factor entail?
the physical or mental effort that people contribute to the production process.
what does the labor factor entail?
the man-made FoP used to produce goods/services.
what does the capitol factor entail?
skill possessed by some people of creatively combining or organizing the other factors of production into a good/service.
what does the entrepreneur factor entail?
the income received for supplying factors of production
what are factor payments?
land gets you rent
what is the factor payment of land?
labor gets you wages
what is the factor payment of labor?
capitol gets you interest
what is the factor payment of capitol?
entrepreneurship gets you profit
what is the factor payment of entrepreneurship?
the value of the next best alternative that must be given up in order to obtain something else
opportunity cost definition
3
how many basic economics questions are there?
1. What to produce? - what goods/services are we going to produce?
what is the first basic economics question?
2. How to produce? - how are we going to use our resources to produce the goods/services we want/need?
what is the second basic economics question?
3. For whom to produce? - how are goods/services going to be distributed amongst the population?
what is the third basic economics question?
resources are owned privately and it's up to producers and consumers to make economic decisions
market method definition
resources are owned by the government who make the economic decisions
command method definition
free economy, mixed economy and command economy
what three types of economies are there?
an economy without government intervention and individuals own the factors of production. Businesses make goods/services to make profit
What is a free economy?
an economy where the factors of production are owned by the government and in which production, investment, prices, and incomes are determined centrally by a government.
what is a planned/command economy?
an economy mixed with free markets and government intervention. the government will pay for public goods, eg roads bridges and public services, eg firefighters and teachers
What is a mixed economy?
the government regulates production and ensures the welfare of labor workers
what is the purpose of government intervention in a mixed economy?
businesses meet society's needs when they seek their own self-interest
invisible hand in the free market
minimum price mean minimum wage
what does minimum price mean?
represents all combinations of the maximum amounts of two goods that can be produced by an economy, given its resources and technology, when there is full employment of resources and efficiency in production.
What is a PPC (Production Possibilities Curve)?
all factors of production are being used to their maximum
what does it mean when all resources are being fully employed?
resources are not being wasted and output i being produced with the least amount of resources possible
what does it mean when all resources are being efficiently used?
Constant and increasing
what are two types of PPCs that represent opportunity cost?
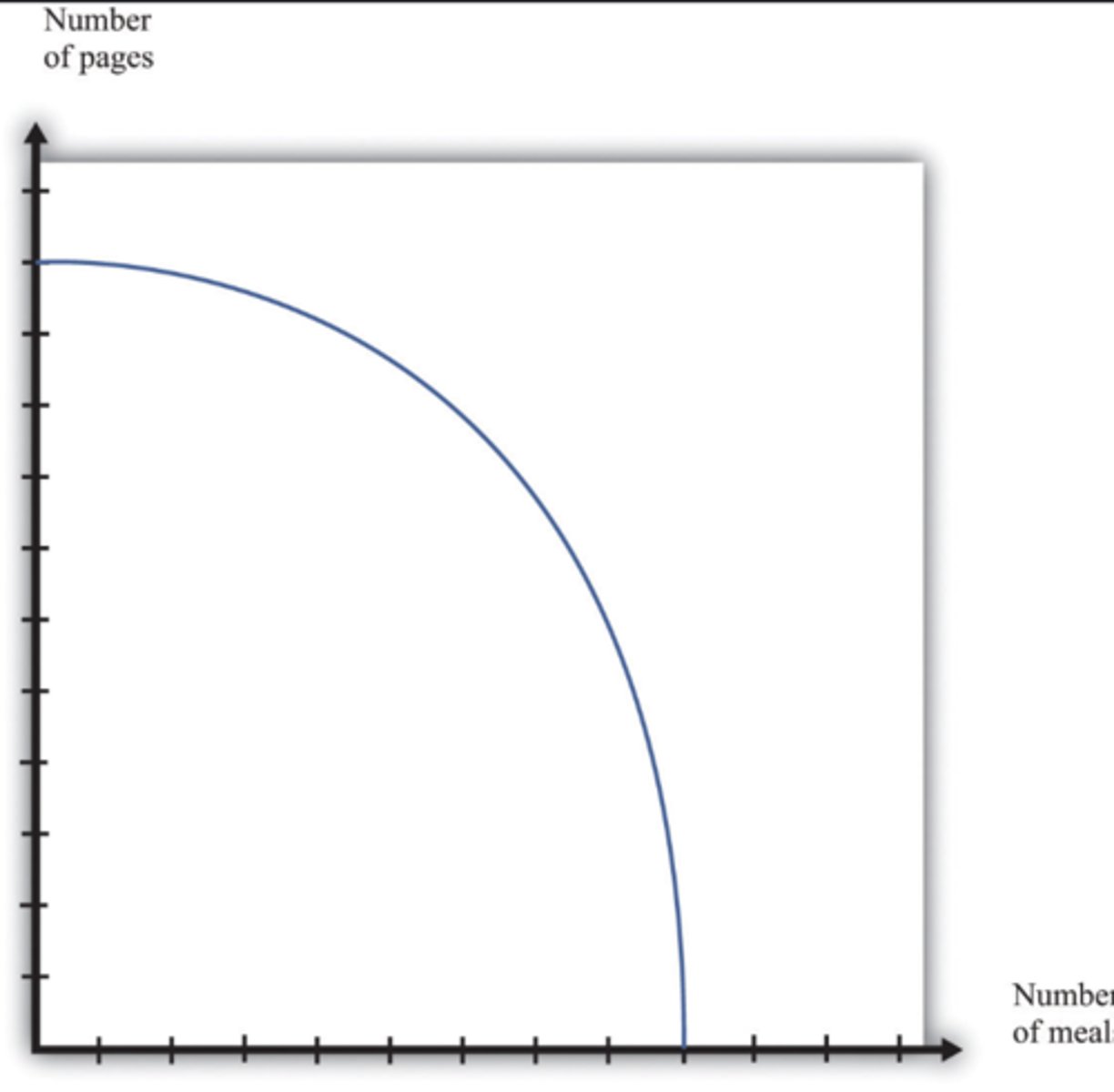
increasing opportunity cost
1. what does this PPC represent?
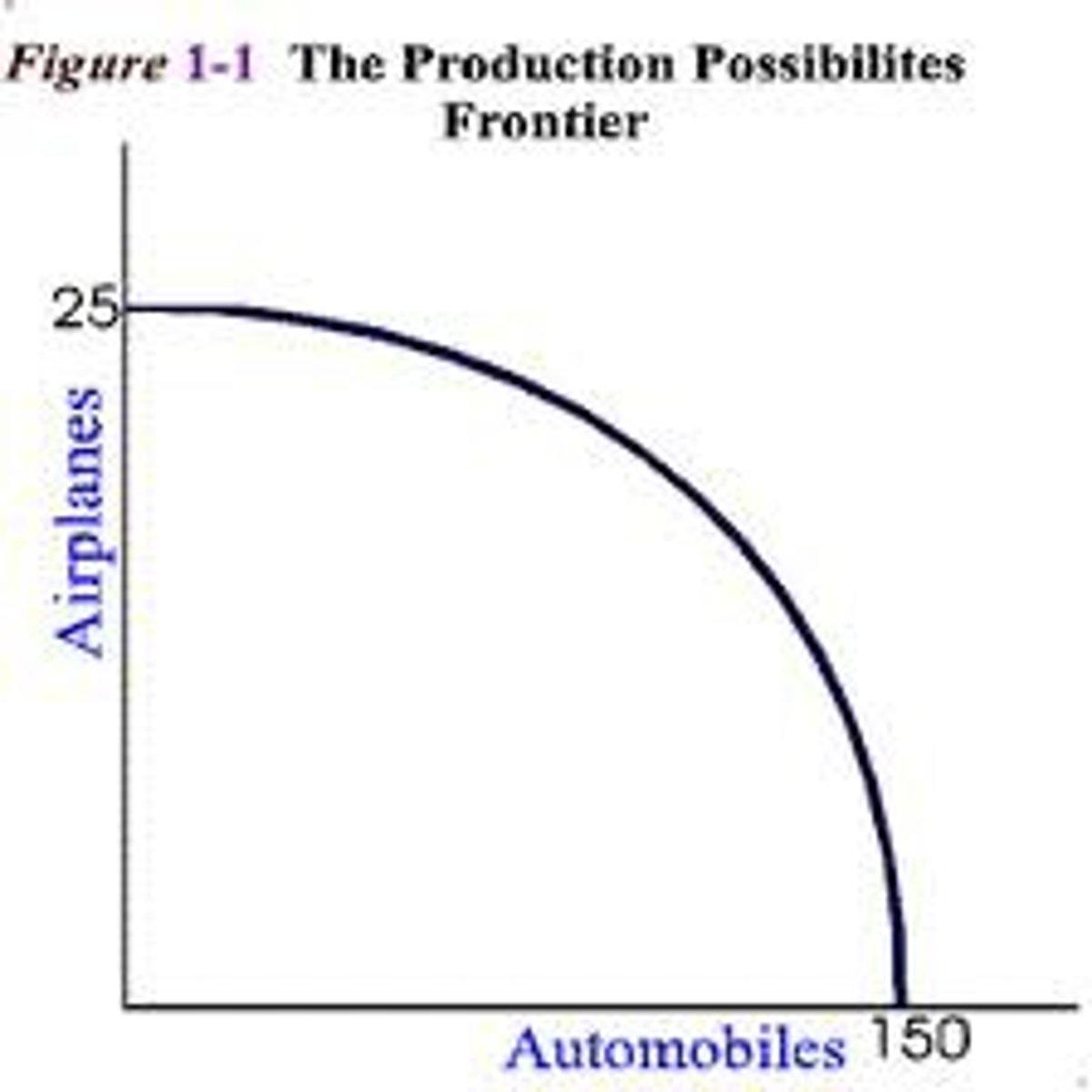
constant opportunity cost
2. what does this PPC represent?
an economy will not be able to produce outside the PPC, there is no availability of the factors of production to produce the output
what does scarcity mean in terms of a PPC?
scarce resources mean that countries need to make choices about the goods/services or combination of goods/services they want to produce.
Choice definition (in terms of scarcity)
any choice between choosing more or less of a good/service means there will be an opportunity cost for that choice.
opportunity cost - refer to choices
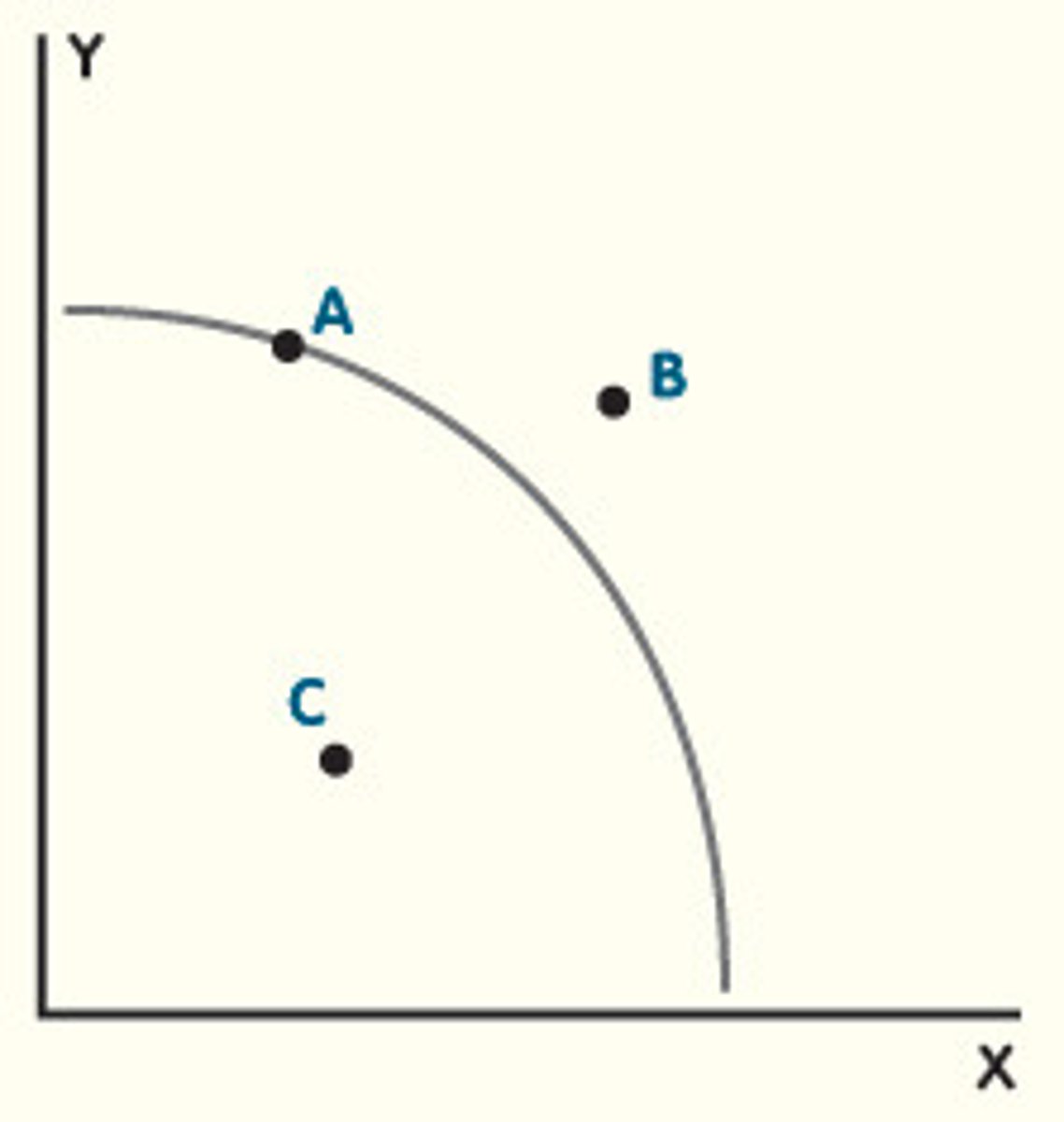
fully efficient use of resources and no unemployment
what does point A on the PPC graph represent?
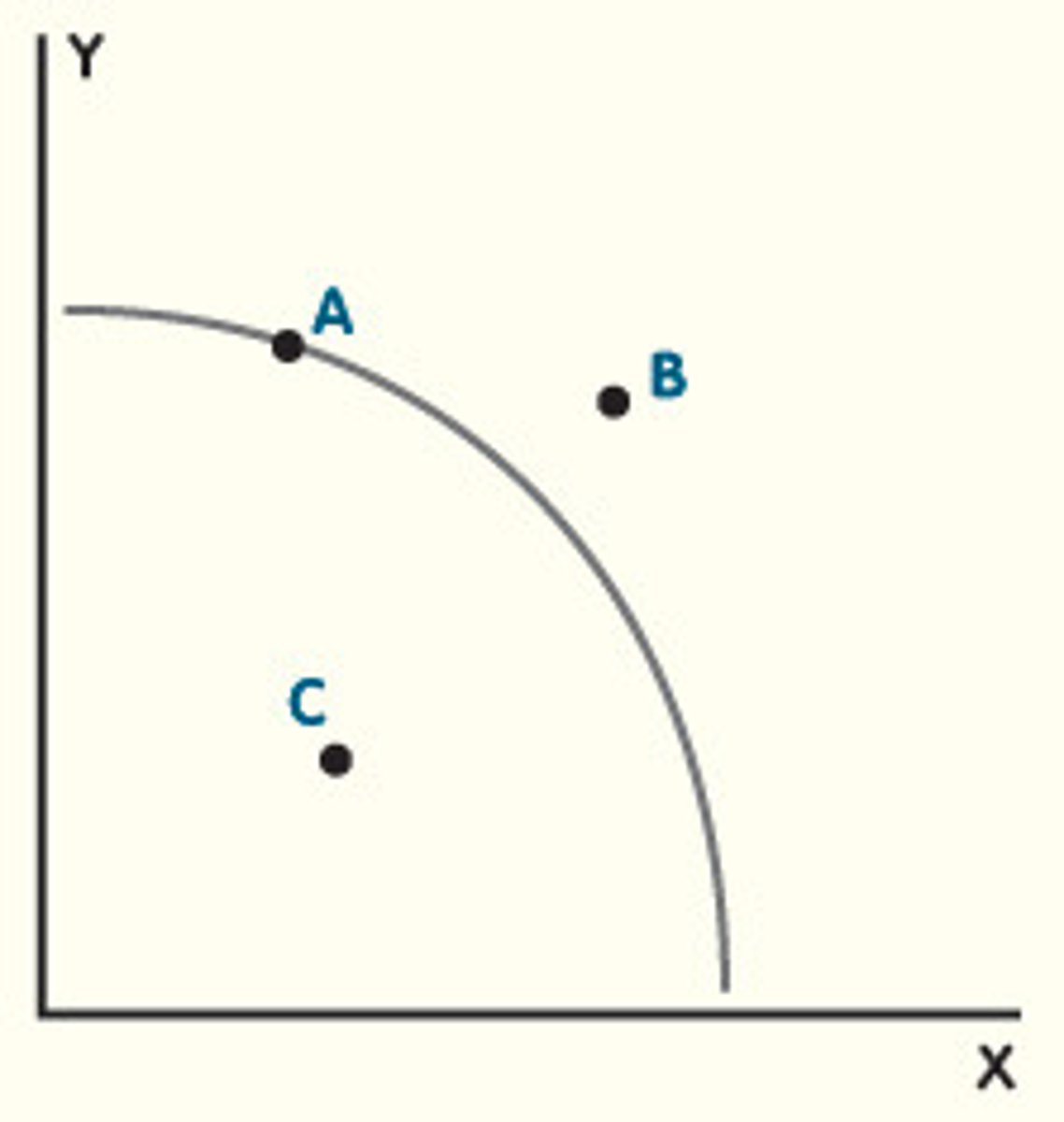
scarcity as the point is inadmissible - market is unable to produce the good/service given its resources
what does point B on the PPC graph represent?
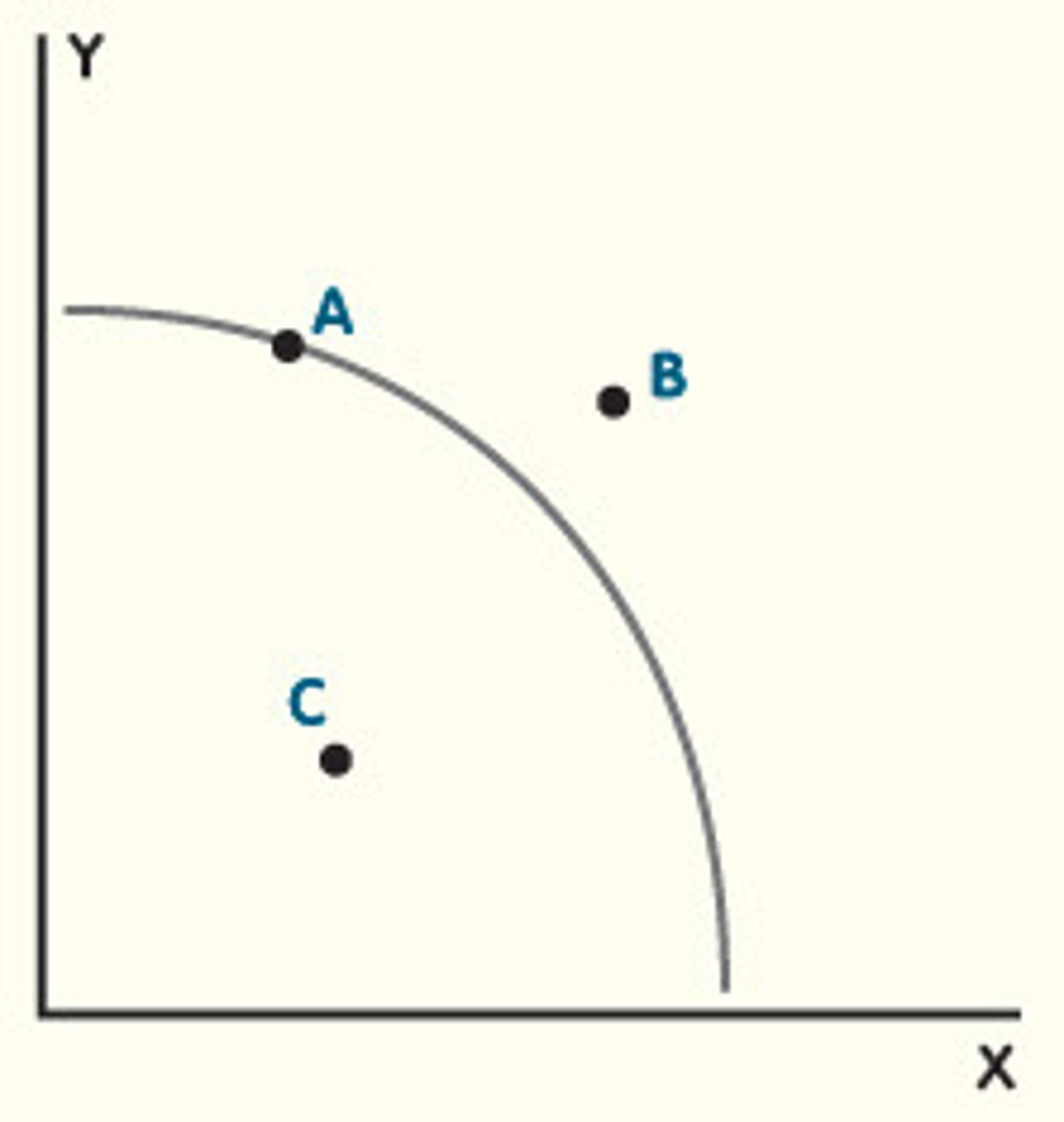
inefficient use of resources and unemployment
what does point C on the PPC graph represent?
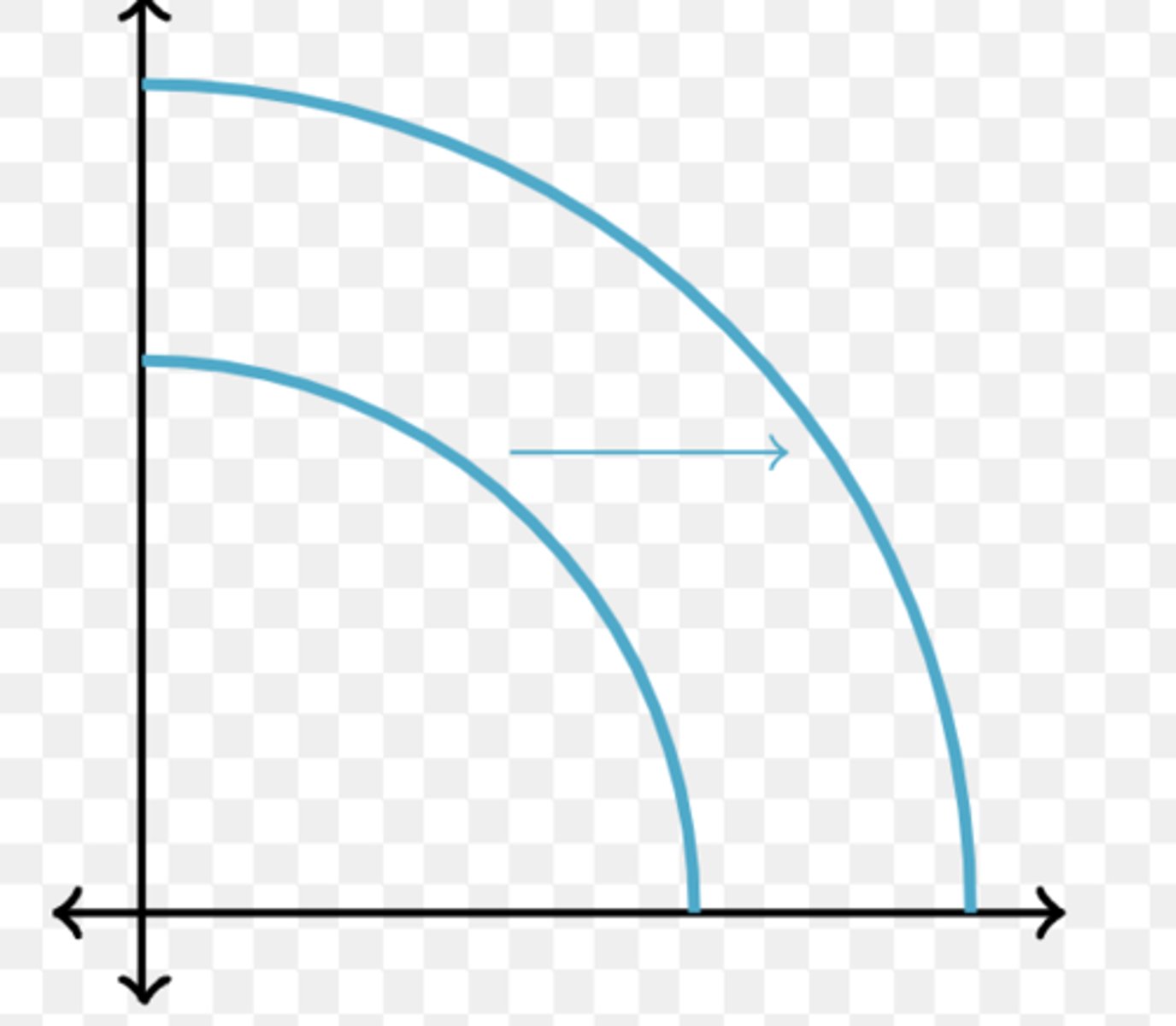
the increase in the quantity of output produced in an economy over a period of time
economic growth definition
caused by reduction in unemployment and increases in efficiency in production
Actual growth definition
caused by an increase in the quality or quantity of resources (factors of production)
growth in production possibilities definition
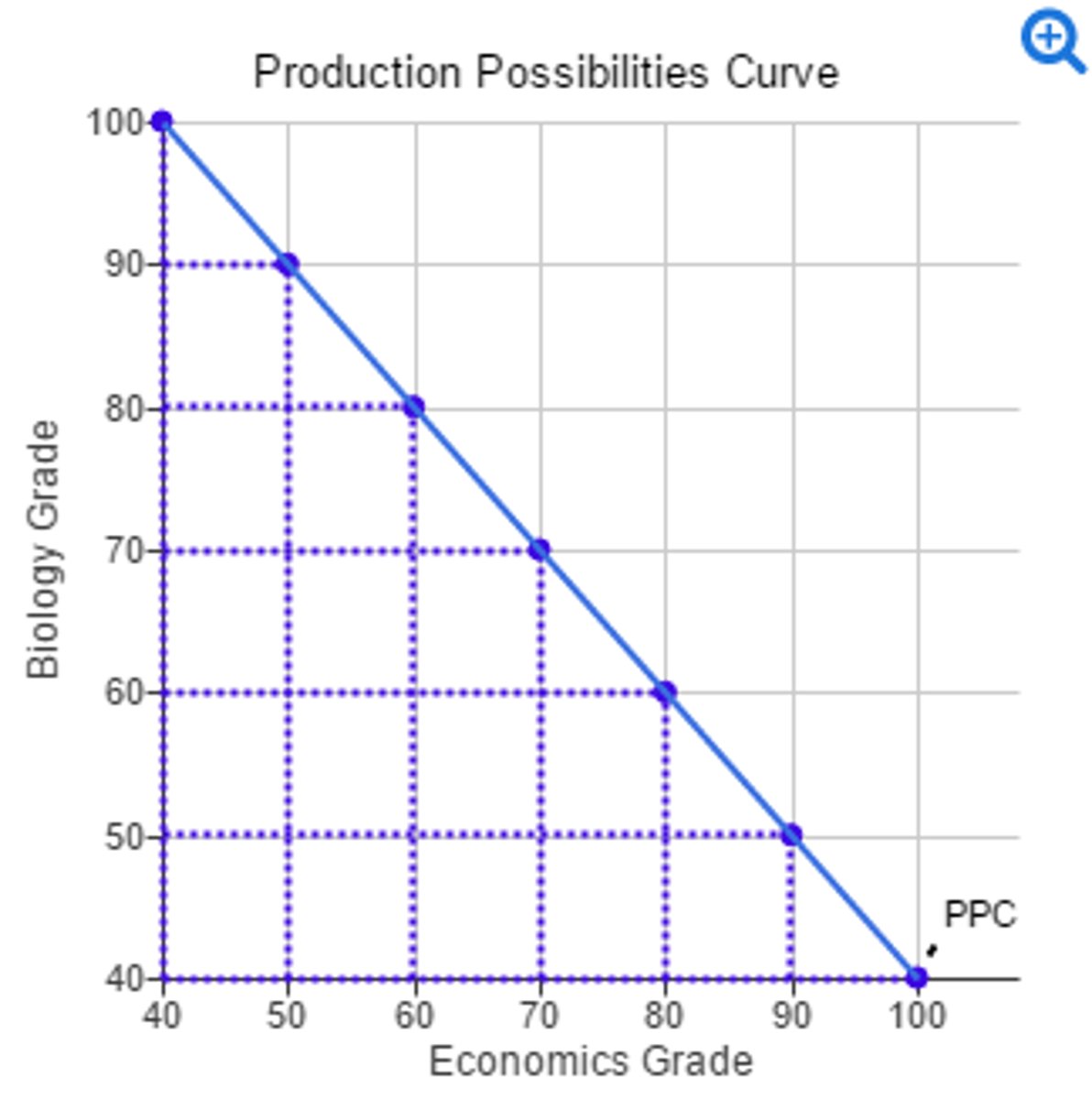
increase in actual growth
1. what is this image an example of?
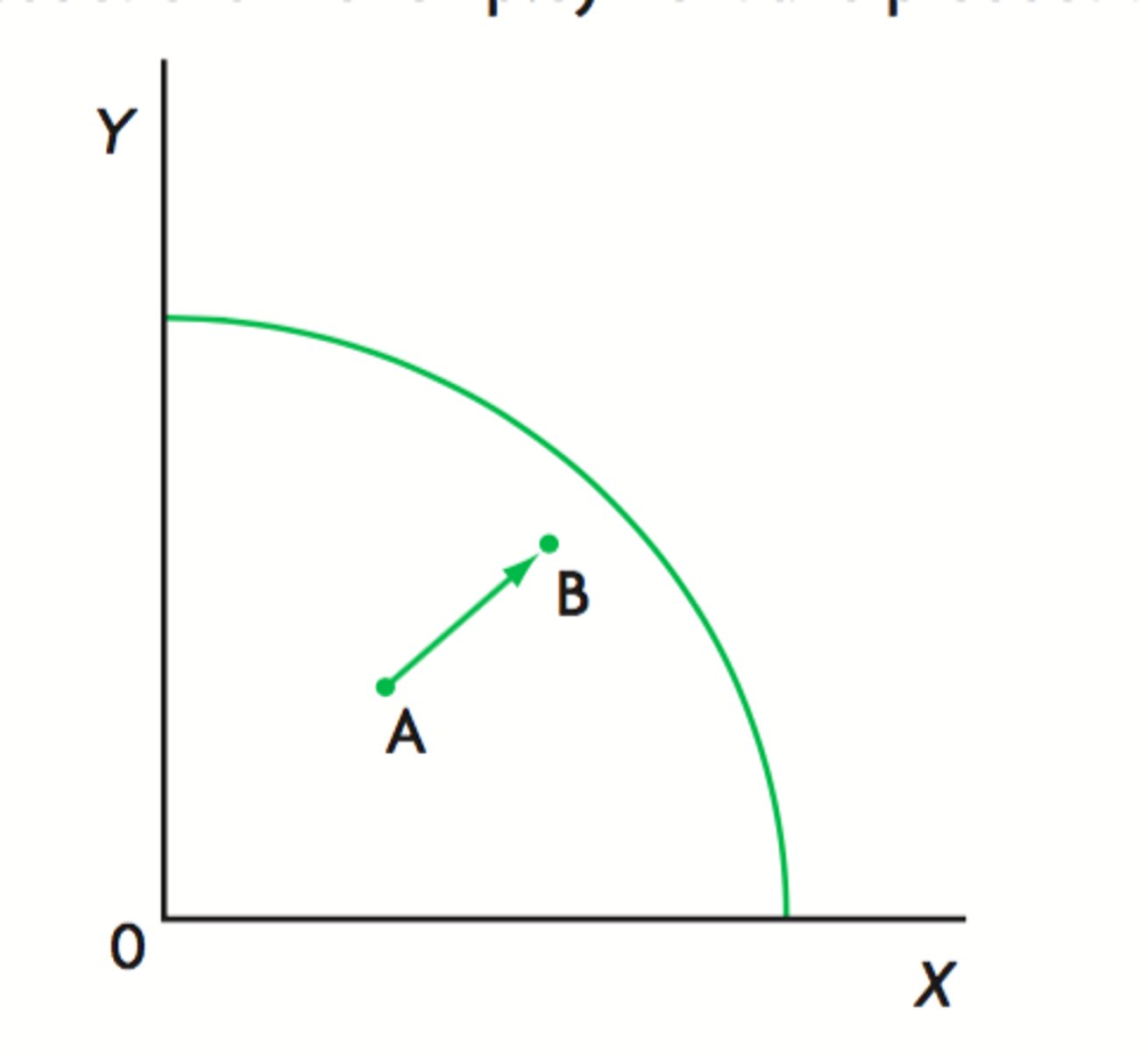
economic growth, increase in production possibilities
2. what is this image an example of?
government payments to businesses or households designed to meet a specific objective
transfer payment definition
shows that in any given time period the value of output produced in an economy is equal to the total income generated in producing that output, which is equal to the expenditures made to purchase that output.
Circular flow of income
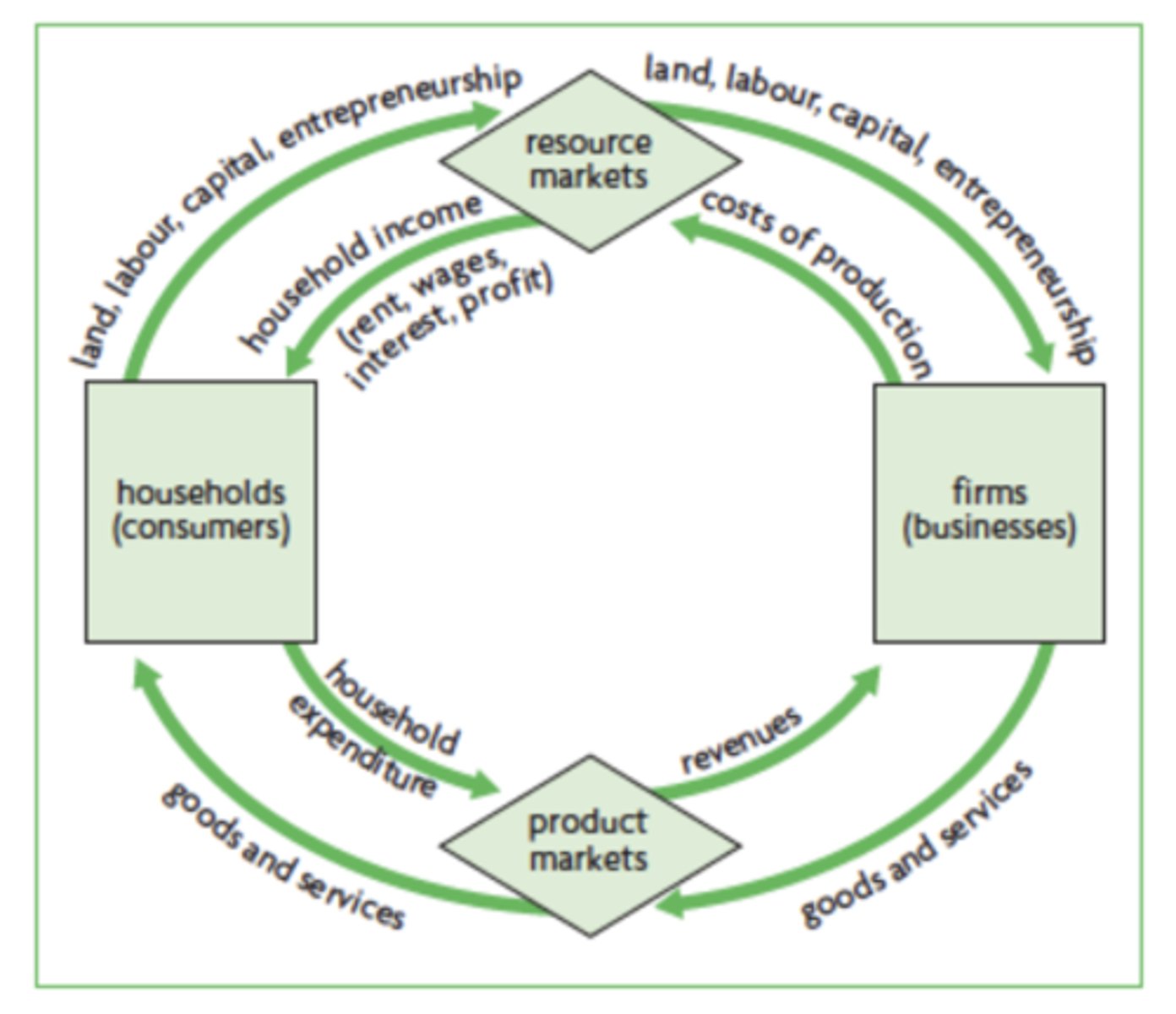
because everything works in a cycle
how can households & firms be buyers and sellers simultaneously?
withdrawals from the economy and come in the form of savings, taxes, and imports.
leakages definition
investments into the economy and come in the form of investments, government spending, and exports.
injections definition
economic growth is when there are less leaks and more injections into the economy
economic growth in terms of leaks and injections
firms get more money
what happens to the size of the economy when injections are bigger than leaks?
not enough resources, economy becomes unstable and firms get no money
what happens to the size of the economy when leaks are bigger than injections?
buyers of goods and services
sellers of factors of production (resources)
what are households sellers and buyers of?
buyers of factors of production (resources)
sellers of goods and services
what are firms sellers and buyers of?
they get revenue
when households use factor payments to spend on expenditures (to obtain goods and services), what do firms get?
the study of economics based on the scientific method used to arrive at knowledge about the economic world which includes descriptions, models, hypotheses, theories and laws. - they can describe, explain or predict
positive economics definition
forms the basis of judgements about what economic goals and economic policies ought to be. It is based on value judgements, because it identifies important economic problems that should be addressed and prescribes what should be done to solve them.
normative economics definition
are any kind of arrangement where buyers and sellers of goods services, or resources are linked together to carry out an exchange
markets definition
Competitive markets involve numerous sellers and buyers acting independently, allowing no single seller to control product prices. Price is determined by supply and demand forces and the interaction of many sellers and buyers.
competitive markets definition