Electromagnetics Principles and Rules in electric machines
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
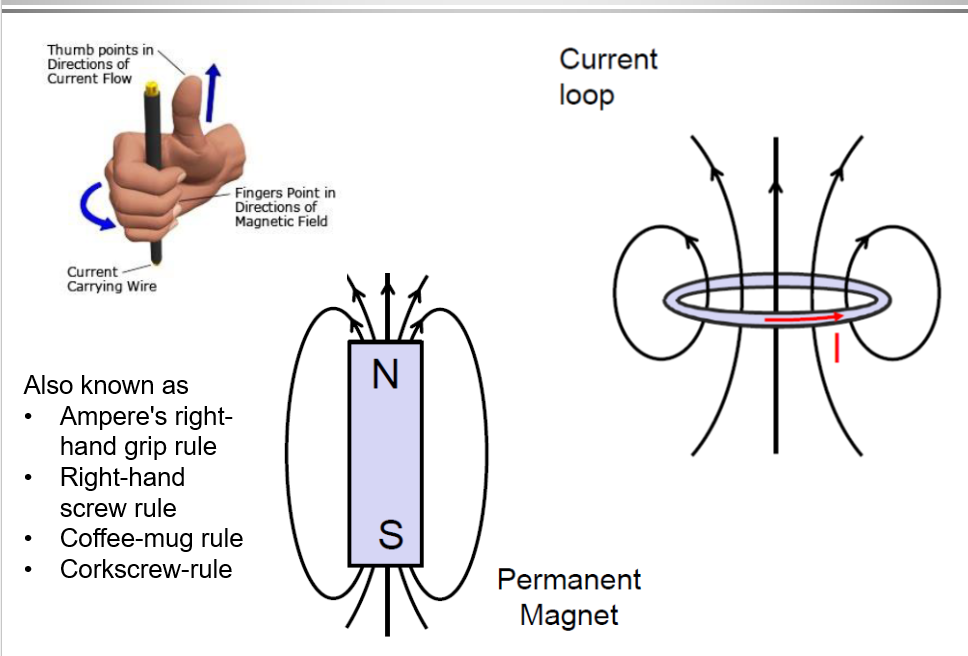
Right Hand Rule
A principle used to determine the direction of magnetic flux in coils.
Faraday’s Law
States that a changing magnetic field can induce a voltage and current in a conductor.
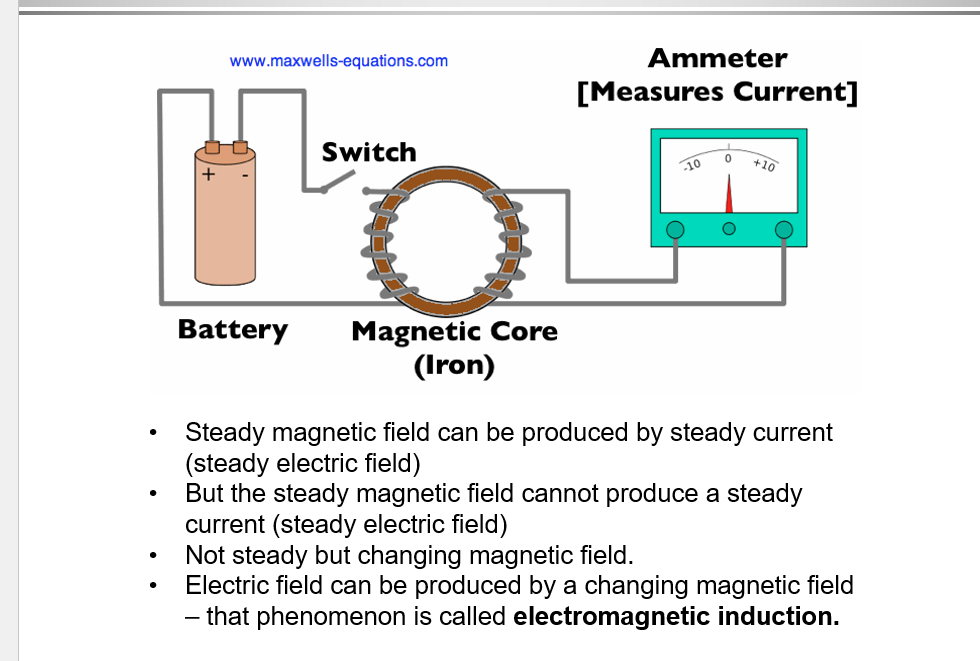
Steady Magnetic Field
A magnetic field produced by a steady current, which cannot induce a steady current itself.
Therefore a steady magnetic field can’t produce a steady current it will need to be alternating to produce a current (faradays law)
AC Source
An alternating current source that can induce voltage in a secondary coil without physical connection.
Lenz's Law
A principle stating that induced current will flow in a direction that opposes the change in the magnetic field.
Permanent Magnet
A magnet that produces a constant magnetic field, used by Lenz to induce current in a coil.
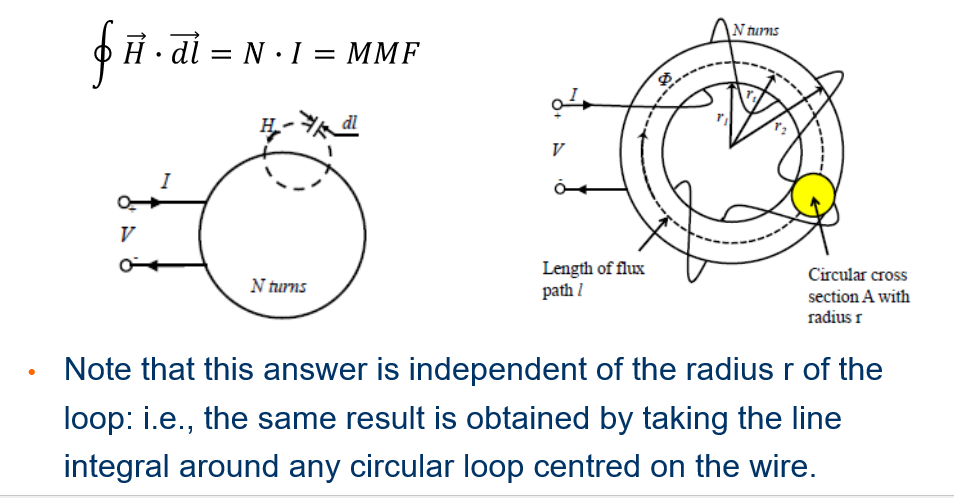
Ampere’s Law
Relates the magnetic field intensity (H) to its source (N * I) along an average path at the mean radius r.
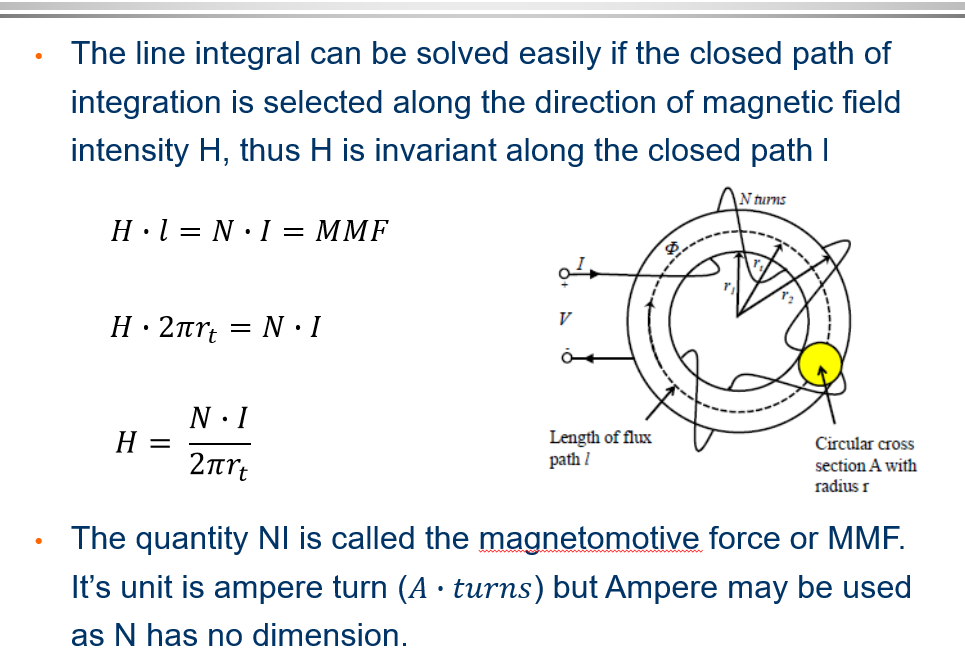
Magnetic Flux
The magnetic flux intensity H describes the field produced by the Magnetic Motor Force MMF.
The magnetic field intensity produces a magnetic flux density B everywhere it exists
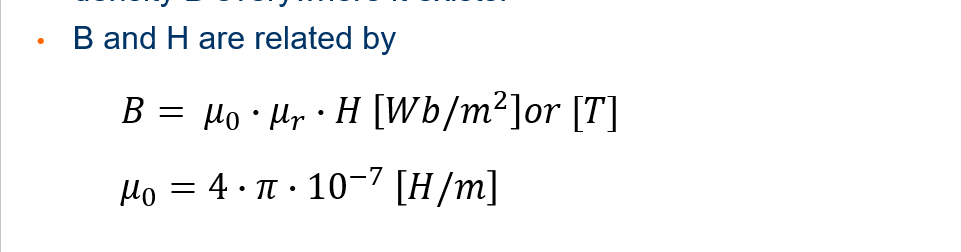
Magnetic Flux Density.
What’s the equation?
B?,φ?,μ?
A measure of the amount of magnetic flux through a unit area.
So the flux per unit cross sectional area
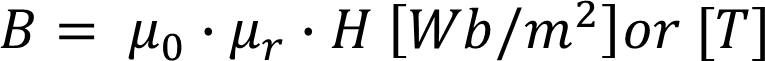
B=φ/A [T] or [Gauss]
So
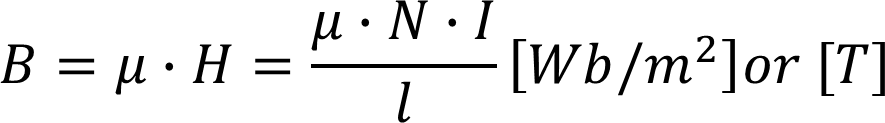
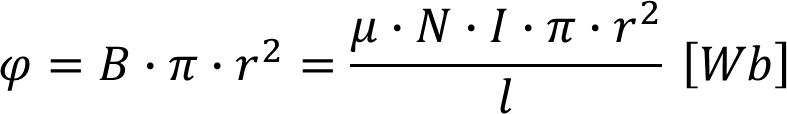

![<p>A measure of the amount of magnetic flux through a unit area.</p><p>So the flux per unit cross sectional area</p><p></p><p></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e287a7d4-afd3-48ec-bcb1-c683378397eb.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p><span style="font-size: 28pt; font-family: Cambria Math">B=φ/A</span> [T] or [Gauss]</p><p>So</p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/de3337a2-b819-499b-b8ba-d8752c8fa556.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/13422299-48df-403b-8573-aa0f97685964.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p></p><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6a158cc4-125b-4db0-bbe9-ae6dda8b5c1d.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center"><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e36c5312-cab8-4d5c-a6f5-c2695fae02e1.png)
Magnetic flux linkage
•The product of the winding turns N and the flux that link them is the flux linkage and is expressed as
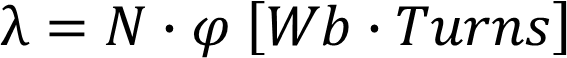
Fringing?
What does this mean to the core
The phenomenon where magnetic flux spreads out at the edges of a magnetic material.
•Very difficult to calculate it analytically. It makes flux density in core lower as useful MMF is used for developing the leakage flux.
•Usually accounted for by ignoring effect or adding air-gap length to both dimensions of cross section of air-gap.
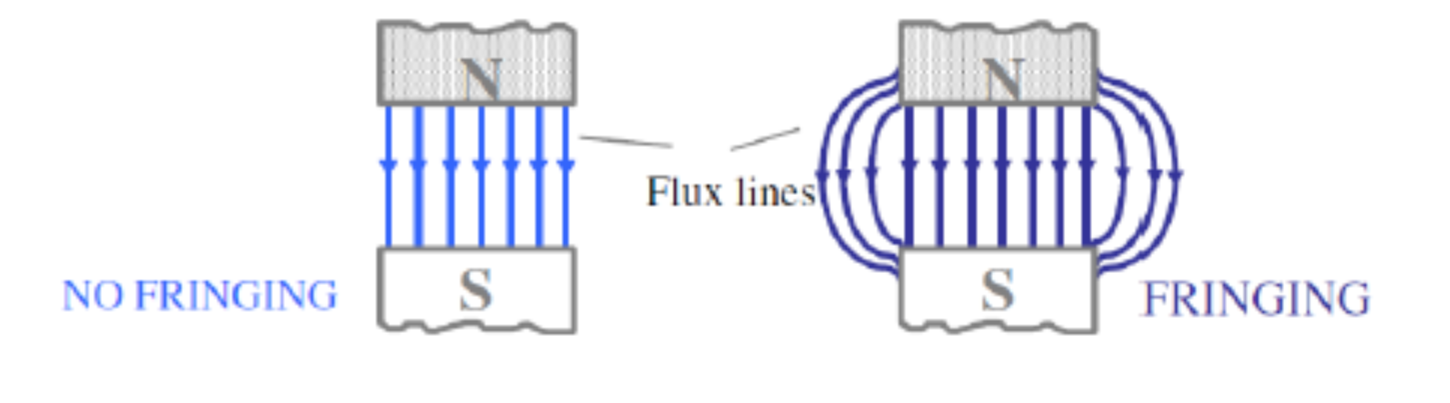
Air Gap Fringing
The behavior of magnetic flux across an air gap, which is not confined to the iron core's surface area.
Leakage
The phenomenon where magnetic flux deviates from the desired path, often passing through air or non-preferred magnetic paths.
E.g in transformers this is the flux that doesnt link primary and secondary coils
Power Flow Diagram
A representation of how input power is lost in various components before reaching the output.
Iron Losses
Energy losses that occur in the iron core of a magnetic system.
Efficiency
A measure of how much input power is converted to useful output power, accounting for losses.