BIO100: QUIZ 2 [DOC VER]
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the divisions and function of nervous system?
Peripheral Nervous System: Associated with the tissue outside the CNS
Afferent / Sensory: Brings sensory information to the CNS
Somatic: monitor skeletal muscles and joints
Visceral: monitor smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, internal organs
Efferent / Motor :Carries motor commands to muscles and glands
Somatic: skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system: control internal organ activities
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Function: Provides sensory information to the CNS and carries motor commands away from CNS – “It sends messages to the brain and sends instructions back to the body.”
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: brain and spinal
Function:
Integrating, processing, coordinating sensory input & motor output
origin of intelligence, memory, learning, emotion
How are receptors classified
Interoceptors: Monitor internal organ activity
Exteroceptors: External environment (touch, temperature, pressure, sight, smell, hearing)
Proprioceptors: monitor position and movement of body
What information is carried by the spinocerebellar tract?
Balance
Motor coordination
What is the lateral spinothalamic tract, and what information does it carry?
What: Origin is spinal cord and destination is the
Consists of:
lateral spinothalamic tract: pain, thalamus, & temperature sensations
Anterior spinothalamic tract: light / pressure touches thalamus
What are the three meninges,
Dura mater: Outer
Arachnoid Mater: Middle
Pia mater: Inner
what is the blood–brain barrier (BBB)?
Tight junction which allows lipid soluble material pass from blood to brain and spinal cord (selective permeability)
What structure produces cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and what structure absorbs CSF?
function: prevents contact, provides support for brain, transport nutrients and wastes to and away for CNS
Produce: choroid plexus of ventricles
Absorbs: arachnoid granulation
What is the reticular formation?
Arousal
Controls sleep–wake cycle
Keeps awake and conscious state
What does the pineal gland secrete?
Location: epithalamus
Produces: Melatonin & maintain circadian rhythm
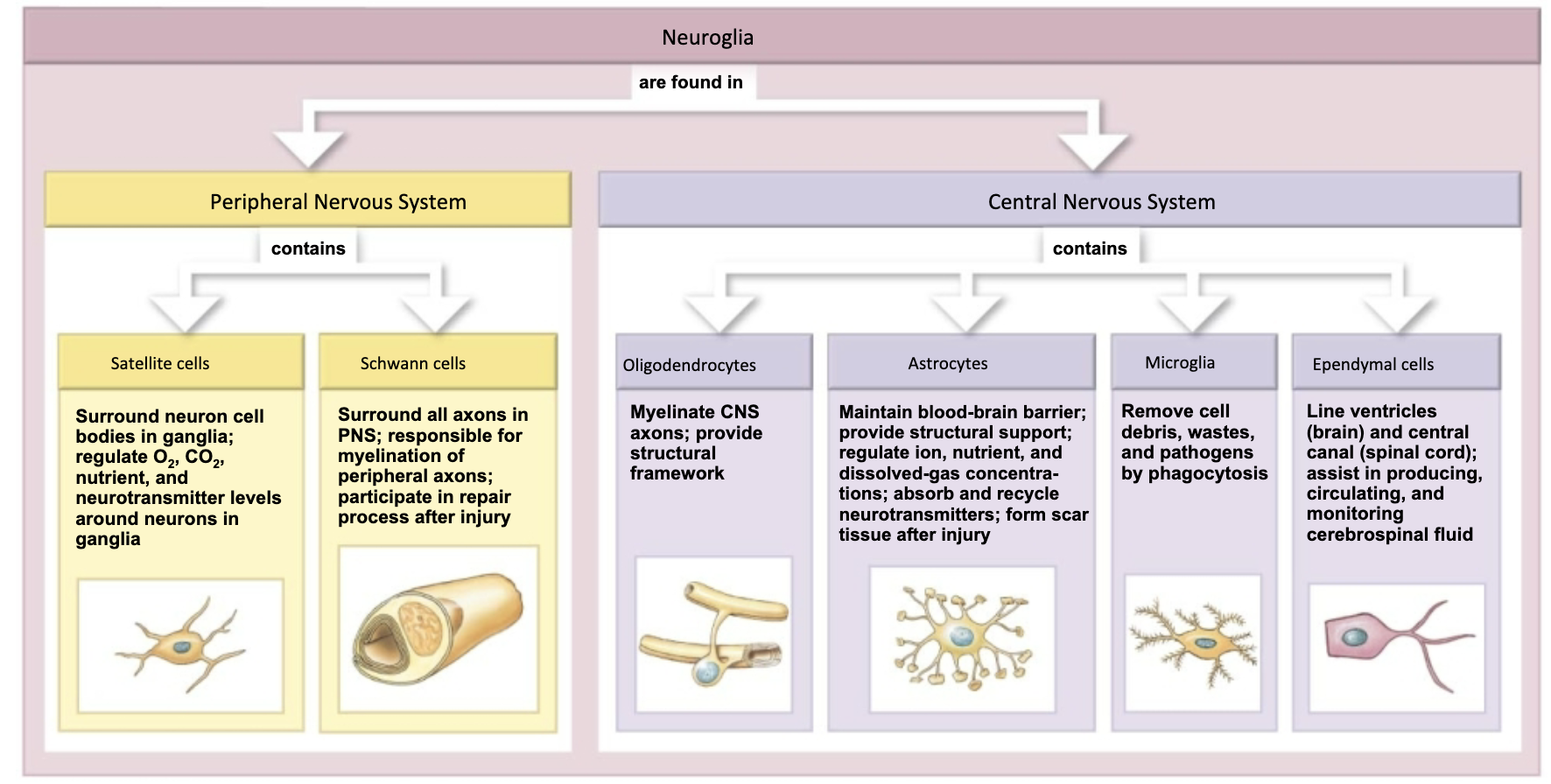
What are the different glial cells, and what are the functions of Schwann cells, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells? (DRAW IT)
what are effectors?
body's muscles and glands that carry out responses to stimuli, triggered by the nervous system
What is myelin,
what is the axon hillock
Myelin
What: layer of insulation of the axon
Produced by: schwann cells (PNS), Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Axon hillock:
connects the axon with the cell body
Function: where nerve impulses begin
What are preganglionic neurons and postganglionic neurons?
Pre: type of axon that leave CNS and travels to ganglion, always found in CNS
Post: type of axon that begin in the ganglion and goes to target organ
Collection of neuron cell bodies in ANS (A ganglion is a collection of neuron cell bodies in the ANS where signals from preganglionic neurons are relayed to postganglionic neurons.)
What is the structural classification of neurons based on?
Processes are the axons and dendrites of a cell body, the number and shape determines the structural type of neuron