Concept 10.2: Photosynthesis converts light energy to the chemical energy of food
1/14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Chloroplasts
Organelles within plants and other photosynthetic organisms that are structurally similar to and likely evolved from photosynthetic bacteria
Structure allows for chemical reactions of photosynthesis
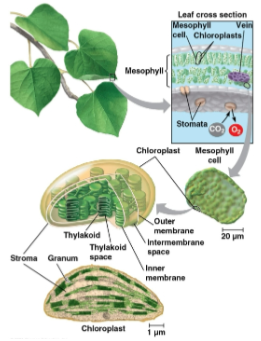
Leaves
The area of most photosynthesis in plants
Mesophyll
The interior tissue of the leaf where chloroplasts are mainly found
Stomata
Pores in a plant’s leaf where CO2 enters and O2 exits for gas exchange
Veins
Structures within a plant that transport water from the roots and export sugar to nonphotosynthetic parts of the plant
Stroma
Dense fluid within the chloroplast envleloped by two membranes
Thylakoids
Connected sacs in the chloroplast that compose a third membrane system, stacked in columns called grana
Chlorophyll
The pigment that gives leaves their green color that resides in thylakoid membranes
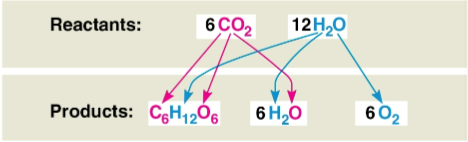
Photosynthesis
A complex series of reactions represented by the equation 6CO2 + 12H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
Represents the effective reverse of cellular respiration in electron flow to make sugar in two stages
Oxidizes H2O and reduces CO2 in an endergonic process powered by light
Water
Substance used in photosynthesis as it is split into hydrogen and oxygen
Electrons from hydrogen are used to create sugar molecules while releasing O2 as a by-product
Hydrogen may also be obtained via other sources, such as from H2S that creates S2 as a waste product
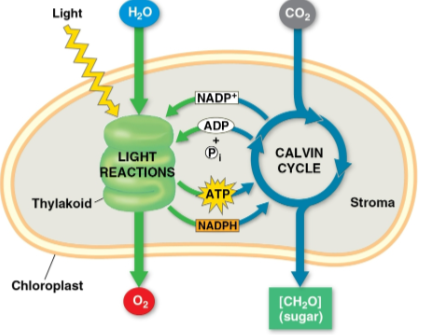
Light reactions
The first part of photosynthesis that occurs in the thylakoids
Splits H2O, recieving electrons and protons as H+
Releases O2 as a by-product
Reduces the electron acceptor NADP+ to NADPH
Generates ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation
NADP+
An electron acceptor reduced in the light reactions in the thylakoids to NADPH for transfer to oxygen
Photophosphorylation
The generation of ATP from ADP in the light reactions in the thylakoids
Calvin cycle
Second part of photosynthesis within the stroma that makes sugar from CO2, using ATP and NADPH generated from light reactions
Begins with carbon fixation, incorporating CO2 into organic molecules
Reduces fixed carbon to carbohydrate by transferring electrons from NADPH
Carbon fixation
The incorporation of carbon from CO2 into organic molecules via the Calvin cycle in the stroma