chapter 19 - bone marrow failure
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
fatigue, infection, bleeding
clinical consequences of pancytopenia include:
unknown cause
idiopathic acquired aplastic anemia is due to:
destruction of stem cells by autoimmune T cells
pathophysiologic mechanism in acquired idiosyncratic aplastic anemia is:
very severe
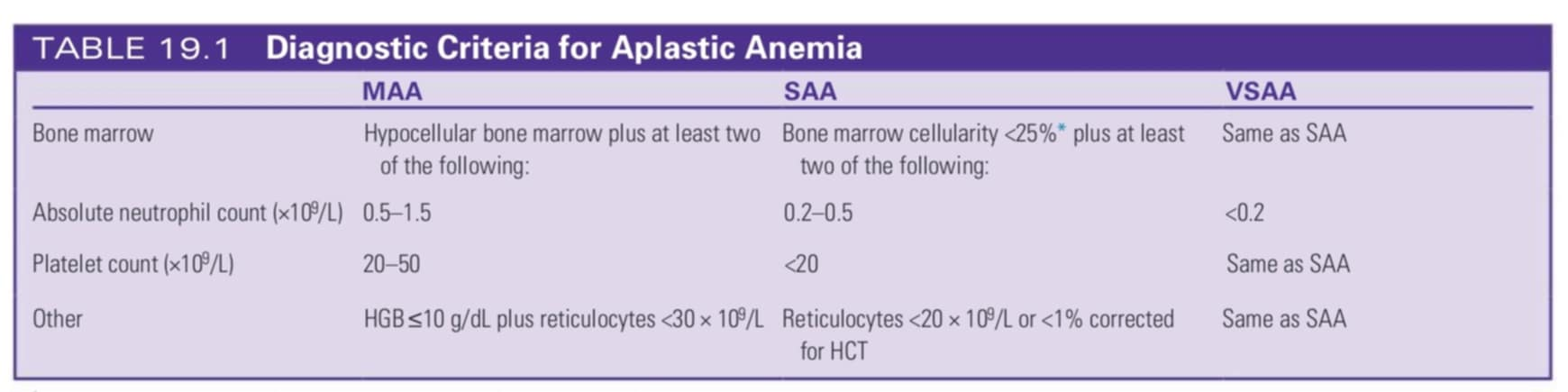
what is the aplastic anemia classification of a 15-year-old with
bone marrow cellularity — 10%
Hgb — 7 g/dL
absolute neutrophil count — 0.1 × 109/L
platelet count — 10 × 109/L
macrocytosis, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia
most consistent peripheral blood findings in severe aplastic anemia
bone marrow transplant with an HLA-identical sibling
treatment that has shown best success rate in young px with severe aplastic anemia
diepoxybutane-induced chromosome breakage
test that is most useful in differentiating Fanconi anemia from other other causes of pancytopenia
premature death of hematopoietic growth factors
in dyskeratosis congenita, mutations in genes that code for the telomerase complex may induce bone marrow failure by causing which?
only erythropoiesis is affected
diamond-blackfan anemia differs from Fanconi anemia in that the former:
congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
anemia that should be suspected in a patient with refractory anemia, reticulocytopenia, hemosiderosis, and binucleated erythrocyte precursors in the bone marrow
inadequate production of erythropoietin
primary pathophysiologic mechanism of anemia associated with chronic kidney disease:
reticulocytosis
findings not consistent with myelophthisic anemia