2MM3
1/245
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
246 Terms
What is a randomized control trial used for?
effectiveness of a prevention or treatment/therapy/intervention
What is a randomized control trial?
strongest design, people randomly selected to receive the intervention or not to
What are pros of randomized control trial?
random selection and longitudinal
What are cons of randomized control trial?
cost, long period follow up, generalizability
What is the mechanism of a randomized control trial?
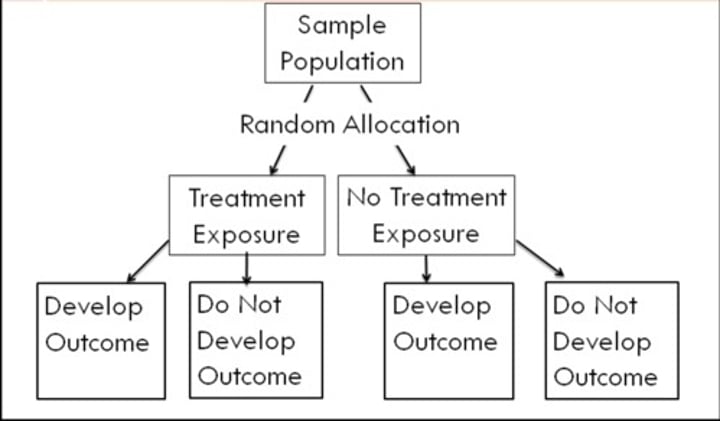
What are cohort analytic studies used for?
effectiveness of a prevention, treatment, intervention
What is a cohort analytic study?
longitudinal, prospective study
- 2 groups people select control or experimental
- NO randomization
- group differences may be due to factors that were there prior to intervention
What are cons of cohort analytic study?
increased bias, expensive
Cohort analytic study
Eligible participants --> non random allocation
--> a) school based --> i) outcome ii) no outcome
--> b) diet exercise --> i) outcome ii) no outcome
What is investigator triangulation?
more than 1 data collector
What is theory triangulation?
findings are examined in relation to existing theories
What is member checking?
come up with an idea and go back to ask the participant
What is PICO?
Population, intervention, comparison, outcome
What is a case control study used for?
exposure is related to an outcome
What is a case-control study?
looks at 2 groups of people, those that were exposed to the intervention and those that weren't (look back in time)
What are pros of case-control studies?
allows assessment of unreachable populations, control group included
What are the negative of case-control studies?
hard to get control group that matched perfectly
What is the mechanism of case-control studies?
Eligible participants
--> outcome --> i) exposure ii) no exposure
--> no outcome --> i) exposure ii) no exposure
What is a cohort study used for?
What is the likelihood that a person will experience or develop the outcome if they are exposed to a disease
What is a cohort study?
participants are followed over time, ensure the disease preceded outcome
What is the mechanism of a cohort study?
eligible participants with exposure
--> outcome
--> no outcome
What is a phenomenological approach?
the lived experience of individuals
What is grounded theory?
the process that shapes behaviour and interaction
What is ethnographic study?
how cultural knowledge, norms, values influence one's life experience within social context of a culture or subculture
What is homogenous sampling?
select participants who have similar narratives of a phenomenon
What is heterogenous sampling?
select participants who can provide different narratives of a phenomenon
What is snowball sampling?
used when no sampling frame exists
What is theoretical sampling?
associated with grounded theory, aim to seek data that challenge emerging ideas
What is environmental data?
home characteristics, community characteristics, access to healthcare
What is the Friedman family assessment model?
identifying data, developmental stage and history, family structure, family function, family coping
What is the Calgary family assessment model?
developmental stages, structural, developmental, functional
What is ethnicity?
a family's cultural, historical, linguistic and ethnic origin
What is race?
influences individual members and group identification
What is social class?
shaped by education, income and occupation
What is religion and spirituality?
can influence their ability to cope with or manage an illness or health concern
What is environment?
the larger community, neighbourhood and home contexts
What is gender?
a set of beliefs or expectations of masculine and feminine behaviours and experiences
What is rank order?
order of children by age and gender
What are subsystems?
smaller groups of relationships within a family
What is a functional assessment?
how family members interact and behave towards each other
- instrumental functioning
- expressive functioning
What is instrumental functioning?
the normal activities of daily living
What is expressive functioning?
the ways in which people communicate
- emotional communication
- verbal communication
- nonverbal communication
- circular communication
- problem solving
- roles
What is developmental assessment?
interactions between an individuals development and the phase of the family developmental lifestyle
1) family life stages
2) tasks
3) attachments
What is the McGill/Developmental Model?
family as a subsystem, health as the focus of worth, learning the process through which the health behaviours are acquired
What is the effect of smoking on surgery?
smokers are at an increased risk for post op complications
- increased mucous thickness
- greater difficulty clearing airways
What is the effect of alcohol/substance abuse on surgery?
predispose the patient to adverse reactions of anesthetic, cross-tolerant, withdrawal
What is the effect of obesity on surgery?
reduce respiratory and cardiac function, increased risk of embolus, pneumonia, poor wound healing, dehiscence
What is the effect of immunocompetence on surgery?
excess thinning of skin, destruction of collagen, impaired vascularization, infection, poor wound healing
What is the effect of malnourishment on surgery?
poor tolerance of anesthesia, delayed blood clotting mechanism, infection, poor wound healing
What is the effect of young age in surgery?
less BV, dehydration, over hydration, airway management, temperature management
What are respiratory complications of surgery?
airway obstruction, hypoxemia, hypoventilation, atelectasis (collapsed lung)
What are cardiovascular complications of surgery?
hypotension, hypertension, dysrhythmia, fluid retention, DVT, syncope
What are the neurological complications of surgery?
delirium, delayed awakening
What are the GI/GU complications of surgery?
nausea and vomitng, post operative ileus, paralytic ileus, low urine output, urinary retention
What are integument complications of surgery?
surgical site infections
What are psychological complications of surgery?
anxiety, depression, confusion, delirium, disturbed sleep pattern, body image
What is delirium?
state of acute mental confusion
What is delirium characterized by?
acute onset, fluctuating course, altered LOC
What are predisposing factors?
present at the time of admission, demographic, cognitive status, functional status, coexisting conditions
What are precipitating factors?
noxious insults related to hospitalization, surgery, drugs, incurrent illness
What is hypoactive delirium?
decreased alertness, decreased psychomotor activity
What is hyperactive delirium?
Agitation, restlessness and hallucinations
What is mixed delirium?
alternating periods of hyperactive and hypoactive
What is dementia?
impaired memory, slow gradual decline, chronic, decreased orientation, decreased ability to perform ADL's
What is vascular dementia?
cause by stroke or chronically damaged/narrowed brain blood vessels
What are signs and symptoms of vascular dementia?
difficulty concentrating and analyzing situations, unsteady gait, restlessness, agitation, incontinence
What are risk factors for vascular dementia?
aging, increased BP, atherosclerosis, diabetes
What is Parkinson's dementia?
a progressive neurodegenerative disease of the CNS
What are signs and symptoms of Parkinson's dementia?
dysphagia, difficulty concentrating, confusion
What is the progression of Parkinson's dementia?
gradual onset, ongoing progression
What is Alzheimer's disease?
abnormal protein deposits form plaques and tangles in the brain (connections b/w cells die off)
What are signs and symptoms of Alzheimer's disease?
memory loss, disorientation, reduced cognition, decline in social skills
What are risk factors for Alzheimer's disease?
older population, genetic, hospitalization, medical conditions
What are treatments for Alzheimer's disease?
creating a safe and supportive environment, cholinesterase inhibitors
What is lewy body dementia?
protein deposits in nerve cells, accumulation of Lewy bodies results from the loss of neutrons that create ACTH and dopamine
What are signs and symptoms of Lewy body dementia?
cognitive fluctuations, hallucinations, motor disturbances
What are risk factors for Lewy body dementia?
60+, male, family history
What is fronto-temporal dementia?
degeneration of the frontal, temporal, or both sides (tau protein)
What are signs and symptoms of fronto-temporal dementia?
behavioural: loss of inhibitions, depression, compulsivity, loss of empathy
language: aphasia, loss of semantics
What is the progression of fronto-temporal dementia?
gradual decline, stepwise, rare, more common younger
What is Huntington's dementia?
A progressive brain disorder caused by a single defective gene on chromosome 4
What are signs and symptoms of Huntington's dementia?
involuntary jerking, slow abnormal eye movement, impaired gait, difficulty with speech and swallowing
What are cognitive changes of Huntington's dementia?
disorganized thinking, behavioural/emotional instability, lack of awareness
What are behavioural changes of Huntington's dementia?
depression, irritability, social withdrawal, insomnia, fatigue
What is prediabetes?
blood sugars that are higher than normal, can turn into type 2
What are risk factors for prediabetes?
high BP, high cholesterol, high BMI, sleep apnea, psychiatric disorders
What is gestational diabetes?
occurs during the 2nd or 3rd trimester of pregnancy
What is metabolic syndrome?
cluster of metabolic disorders, abdominal obesity, increased TG levels, decreased HDL levels, hypertension, increased glucose levels, insulin resistance
What is type 2 diabetes?
insulin resistance or dysfunctional secretions
What are risk factors for type 2 diabetes?
40+, family history, history of prediabetes, heart disease, hypertension, high cholesterol, overweight, sleep apnea
What are signs and symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
non specific manifestations, fatigue, weight gain, tingling/numbness, prolonged wound healing
What is type 1 diabetes?
the pancreas does not produce any insulin, rapid onset, acute manifestations
What are signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes?
polyuria, polydipsia, polyphasic, weight loss, weakness, fatigue
What is nephropathy?
microvascular complications associated with damage to the SBV's that supply the glomeruli of the kidney
What is neuropathy?
nerve damage that occurs because of the metabolic derangements associated with diabetes
What is retinopathy?
microvascular damage to the blood vessels of the retina
What is hypoglycaemia?
extremely low blood glucose levels
What are risk factors for hypoglycaemia?
alcohol intake without food, loss of weight without change in dose, taking too much meds/insulin, pregnancy
What are symptoms of hypoglycaemia?
cold/clammy skin, headache, hunger, nervousness, tachycardia, confusion, nausea, numbness/tingling
What is hyperglycaemia?
high blood glucose levels