Nose, Sinuses, Mouth, and Throat Anatomy Flashcards
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the anatomy of the nose, sinuses, mouth, and throat.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
List the functions of the nose.
Olfaction (smelling), Respiration (breathing), Filtration of dust, Humidification of inspired air, Reception and elimination of secretions
Name the bones and cartilages that form the external nose.
Bones: Nasal bones. Cartilages: 2 lateral, 2 alar, and septal cartilage.
What structures divide the internal portion of the nose into right and left cavities?
Nasal septum.
Name 3 internal structures of the nose.
Cochae/turbinates, olfactory bulb, Eustachian tube meatus
What are the names of the nasal turbinates/conchae?
Superior, Middle, and Inferior.
Name the components of the nasal septum.
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid, Vomer, Septal cartilage, Nasal crests of maxillary and palatine bones.
Where are olfactory receptors located?
Upper nasal cavity.
What nerve do olfactory receptor cell fibers synapse with?
Olfactory bulbs (CN I).
List the paranasal sinuses.
Frontal, Maxillary, Ethmoidal, and Sphenoid sinuses.
Which cranial nerve innervates the frontal sinuses?
Supraorbital nerves (CN V1).
Where does the maxillary sinus drain?
Inferior to the middle turbinate.
What important structures are located near the sphenoid sinuses?
Optic nerves, optic chiasm, pituitary gland, internal carotid arteries, and cavernous sinuses.
What is Kiesselbach's area and why is it important?
Anterior 1/3 of the nasal septum is rich in anastomoses of all five arteries and is a common site for nosebleeds (epistaxis).
What structures are included in the upper respiratory tract?
Nostril (nasal passages/nares), Turbinates, Paranasal sinuses, Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx, Larynx (cricoid cartilage).
When does digestion begin?
Digestion begins in the mouth
What is the oral cavity?
Chamber between the palate and tongue, surrounded by the lips and cheeks.
What are the components of the oral region?
Oral cavity (mouth), Lips, Teeth, Hard & soft palate, Tongue and muscles, Gingivae (gums), Palatine tonsils, Uvula, Buccal mucosa.
What forms root and floor of oral cavity?
Roof = hardpolate,soft palate and
Floor = the tongue
What muscle is contained in the cheeks that keep food between teeth?
Buccinator muscle.
List the functions of the tongue.
Mastication (chewing), taste, deglutition (swallowing), articulation (speech), and oral cleansing.
What type of muscle is tongue composed of?
Skeletal muscle
Name the four types of tongue papillae and their locations.
Foliate (posterior lateral), Vallate (posterior), Filiform, Fungiform (apex and sides).
What are functions of intrinsic and extrinsic muscles?
Intrinsic changes the shape of tongue while extrinsic moves the tongue.
What are the 5 main types of tastes and their locations?
Sweet is the tip, sour is the sides, salty is the entire, and bitter is the back of tongue.
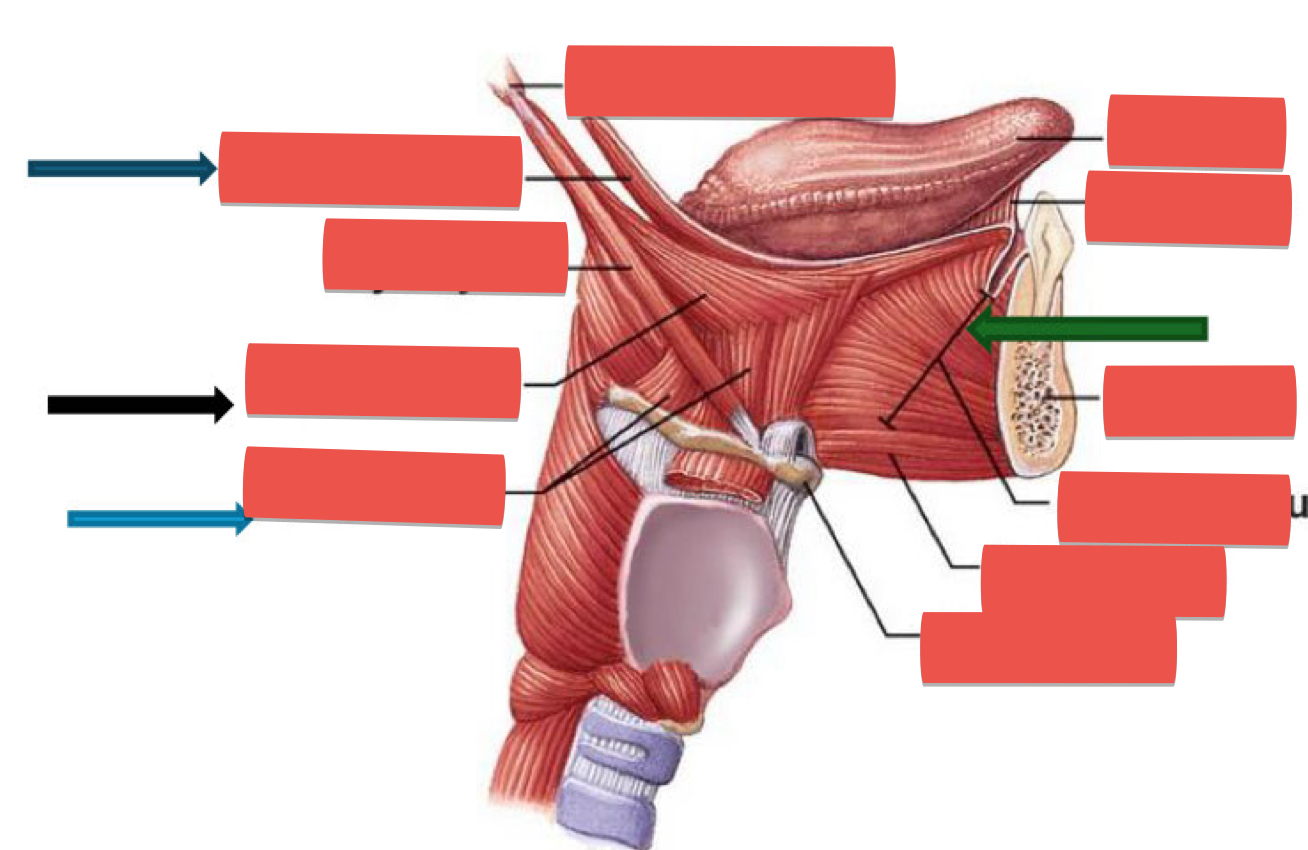
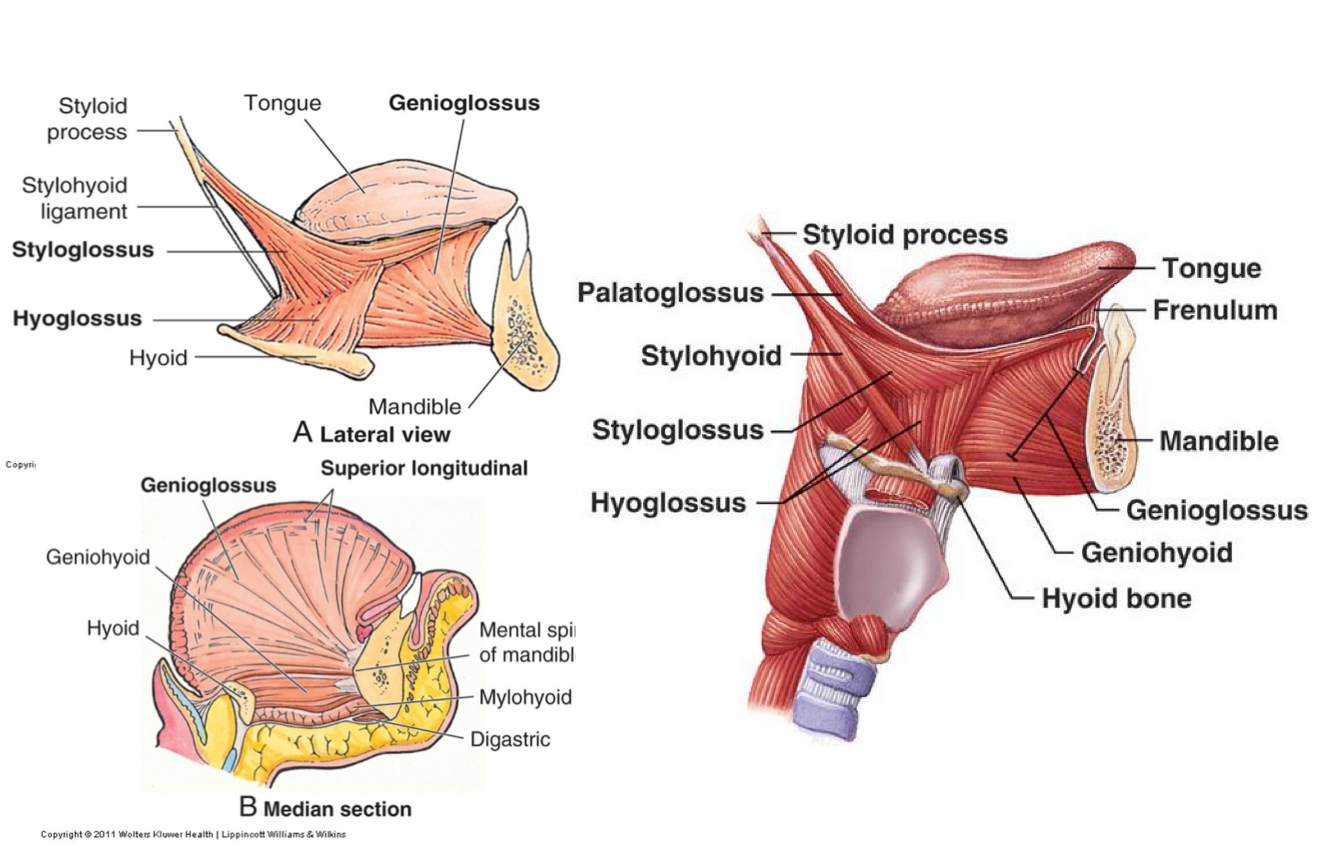
List the four extrinsic muscles of the tongue
Genioglossus m., Styloglossus m., Palatoglossus m., and Hyoglossus m.
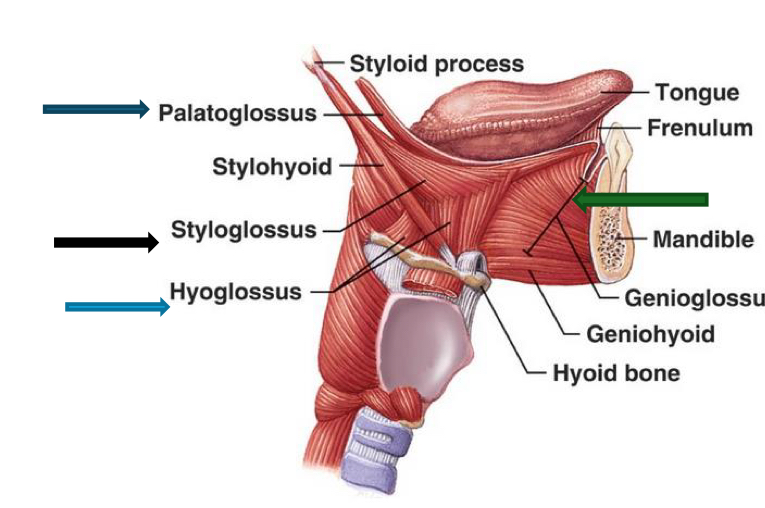
What are functions of each of the 4 extrinsic muscles?
Genioglossus - Depresses tongue, especially the center Protrudes tongue
Hyoglossus - Depresses tongue and retracts tongue
Styloglossus - Retracts the tongue and elevates the tongue
Palatoglossus - elevates posterior part of tongue and depresses the soft palate
Which nerve innervates all muscles of the tongue, except for palatoglossus?
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII).
Which nerve innervates the palatoglossus muscle?
Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve (CN X).
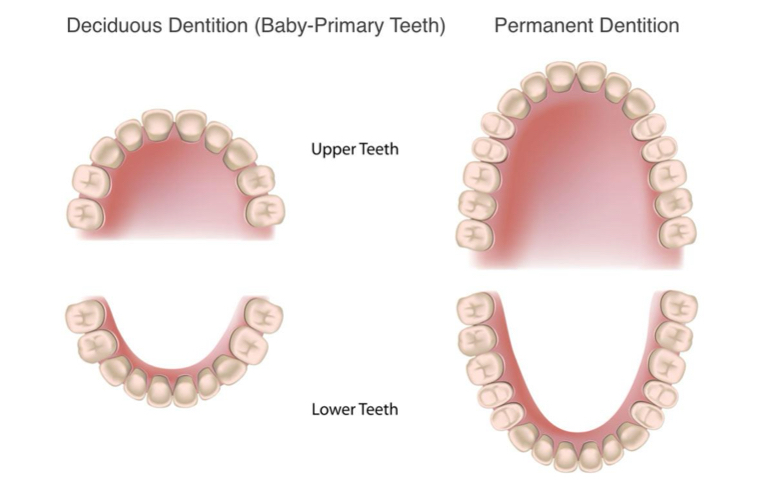
How many deciduous (primary) teeth do humans have?
20
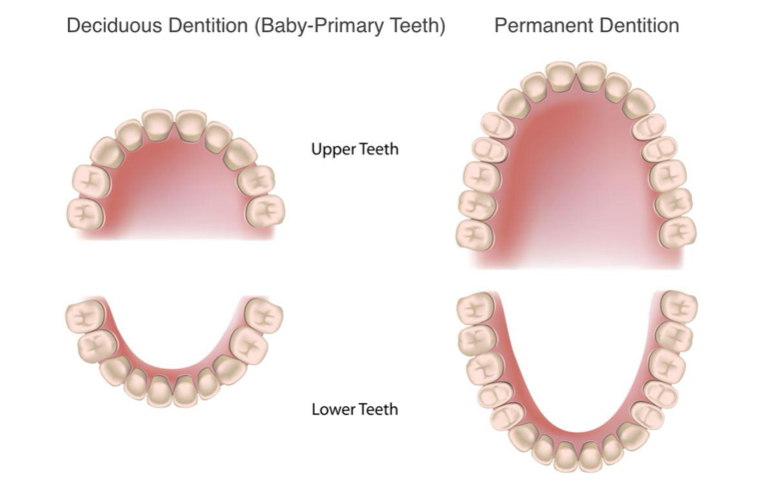
How many permanent (secondary) teeth do humans have?
32
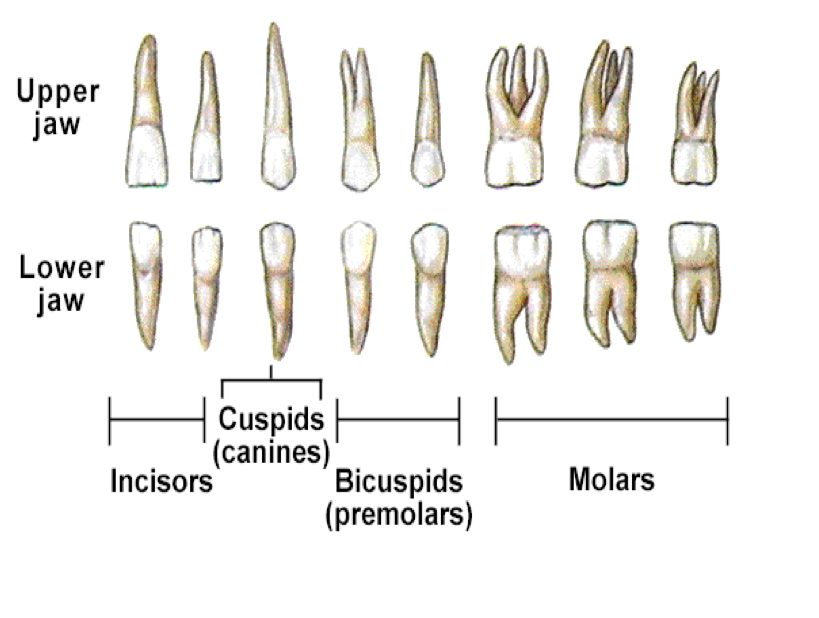
List the different types of teeth and their functions.
Incisors (biting), Canines (tearing), Premolars & Molars (crushing and grinding).
What are the three main parts of a tooth?
Crown, root, and neck.
What is the hardest substance in the human body?
Enamel.
What structures separate the oral cavity from the nasal cavity?
Hard palate
What structures separate the oral cavity from the nasopharynx?
Soft palate
What is the function of the soft palate?
Closes off the nasal cavity during swallowing.
What is the function of saliva?
Moistens food, begins chemical digestion of carbohydrates, lubrication, moistening, cleaning and prevention of tooth decay, and allows for the ability to taste.
Name the three pairs of major salivary glands.
Parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands.
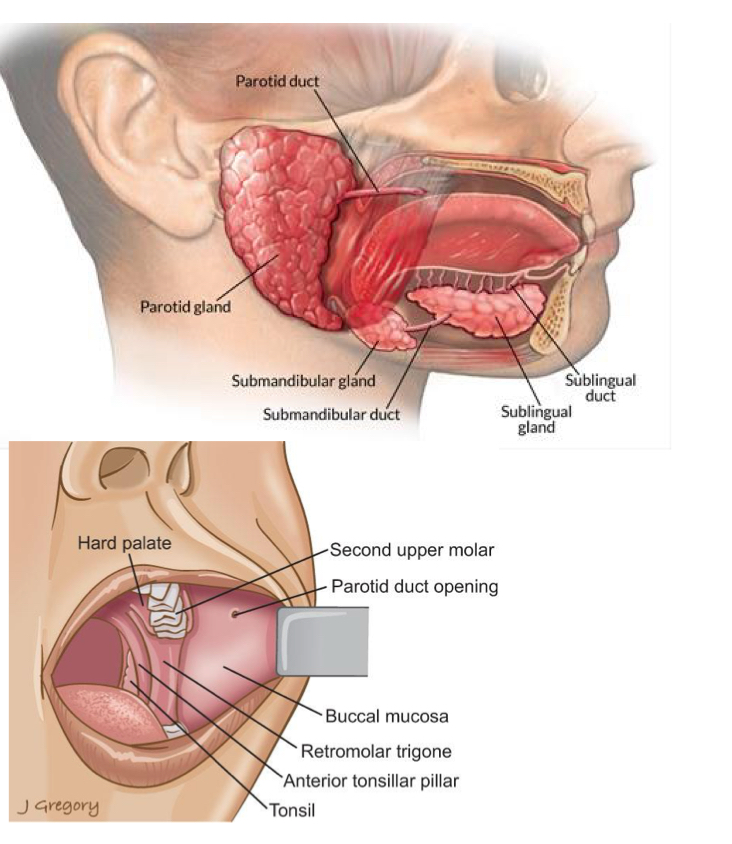
Which of 3 salivary glands is the largest?
Parotid glands -The largest; they lie anterior and slightly inferior to each ear
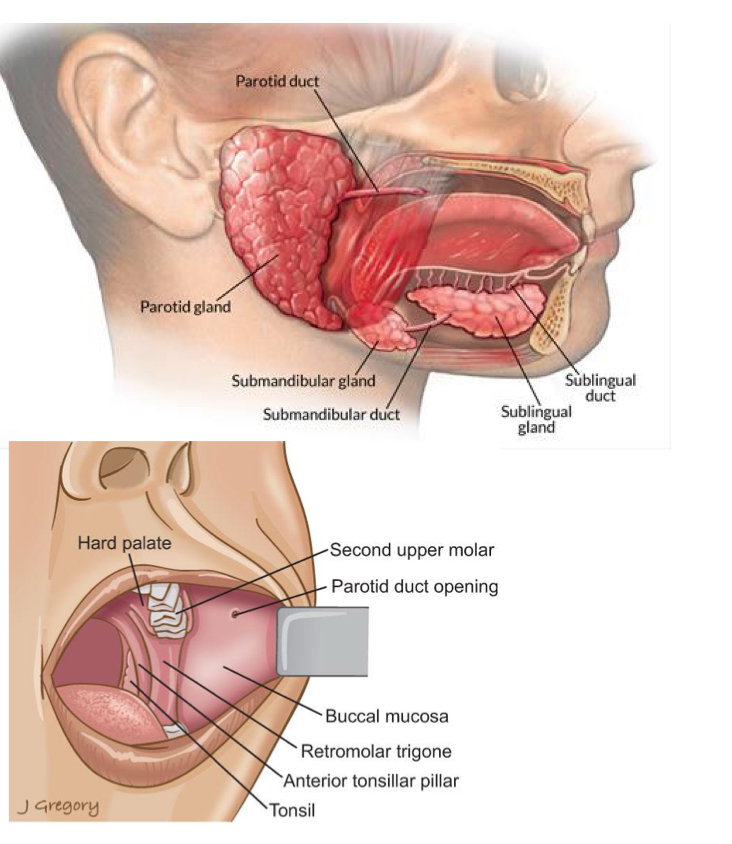
Which of the 3 salivary glands is the smallest?
Sublingual gland is the smallest and they lie on floor of the mouth inferior to tongue between the mandible and genioglossus muscle.
Where does parotid gland drain into?
Drains into oral cavity- Stenson’s duct
What ducts drain the submandibular glands?
Wharton's duct.
True of false: all salivary glands have ducts that empty into the oral cavity
True!
Where are the pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids) located?
Posterior pharynx above the border of the soft palate.
List the three regions of the pharynx.
Nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
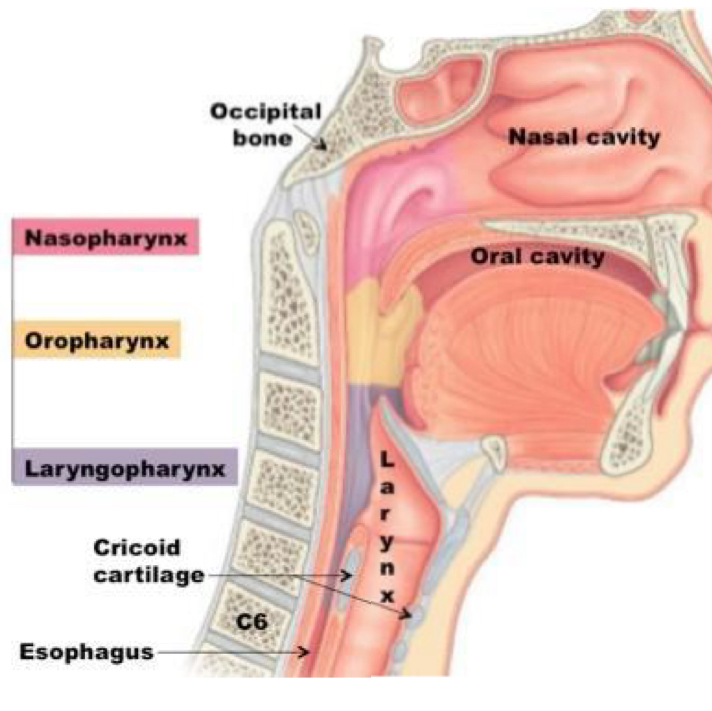
What is the general function of the pharynx?
Passageway for air and food, helps produce speech sounds.
What is the function of the larynx?
Voice production (aka voice box) and protecting the air passageway, especially during swallowing.
What are the stages of swallowing?
• Stage 1 (Voluntary): The bolus is consciously pushed into the oropharynx.
• Stage 2 (Involuntary/Pharyngeal): The soft palate elevates to close off the nasopharynx, while suprahyoid muscles elevate the larynx, protecting the airway.
• Stage 3 (Involuntary/Esophageal): Sequential contraction of pharyngeal constrictor muscles propels the bolus down the esophagus.
What structures make up the larynx?
Cartilage joined by ligaments and membranes. For example:
Epiglottis - protects food from getting in trachea
thyroid cartilage aka Adam’s apple
cricoid cartilage - around entire airway and typically detected while intubating patients
Describe the function of vocal cords: upper (false) and lower (true) folds.
Upper folds (false vocal cords or vestibular folds): Do not produce sound; assist in closing the airway during swallowing.
Lower folds (true vocal cords or vocal folds): Produce sound by vibrating as air passes between them.
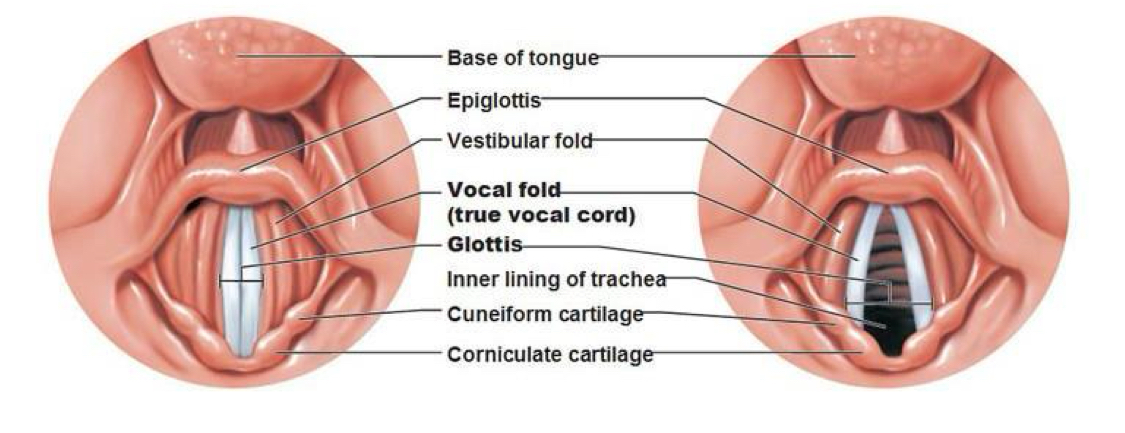
What are the two sets of vocal cords and their functions?
False vocal cords (vestibular fold) which help close the airway during swallowing, and true vocal cords (vocal
Describe location of trachea
The trachea extends downward anterior to the esophagus into the thoracic cavity, where it splits into the right and left bronchi.
Which is the most common nerve to be injured during thyroid surgery?
Recurrent laryngeal n. - lateral to trachea, medial common carotid a posterior aspect of thyroid
Which nerve forms the recurrent laryngeal nerve which innervates the vocal cords?
Vagus nerve (CNX) and if severed will not be able to speak
Which nerve innervates larynx?
Recurrent laryngeal nerve
What structures assist with respiratory?
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea