4. innate sensing of pathogens
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
microbial non-self
recognition of molecules ONLY present in microbes
macrophages, dendritic cells, epithelial cells
missing self
recognition of cells NOT expressing “self” molecule
natural killer cells
characteristics of pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
important for recognition of microbial non-self
gene products unique to microbes → molecular signatures of microbial invaders
conserved among microbes of a given class → broad detection ability
essential for microbial survival
ex. LPS (gram -); peptidoglycan (gram +)
damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs)
molecules that are released from damaged or necrotic cells
stimulate elimination of damaged cells and initiate tissue repair
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
recognize PAMPs and DAMPs
receptors expressed on macrophages, dendritic cells, lymphocytes, epithelial/endothelial cells
signal to induce inflammatory cytokines & activate host defense mechanisms
what are the 5 families of PRRs?
toll-like receptors (TLRs)
C-type lectin receptors (CLRs)
NOD-like receptors (NLRs)
RIG-like receptors (RLRs)
cytosolic DNA sensors (CDSs)
what does TLR-2 bind to?
peptidoglycan → gram + bacteria
what does TLR-4 bind to?
LPS → gram - bacteria
what do TLR-3, -7, -8 bind to?
viral RNA
what does TLR-9 bind to?
bacterial DNA → unmethylated cytosine-guanine sequence/motifs (CpGs)
less cytosine methylation in bacterial genome than mammalian genome
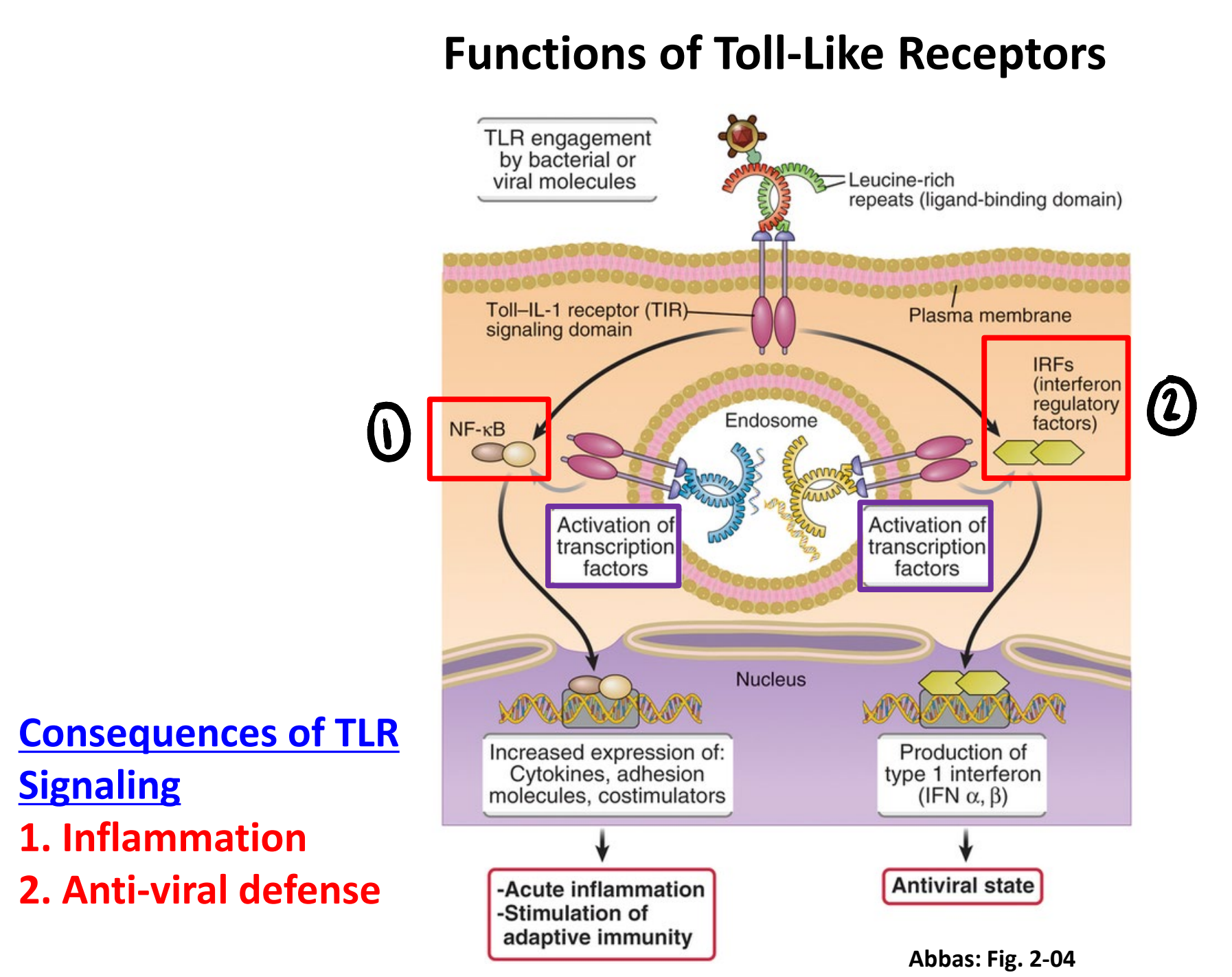
what are the two signal pathways following TLR activation?
inflammatory pathway
NF-κB → acute inflammation & stimulation of adaptive immunity
anti-viral defense
interferon regulatory factors → production of type-1 interferons → antiviral state
what do NOD1 and NOD2 bind to?
peptidoglycan in the cytosol
NLRP3
expressed in macrophages, neutrophils, keratinocytes, and other cells
detects PAMPs (bacteria)
detects DAMPS → extracellular ATP, uric acid crystals from nucleic acids, etc.
urate, cholesterol crystals
what is the role of caspase-1 in the inflammasome?
cleaves pro-IL1β → active IL-1β (pro-inflammatory cytokine)
how can pathogens resist/evade innate immune system?
prevent phagolysosome formation
escape phagosome into the cytoplasm
capsule inhibits phagocytosis
production of catalase → breaks down reactive oxygen intermediates