Physics - 15 Electromagnetism - 15.1 Magnetic Fields & 15.2 Magnetic Fields of Electric Currents & 15.3 Electromagnets in Devices
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Pole
end of a magnet where the magnetic force is maximum
The south pole of a magnet is generally (positive/negative)
positive
The north pole of a magnet is generally (positive/negative)
negative
Magnetic field lines point from ...
north to south
North-seeking
points towards the north pole when suspended freely
South-seeking
points towards the south pole when suspended freely
Magnetic field
area around a magnet where magnetic influence is felt
Magnetic metals [3]
- iron
- cobalt
- nickel
Magnetic field line
lines of force in a magnetic field
Magnetic domain
grouping of atoms that have their magnetic fields aligned
Permanent magnet
magnet made of material that keeps its magnetism
Magnetise
make into a magnet by aligning magnetic domains
Demagnetise
remove magnetic properties from a magnet
Why is steel used for permanent magnets?
magnetised steel retains its magnetism
Induced magnetism
when a magnetic material (usually iron) becomes temporarily magnetised in the presence of a magnetic field
What does it mean for a magnetic material to be 'hard'?
it doesn't easily lose its magnetism
When a current passes through a wire ...
a magnetic field is set up around the wire
What shape are the magnetic field lines caused by a straight current-carrying wire?
concentric circles
Right-hand rule [2]
- thumb defines direction of current
- fingers define direction of magnetic field
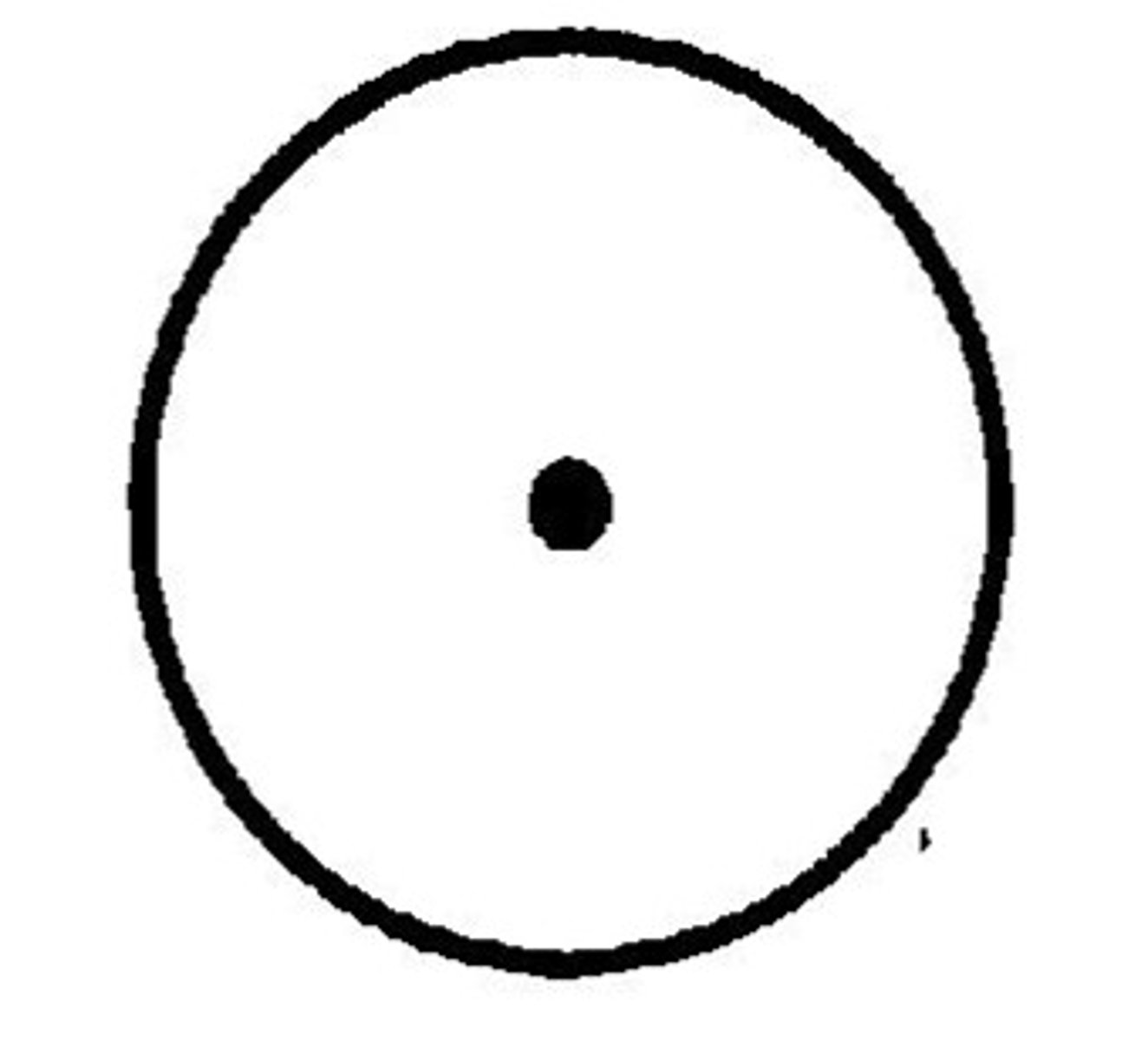
Current exiting page
circle with dot, representing tip of arrow, labelled with I
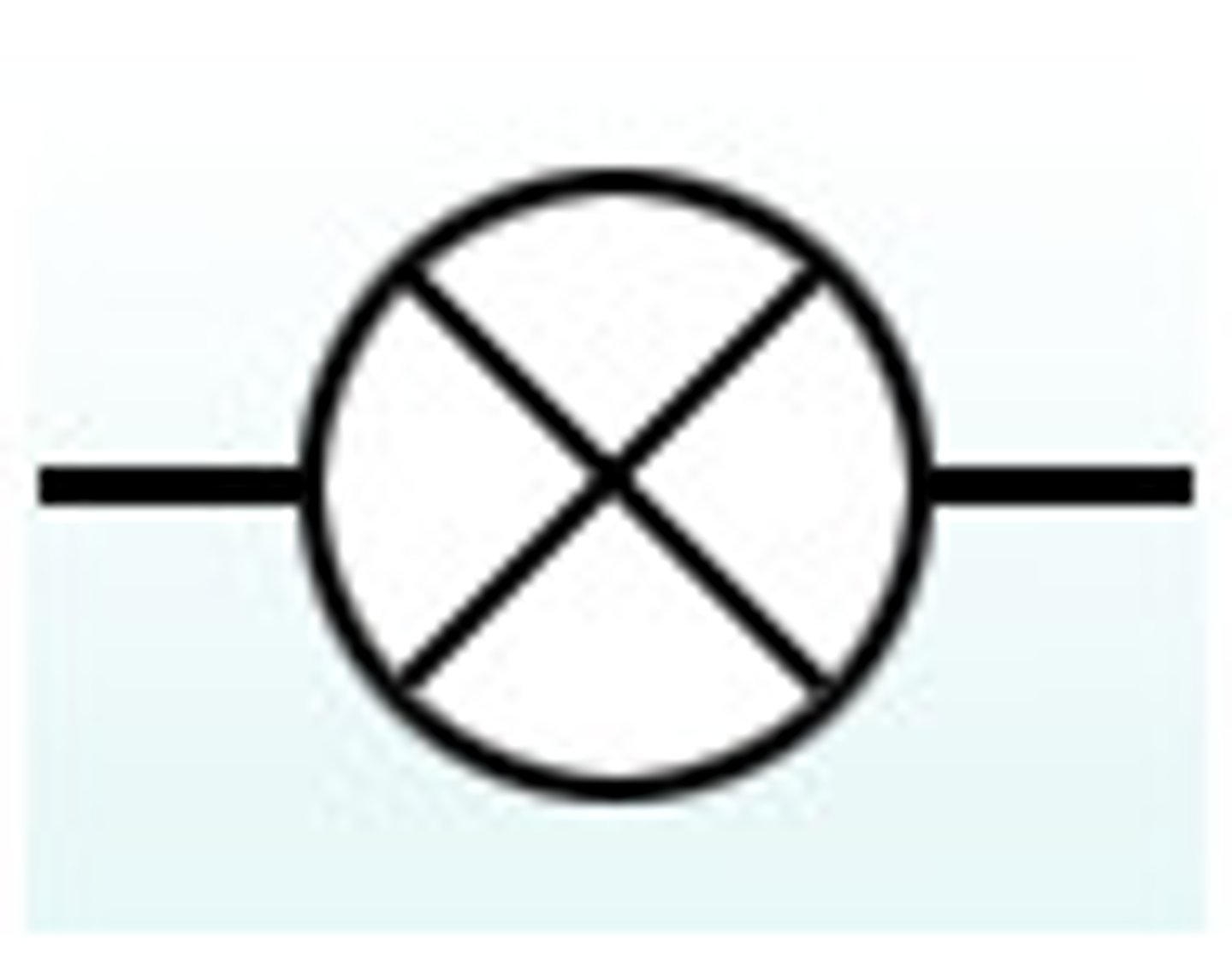
Current entering page
circle with cross, representing shaft of arrow, labelled with I
Solenoid
coil of insulated wire
If the current is increased, the magnetic field strength will (increase/decrease)
increase
If the number of turns in the coil is increased, the magnetic field strength will (increase/decrease)
increase
How to describe the field lines inside a solenoid [2]
- parallel to the solenoid's axis
- in a uniform direction
Electromagnet
solenoid in which the wire is wrapped around an iron core
Uses of electromagnets [4]
- scrapyard crane
- circuit breaker
- electric bell
- relay
Scrapyard crane [2]
- powerful electromagnets lift steel vehicles when a current flows through them
- drop them when the current stops
Circuit breaker [3]
- a circuit contains both a switch and an electromagnet
- if a current that is too high flows, the electromagnet increases in strength
- it then pulls the switch open, stopping the current
Electric bell [5]
- when a current flows, electromagnet activates
- attracts iron armature, which strikes bell
- iron armature disconnects from contact, stopping current
- electromagnet deactivates and armature returns to contact
- current flows again
Relay [4]
- current flows in a small circuit, activating an electromagnet
- electromagnet attracts a switch attached to a spring
- switch touches contact, allowing current to flow in larger circuit
- when electromagnet is deactivated, spring pulls switch back to rest