Bio 163 - Group 1 - Anatomy of Long Bone
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
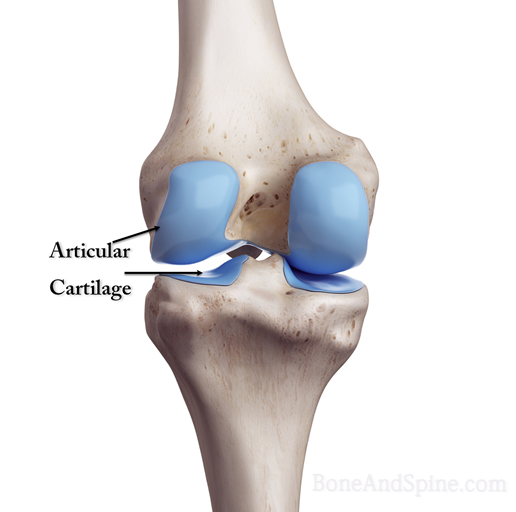
Articular (hyaline) Carilage
a type of smooth, translucent connective tissue that lines the surfaces of joints, providing a low-friction surface for bone movement.
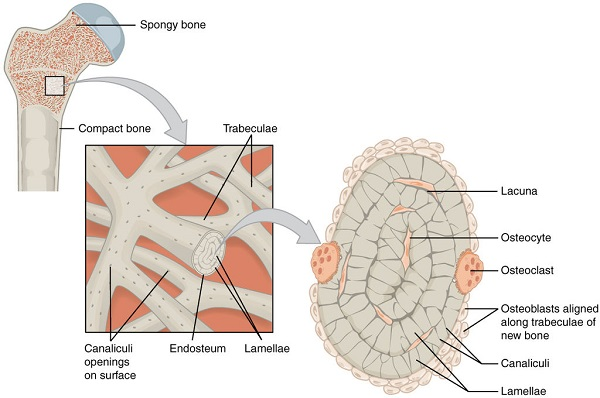
Canaliculus (canaliculi)
tiny channels in the eyelids that drain tears into the tear sac
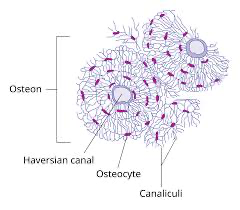
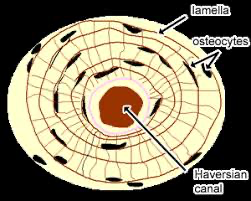
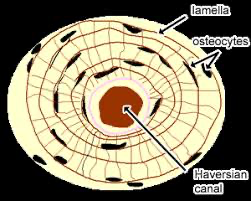
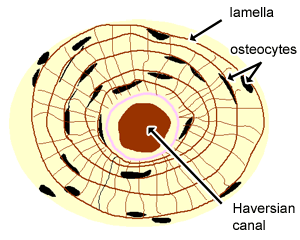
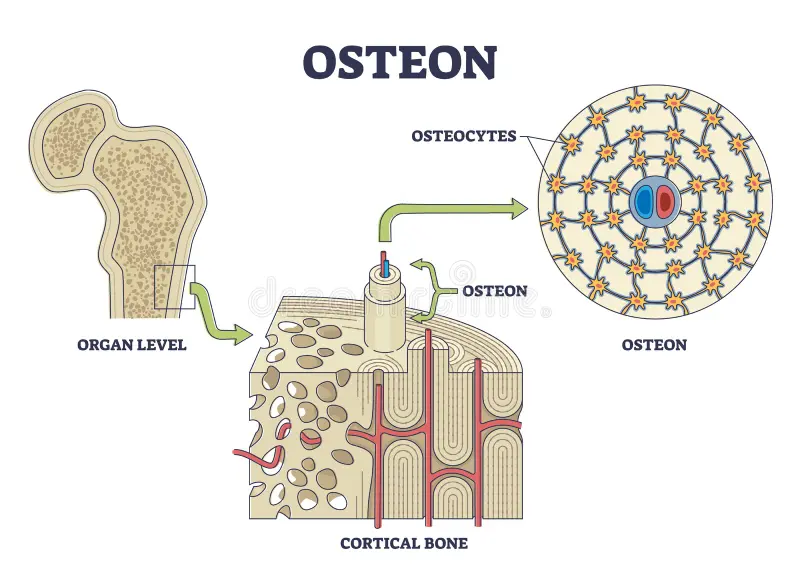
Central (Haversian) canal
the central channel in compact bone that contains blood vessels and nerves, facilitating nutrient and waste exchange.
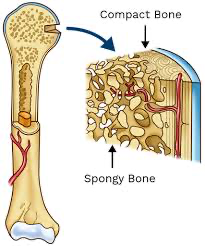
Compact bone
the dense, strong type of bone that forms the outer layer of bones, providing structural support and protection.
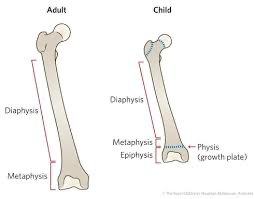
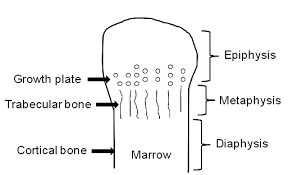
Diaphysis
the elongated shaft of a long bone, primarily composed of compact bone and serving as a support structure.
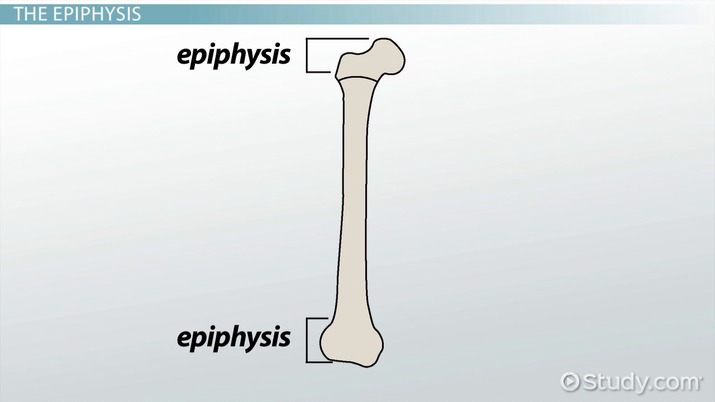
distal epiphysis
the end part of a long bone, opposite the proximal epiphysis, which typically articulates with other bones and is involved in joint movement.
Endosteum
a thin membrane lining the medullary cavity of long bones, containing osteoblasts and osteoclasts that aid in bone growth and repair.
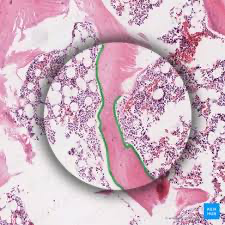
Epiphyslal growth plate
a hyaline cartilage layer located at the ends of long bones, facilitating their growth in length during childhood and adolescence.
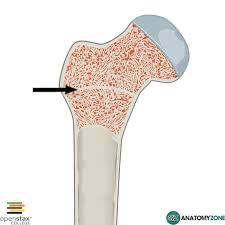
Epiphyseal line
the remnant of the epiphyseal growth plate in adults, indicating the cessation of bone lengthening.
Lacuna(ae)
small spaces in bone that house osteocytes, mature bone cells
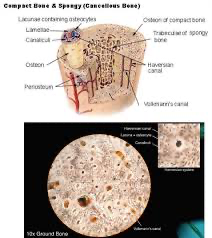
Lamellae
thin layers of bone matrix that contribute to the structure of compact bone.
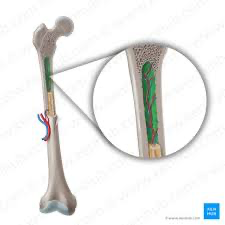
Medullary cavity
a hollow space located within the diaphysis (shaft) of long bones.
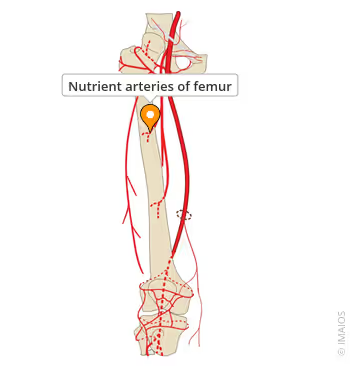
Nutrient artery
a blood vessel that supplies the inner portion (medulla) of long bone
Osteocyte
cells embedded in the bone matrix that play a crucial role in maintaining and regulating bone health.
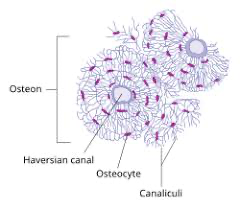
osteon
a cylindrical unit of bone that is the fundamental functional unit of compact bone
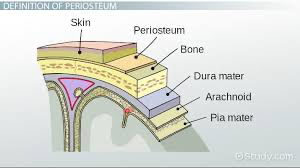
Periosteum
a fibrous sheath that covers bones.
Proximal epiphysis
the end of a long bone that's closest to the body's center
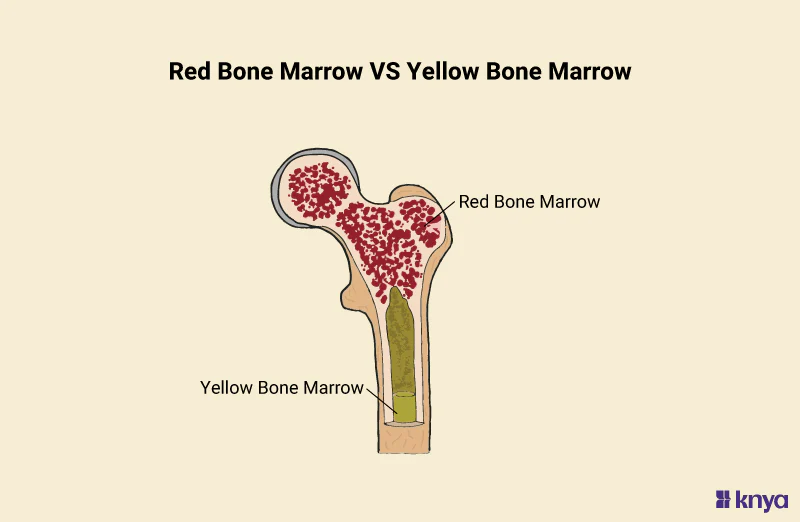
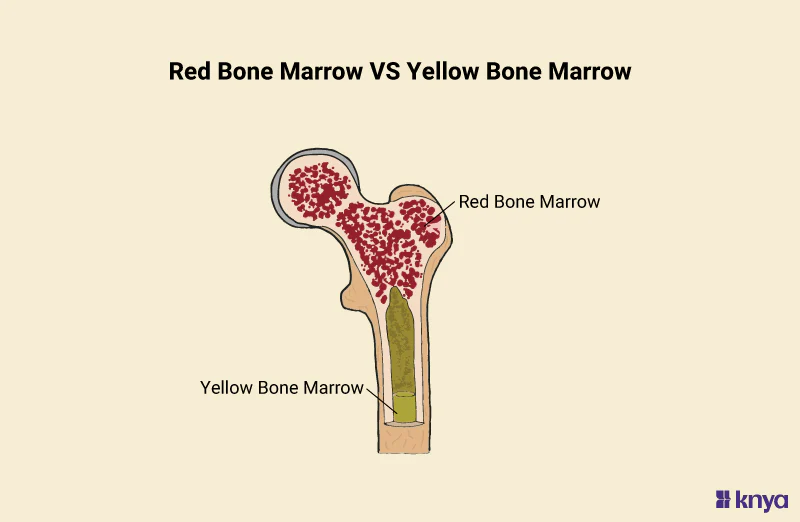
Red bone marrow
a soft, spongy tissue found inside certain bones
Perforating (Sharpey’s) fiber(s)
collagen bundles that connect the periosteum to bone

Perforating (Volkmann’s) canal(s)
small channels in bones that carry blood vessels into and out of bones
Spongy (cancellous) bone
a type of bone tissue that is characterized by its porous and honeycomb-like structure
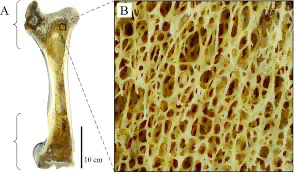
Trabecula(ae)
a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ.
yellow bone marrow
a type of soft, fatty tissue found inside the hollow center of long bones, such as the femur and humerus.