Chapter 34B: Tetrapods (Amphibia and Amniotes)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Tetrapods
Gnathostomes (jawed animals)
four limbs
Evidence = evolved from lobe-finned fish
Ex: amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals
Specific adaptations of Tetrapods
4 Limbs, feet with digits
A neck
Absence of gills
Ears for detecting airborne sounds

Class Amphibia
Tetrapods;
able to live on land and water (“both ways of life”)
first vertebrates to walk on land
direct descendants of fishes
Ichthyostega
word meaning “fish” + “roof”
earliest amphibians
fish with legs
Eggs of Class Amphibia
fertilized in water
no shell
covered with gelatin
Aquatic larva
Class Amphibia;
tail
lateral line
gills
no legs
Metamorphosis
Class Amphibia;
tadpole larva → terrestrial adult
Modern Amphibians
gills usually lost by adulthood
lungs function
breathe through skin
3-chambered heart
Orders of Class Amphibia
Anura — frogs and toads
Urodela — Salamanders
Apoda — Apodans (burrowing amphibians)

Order Urodela
Orders of Class Amphibia;
retain their tail as adults
Ex: Urodeles/Salamanders

Order Anura
Orders of Class Amphibia;
lack a tail as adults
Ex: Anurans (frogs and toads)

Order Apoda
Orders of Class Amphibia;
legless
burrowing
Ex: Apodans, caecilians
Amniotes
Tetrapods;
free of life cycle dependent on aquatic environments
adapted to life on land (waterproof outer layer; thoracic/pulmonary breathing)
Amniotic Egg
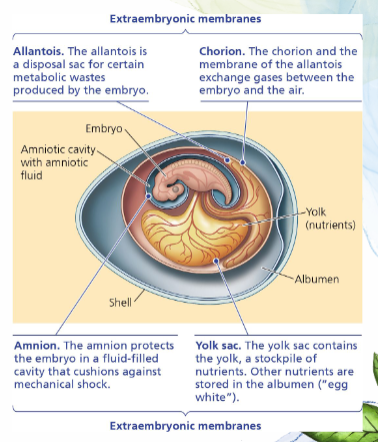
Amniotic Egg
Amniotes;
“Extraembryonic Membranes”
Allantois, Chorion, Amnion, Yolk Sac
Egg Shell
Allantois
Amniotic Egg;
disposal sac for certain metabolic wastes produced by the embryo
Chorion
Amniotic Egg;
exchange gases between the embryo and the air, along with the allantois membrane
Amnion
Amniotic Egg;
protects the embryo in a fluid-filled cavity that cushions against mechanical shock
Yolk Sac
Amniotic Egg;
contains the yolk
a stockpile of nutrients
other nutrients = stored in albumen (“egg white'“)
Egg Shell
Amniotic Egg;
prevents desiccation
allows complete life on land

Class Reptilia
Amniotes;
first true land animals
no feathers
shelled egg
internal fertilization
Ectothermic
Improved heart
Keratin scales
Keratin scales
Class Reptilia;
prevent desiccation and abrasion
Ectothermic
Class Reptilia;
absorb heat form the environment as main source of body heat
lower energy requirement (10% less than similar size mammal)
Improved heart
Class Reptilia;
Right and Left Atria
1 ventricle

Anapsids
Turtles

Lepidosaurs
Class Reptilia;
Tuataras
Lizards: iguanas, geckos, chameleons, Komodo dragons
Snakes

Snakes
Lepidosaurs;
descended from lizard with legs
vestigial pelvic and limb bones seen in some species
“legless lizards”
carnivorous, venomous teeth

Crocodilians
Class Reptilia;
True, 4-chambered heart
found only in warmer regions of the globes
little change over millions of years of evolutions
Ex: crocodiles, alligators
Class Aves: Birds
Amniotes;
Adaptations that facilitate flight
wings (keratin feathers)
flight skeleton (thin, hollow bones; keeled sternum)
4-chambered heart
Endothermic
Super-efficient respiration
no urinary bladder
Females = one ovary; Males = small gonads
Endothermic
Class Aves;
maintains a relatively constant body temperature, regardless of the surrounding temperature
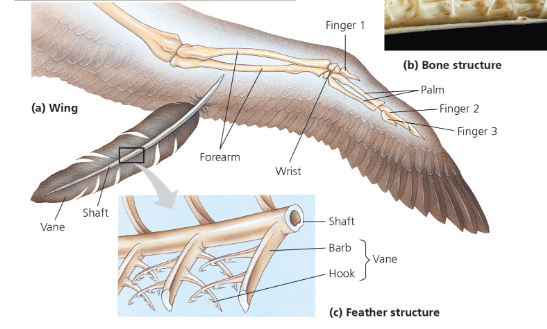
Benefits of flight and feathers
Class Aves;
enhanced scavenging and hunting
feeding on flying insects
escaping from predators
migration
Ratites
Class Aves;
flightless birds
Ex: Emu, Ostrich
Passeriformes
Class Aves;
perching birds
60% of birds
Ex: songbirds