Anatomy Lab Practical 1
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
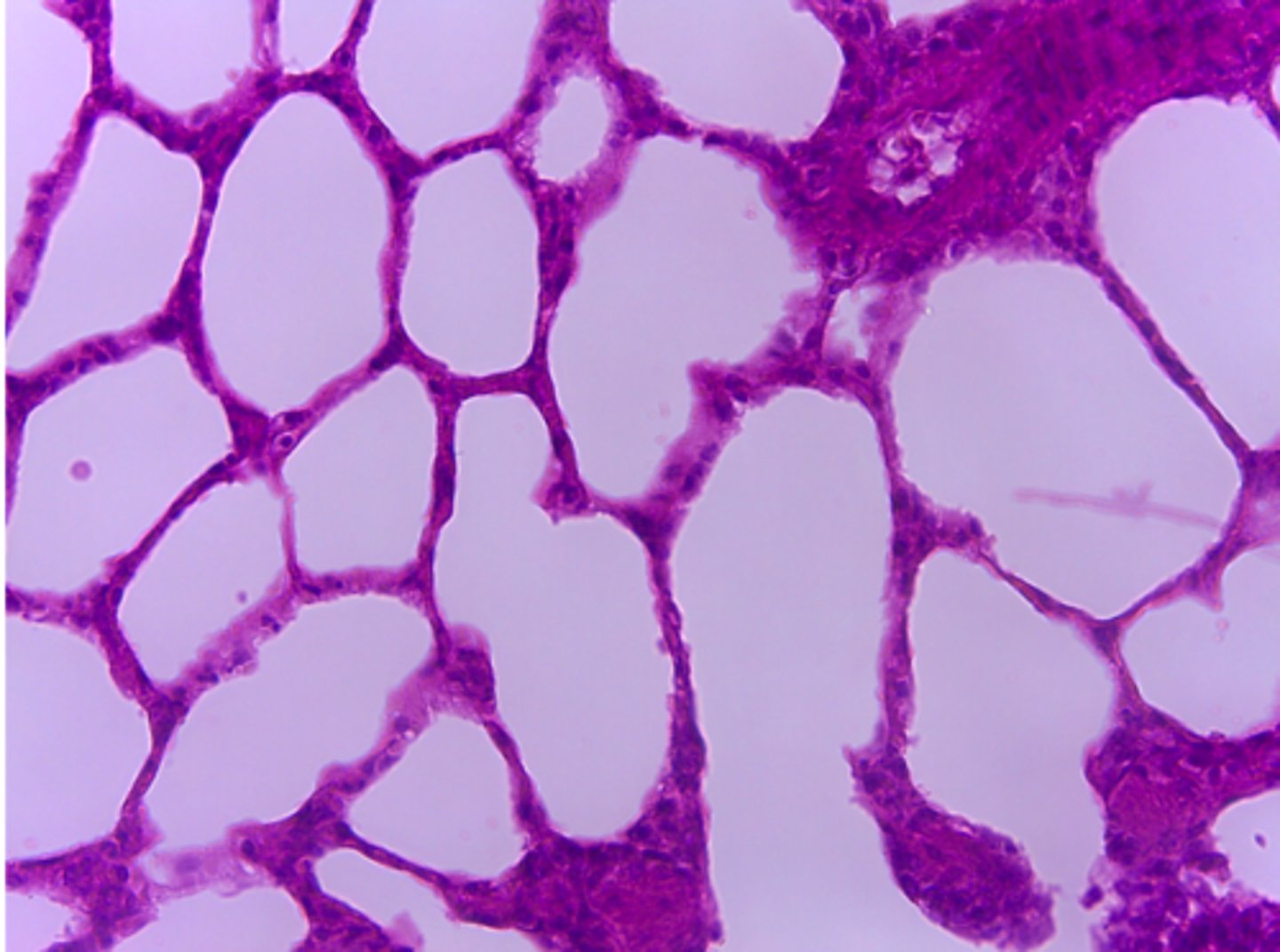
simple squamous epithelium
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
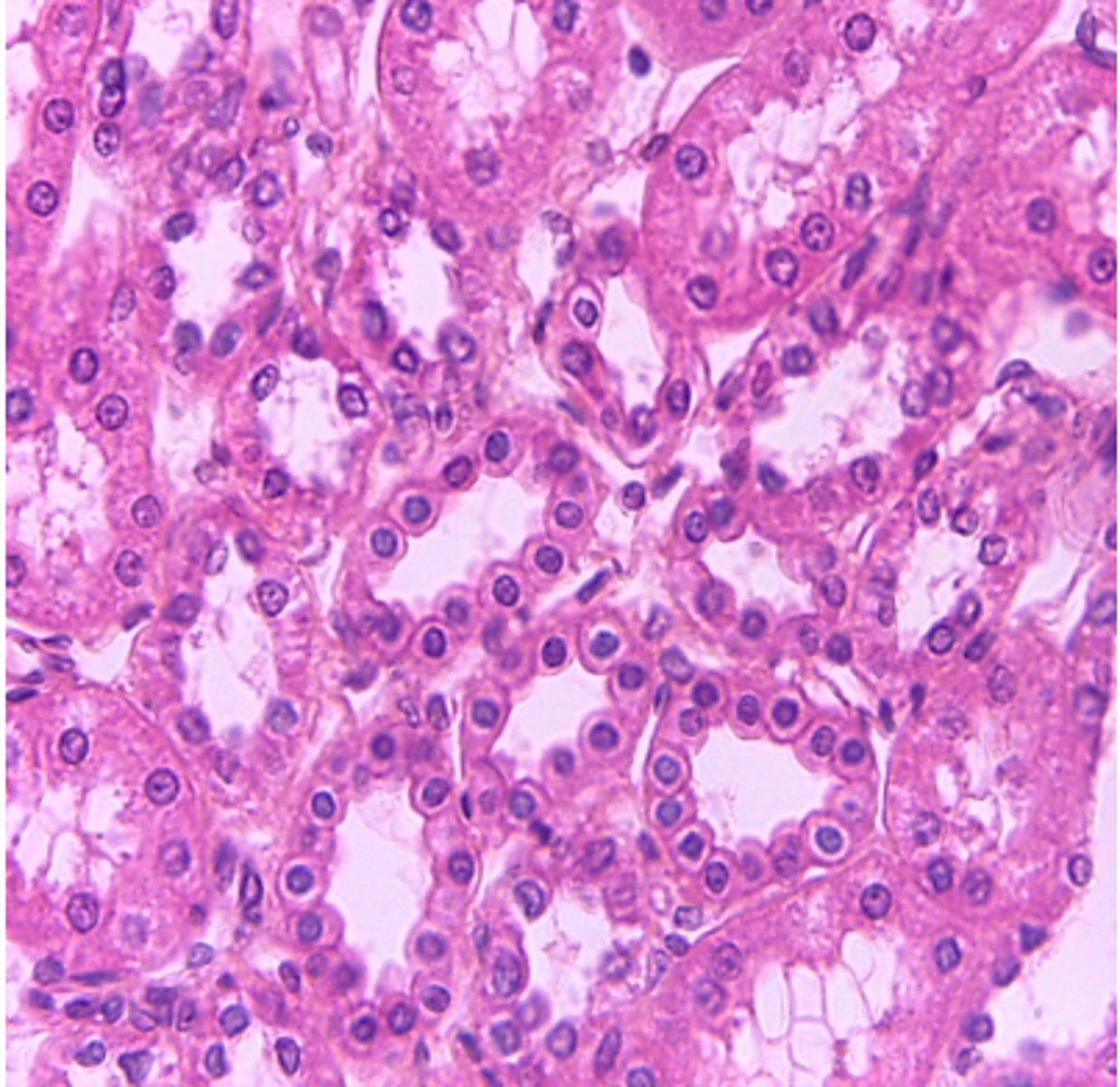
simple cuboidal epithelium
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
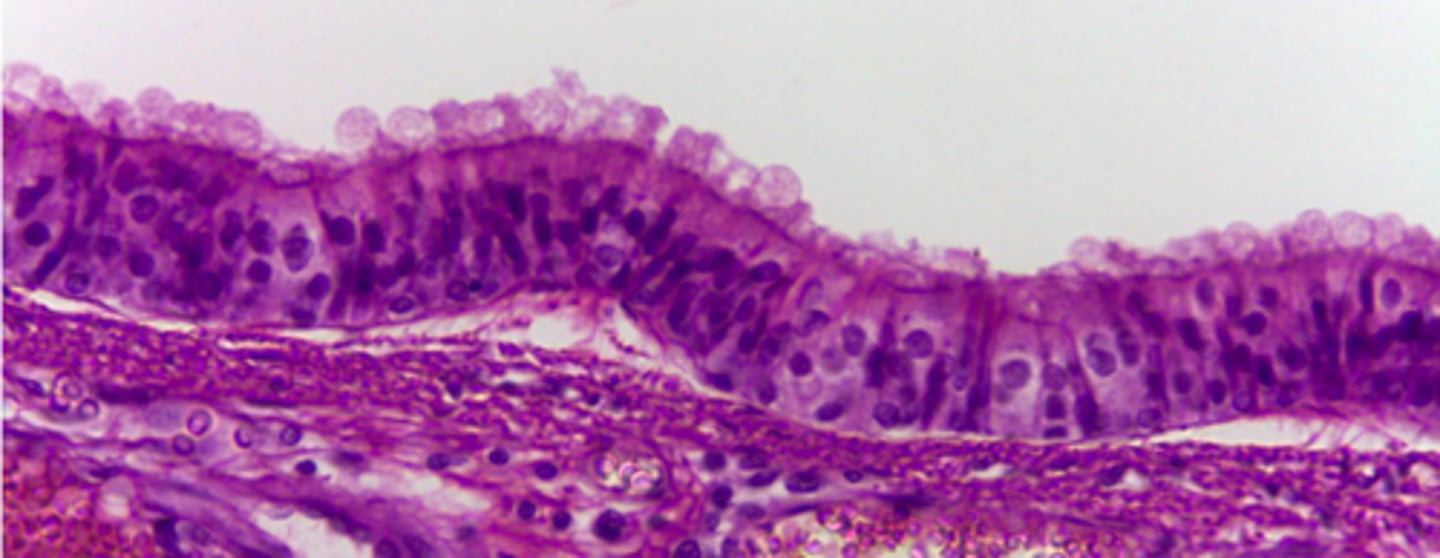
simple columnar epithelium
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
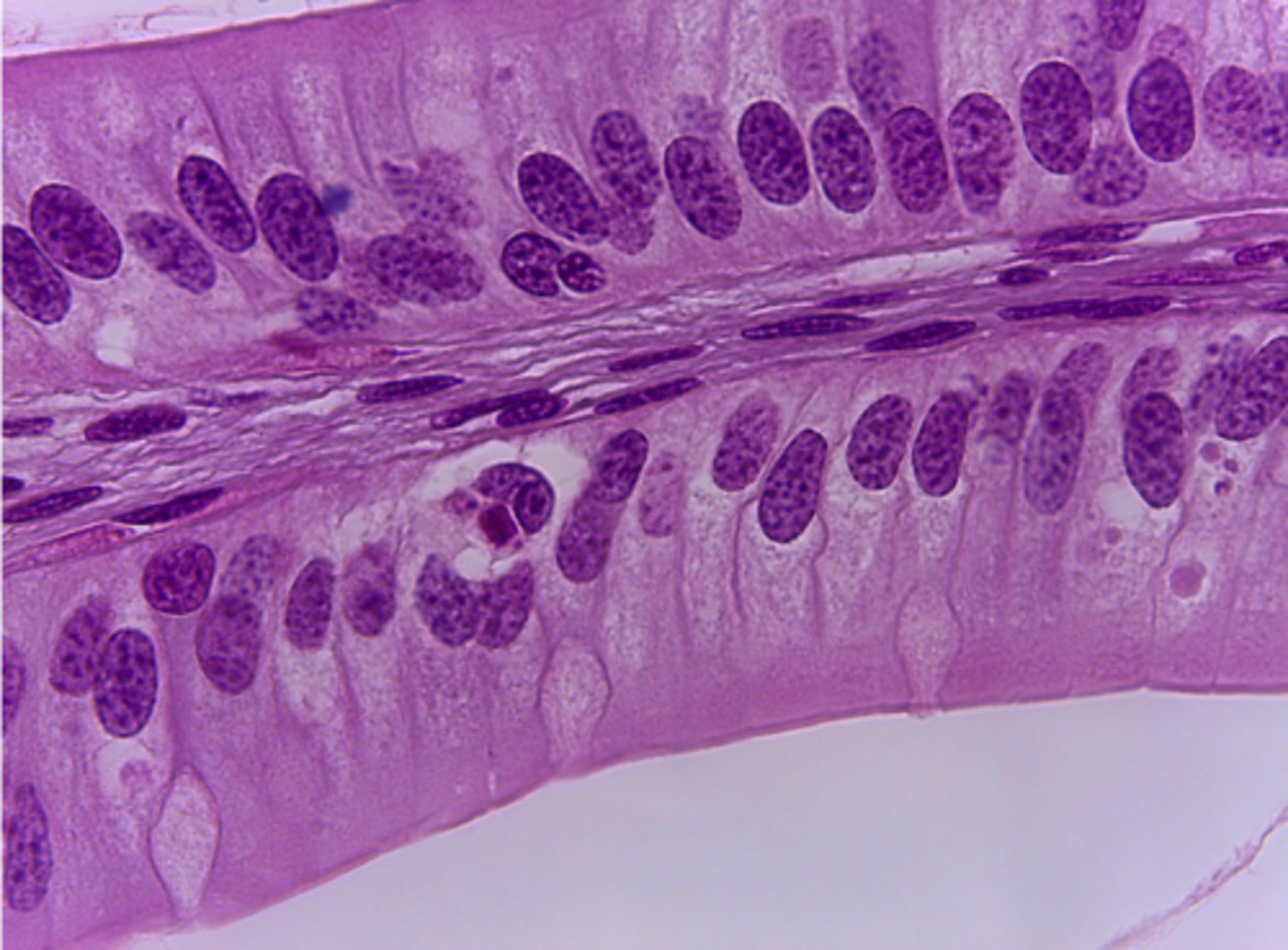
psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
transitional epithelium
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
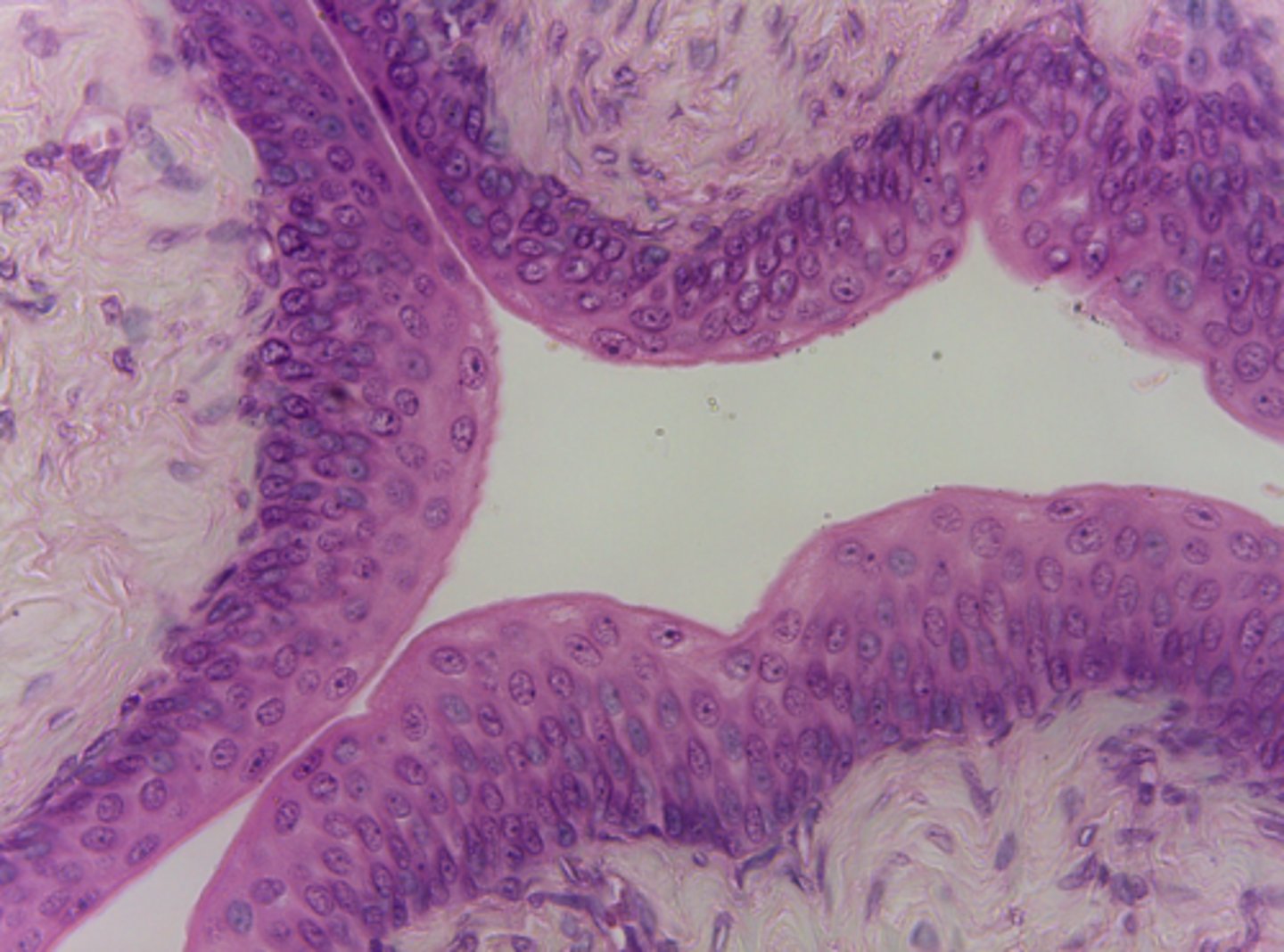
(non-keratintized) stratified squamous epithelium
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
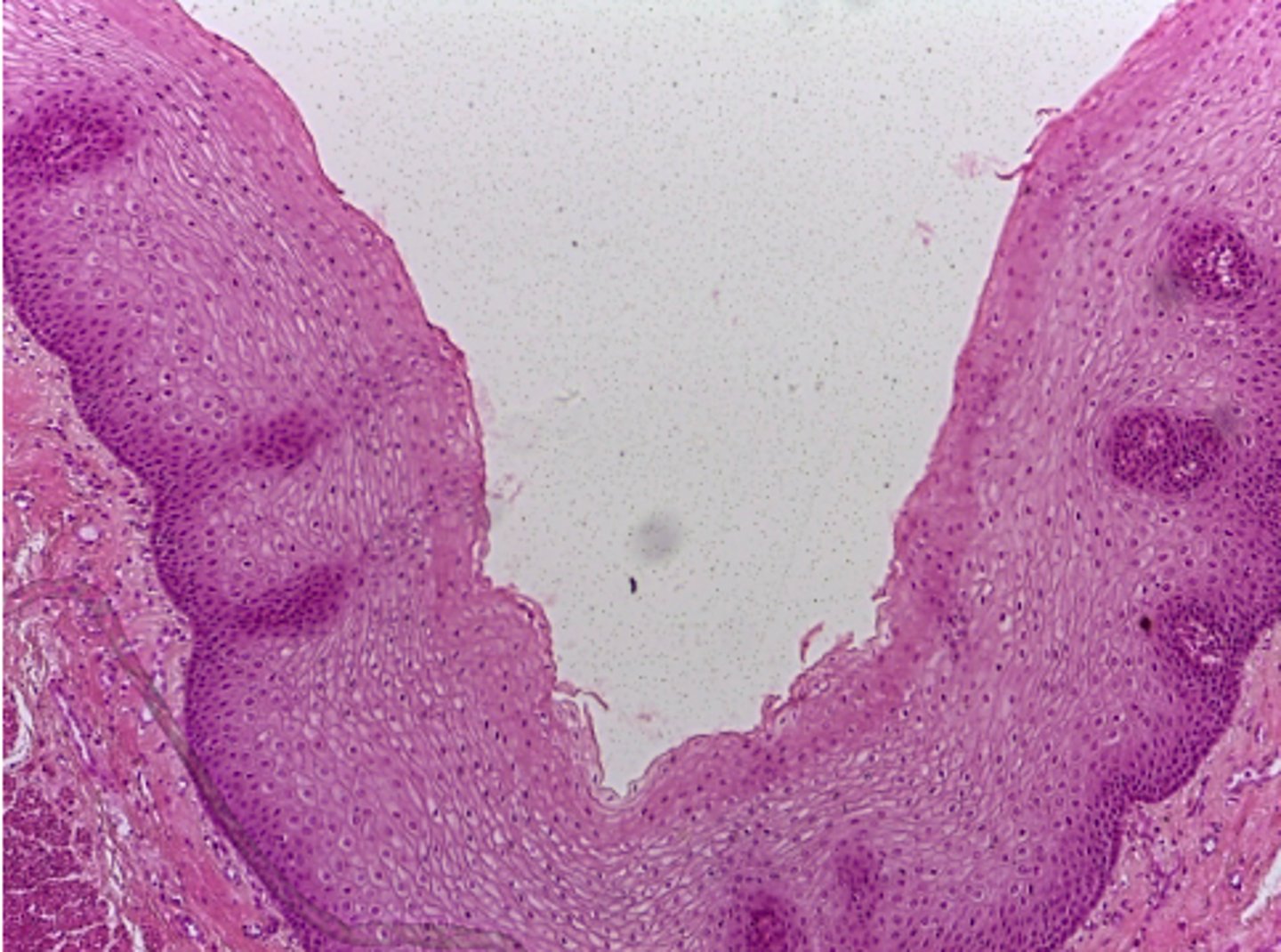
epidermis, oral cavity, esophagus and vagina
Where in the body is the (non-keratintized) stratified squamous epithelium located?
resists abrasion, prevents microbial infections, retard water loss in skin
What is the function of the (non-keratintized) stratified squamous epithelium?
*Dense Regular Connective Tissue
*Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
*Elastic Tissues (3)
What are the three dense connective tissues?
*Reticular Tissue
*Areolar Tissue
*Adipose Tissue
What are the three loose connective tissues?
adipose connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
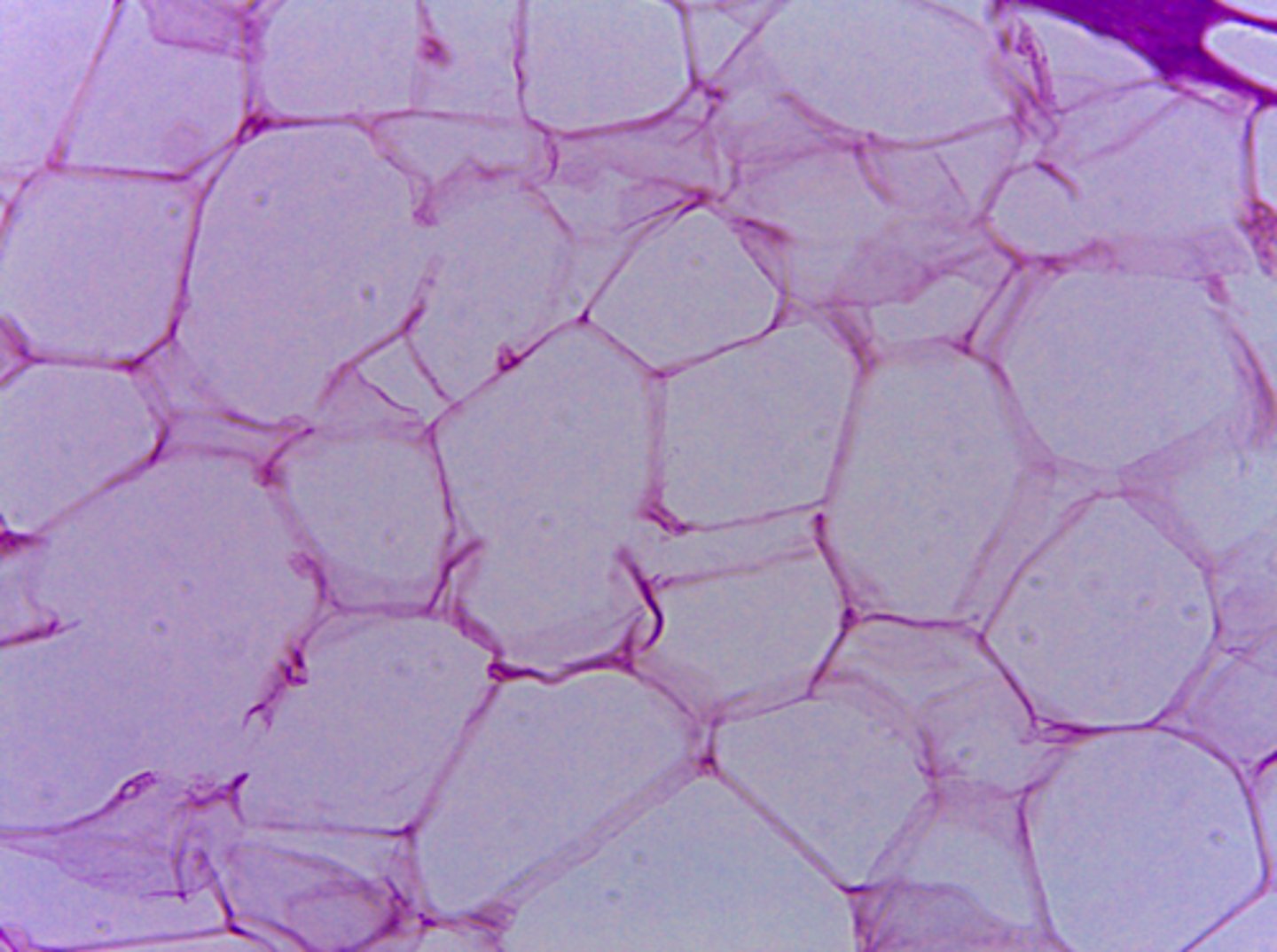
under skin, breast tissue, outside of heart and kidney
Where in the body is the adipose connective tissue located?
energy storage & physical protection
What is the function of the adipose connective tissue?
reticular connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
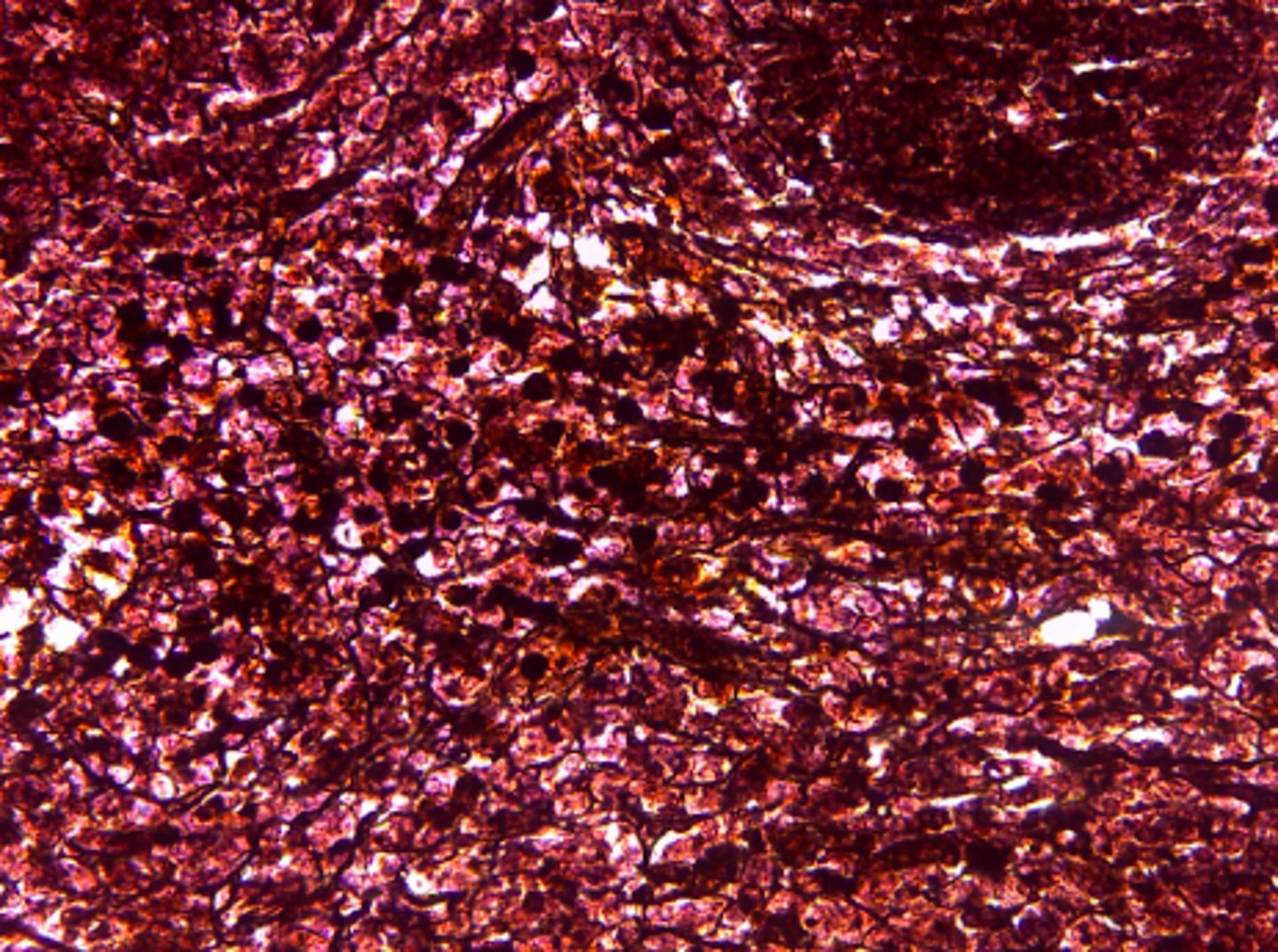
spleen, thymus, lymph nodes and liver
Where in the body is the reticular connective tissue located?
internal skeleton for soft organs (????)
What is the function of the reticular connective tissue?
areolar connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
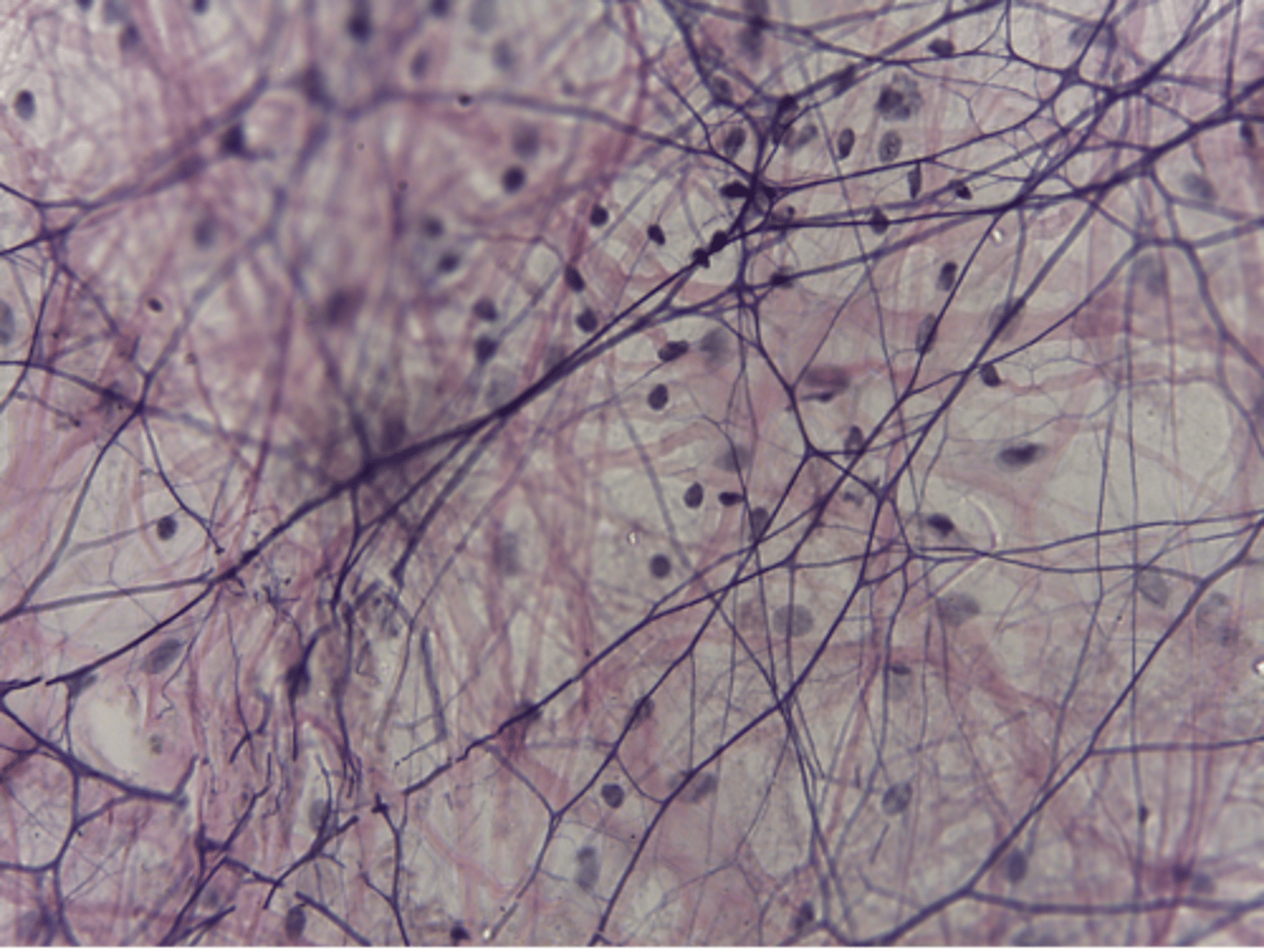
deep to the dermis and surrounding many internal organs
Where in the body is the areolar connective tissue located?
binds epithelia to lower layers, insulates organs from infection
What is the function of the areolar connective tissue?
dermis, sheaths around cartilage and bone
Where in the body is the dense irregular connective tissue located?
structural strength and resists stress against tearing
What is the function of the dense irregular connective tissue?
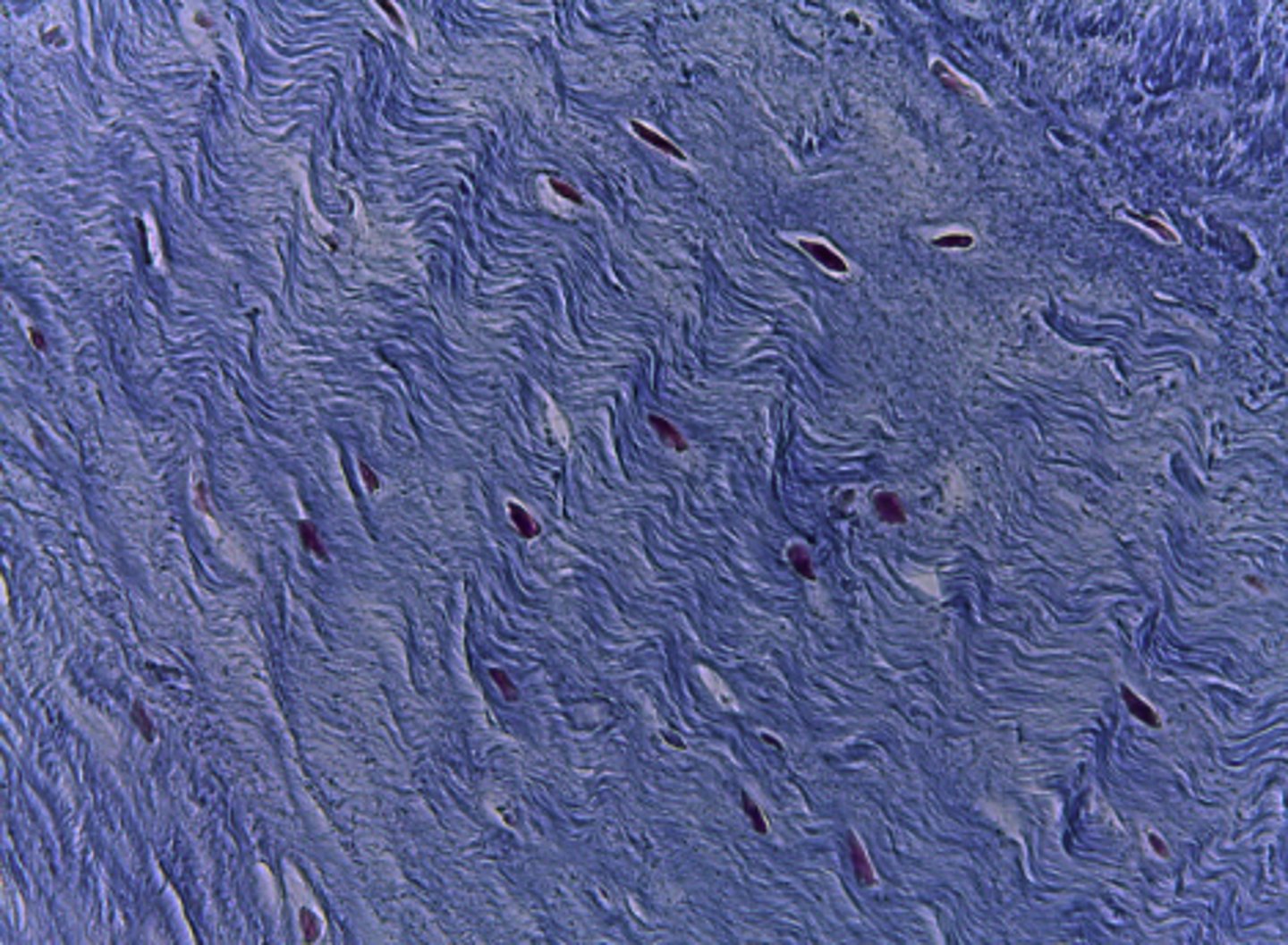
dense regular connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
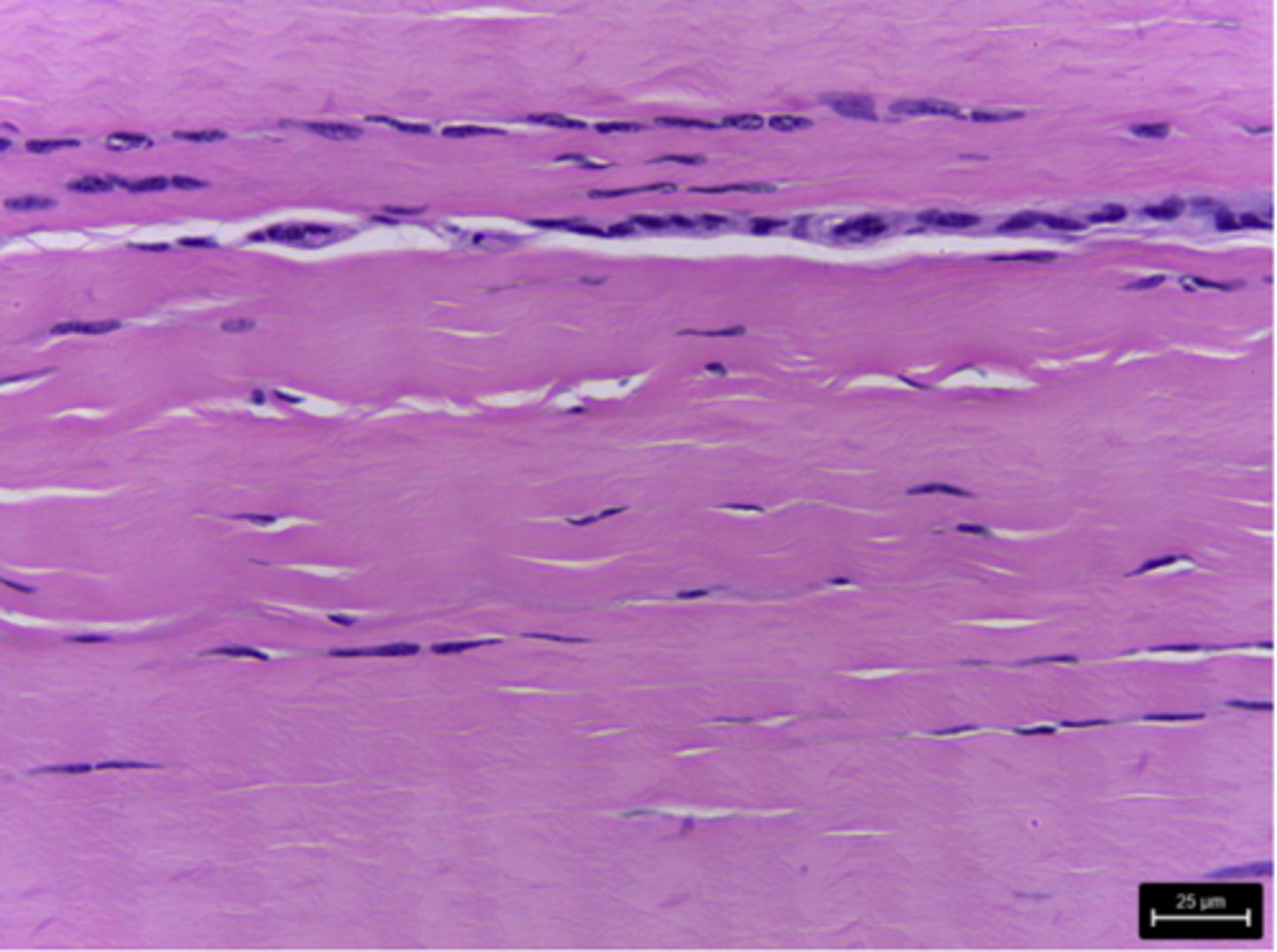
tendons and ligaments
Where in the body is the dense regular connective tissue located?
binds bones together or connects muscle to bone
What is the function of the dense regular connective tissue?
blood fluid connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
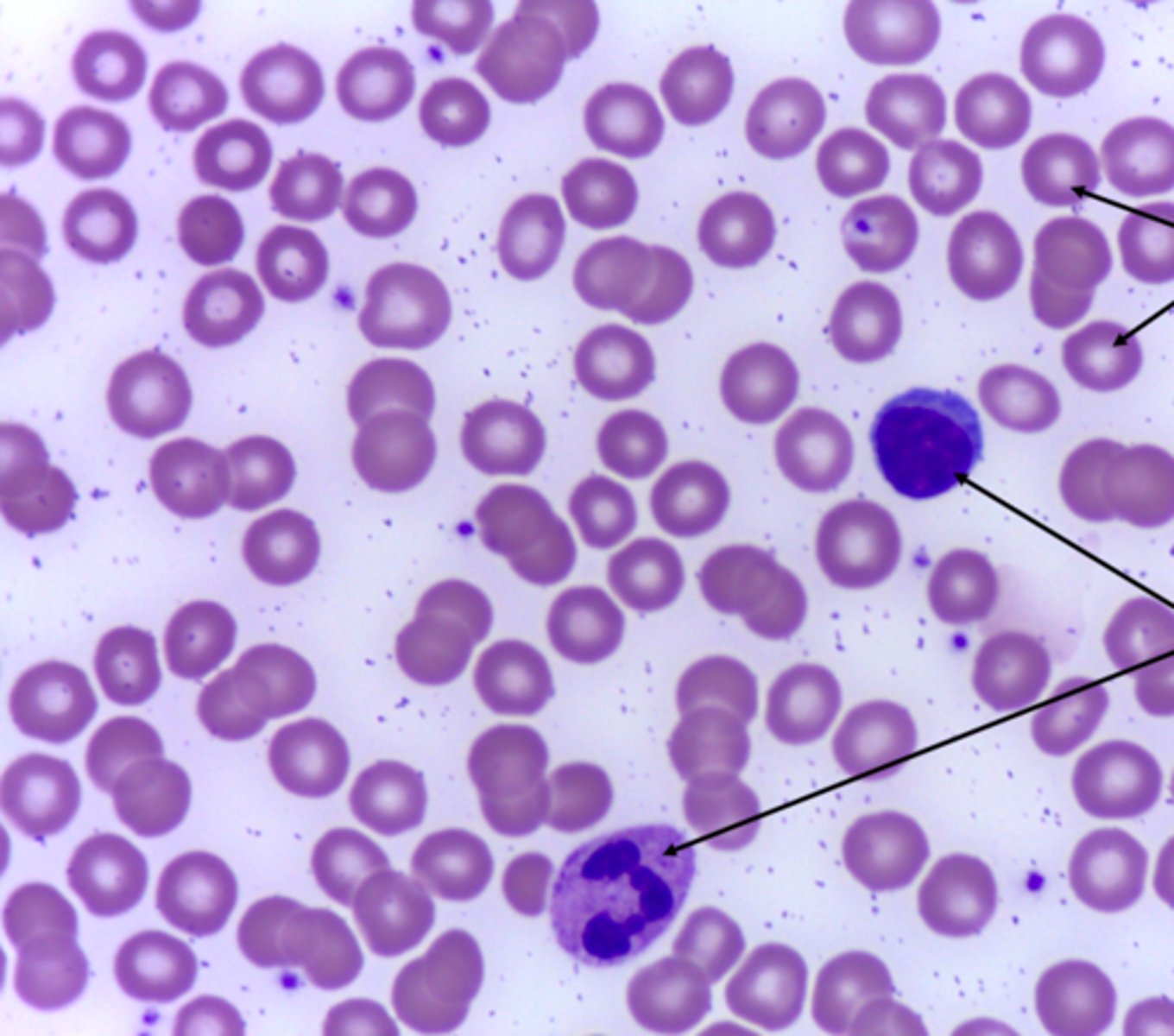
heart and blood vessels
Where in the body is the blood fluid connective tissue located?
transport respiratory gases, nutrients, hormones, water throughout the body, immunity
What is the function of the blood fluid connective tissue?
spongy bone (connective tissue)
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
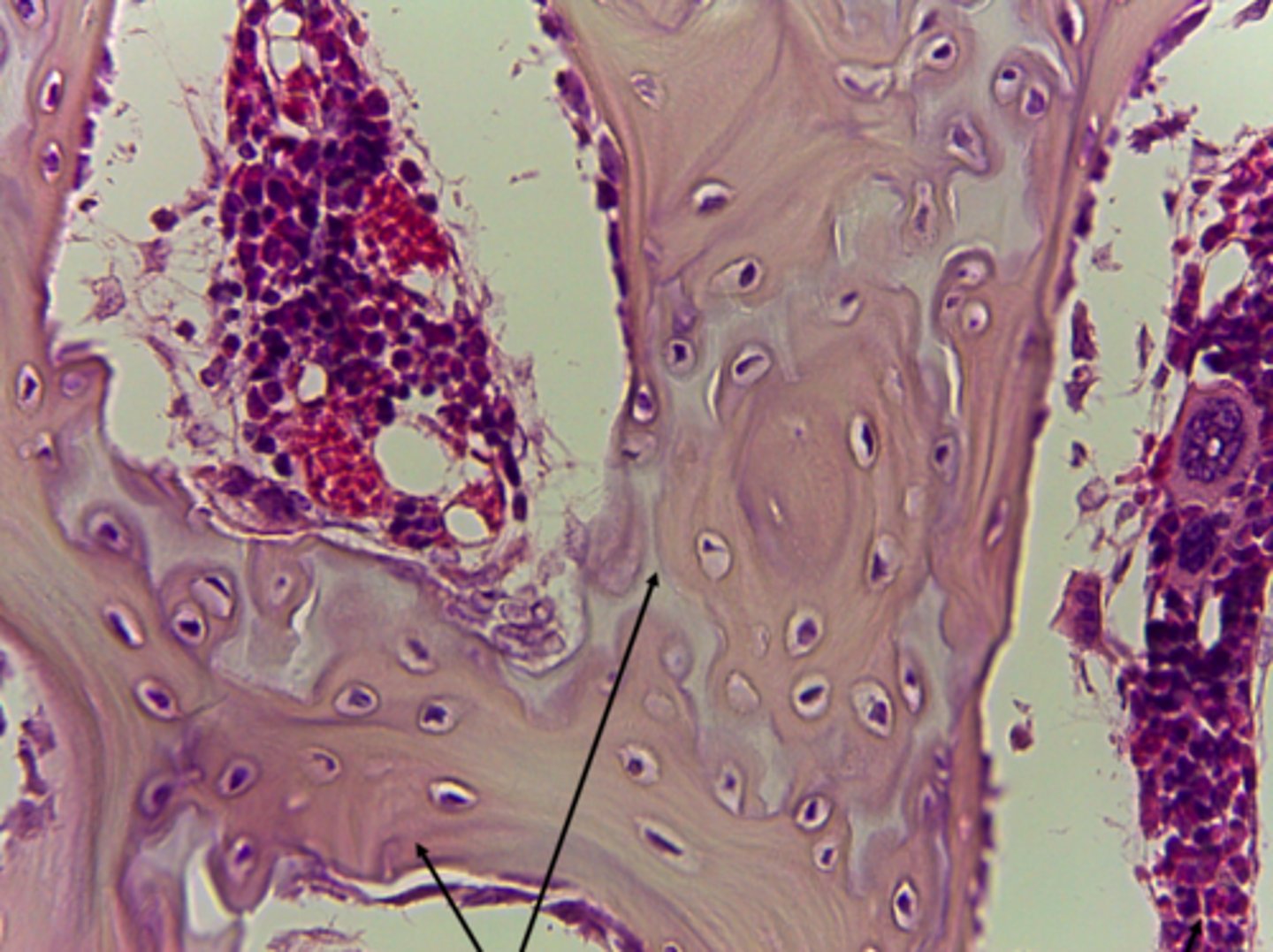
ends of long bones surrounded by compact bone,inside vertebrae, ribs, skull
Where in the body is the spongy bone connective tissue located?
storage of bone marrow, site of erythropoiesis, reduces weight of skeleton, mineral storage
What is the function of the spongy bone connective tissue?
compact bone (connective tissue)
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
skeleton
Where in the body is the compact bone tissue located?
protection of soft organs, locomotion along with muscles, support
What is the function of the compact bone tissue?
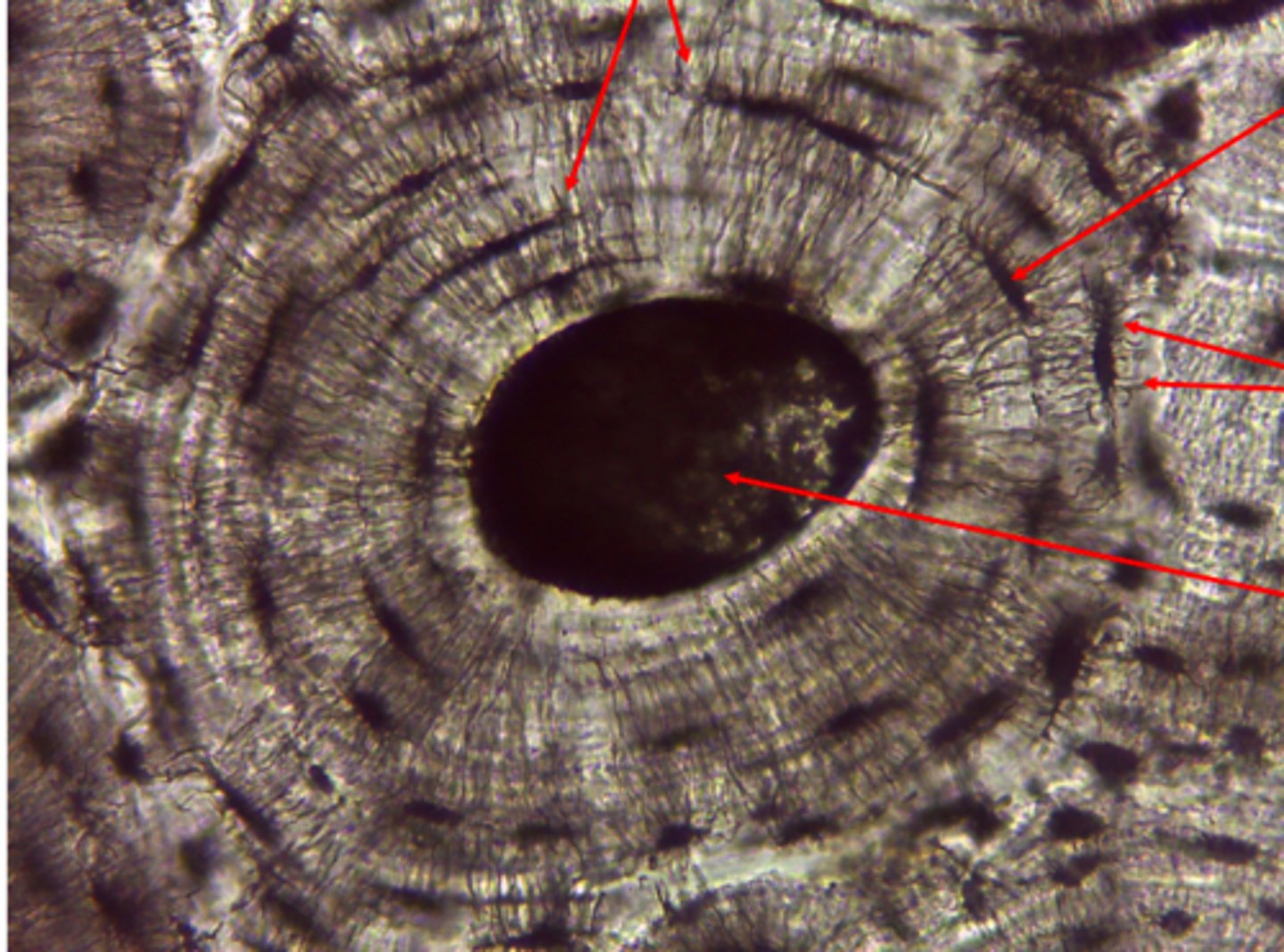
hyaline cartilage connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
ends of long bones, ribs larynx and trachea
Where in the body is the hyaline cartilage tissue found?
forms most of fetal skeleton, reduces friction at joints, keeps air passages open
What is the function of the hyaline cartilage tissue?
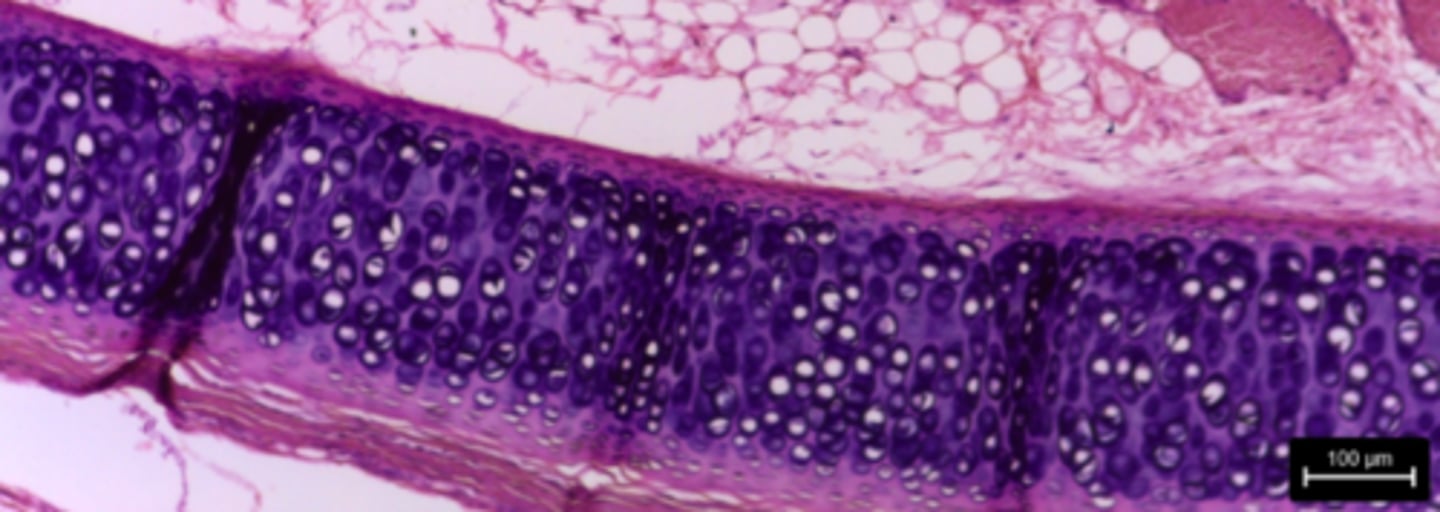
elastic cartilage connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
provides flexible framework
What is the function of the elastic cartilage tissue?
external ear and epiglottis
Where is the elastic cartilage tissue located in the body?
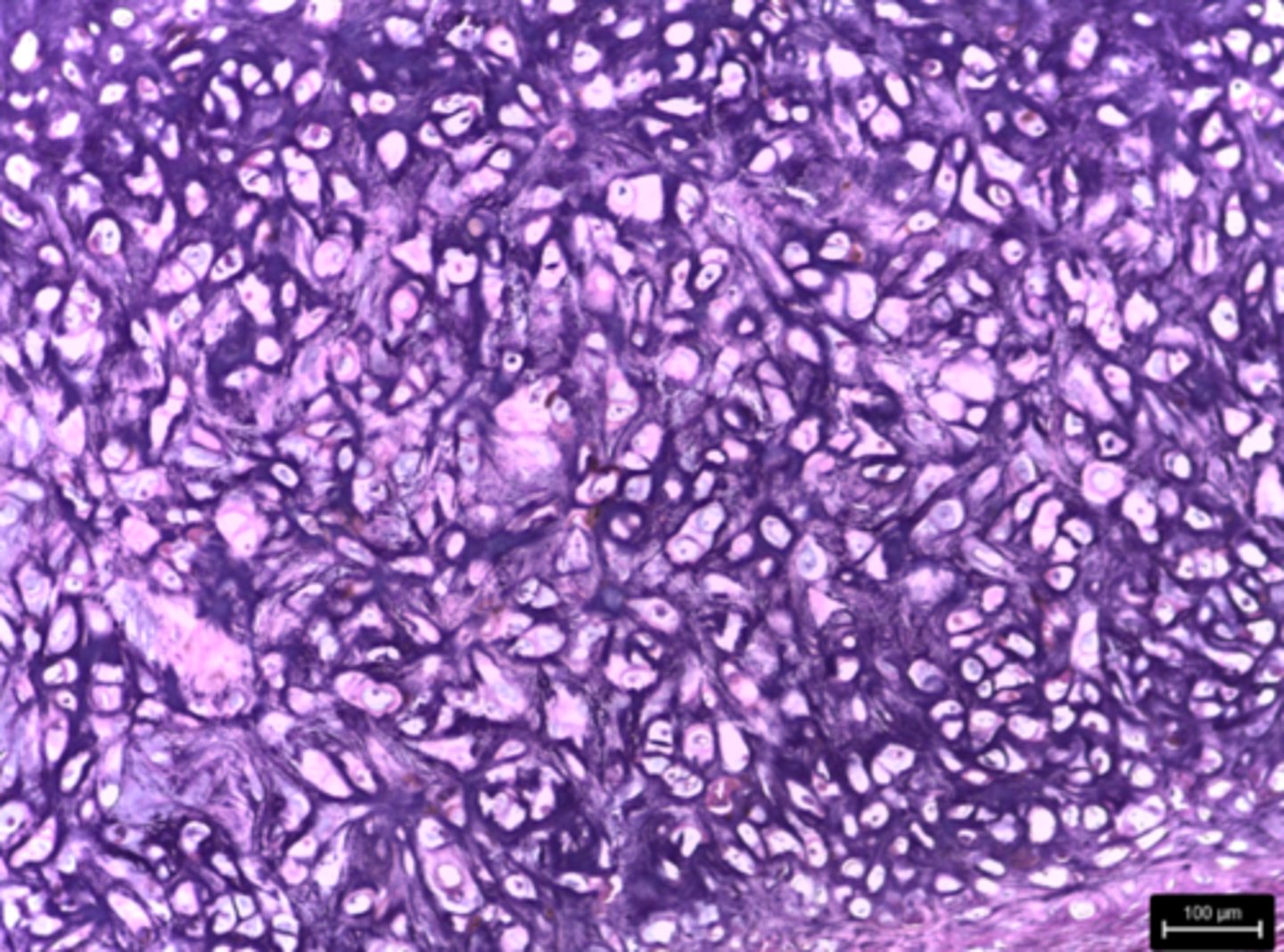
fibrocartilage connective tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis
Where in the body is the fibrocartilage tissue located?
resists compression, reduce wear and tear
What is the function of the fibrocartilage tissue?
skeletal muscle tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
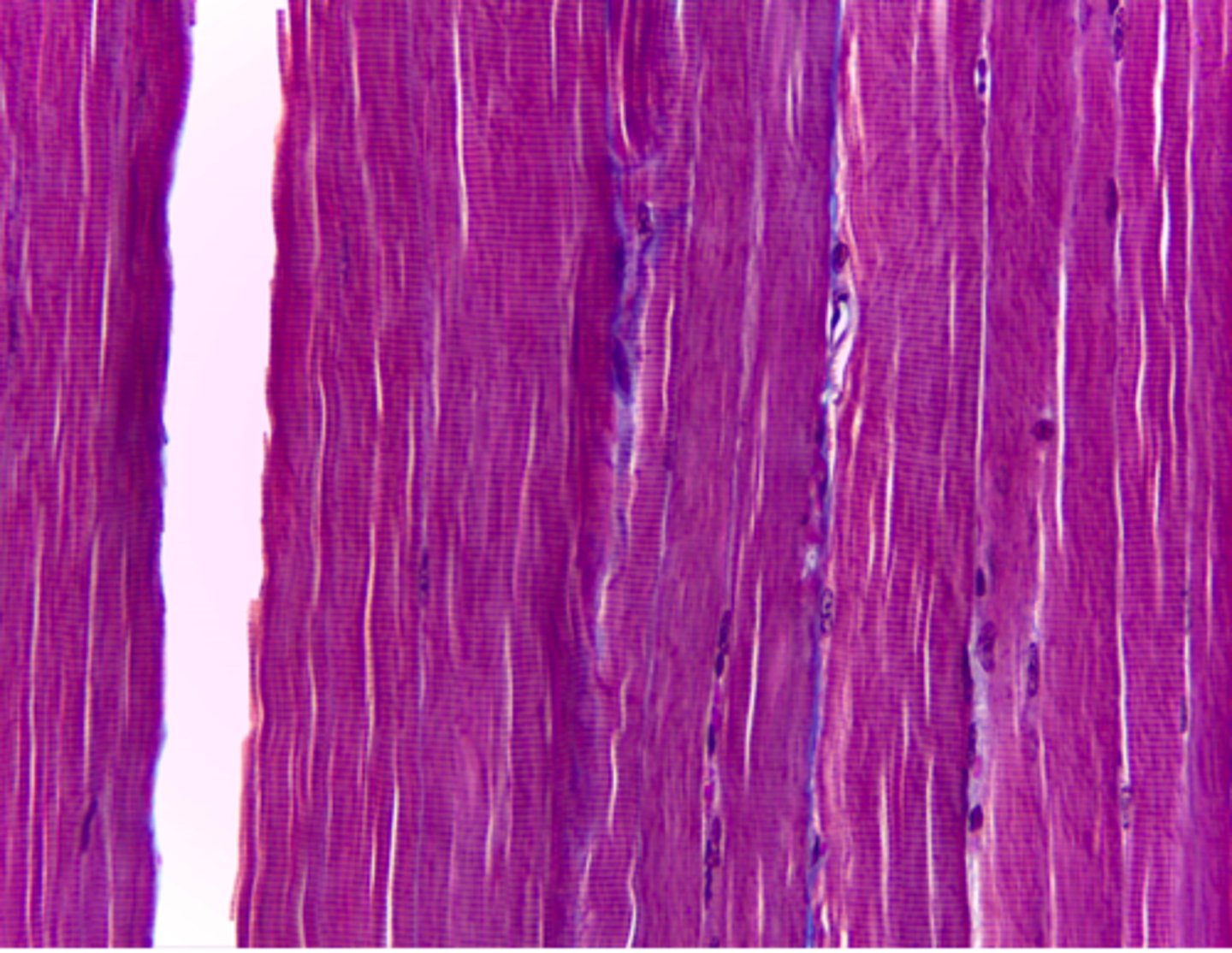
skeletal muscles
Where in the body is the skeletal tissue found?
locomotion (movement)
What is the function of the skeletal tissue?
- voluntary movement
- obvious striations
- many nuclei
Describe the three main characteristics of skeletal muscle tissue:
cardiac muscle tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
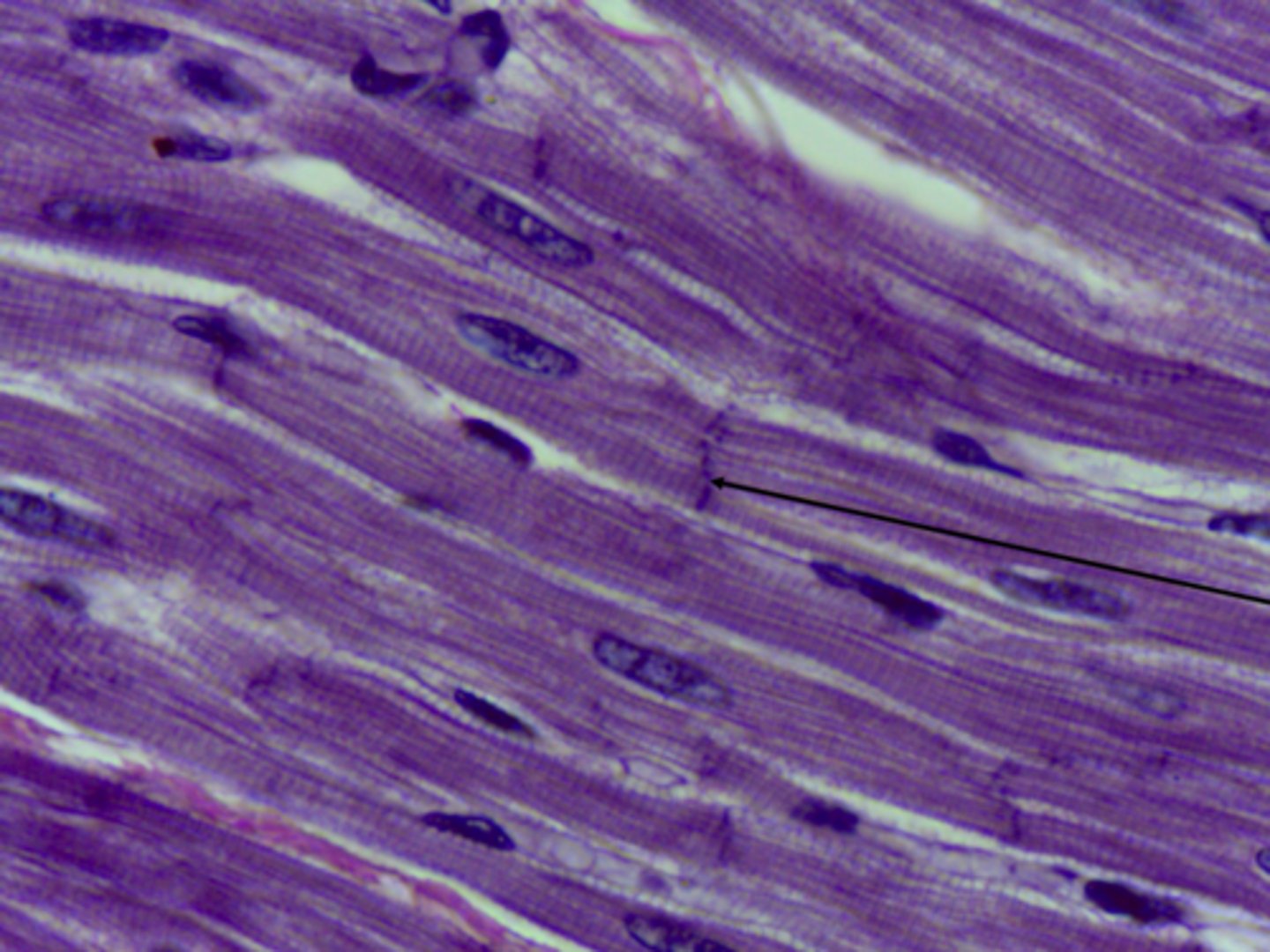
rhythmic contractions of the heart
What is the function of the cardiac muscle tissue?
heart
Where is the cardiac muscle tissue located in the body?
- involuntary movement
- one nucleus
- less obvious striations
++ (intercalated discs)
Describe the three main characteristics of cardiac muscle tissue:
smooth muscle tissue
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
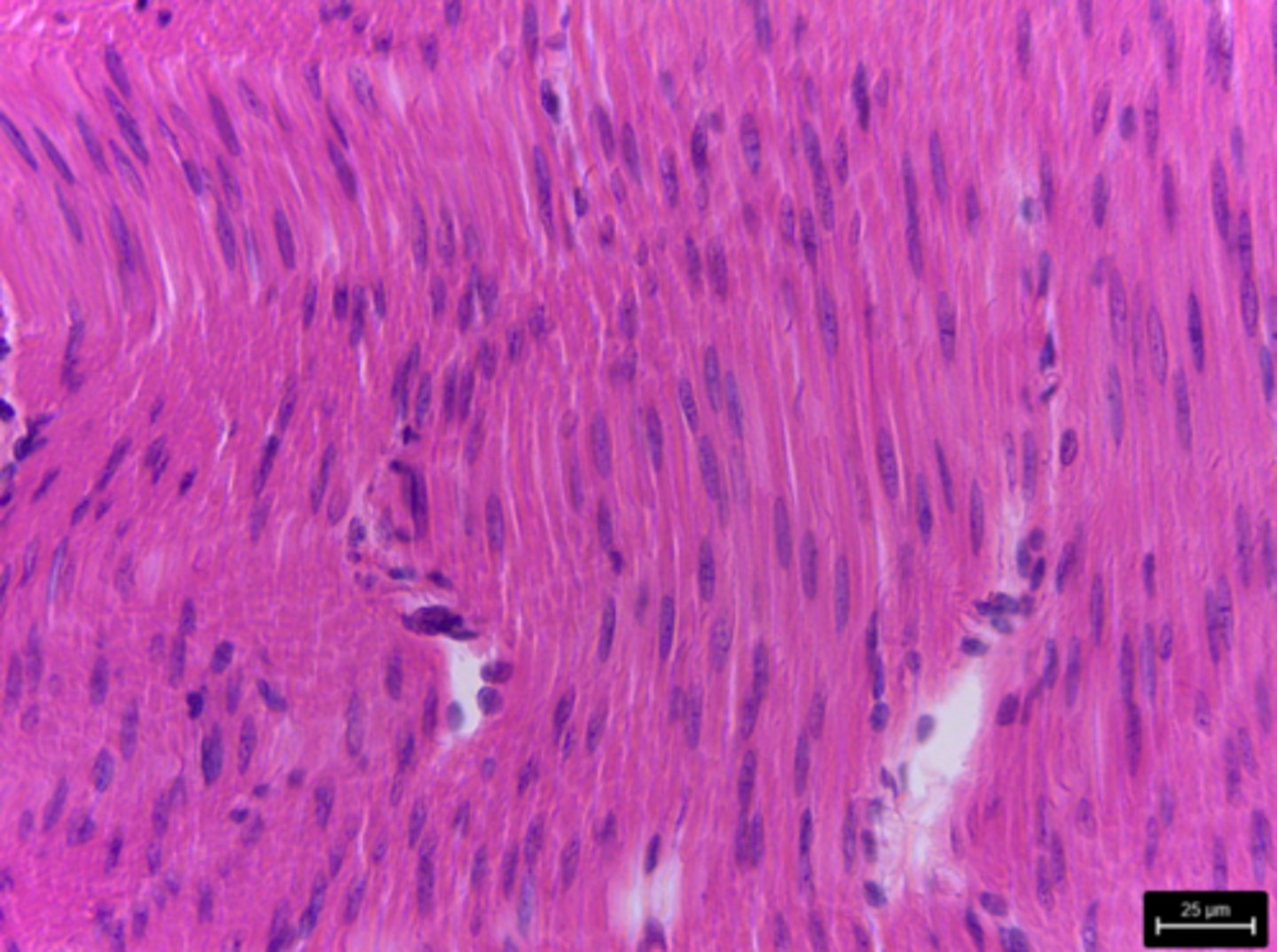
labor contractions, delivery of infant, propulsion of food,
What is the function of smooth muscle tissue?
digestive tract, blood vessels, uterus
Where in the body is smooth muscle tissue located?
- involuntary movement
- one central nucleus
- NO striations
++ (slender shaped cell)
Describe the three main characteristics of smooth muscle tissue:
multipolar neuron (nervous tissue)
What type of tissue is presented on the slide?
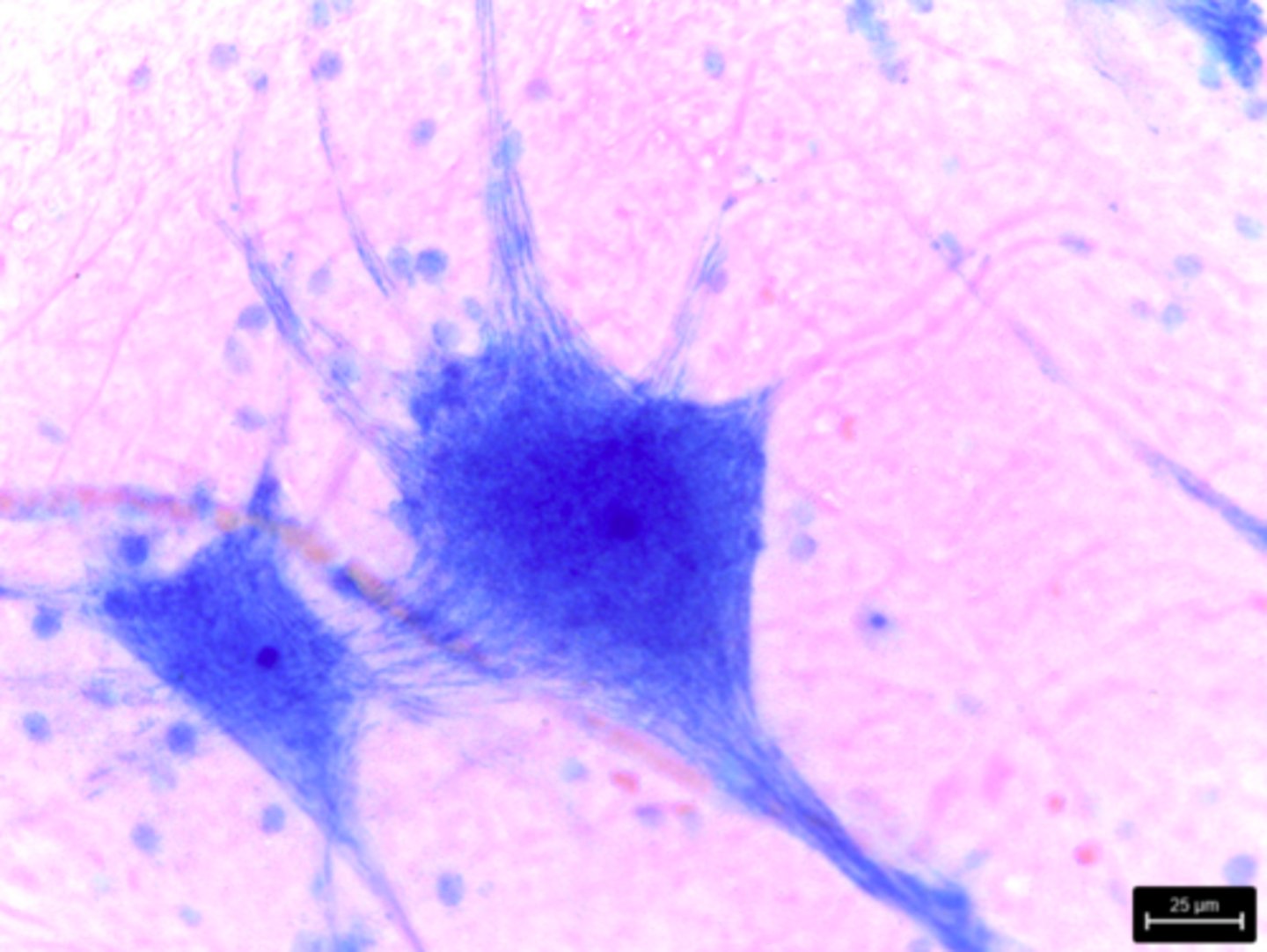
transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors, glial cells support and protect neurons; learning & memory
What is the function of the multipolar neuron tissue?
Brain and spinal cord, nerves and ganglia
Where in the body is the multipolar neuron tissue located?
lungs, inside of heart and blood vessels
Where in the body is the simple squamous epithelium located?
diffusion and secretion
What is the function of the simple squamous epithelium?
kidney tubules and liver
Where in the body is the simple cuboidal epithelium located?
absorption and secretion
What is the function of the simple cuboidal epithelium?
from stomach to intestines, and line the uterine tube
Where in the body is the simple columnar epithelium located?
absorption and secretion
What is the function of the simple columnar epithelium?
respiratory passages
Where in the body is the psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelium located?
secretes mucus and traps dust particles, moving them away from the lung
What is the function of the psuedostratified ciliated columnar epithelium?
urinary bladder
Where in the body is the transitional epithelium located?
stretching of urinary bladder
What is the function of the transitional epithelium?
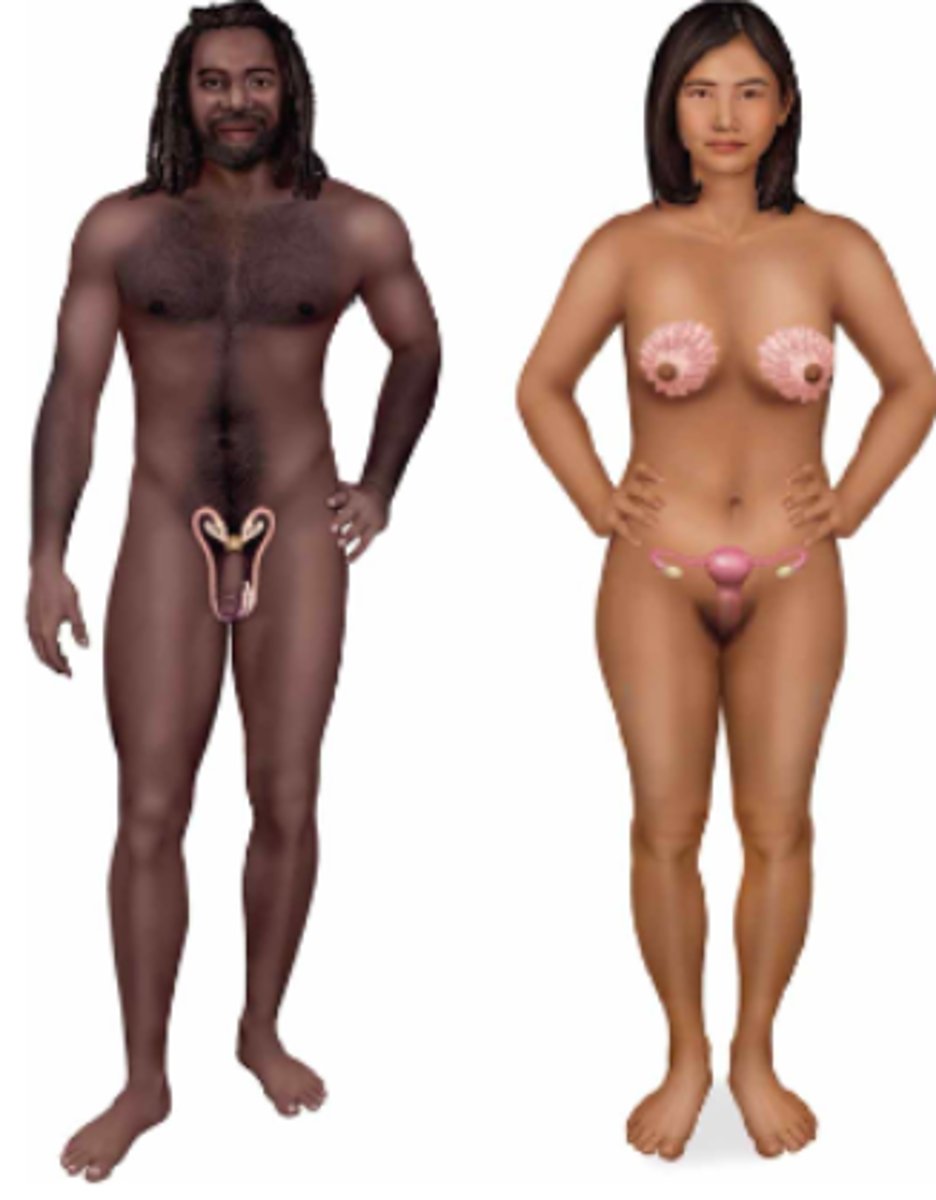
reproductive; testes & ovaries, uterus, vagina, penis, etc.
Name the body system & its included organs

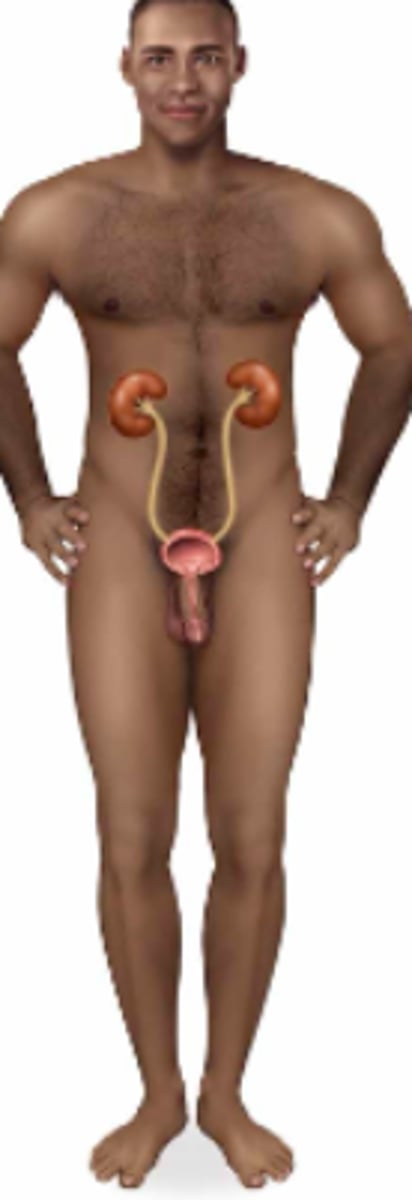
urinary; kidneys, bladder, ureters, & urethra
Name the body system & its included organs
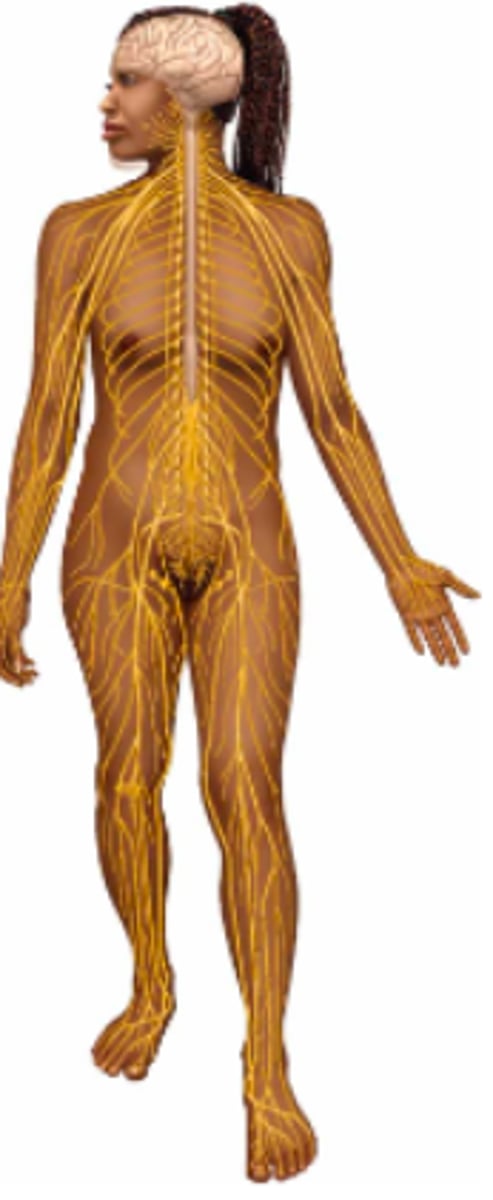
nervous; brain, spinal cord, & nerves
Name the body system & its included organs
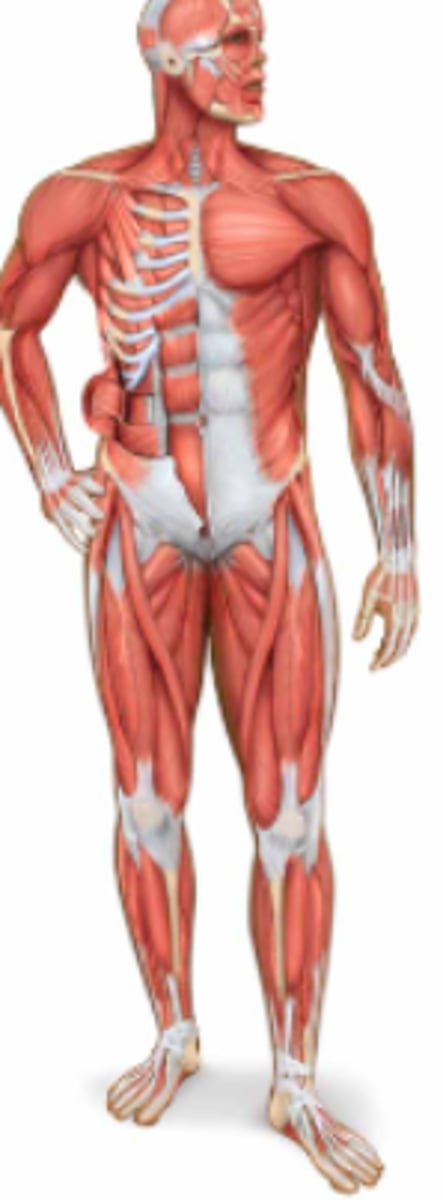
muscular; individual muscles
Name the body system & its included organs
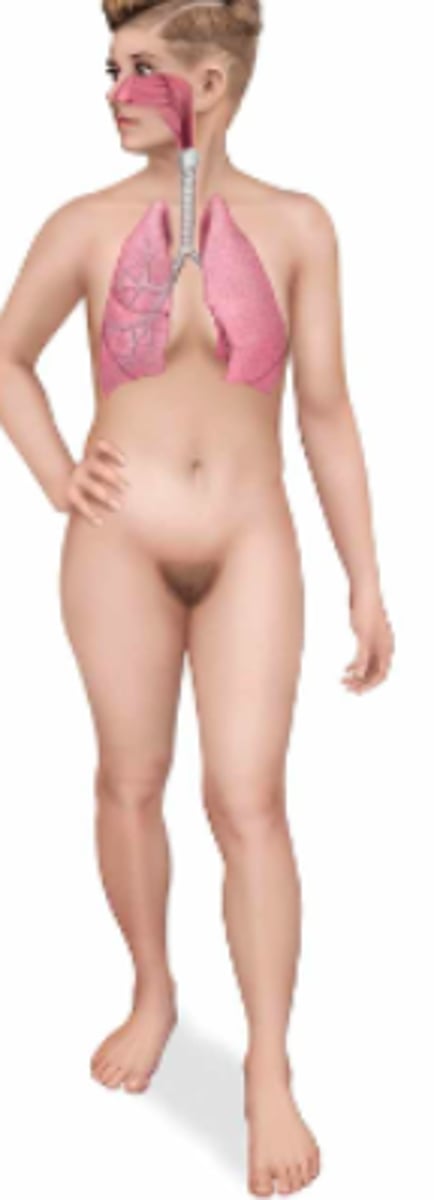
respiratory; nose, larynx, trachea, & lungs
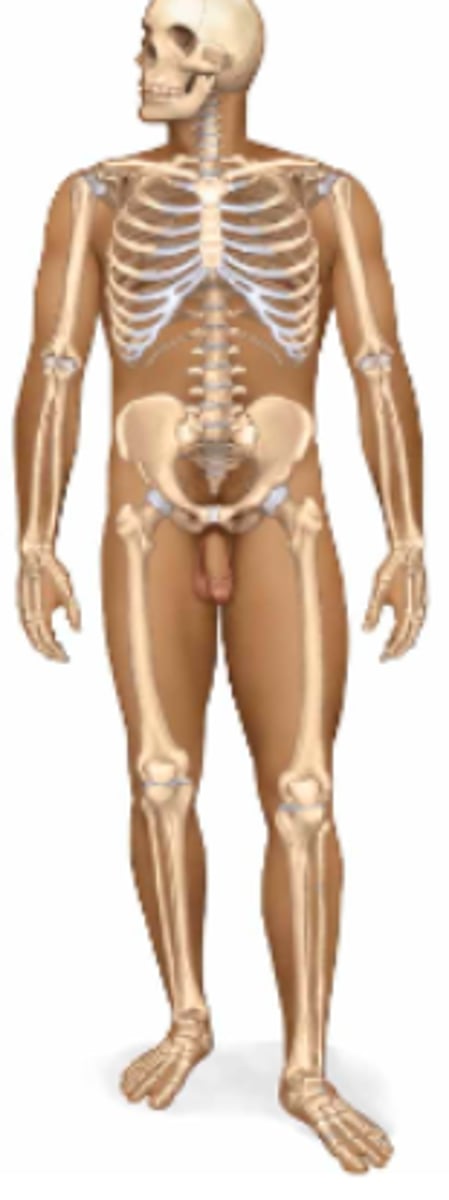
Name the body system & its included organs

skeletal; each bone
Name the body system & its included organs
circulatory; heart & blood vessels
Name the body system & its included organs
endocrine; hormone producing organs (ie: pituitary gland)
Name the body system & its included organs
digestive; mouth, esophagus, stomach, liver, & intestines
Name the body system & its included organs
integumentary; skin
Name the body system & its included organs

lymphatic; lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, & tonsils
Name the body system & its included organs
above
Define the directional anatomical term: superior
below
Define the directional anatomical term: inferior
toward midline
Define the directional anatomical term: medial
toward the side
Define the directional anatomical term: lateral
toward the surface
Define the directional anatomical term: superficial
toward the core
Define the directional anatomical term: deep
to the front
Define the directional anatomical term: anterior
to the back
Define the directional anatomical term: posterior
going toward the trunk
Define the directional anatomical term: proximal
going away from the trunk
Define the directional anatomical term: distal
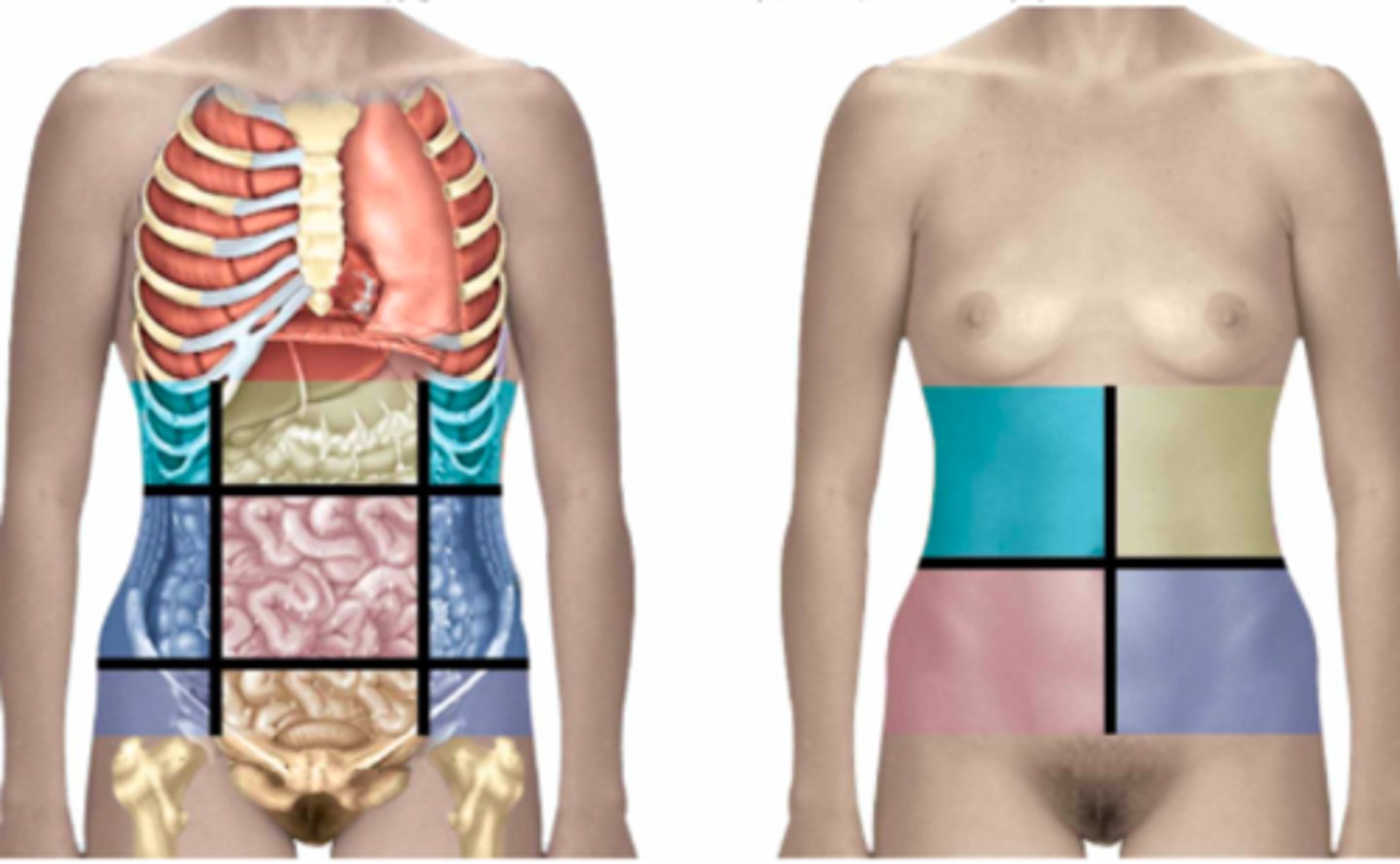
from left to right, top to bottom should line up like:
(Regions 9/9)
right hypochondriac , epigastric , left hypochondriac
right lumbar, umbilical , left lumbar
right iliac , hypogastric , left iliac
(Quadrants 4/4)
right upper quadrant , left upper quadrant
right lower quadrant , left lower quadrant
Use your imagination and pretend to label the abdominopelvic regions & quadrants on the torso
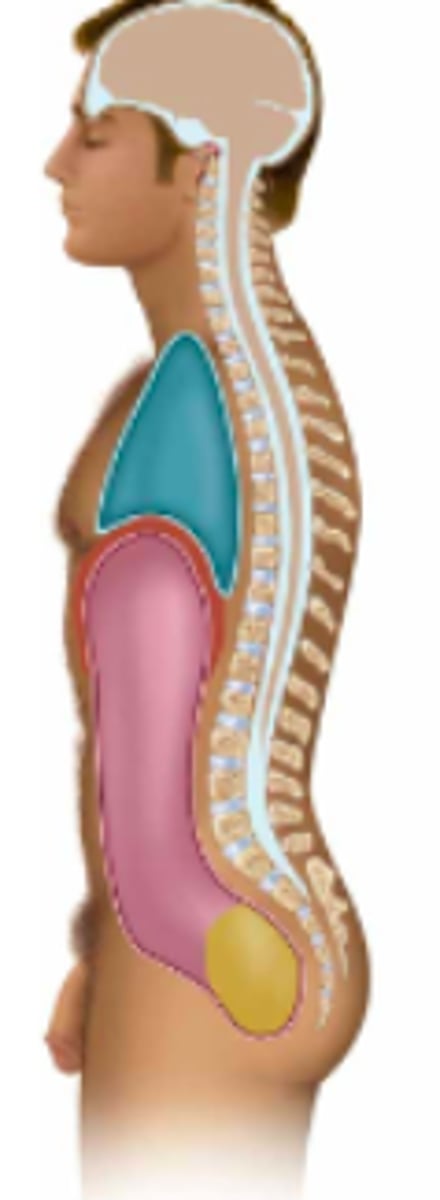
thoracic
Name the body cavity in pink:
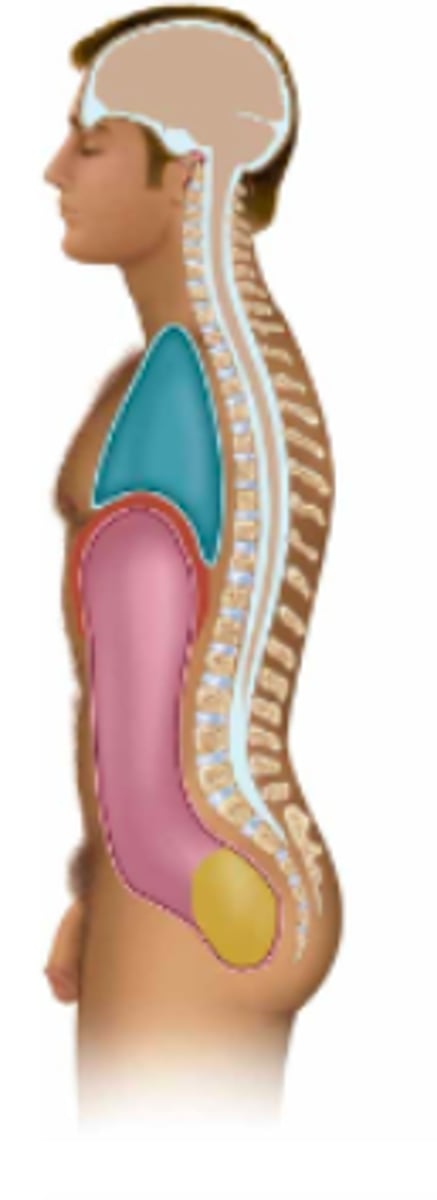
abdominal
Name the body cavity in blue:
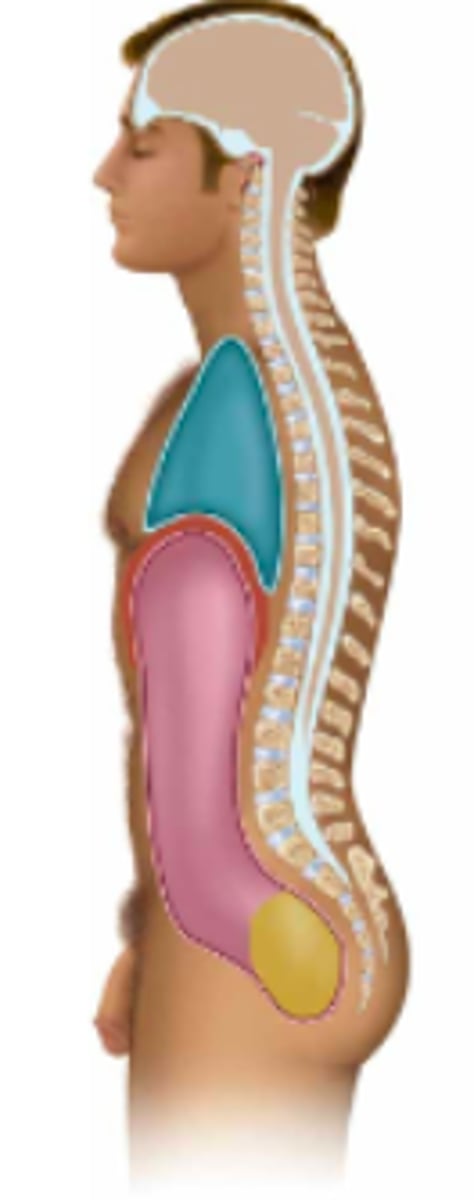
pelvic
Name the body cavity in yellow:
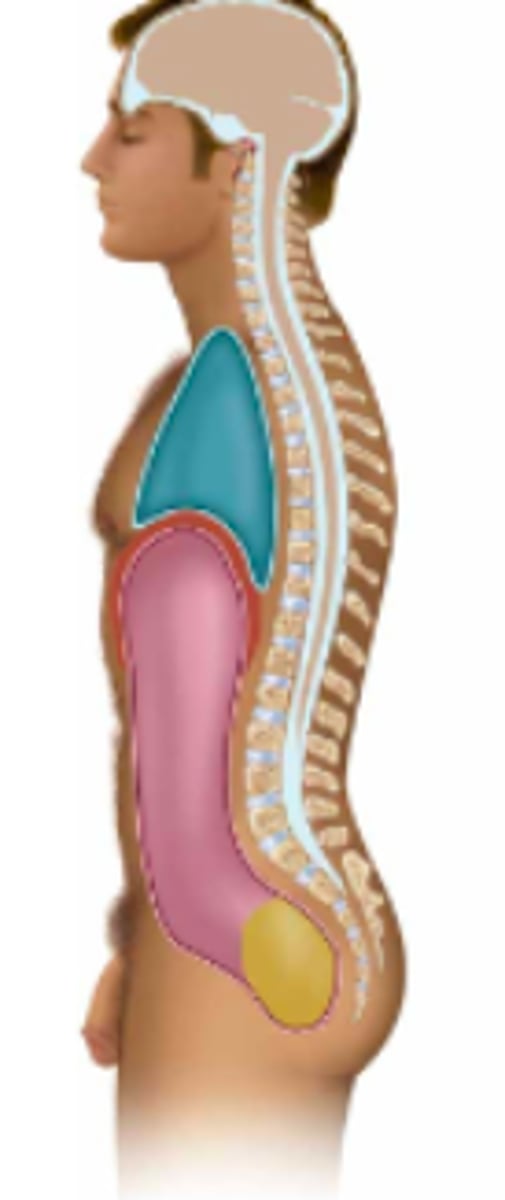
diaphragm
Name the body cavity in between the blue and pink (red?):
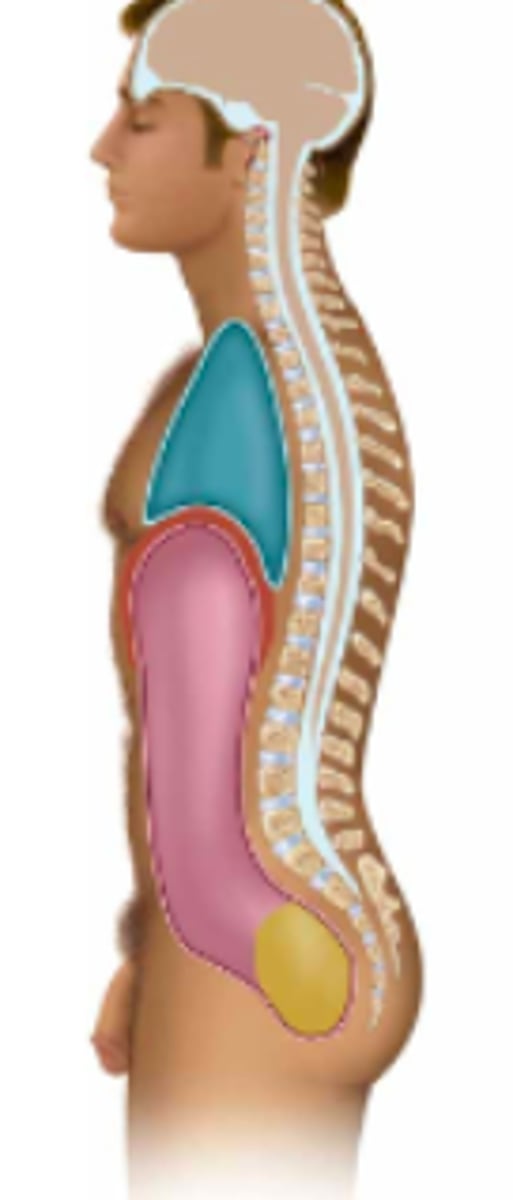
cranial & vertebral
Name the tan body cavity (2 parts):
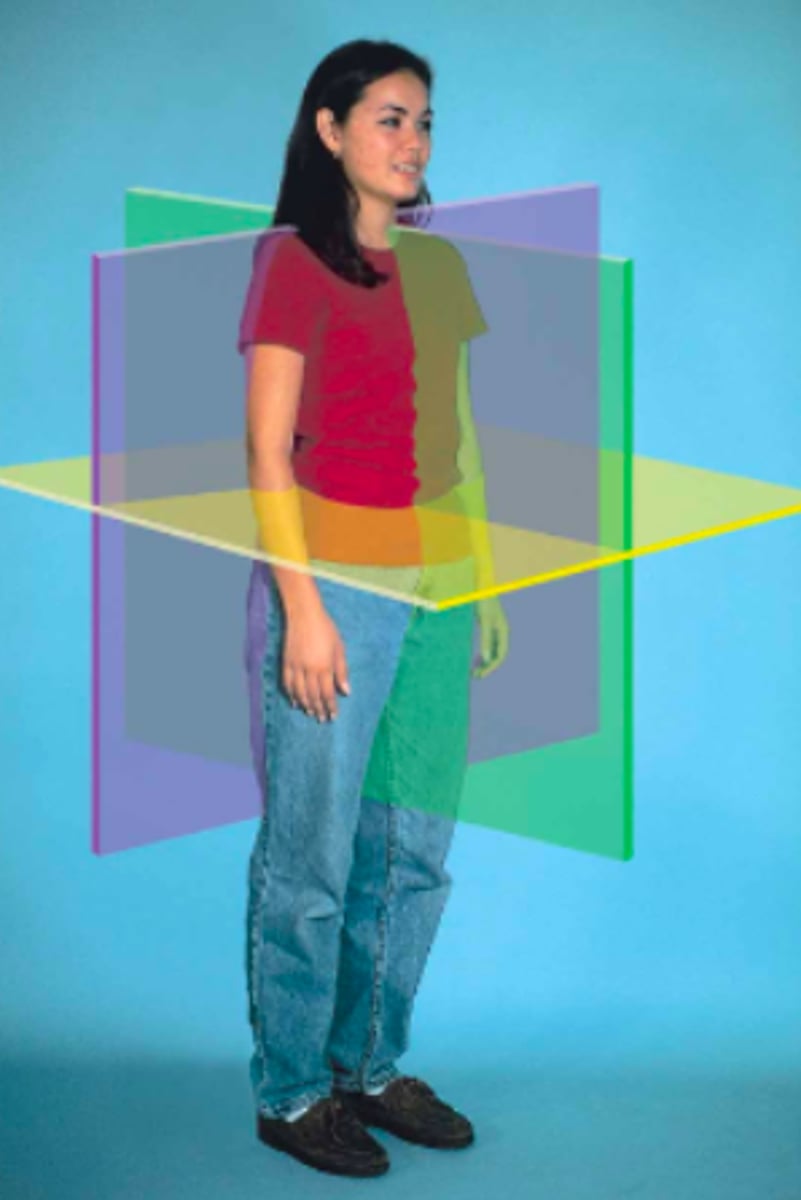
yellow: transverse plane
purple: frontal plane
green: sagittal plane
Identify the body plane that corresponds with each of the three colors:
movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration ( does not require energy; passive process)
Define diffusion:
movement of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from an area where water is more concentrated to an area where water is less concentrated
Define osmosis:
a membrane allows some substances to pass through but blocks others
Define selective permeability:
the process by which a single cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells
define mitosis
cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm of a parent cell into two separate daughter cells (it starts during late anaphase or telophase and completes after nuclear division)
define cytokinesis