Ch. 1 - Nerve Cells & Impulses
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
neurons, glia
human nervous system is comprised of two types of cells: ______ & _____
separate
individual cells of the nervous system are structurally ________
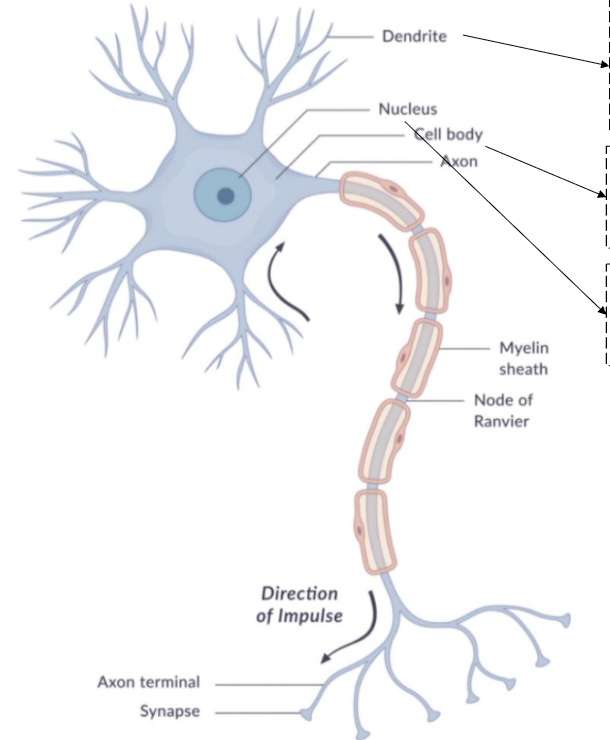
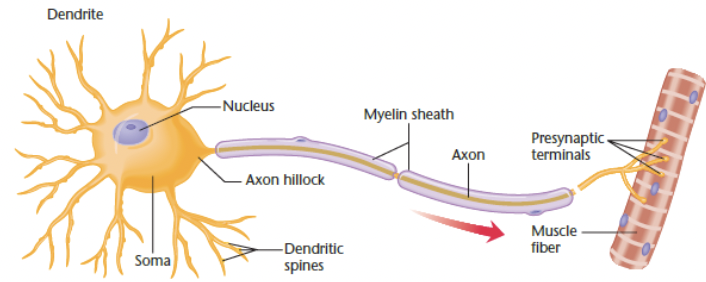
dendrite
receive neurotransmitters
bring information into the neuron
some contain dendritic spines (greater surface area = more information)
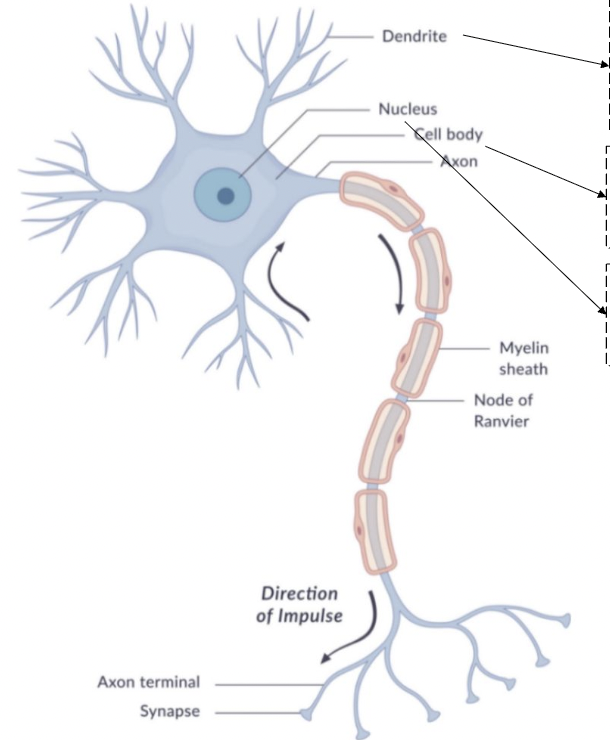
cell body
soma
contains nucleus
metabolic work of the cell
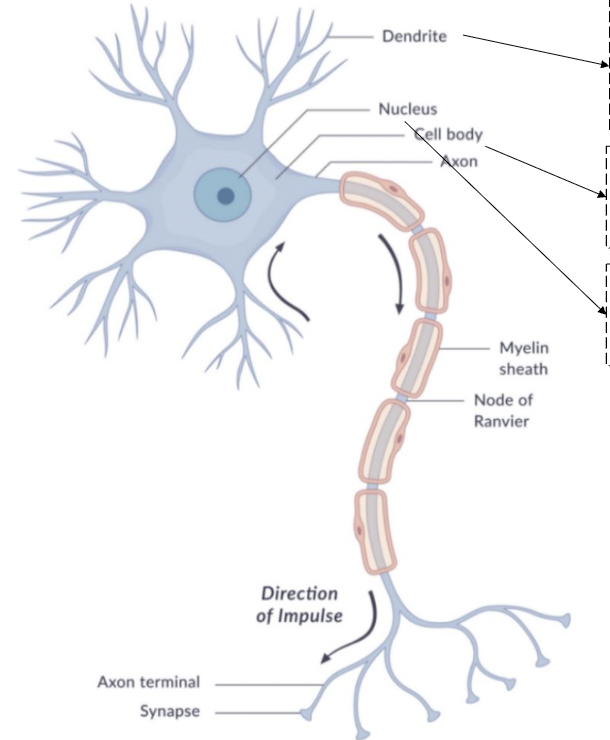
nucleus
contains: endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and chromosomes
regulates all cell function
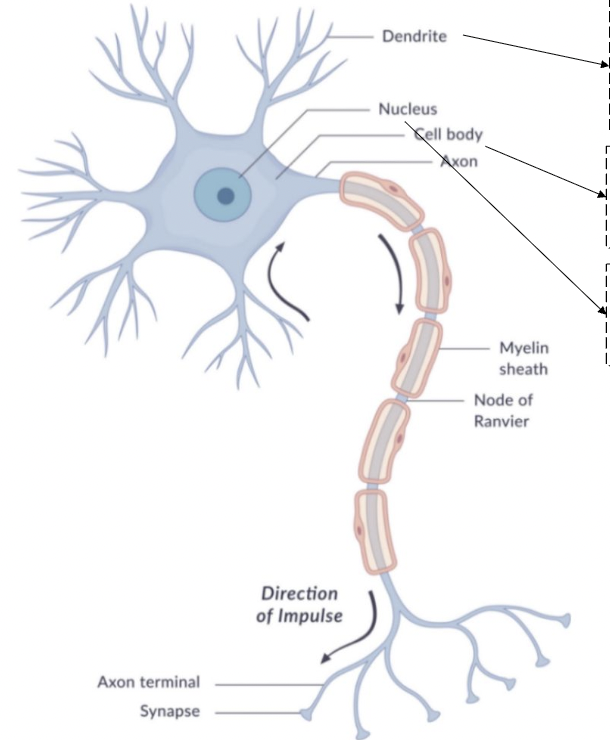
axon
begins with axon hillock
transmits nerve impulse (action potential)
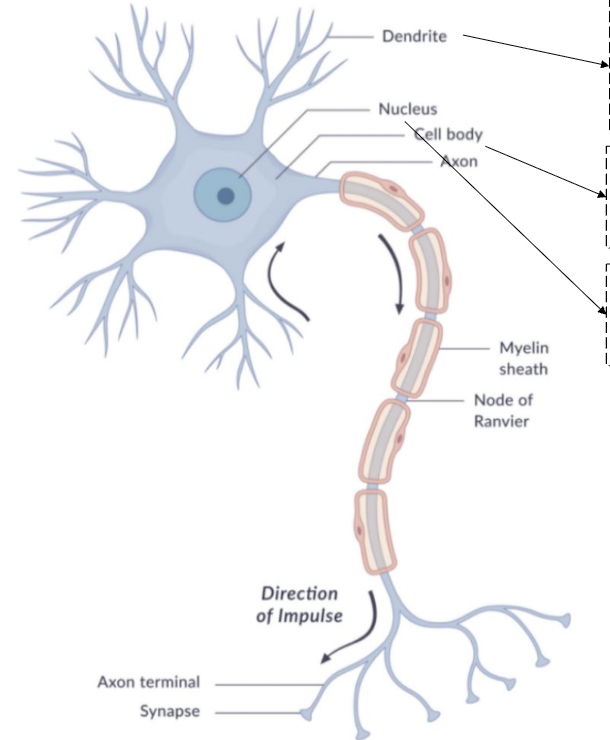
myelin sheath
insulating material that speeds transmission
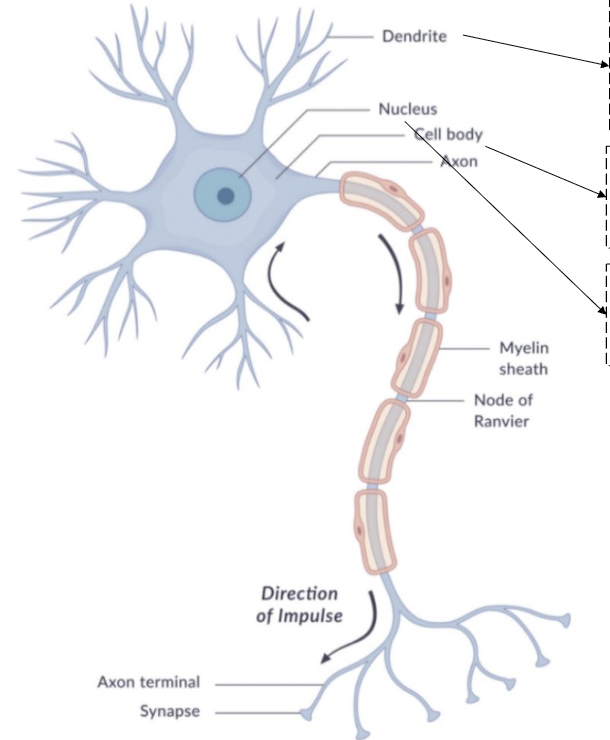
node of ranvier
interruptions in the sheath
allows for saltatory conduction
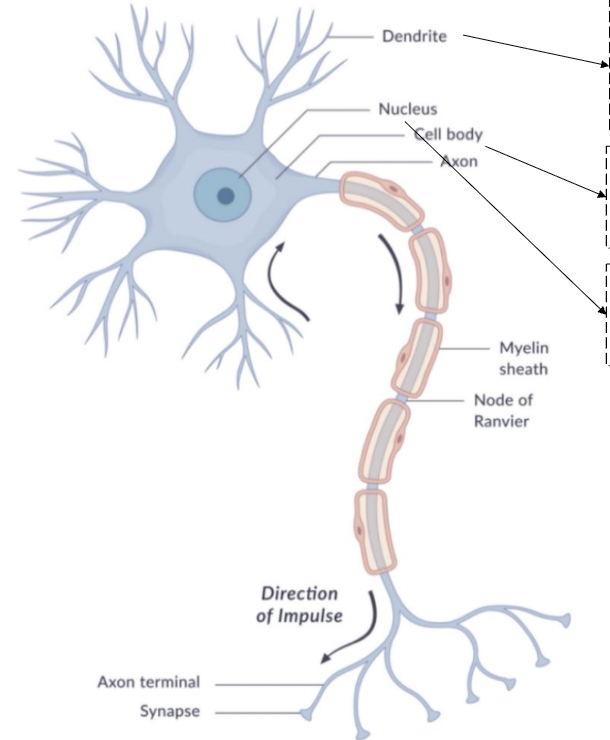
axon terminal
end point of the axon
releases neurotransmitters at the synapse
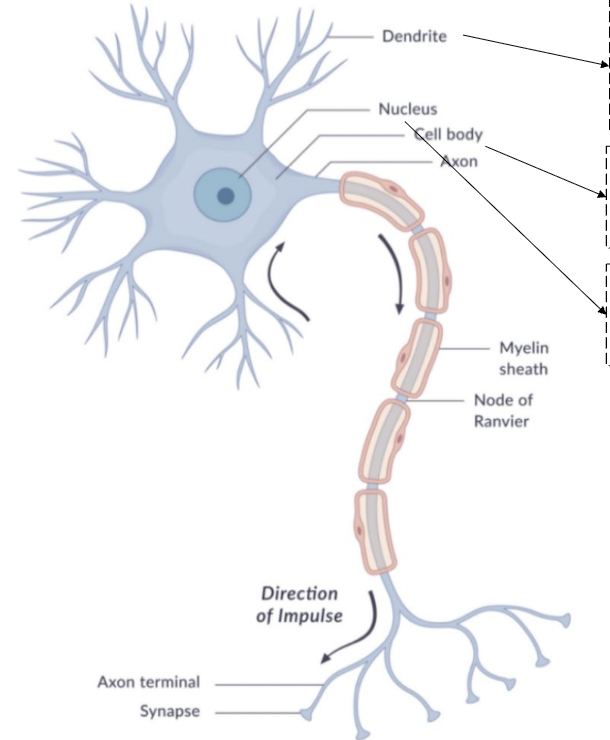
synapse
gap between pre-synaptic neuron and post-synaptic neuron
vertebrae motor neuron
soma in the spinal cord receives excitation from other neurons
conducts impulses along its axon to a muscle or gland
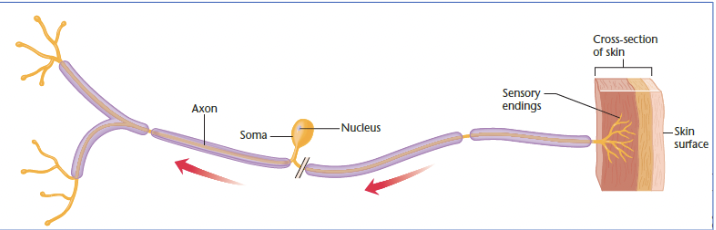
vertebrae sensory neuron
specialized at one end to be highly sensitive to a particular type of stimulation (touch, light, sound, etc)
afferent
bringing info into a structure
efferent
carrying info away from a structure
intrinsic
interneurons
neurons whose dendrites and axons are completely contained within a single structure
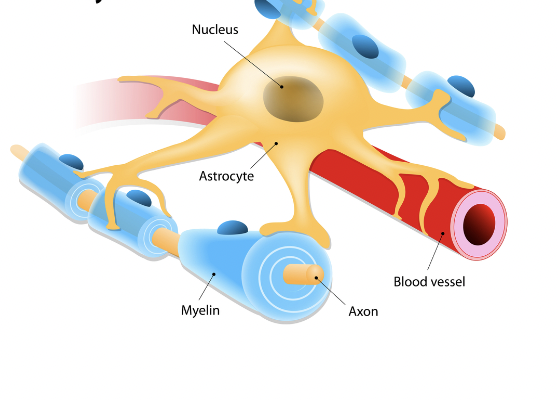
astrocyte
dilates blood vessels to direct nutrients to areas of high activity
help synchronize activity of the axon
microgila
removes waste material, viruses, and fungi from the brain
also removes dead, dying, or damaged neurons
oligodendrocytes, Schwann cells
____________ (central nervous system) and _____ ____ (peripheral nervous system) build the myelin sheath that surrounds and insulates certain vertebrae axons
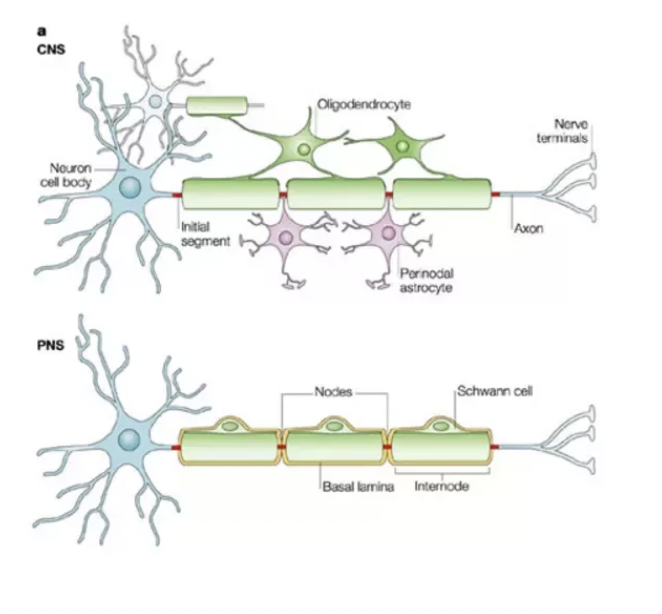
axons, dendrites
after embryonic development most _____ and _______ differentiate into neurons (smaller number differentiate into astrocytes and oligodendrocytes)
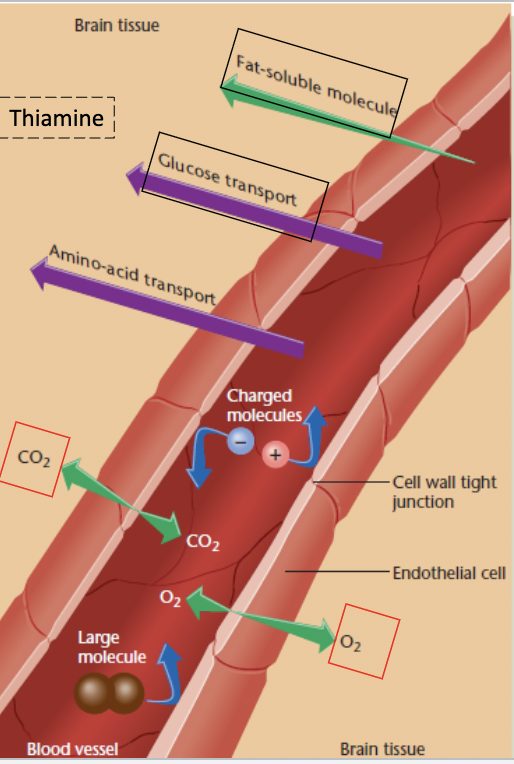
blood-brain barrier
mechanism that surrounds the brain and blocks most chemical from entering
immune system destroys damages or infected cells throughout the body
neurons in brain generally do no regenerate
certain beneficial chemicals have difficultly passing into the brain (ex: chemotherapy for brain cancer)
nerve impulse
electrical message transmitted down the axon of a neuron
does not travel directly down the axon
regenerated at points along the axon (nodes of Ranvier) so that it is not weakened
speed of nerve impulses range from less than 1 m/s to 100 m/s
resting potential
state of the neuron prior to sending a nerve impulse
membrane maintains an electrical gradient known as polarization
- charge inside membrane (-70 millivolts)
higher conc. of Na+ outside of cell
higher conc. of K+ inside of cell
neuron membrane
membrane is selectively permeable
Na, K, Ca, Cl
during a resting potential:
Na+ channels are closed
K+ channels are partially closed (slow passage of potassium)
both passive channels (rely on gradients to move ions when open)
threshold of excitation
a level above which any stimulation produces a massive depolarization (action potential)
depolarization
decreasing the polarization
hyper-polarization
increasing the polarization
polarization
difference between the electrical charge of two places
regenerated
at each node of Ranvier (unmyelinated sections of the axon) the action potential is ________
salatory conduction
“jumping” of the action potential from node to node (rapid conduction of impulses)
absolute refractory period
first part of the period, membrane cannot produce an action potential
relative refractory period
second part of the period; a stronger than usual stimulus would be required to trigger an action potential
all-or-none law
it either fire or doesn’t (no such thing as a small action potential vs. a big action potential)
amplitude and velocity of an action potential are independent of the intensity of the stimulus that initiated it