Unit 8: Evolution
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Define genetic variation
The diversity of alleles and genotypes within a population or species
What are two causes or sources of variation in populations?
Mutations and genetic recombination
What is natural selection? (use VEAR to help)
The process by which organisms with traits that are better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more successfully, while those with less favorable traits are eliminated.
What is VEAR?
Variation, Environment, Adaptation, and Reproduction, which are key components of natural selection.
Define variation
Small differences between members of the same species.
What are examples of variation?
Mutations create new alleles, Meiosis and sexual reproduction "shuffle" the alleles.
Define environment
Place where the population olives (includes trophic and non-trophic relationships)
How might the environment cause species to evolve?
The environment presents different challenges and possibilities that allow a species to adapt.
What are examples of different challenges and possibilities that allow a species to adapt?
Change in environment/climate (non-trophic)
New predator (trophic)
Loss in food/resources (trophic)
Disease (trophic)
Define advantage
To be placed in a favorable position.
What sorts of traits might be advantageous?
Some individuals have an advantageous trait (genes) and survive easier, while others may not have that trait-not likely to survive.
Define reproduction
The production of offspring
What is natural selection?
The mechanism behind evolution, which populations adapt and change.
What is extinction?
The complete disappearance of a species from Earth.
Why does extinction happen?
This happens when species cannot adapt to changing environments and do not produce offspring.
Through natural selection within a population, adaptation or extinction may be more likely to occur depending on what?
The rate and amount of environmental change
The existing genetic variation
Characteristics such as: reproduction rate, life strategy, population size and habitat range.
Why is it more correct to speak of the evolution of populations rather than individual organisms?
Evolution occurs at the population level because it involves changes in allele frequencies over generations within a population, not within individual organisms.
The brown anole is a species of lizard that lives in Cuba and the Bahamas. When humans first came to these islands, they accidentally brought rats hiding on their ships. Rats sometimes eat these lizards, and the lizards did not have a predator like rats until humans brought them.
How did the lizard population adapt when rats came into their environment?
The lizards that already had certain physical traits or behaviors to help them avoid the rats were more likely to survive and reproduce than other lizards.
Canada geese have a large population size, and many populations are interconnected because geese can fly between different locations-will the population adapt or go extinct?
Adapt
Ladybugs have a lot of genetic variation within their populations-will the population adapt or go extinct?
Adapt
Sea otters have very low levels of genetic variation because humans hunted them for their fur in the 1800s-will the population adapt or go extinct?
At risk of extinction due to low genetic variation.
Hibiscus plants need bright sunlight to survive. Imagine that a volcano erupts in the plants' environment. The eruption rapidly changes the environment by creating clouds of ash and smoke that block out the sun for a long time-will the population adapt or go extinct?
At risk of extinction due to environmental change.
What is a mutation?
A change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
What is an example of a mutation as an evolutionary force that can change the genetic variation in a population?
Mutations create new alleles
Meiosis and sexual reproduction "shuffle" the alleles
Do mutations increase or decrease variation? Why?
Increase genetic variation because they introduce new alleles into the gene pool due to random changes in DNA sequences and chromosome structure creating genetic differences.
What is non-random mating?
Mates are not chosen by chance. Some individuals have a higher/lower chance of reproducing.
What is an example of a non-random mating as an evolutionary force that can change the genetic variation in a population?
There is not much variation in color among male cardinals-females prefer red colored male cardinals.
Humans use non-random mating to domesticate animals and plants (species must start with lots of genetic variation)
Does non-random mating increase or decrease variation? Why?
Can decrease variation disadvantageous traits may become very uncommon.
What is the bottleneck effect?
Population shrinks suddenly
What is an example of the bottleneck effect as an evolutionary force that can change the genetic variation in a population?
Natural disasters or human activities-habitat destruction, overharvesting.
Does the bottleneck effect increase or decrease variation? Why?
Decreases variation because it reduces the number of alleles in the gene pool.
What is migration?
Individuals move between populations.
What is an example of migration as an evolutionary force that can change the genetic variation in a population?
Male elephants travel long distances to find mates, which makes it less likely for populations to experience a bottleneck.
Does migration increase or decrease variation? Why?
Increases genetic variation by introducing new alleles into populations and reducing genetic differences between populations.
What are the 3 types of natural selection?
Directional, stabilizing, and disruptive selection
What is directional selection?
One extreme phenotype is more fit than all the other phenotypes.
What is stabilizing selection?
Intermediate phenotypes are more fit than extreme ones.
What is disruptive selection?
Both extreme phenotypes are more fit than those in the middle.
What is speciation?
When one species diverges (splits) into 2 DIFFERENT species (their DNA cannot be identical once they diverge)
Which type of selections could lead to scientists classifying different populations of organisms as 2 different species?
Directional and disruptive selection
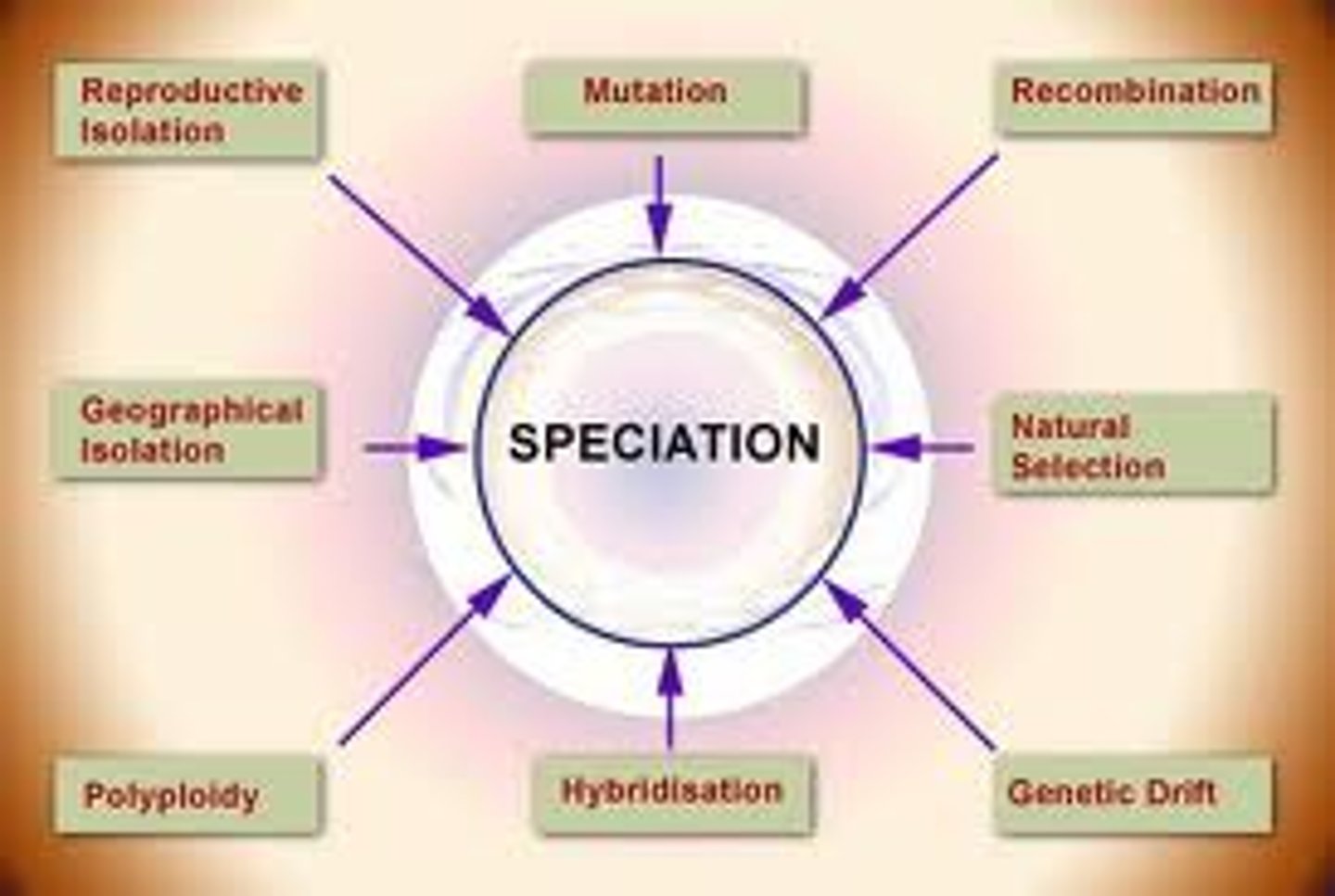
What are the mechanisms for speciation?
Geographical and reproductive isolation
What is geographical isolation?
Physical separation of members of the same species.
What is reproductive isolation?
Various mechanisms that prevent species from producing fertile offspring.
What is divergent evolution?
The process by which closely related species evolve different traits or characteristics due to adapting to similar environments.
What is convergent evolution?
The process by which unrelated species evolve similar traits or characteristics due to adapting to different environments.
What are types of evidence for evolution?
Fossils, vestigial structures, homologous structures, analogous structures, embryology, biochemical similarities
What are fossils?
Preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms.
What do fossils show us?
Species have become extinct and new species have formed.
Modern species evolved from past life forms.
What are vestigial structures?
Have no function, but had a function in the species' ancestors. Anatomical features that have lost their original function in the course of evolution.
What are homologous structures?
Structures that have similar anatomy because they evolved from a common ancestor (may have different functions)
What are analogous structures?
Have similar functions but different anatomy because they evolved through convergent evolution (NOT from a common ancestor)
What is an embryo?
A young plant/animal in early stages of development.
What are biochemical similarities?
Similarities in amino acids indicate similar DNA. Very solid evidence in common ancestry.
What are adaptations?
Genetic traits that help an organism to survive or reproduce in its environment.
What is a gene pool?
All of the alleles within a population-each individual has 2 alleles for every gene.
Define species
A group of individuals that actually or potentially interbreed in nature.
What is taxonomy?
A system of grouping organisms according to their morphological (physical) characteristics/traits.
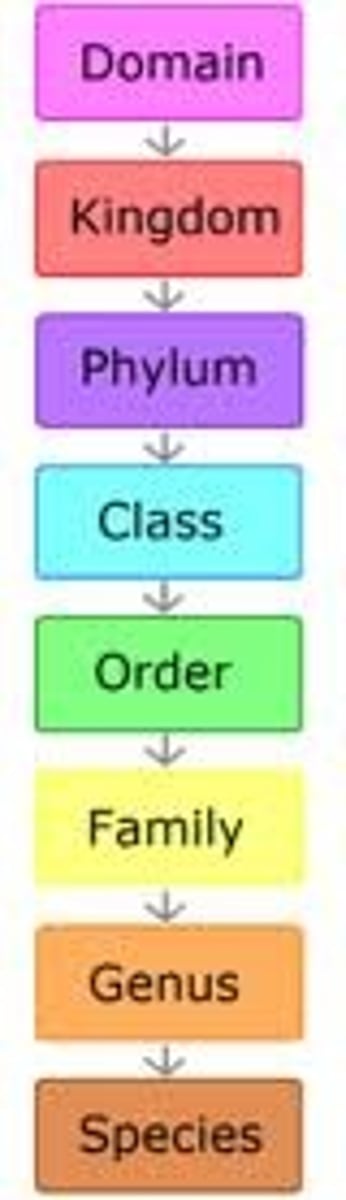
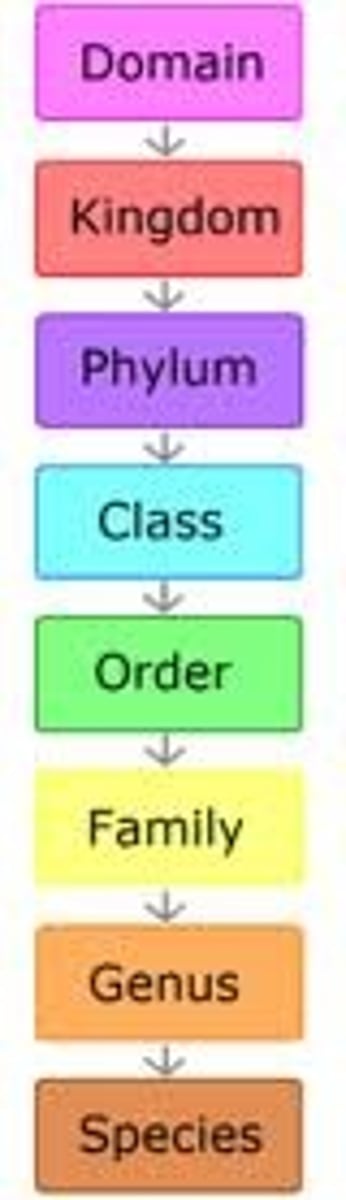
What are Taxa Levels?
8 levels from the most general to the most specific.
What are the 8 Taxa Levels?
Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
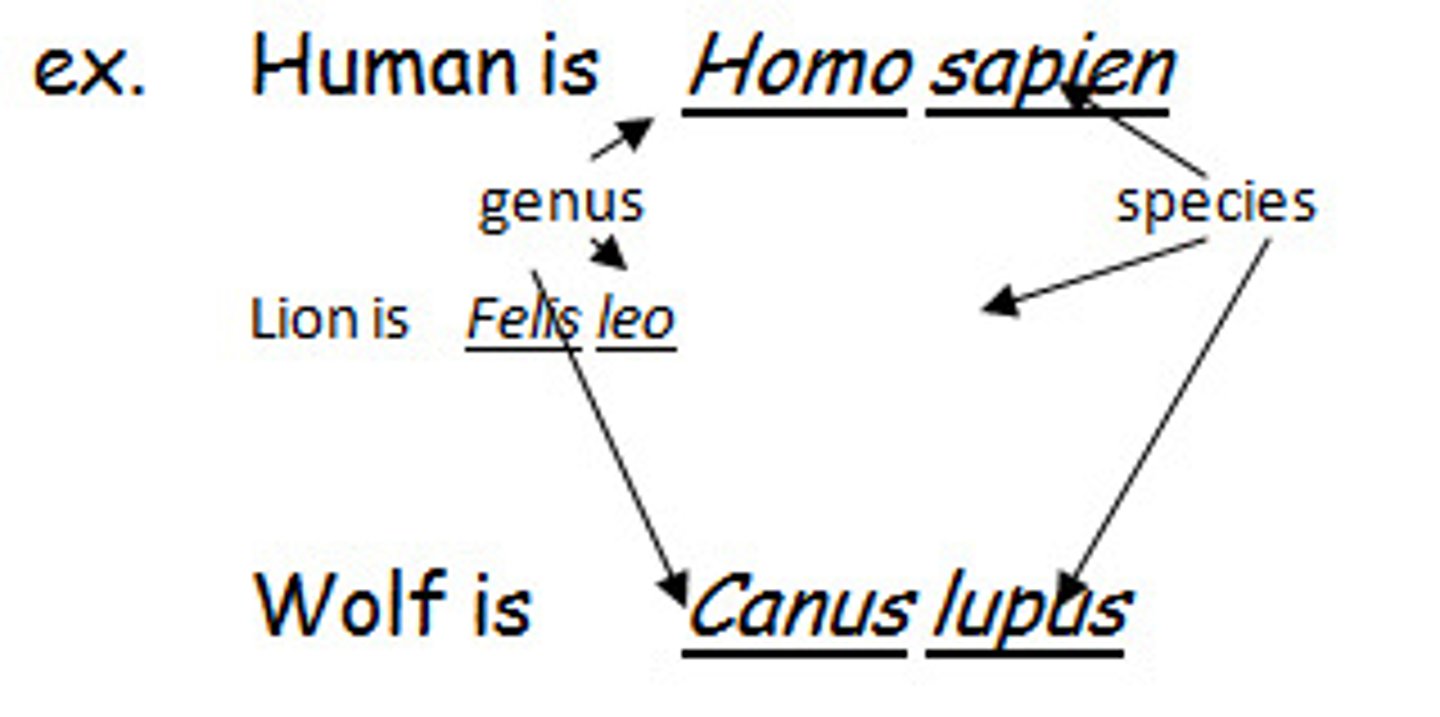
What is Binomial Nomenclature?
2 word naming system-gives each species a scientific name.
What are Cladistics?
A system of grouping organisms based on evolutionary descent.
What evidence do scientists use when classifying organisms?
Morphology (body structure), behavior, molecular (DNA), fossils
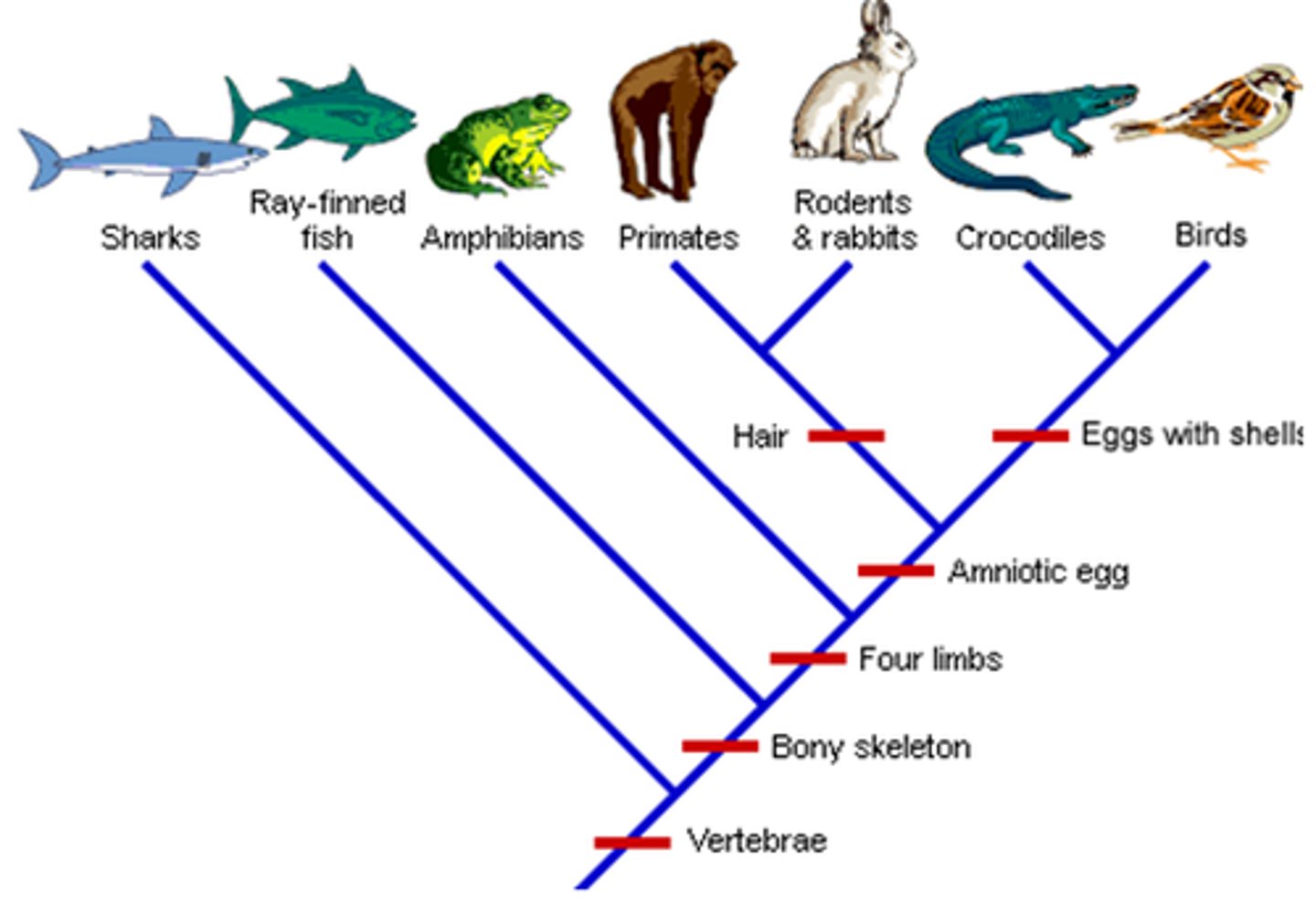
What are Cladograms?
Models that represent how organisms likely evolved from a common ancestor.
What do Nodes represent on a Cladogram?
Represent split into 2 groups
What do Point of Split represent on a Cladogram?
Common ancestor of all groups beyond that point.
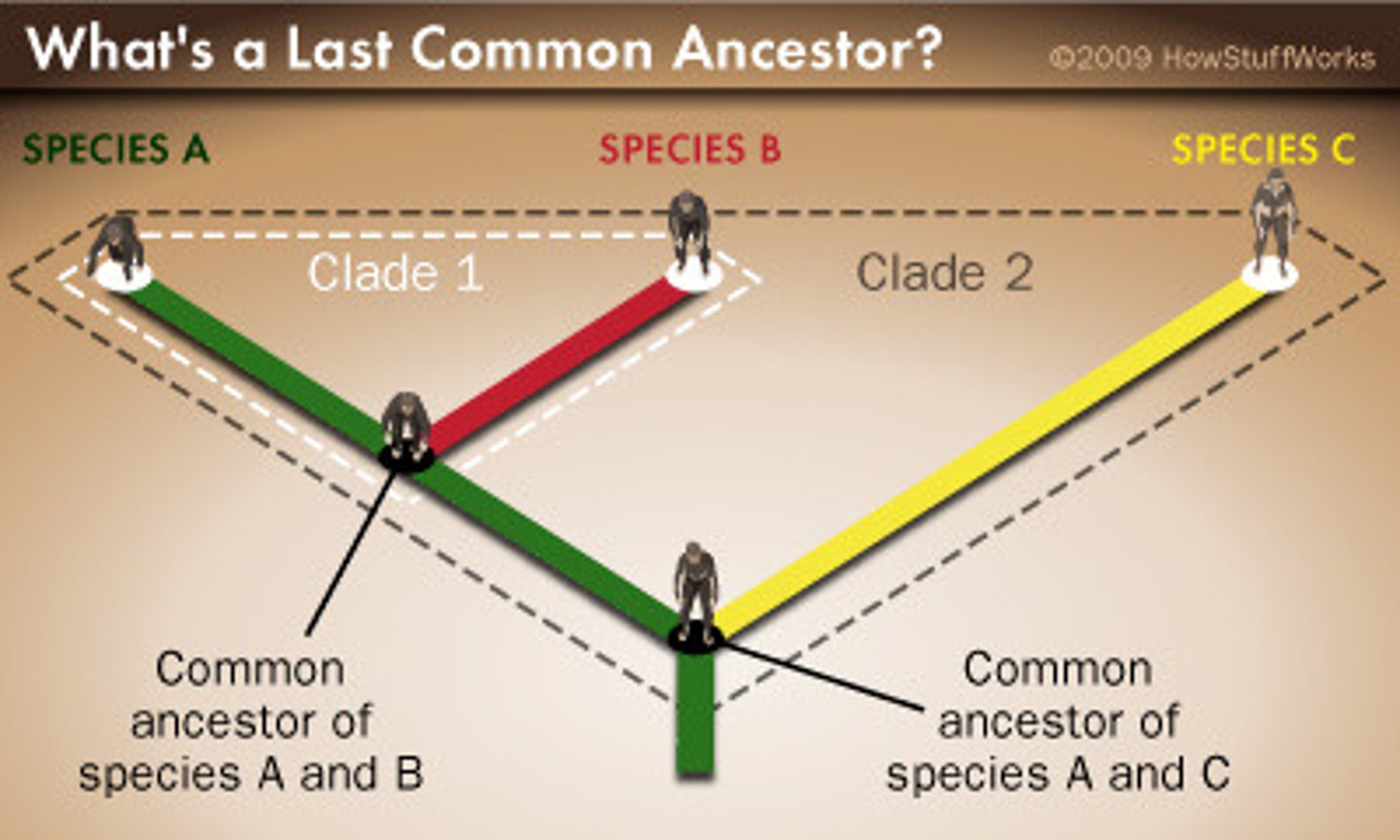
How do you determine if 2 species are more closely related?
They share a more recent common ancestor.
What is a common ancestor?
A species in the past from which new species have evolved.
Theory
The best explanation of an aspect of the natural world, supported by evidence. But is subject to change!

Evolution
Process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms (decent with modification)
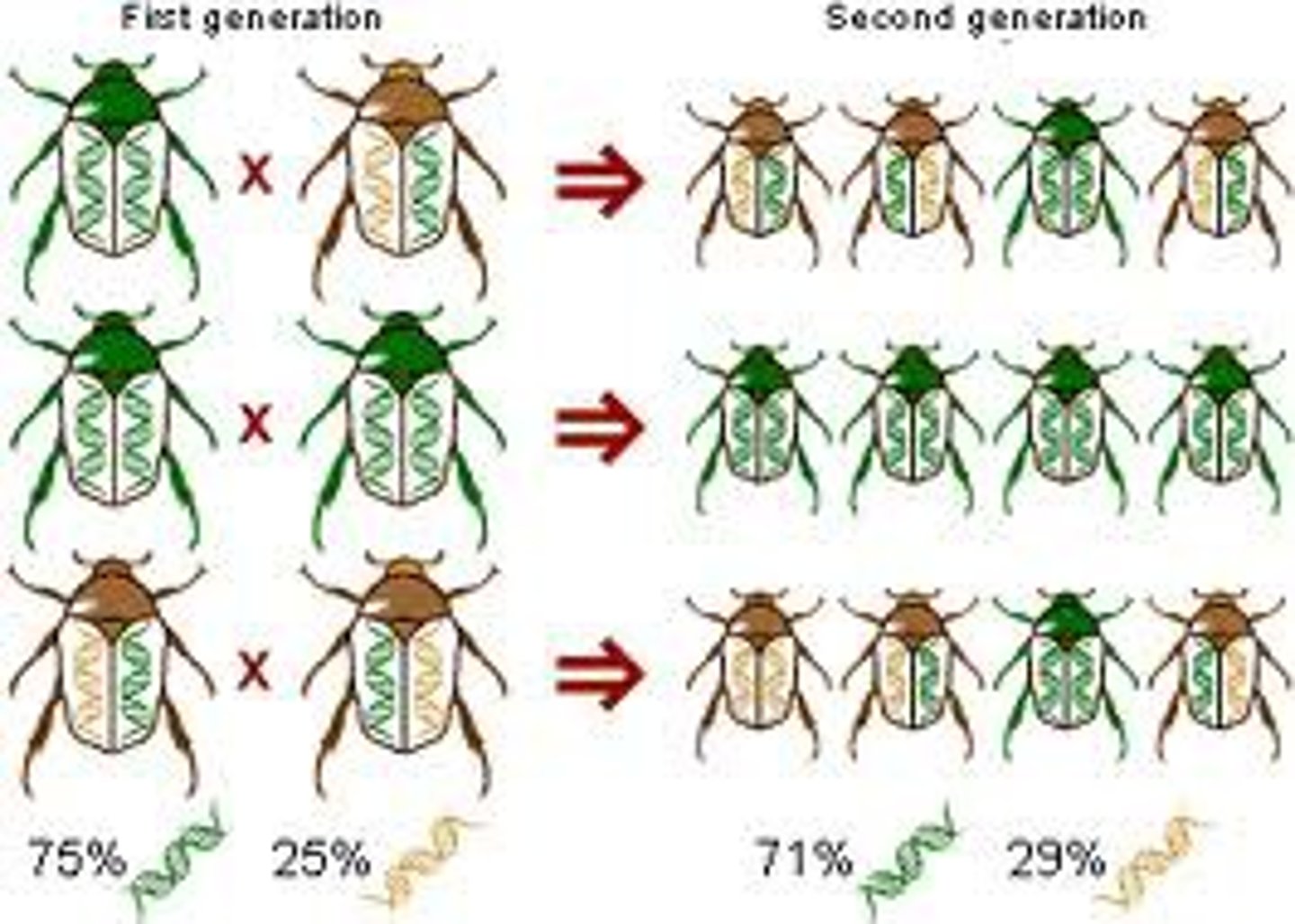
Natural Selection
Those best suited for their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. Passing on beneficial adaptations; also called survival of the fittest
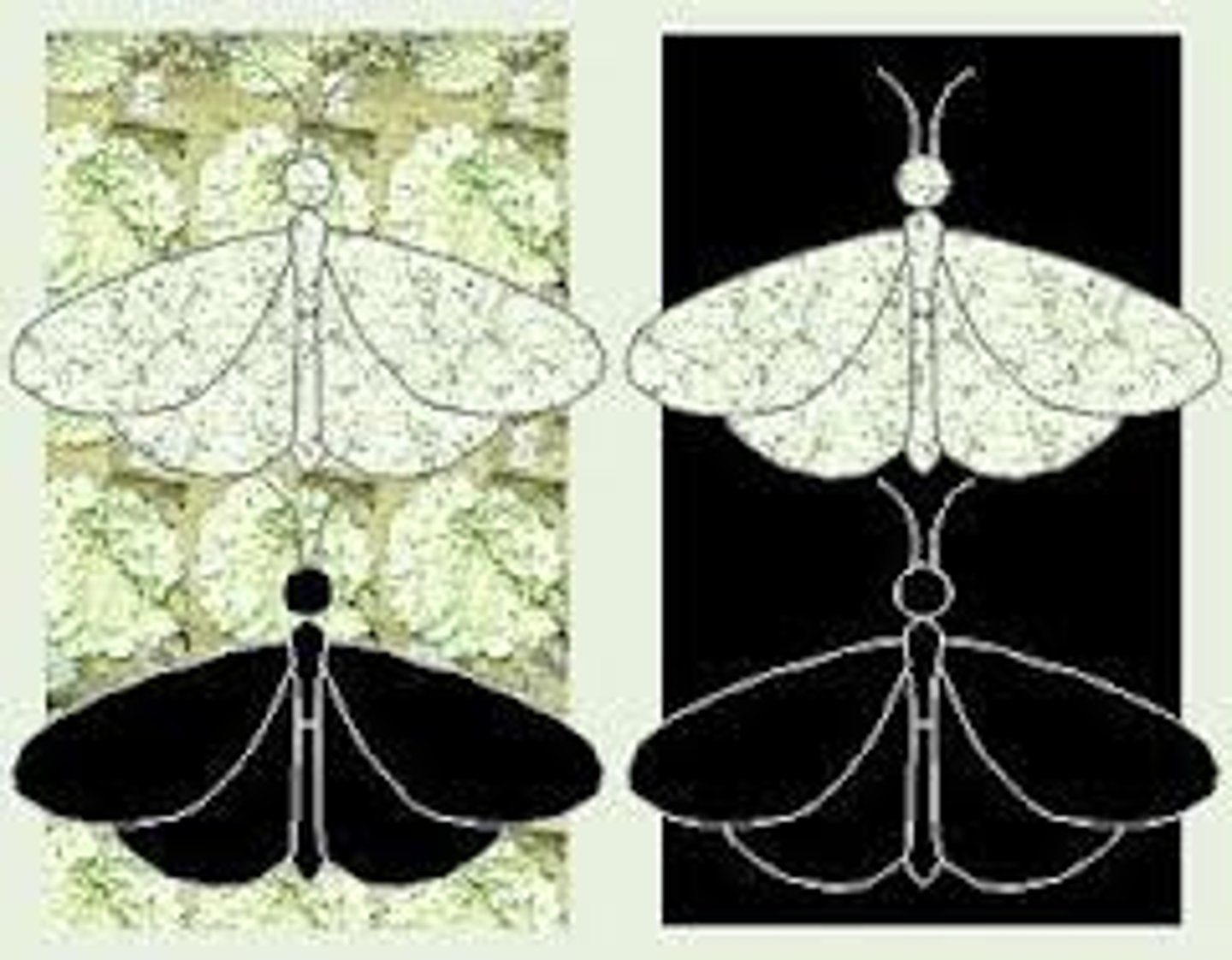
Variation
the differences within a single species (phenotypes ie skin color)

Speciation
formation of new species as a result of geographic or reproductive isolation.
Common Ancestry
a group of organisms share common descent if they have a common ancestor
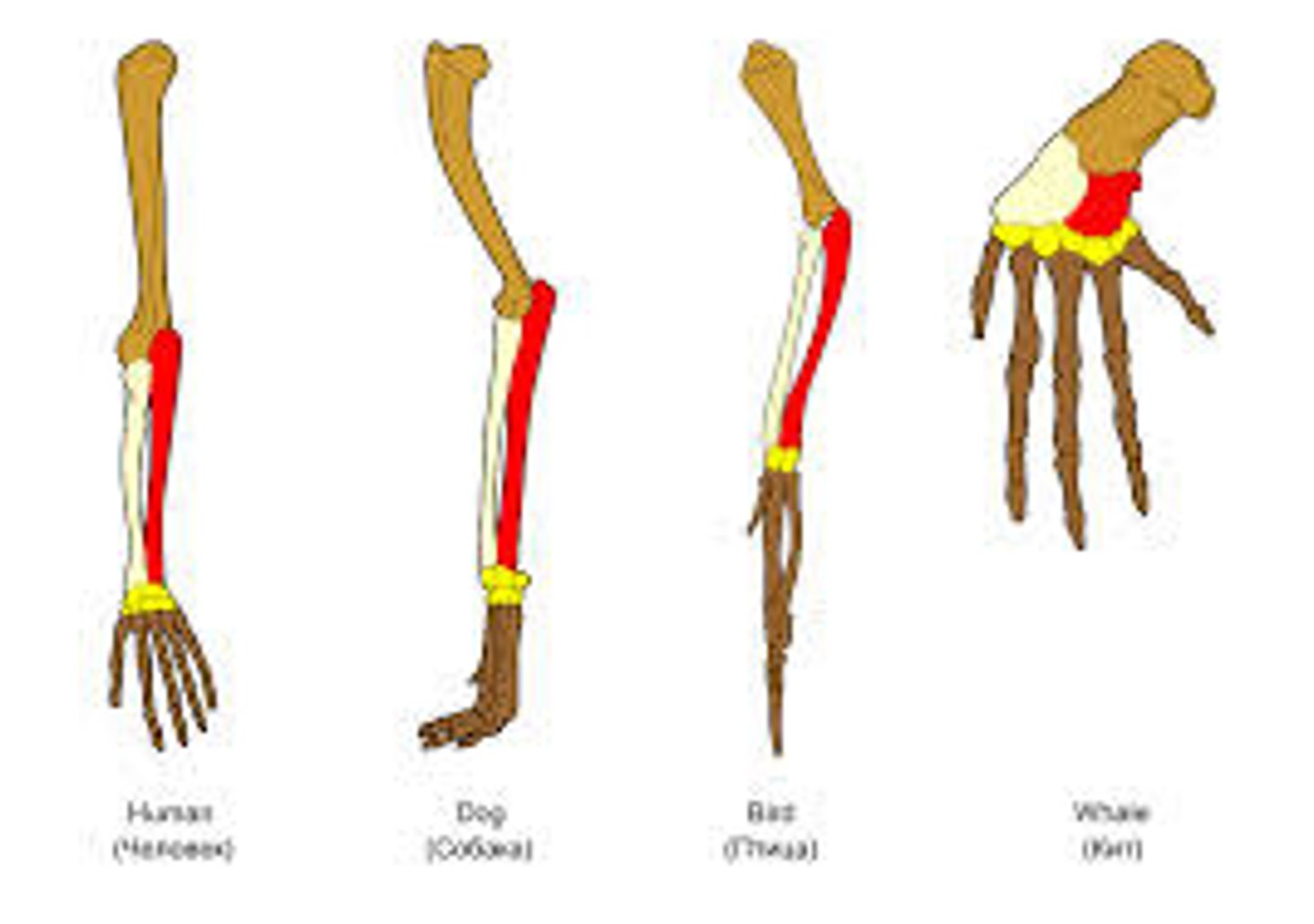
Homologous structures
Similar structures (ie bone arrangement) but different functions/purpose as a result of divergent evolution; evidence of common ancestry
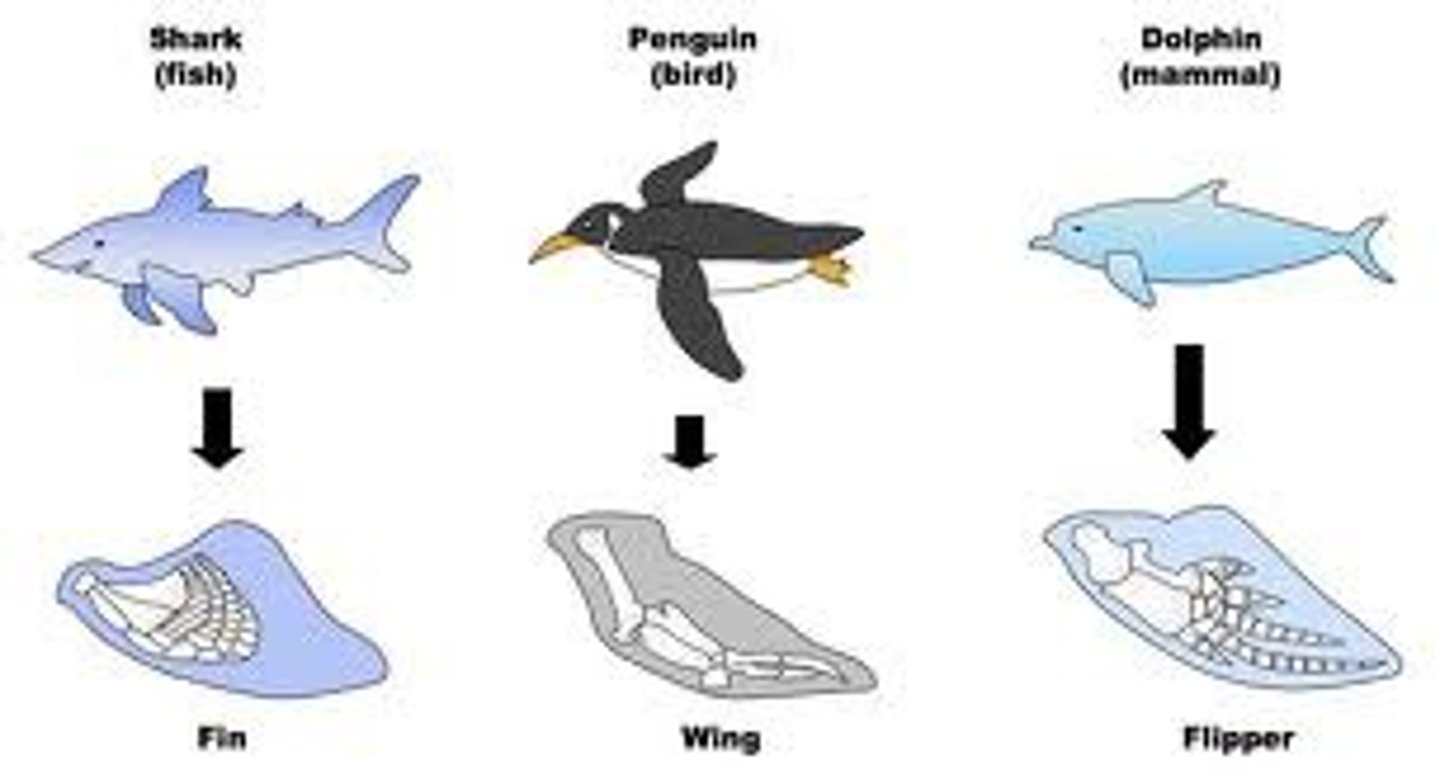
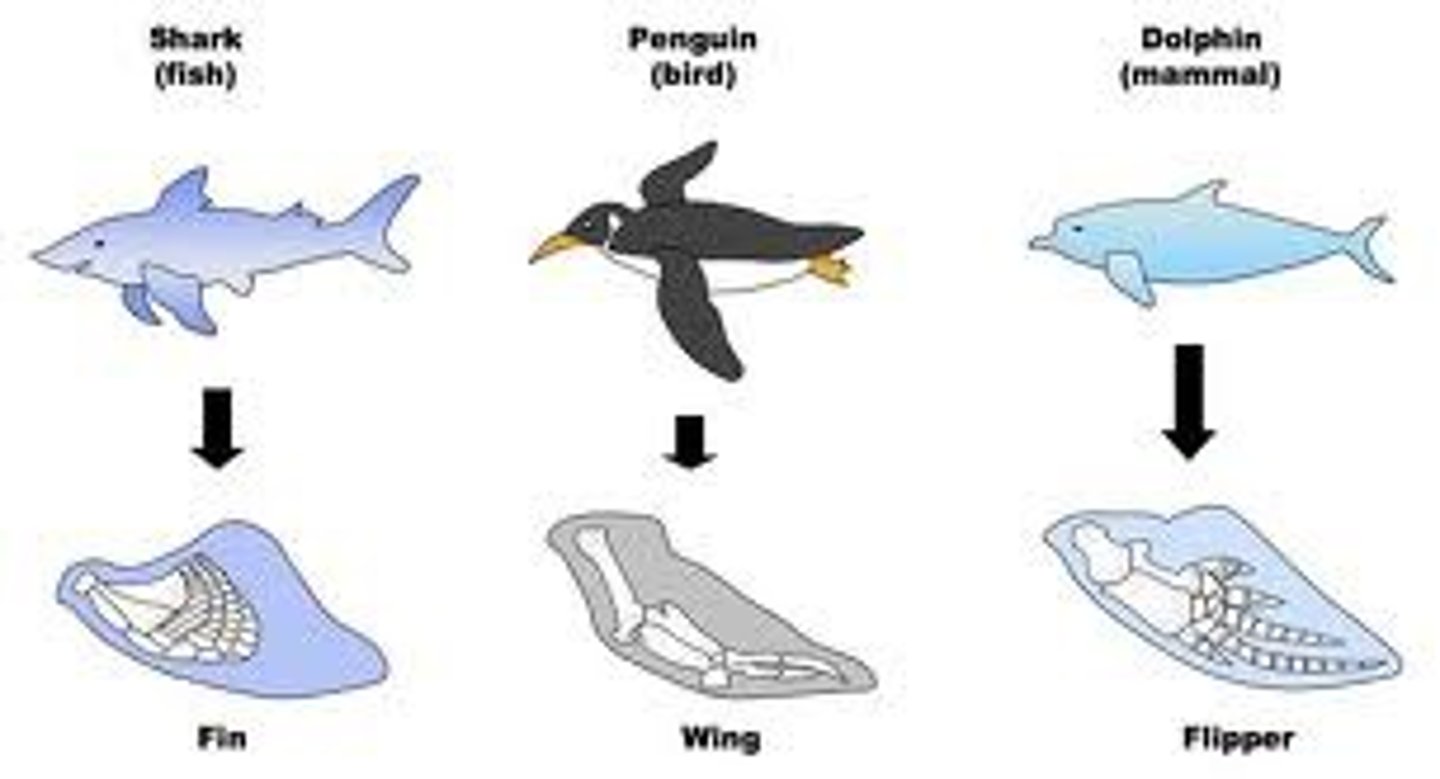
Analogous structures
Similar function/purpose but different structures as a result of convergent evolution. Organisms have DIFFERENT ancestral origins.
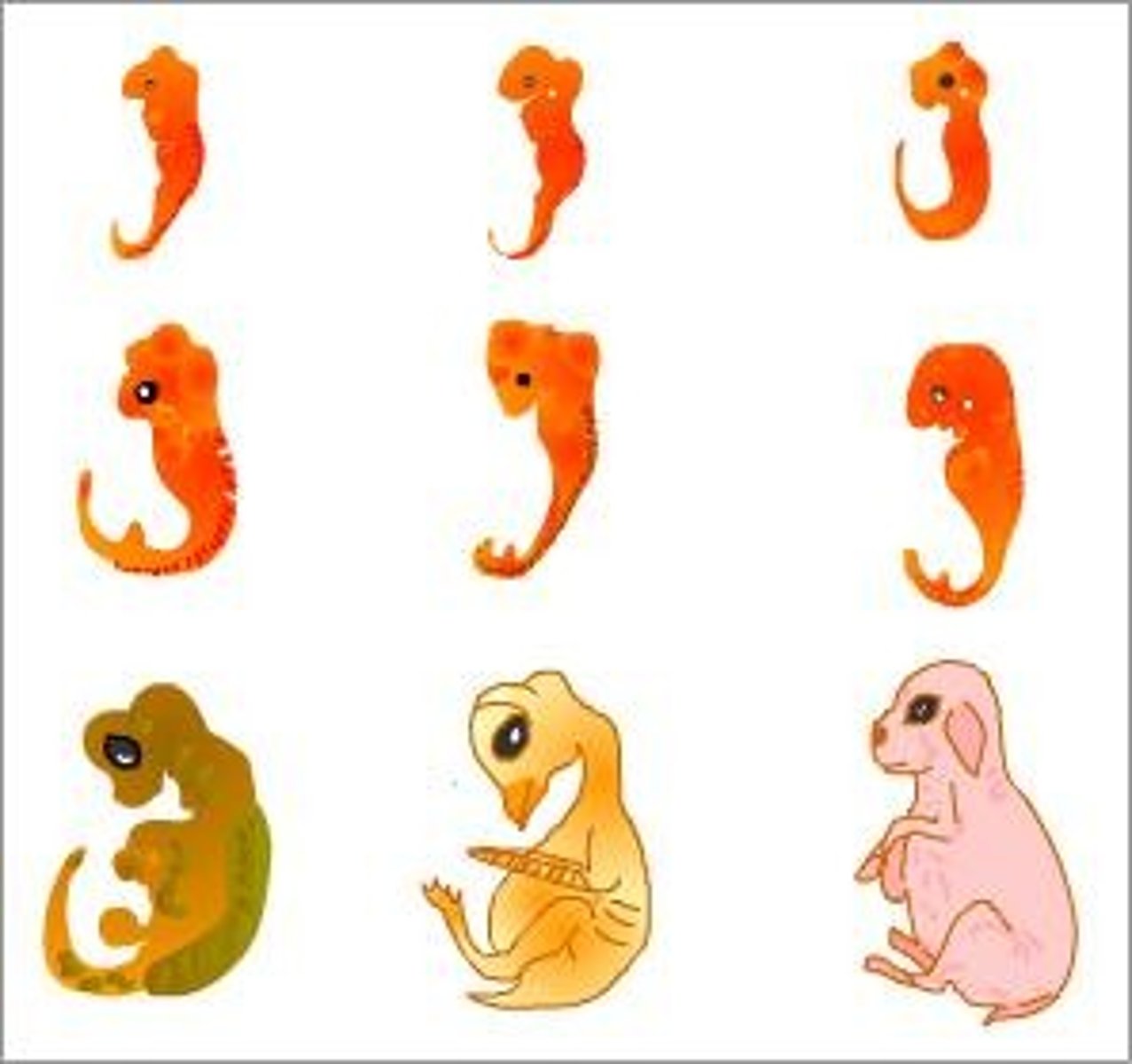
Embryology
Earliest stages of development are similar across species; indicates common ancestry

Proteins & DNA sequences
DNA (and therefore the amino acid sequences of proteins) are similar in related species

Adaptation
inherited characteristic that increases an organism's chance of survival
Divergent evolution
process by which a single species or small group of species evolves into several different forms that live in different ways
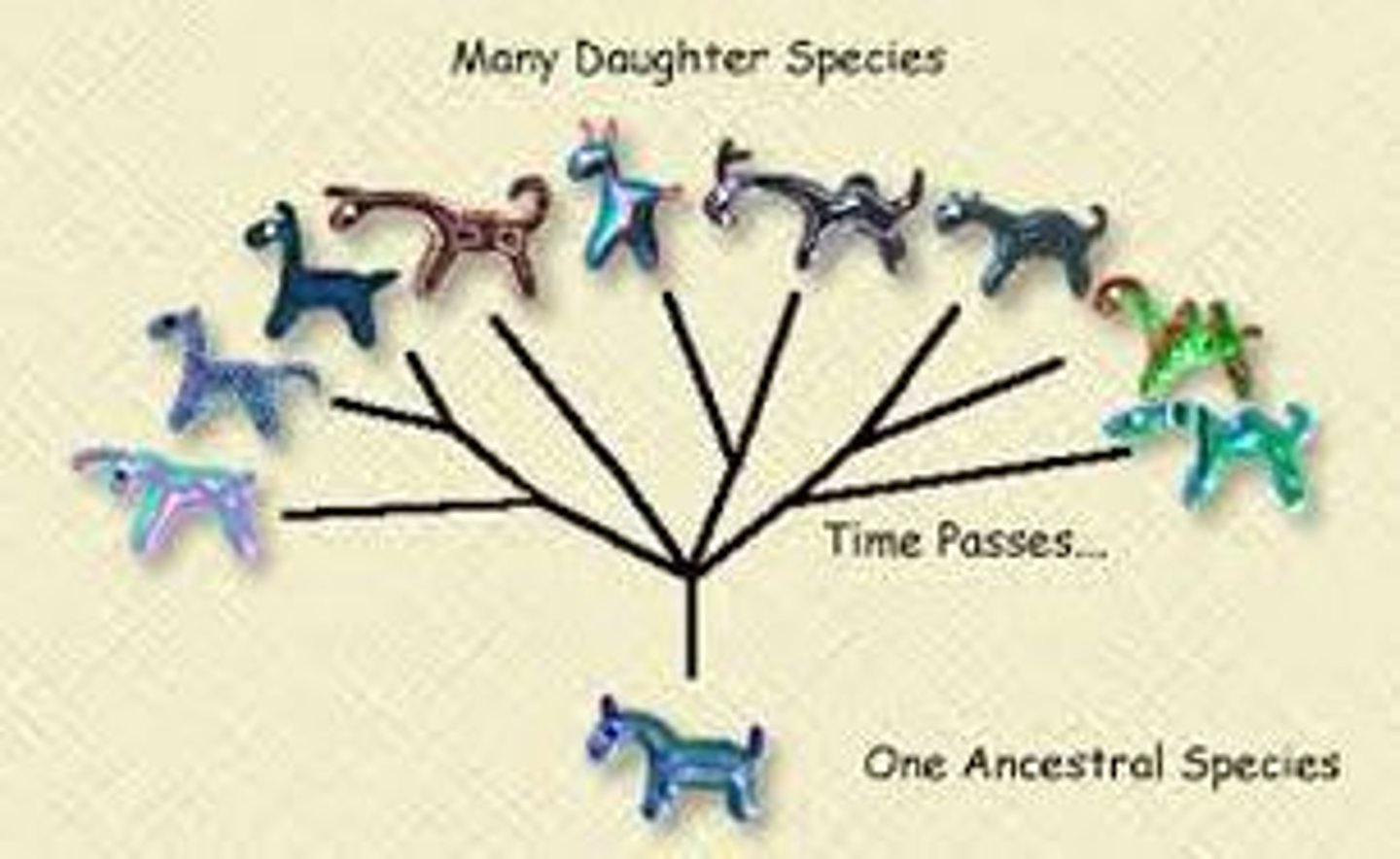
Convergent evolution
process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
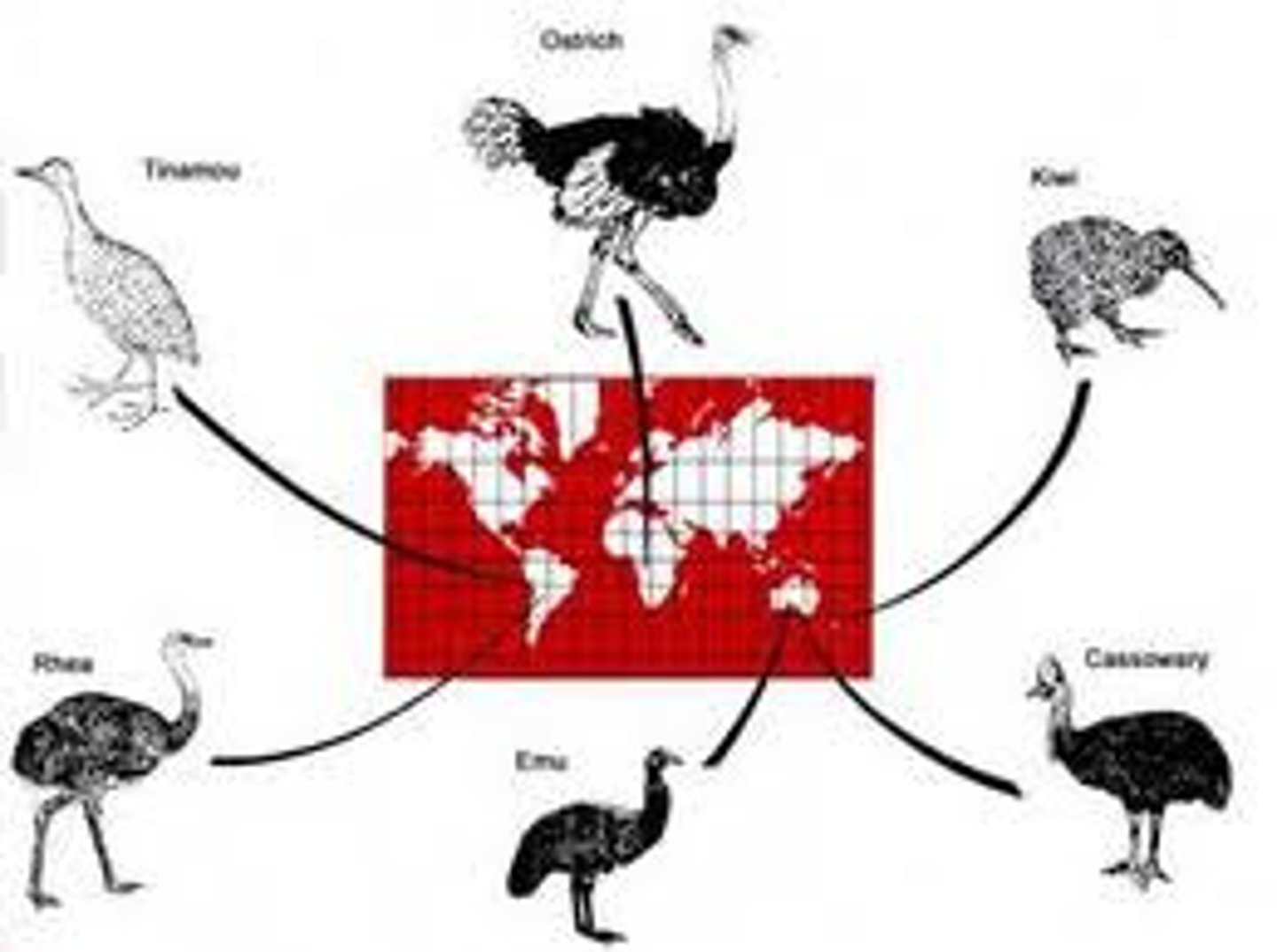
Reproductive isolation
the inability of a species to breed successfully with related species due to geographical, behavioral, physiological, or genetic barriers or differences

Geographic isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water
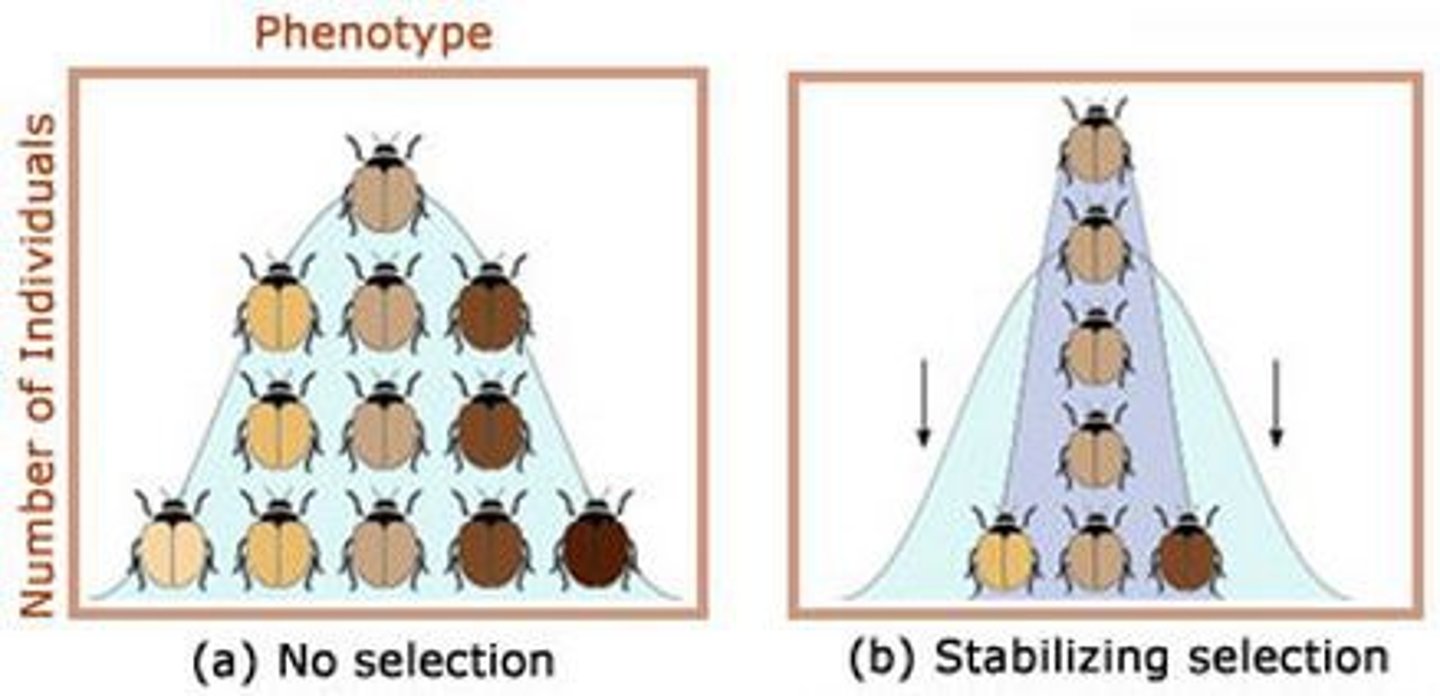
Stabilizing Selection
form of natural selection that occurs when individuals near the center of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals at either end
Directional Selection
form of natural selection that occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
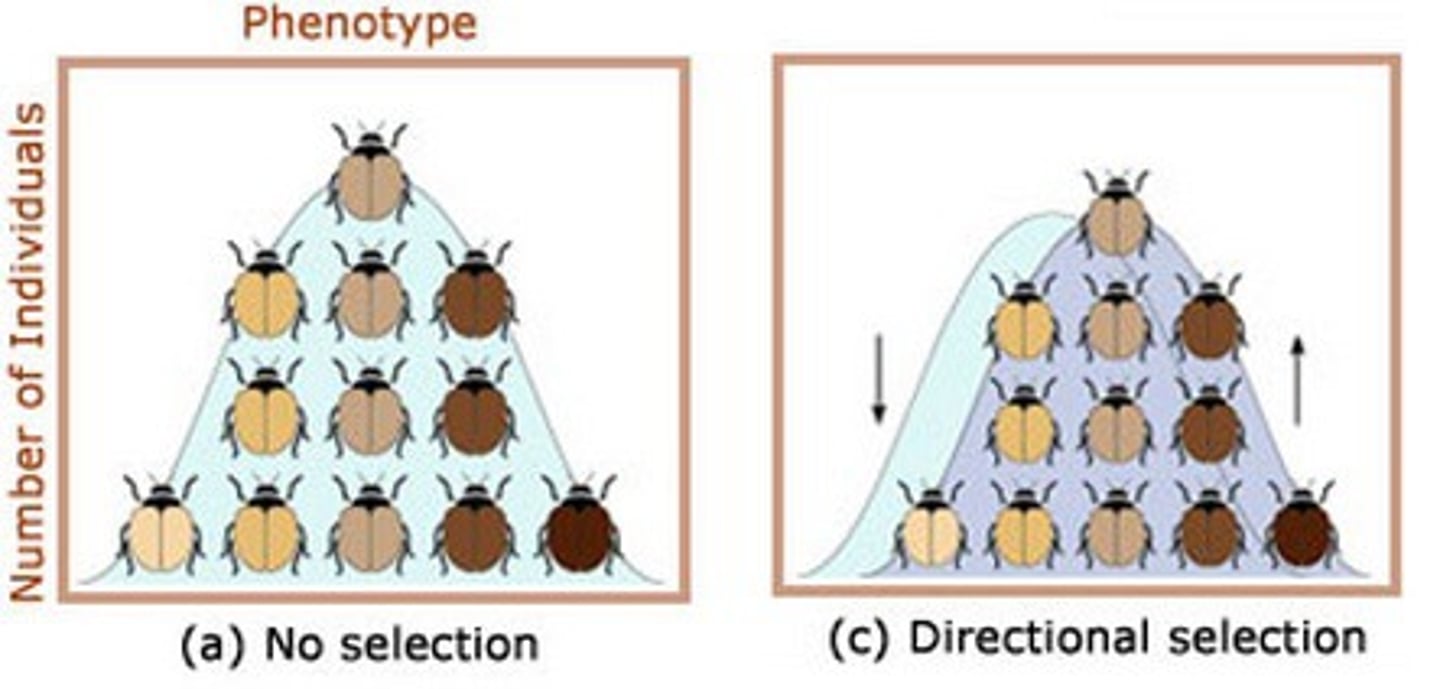
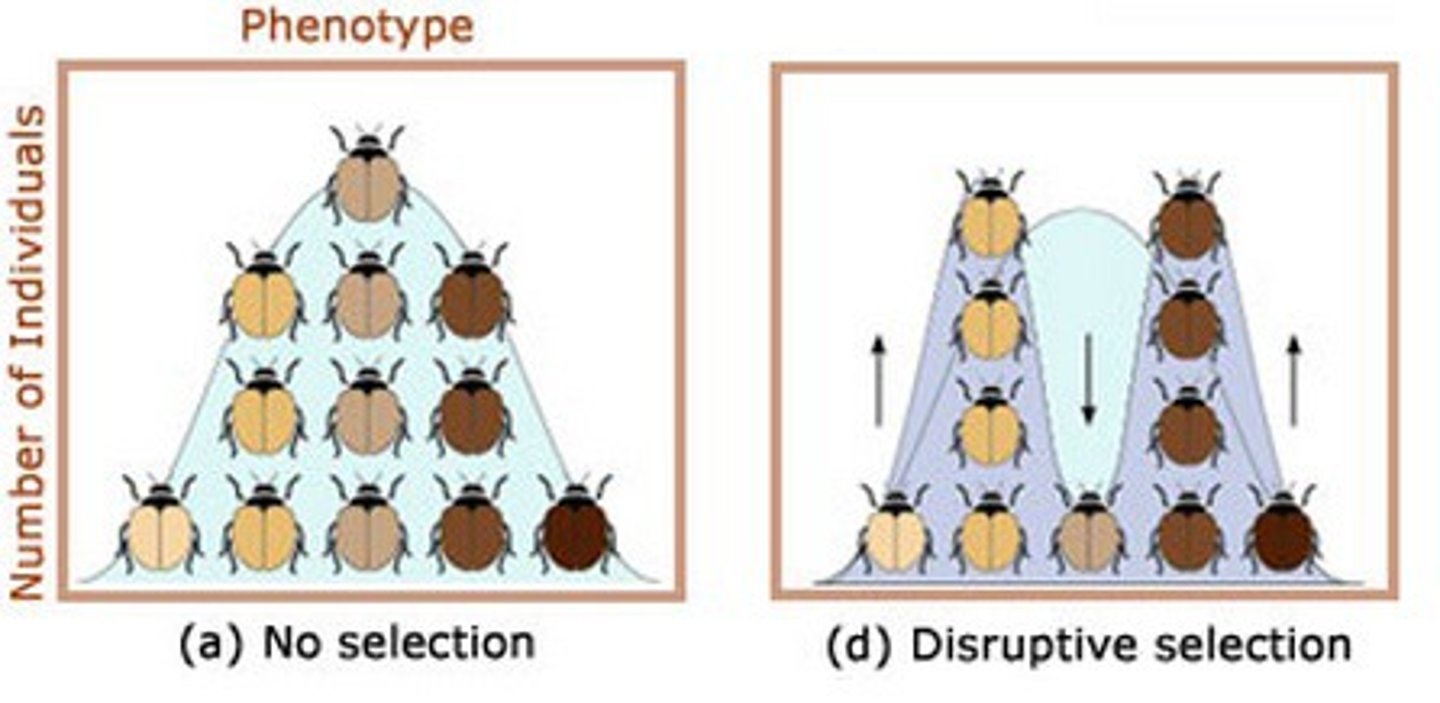
Disruptive Selection
form of natural selection that occurs when individuals at both ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle
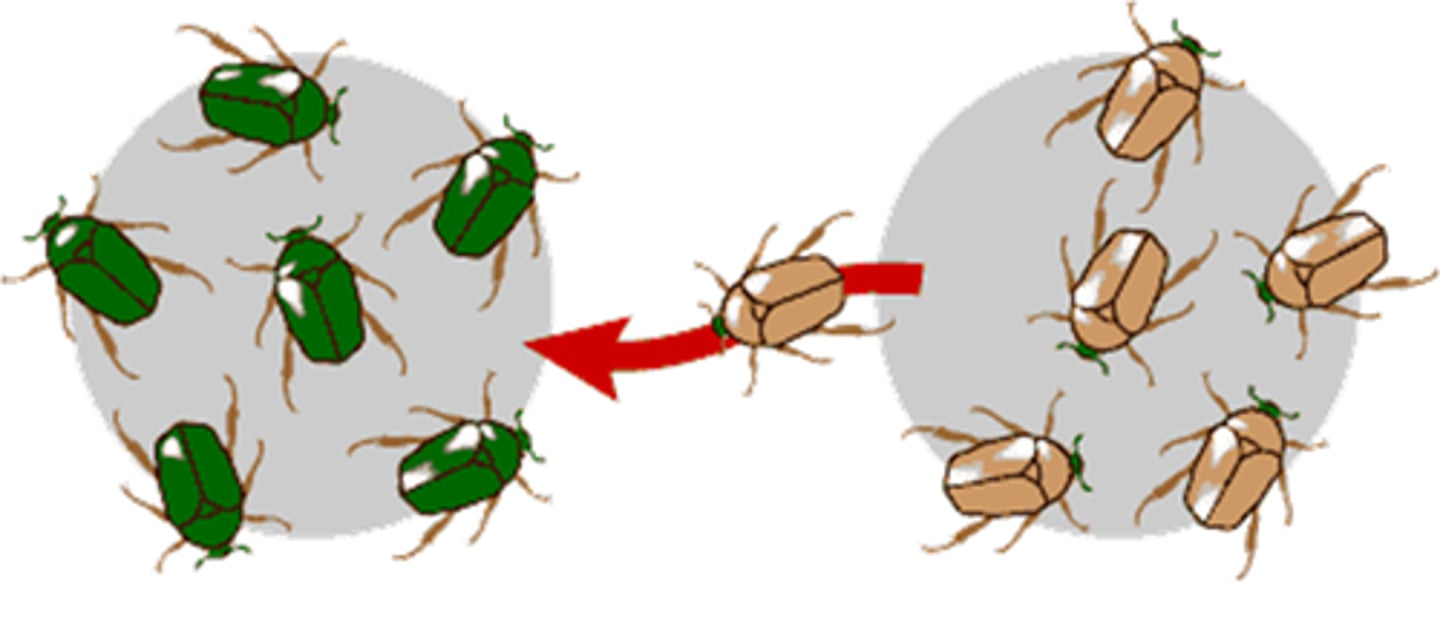
Gene Flow
is the transfer of alleles or genes from one population to another
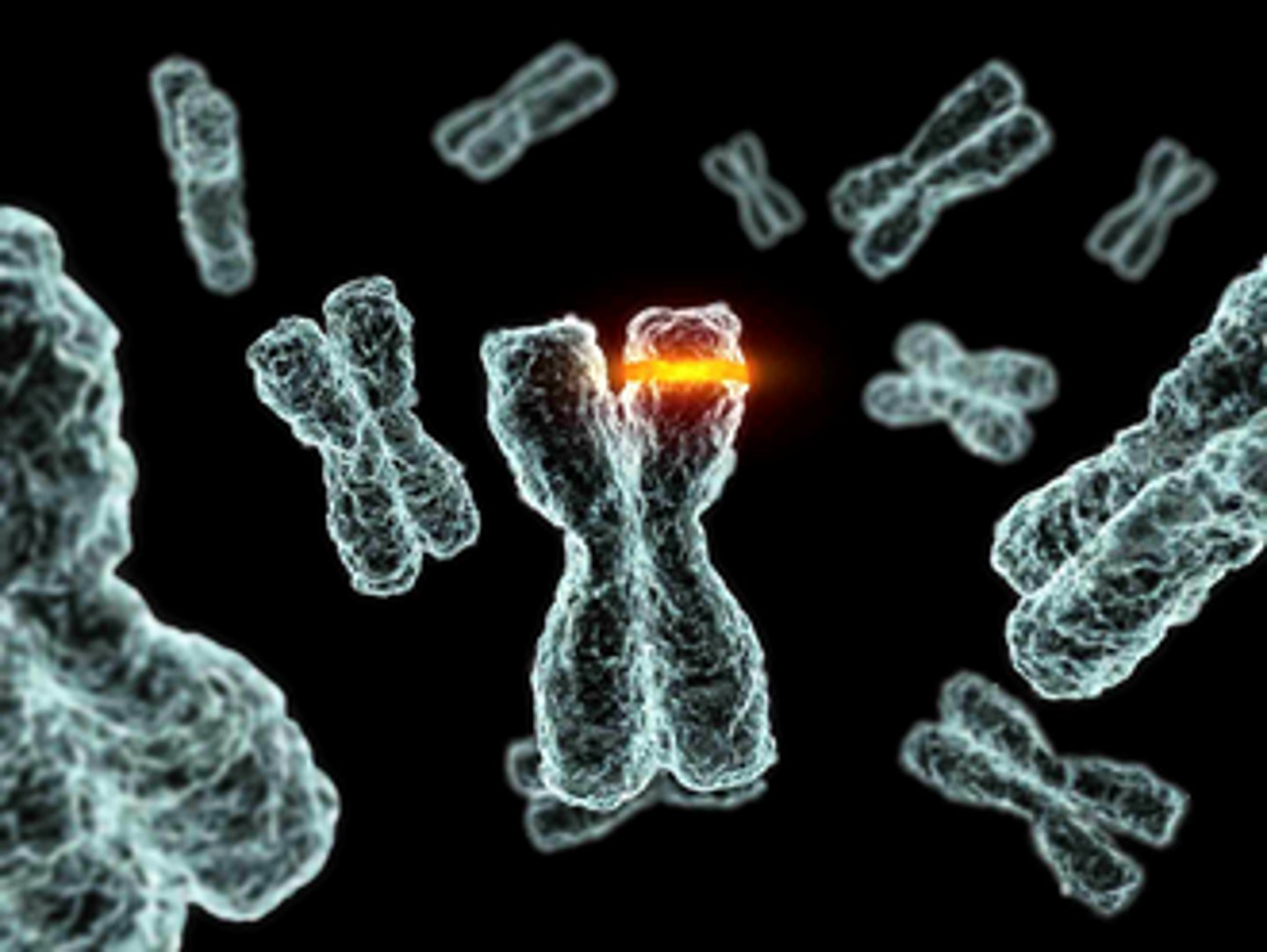
Mutations
Random changes in DNA create new alleles.
Non-random Mating
when individuals (or humans) select mates based on heritable traits (appearance/courtship dance/singing)

Binomial nomenclature
A system for giving each organism a two-word scientific name that consists of the genus name followed by the species name
Species
The most specific taxa level.

Kingdom
The most general taxa level
Taxonomy
The study of how organisms are classified based on physical characteristics
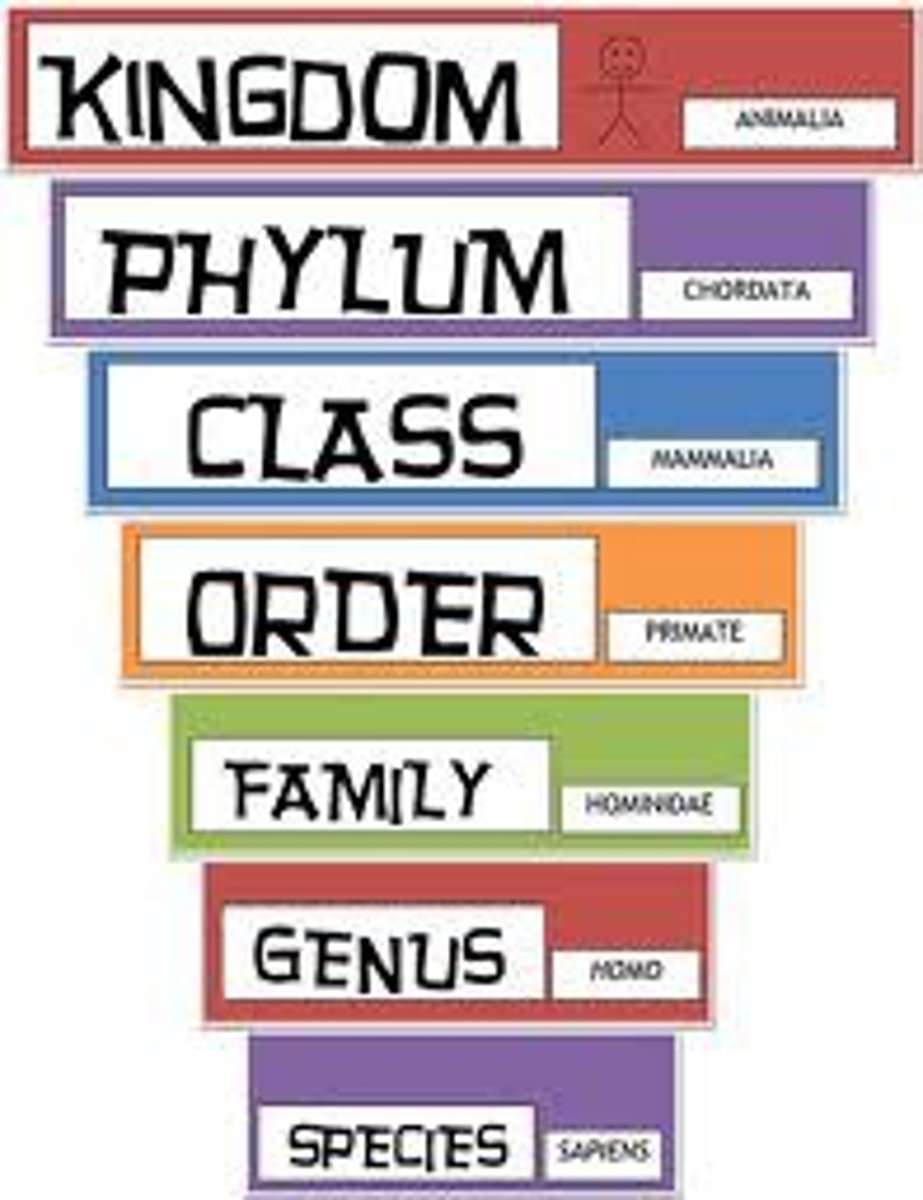
Taxa levels
Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
Scientific name
Genus + species ex: Homo sapiens
Cladogram
Grouping organisms based on evolutionary descent with shared characteristics.
Emphasizes CHANGE