Immunology Module 5: Structure and Function of Antibodies
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Mature into plasma cells and secrete antibody molecules that bind to the pathogen and neutralize it
B-cell membrane immunoglobulins (Ig) bind to epitope and causes it to
4 polypeptides —> 2 identical longer heavy chains and 2 identical shorter light chains
Immunoglobulin (antibody) molecules consists of
Disulfide bonds
The various immunoglobulin (antibody) molecule chains are bridged by
Variable domain heavy chains (VH) and variable domain light chains (VL)
N-terminal domains in each immunoglobulin (antibody) polypeptide chain have
VH and VL domains
Antigen binding site is formed by
Gamma fraction of serum contains immunoglobulins that bind to antigens
1939 Tinelius and Kabat Experiment demonstrated
1939 Tinelius and Kabat Experiment explained
Injected rabbits with ovalbumin antigen and collected the serum dividing it into tubes A & B
Added ovalbumin to test tube B causing it to precipitate
Removed the precipitate and subjected the serums from each tube to electrophoresis
Absorbency results were plotted against migration distance from the initial point of application
Comparison between the electrophoresis profiles of 2 aliquots showed decreased amounts of gamma-globulin fraction in the aliquot that reacted with antigen ovalbumin
Gel filtration and proteins are separated by molecular weight
Gamma globulins are characterized by
Appox. 150,000 daltons
Molecular weight of IgG
Meracaptoethanol, which reduces disulfide bonds
To determine if IgG was composed of polypeptide subunits it was subjected to
50 Kd heavy chains and 25 Kd light chains - to account for the naive molecular weight of IgG it was determined that there must be 2 of each peptide
2 protein peaks revealed by gel filtration after reduction and denaturation
The structure of immunoglobulins
Edelman and Porter experiments deciphered
Edelman and Porter experiments explained
Elucidated IgG strutures using enzyme (Papain) digestion to produce 2 identical 50 Kd fragments with antigen-binding activity and 1 50 Kd fraction without antigen binding activity
Fab
Meaning fragment antigen binding, were fragments with antigen binding activity
Fc
Meaning fragment crystallizable, were the elucidated single 50 Kd fragment that was observed to crystallize in cold storage
Pepsin, into a single 100 Kd fragment with 2 antigen binding sites (F(ab)2)
What enzyme digested the Fab fragment and what was it digested into
Pepsin, into multiple small fragments
What enzyme digested the Fab fragment and what was it digested into
Reacted with heavy and light chain antibodies indicating that the Ag binding site was composed of 1 heavy and 1 light chain
When antibodies were raised against heavy and light chains and tested against Fab and Fc fragments, Fab:
Reacted with the heavy chain antibodies only indicating antigen binding site was composed only of heavy chains
When antibodies were raised against heavy and light chains and tested against Fab and Fc fragments, Fc:
Amino acid sequencing
Critical to understanding the nature of the antigen binding site of immunoglobulins
Due to the heterogeneity of antibodies in serum (the antiserum) because amino acids have a variety of molecular masses and reflect antibody specificities to immunoglobulin array of different antigens
Why is amino acid sequencing difficult?
A pure single species of immunoglobulin molecules
What is needed to elucidate the antigen binding site of the antibody?
Patients with multiple myeloma
Who was the pure source of immunoglobulin is obtained from?
MM patients have a massive quantity of 1 type (type varies with individual patients) of immunoglobulin in their serum
Why were multiple myeloma patients used to obtain a pure source of immunoglobulins
Intact light chains (Bence-Jones protein) in their urine and by heating urine the light chain is precipitated resulting in the pure protein that could be sequence
MM patients excrete
Amino terminal portion of a sequence was variable & the carboxyl-terminal portion was conserved in a sequence
Light chain AA sequencing revealed that
2 types: kappa and lambda
Conserved sequences present in carboxyl-terminus of light chain
Variable domain (VL)
Amino terminal half of light chain
Constant domain (CL)
Carboxyl terminal half of light chain
Variability of AA sequences in positions 1-117 & the rest of the sequence was constant
Heavy chain sequence analysis of Ig from MM patients showed
Mu, Delta, Gamma, Epsilon, Alpha
5 types of heavy chain sequencing patterns (isotypes that determine antibody class
IgM, IgD, IgD, IgE, IgA
Isotype antibodies of Mu, Delta, Gamma, Epsilon, Alpha
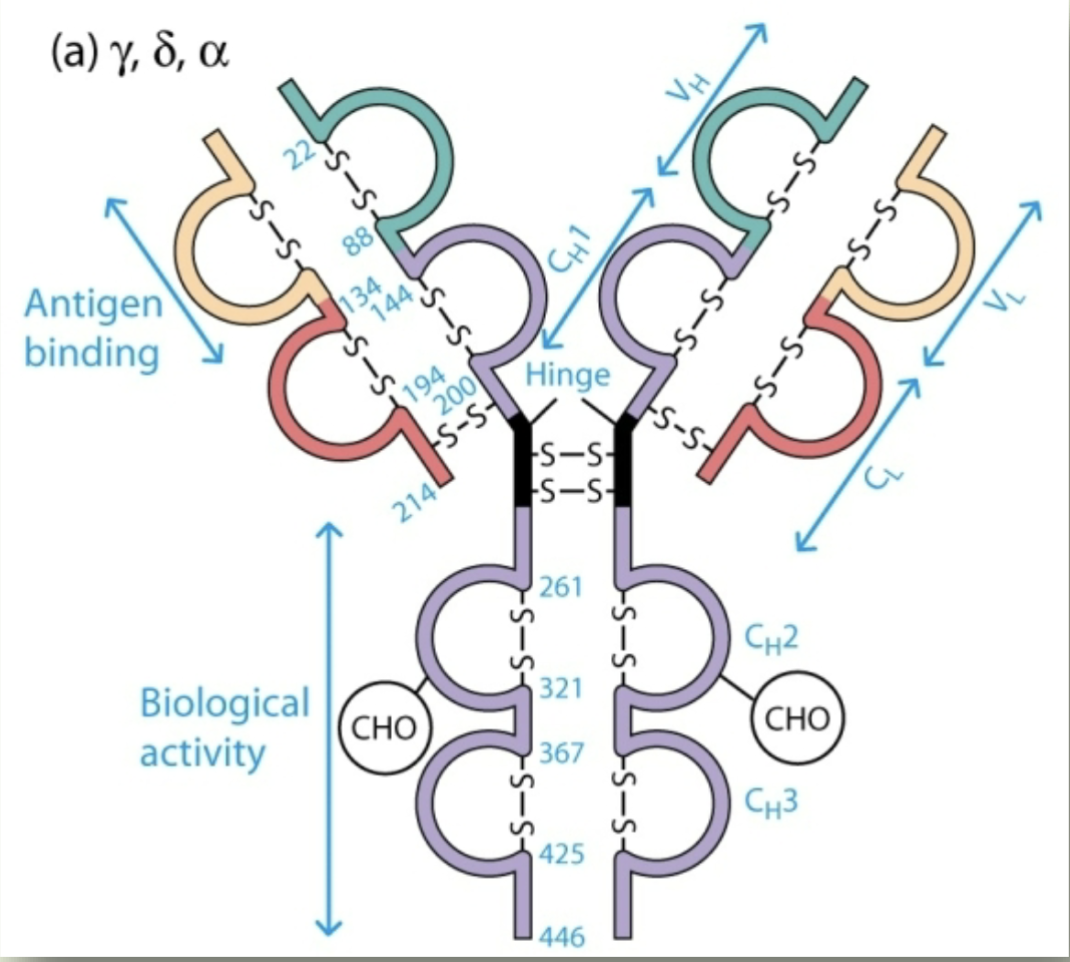
IgG, IgA, IgD
Isotypes that have hinge region between CH1 and CH2 domains - 330 AAs in constant region
Proline, cysteine
Hinge region is rich in ______, ______ which allows the antigen binding site to be flexible
2 Fab arms (connected by disulfide bonds) to bind at various different angles
Hinge’s flexibility allows
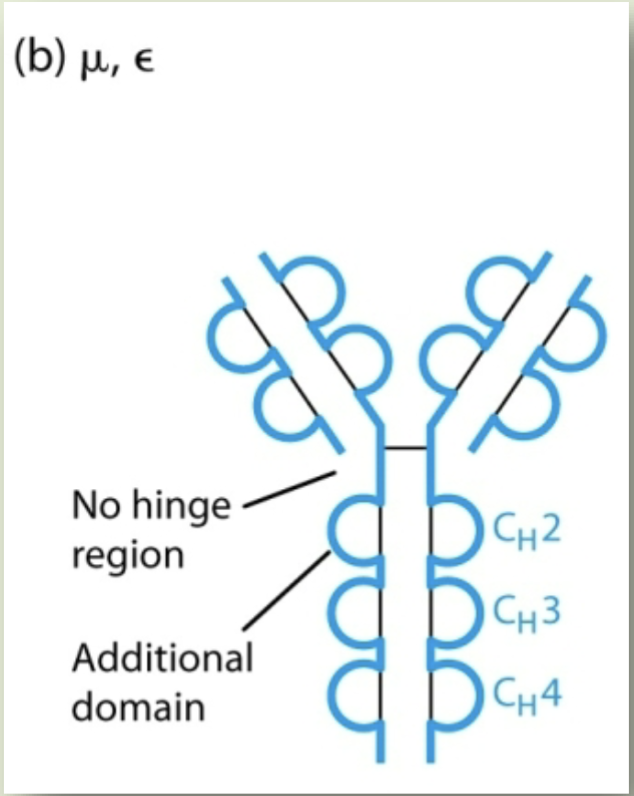
IgM, IgE
Isotypes that do not have hinge region - 440 AAs in the constant region
Subclass IgA1, subclass IgA2
IgA is further classified into 2 sub-isotypes due to minor variations in alpha regions
Subclass IgG1, subclass IgG2, subclass IgG3, subclass IgG4
IgG is further classified into 4 sub-isotypes due to minor variations in gamma regions
Papain and pepsin cleavages
Hinge region exist between
Domains
Distinct functional and structural units in an immunoglobulin; Conserved molecular structure within a protein that confer a unique motif
IgG domain
In immunoglobulin molecules light and heavy chains contain a homologous unit of 110 AA with an internal disulfide bond
1 variable domain (VL) & 1 constant domain (CL)
How man variable domain(s) and constant domain(s) does a light chain have?
1 variable domain (VH) and 3-4 constant domains (CH)
How man variable domain(s) and constant domain(s) does a heavy chain have?
Ig superfamily
Many immune system proteins contain Ig domains which classifies them as part of the
Complementary determining regions (CDR) aka hypervariable regions
Variable regions that contain most of the sequence differences in antibodies that is confined to 3 short regions of the heavy & light chains
All 3 CDRs
Which complementary determining regions are involved in epitope binding (exemplified by Vitamin K)
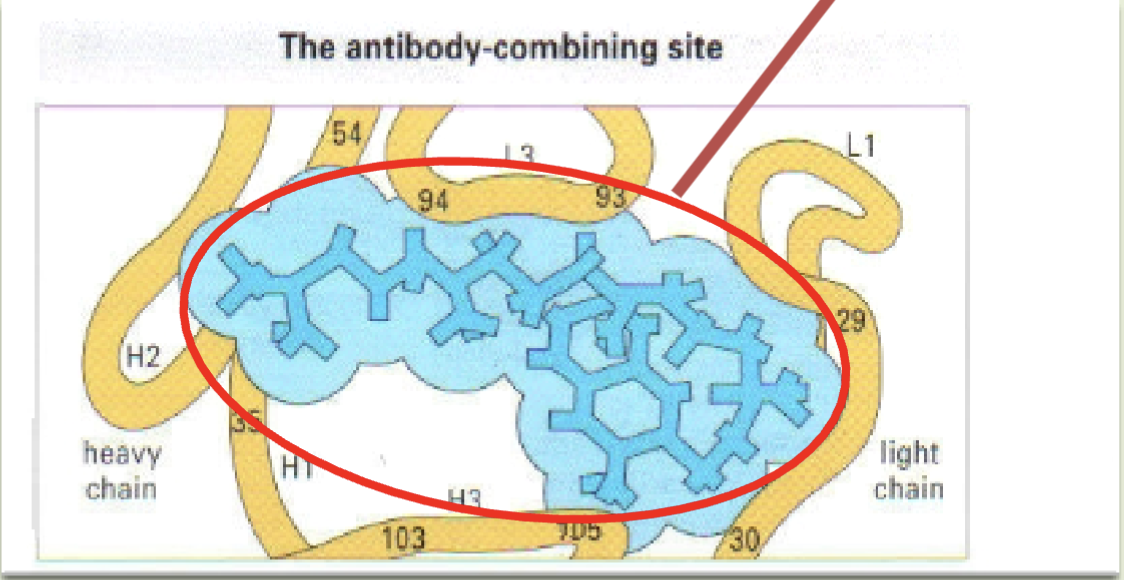
Paratope
Binding site present in the antibody
Opsonization, triggers mast cell degranulation, activates B-lymphocytes, complement activation, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytoxicity (ADCC), or transcytosis
Once antibody binds to antigen, the Fc region undergoes conformational changes causing different effector functions including
Opsonization
The process by which particulate antigens are rendered susceptible to phagocytosis & leads to enhanced phagocytosis
Complement system
Collection of serum glycoproteins in a cascade mechanism that destroy pathogens & remove antigen when activated
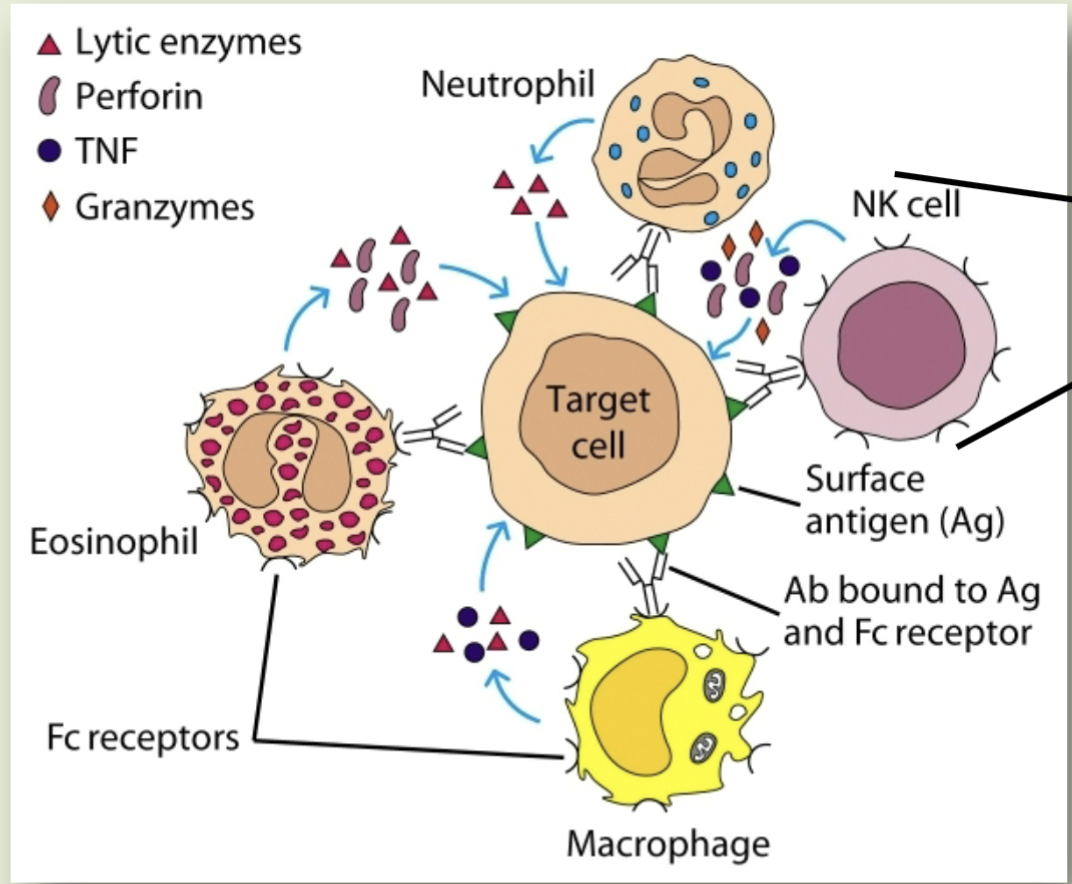
Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
A cell-mediated reaction in which non-specific cytotoxic cells (like neutrophils, natural killer cells, eosinophils, & macrophages recognize bound antibodies on a target cell and destroy the target cell
Dumping toxic substances (like lytic enzymes, preforin, granzyme, and TNF) into the cell
ADCC - once Fc receptor binds to Fc portion of the target-bound antibody the cell kills that target cell by ____ which occurs because of the engagement of the Fc region on the antibody that is bound to the target and Fc receptor of the cells
Transicytosis
Transfer of immunoglobulins across an epithelial layer
Passive immunization
Transfer of IgG from mother to fetus (fetus acquires a repertoire of pre-formed antibodies from the mother that protects the fetus from pathogens)
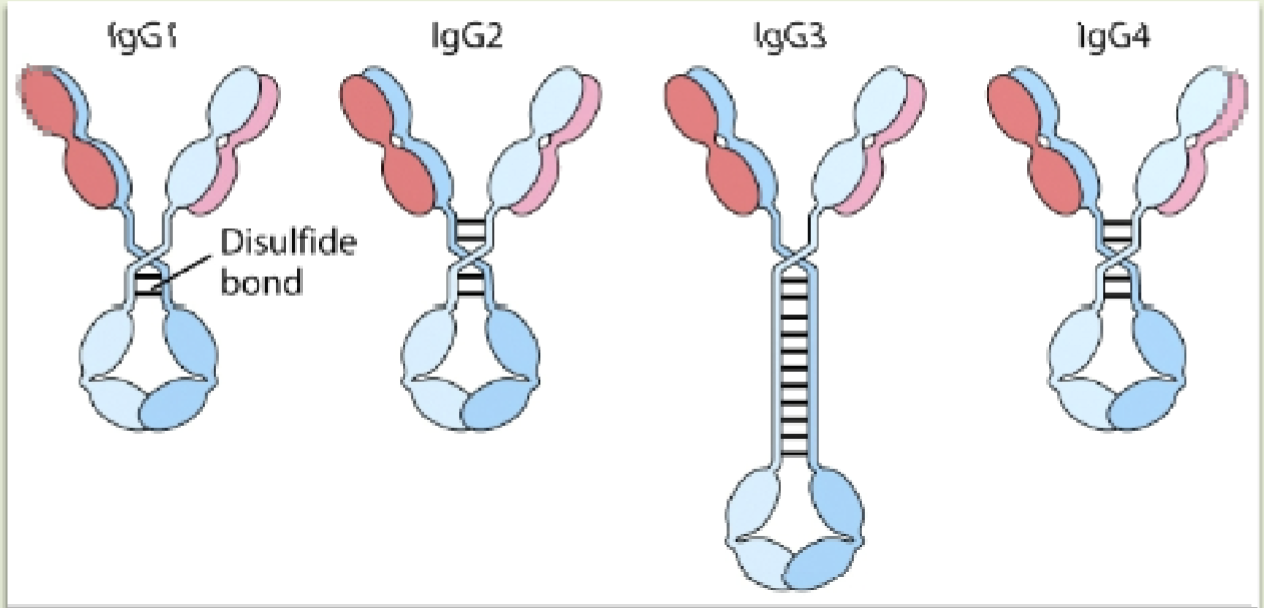
IgG
Most abundant class of Ig that makes up approx. 80% of the total immunoglobulins
Size of the hinge region and the number and position of the interchain disulfide bonds between the heavy chains
4 sub-types of IgG are distinguished from each other based on
IgG1, IgG3, IgG3
Subtypes of IgG that cross the placenta and protect the developing fetus
IgG3
IgG that is a potent complement activator and binds with high affinity to Fc recptor
IgG2
IgG that binds with low affinity to Fc receptor & a less efficient as a potent complement activator
IgG1
IgG that is less efficient as a potent complement activator & binds with high affinity to Fc
IgG4
IgG that binds with intermediate affinity to Fc receptor but not to a complement activator
IgM
The 1st Ig synthesized during the primary immune response and the 1st Ig to be synthesized in newborns (allows newborns to mount a primary immune response when exposed to antigens for the 1st time)
IgM
Ig that is very efficient in binding complex antigens like virus particles (bc it has 10 binding sites) and in activating complement
Monomeric IgM
Membrane bound form of IgM that acts as receptors on B-cells
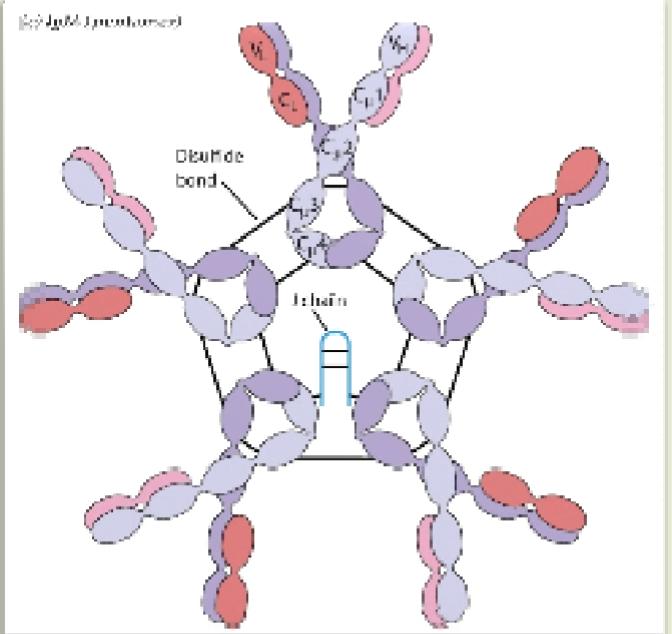
Pentameric IgM
Secreted form of IgM that has disulfide bonds liking CH3 and CH4 domains of adjacent molecules & has a J-peptide that helps to stabilize it
J-chain
What helps to stabilize the IgM pentameter and allows IgM to be transported across the epithelium
IgA
Ig that is the predominant immunoglobulin in external secretions (like breast milk, saliva, tears, mucus, etc.)
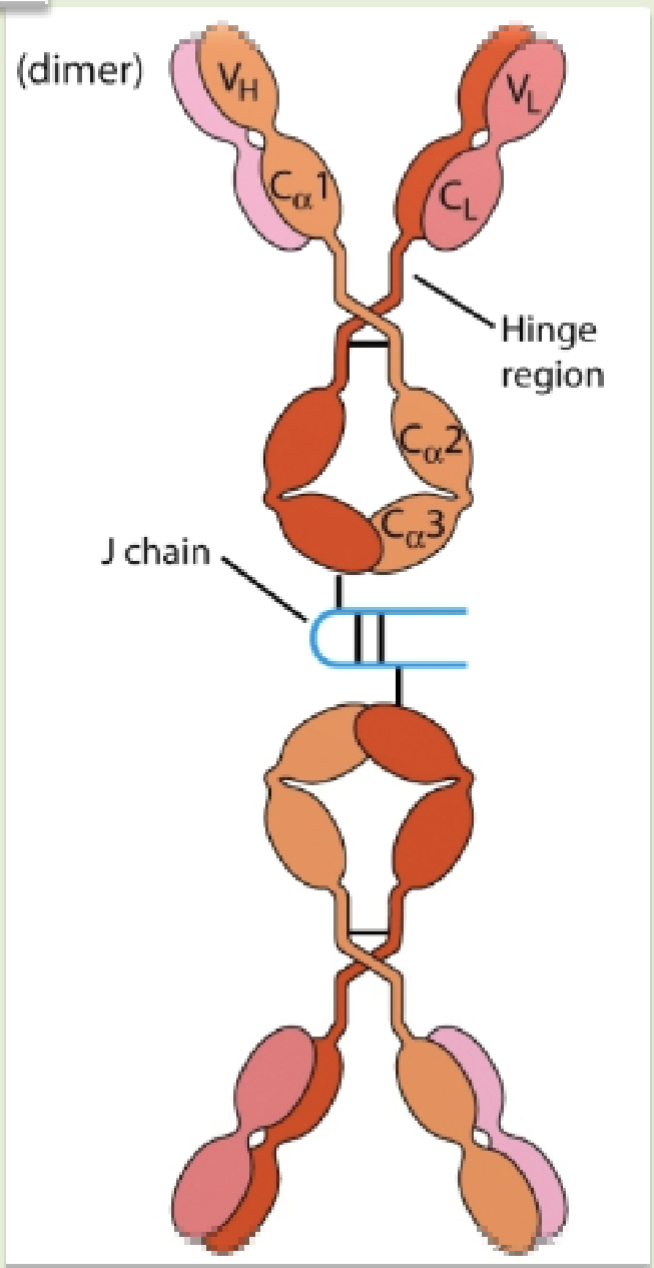
Secretory IgA
Consists of dimers or tetramers together with a J -chain and a secretory component
Secretory IgA and pentameric IgM
What Igs have J-chains
Seceratory component
Peptide chain that functions to protect the IgA from proteases (protease digestion) present in mucosal surface
Secretory component
Fc region of dimeric IgA binds to poly-Ig receptor on the basolateral side of epithelial cells & the bound dimeric IgA with poly-Ig receptor is transported to luminal surface of epithelial cells where poly-Ig is cleaved to form
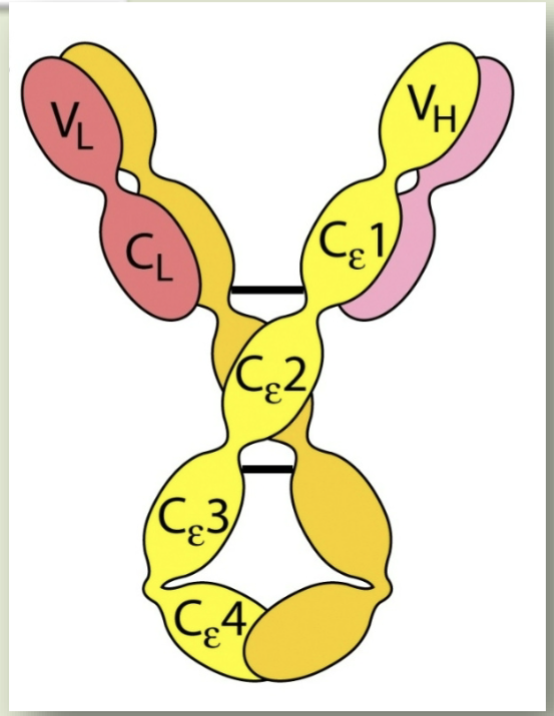
IgE
Ig responsible for immediate hypersensitivity reactions (like hay fever, asthma, hives, anaphylactic shock)
Degranulation
IgE binds to Fc receptors on basophils and mast cells, and this interaction induces
Granules
What have pharmacologically active mediators that are responsible for allergy symptoms
P-K reaction (Prausnitz-Kustner)
Immunologic tests formally used to determine if a patient has an allergic reaction, has been replaced with skin allergy/skin prick test (SPT)
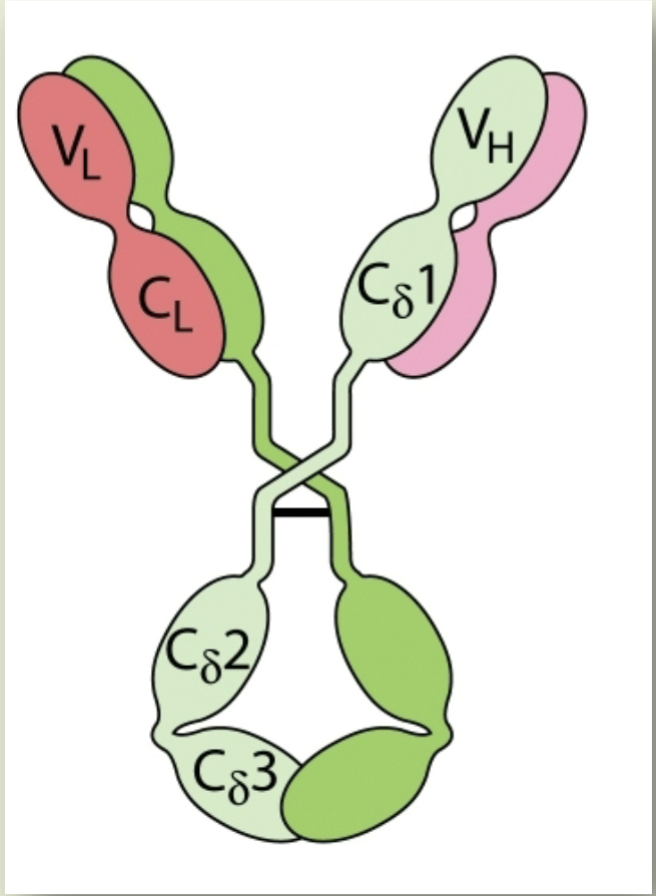
IgD
Ig that is a major membrane-bound Ig expressed in mature B-cells, but doesn’t otherwise have a biological function that has been identified
IgG3, IgM, IgG1
Ig that activates the classical complement pathway
IgM, IgD
Igs present on the membranes of mature B-cells
IgG1, IgG3, IgG4
Igs that bind Fc receptors of phagocytes
IgA1, IgA2, IgM
Igs involved in mucosal transport
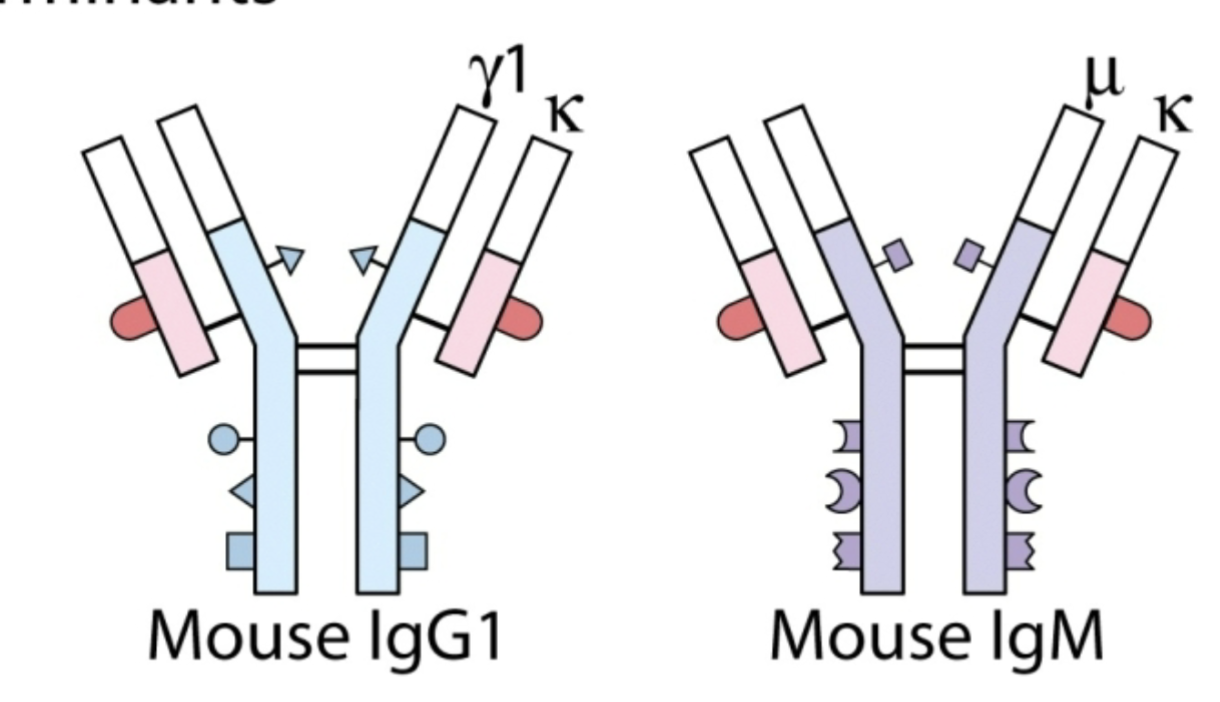
Isotype
Constant region determinants that define each heavy chain class and sub-class & each light chain type & sub-type
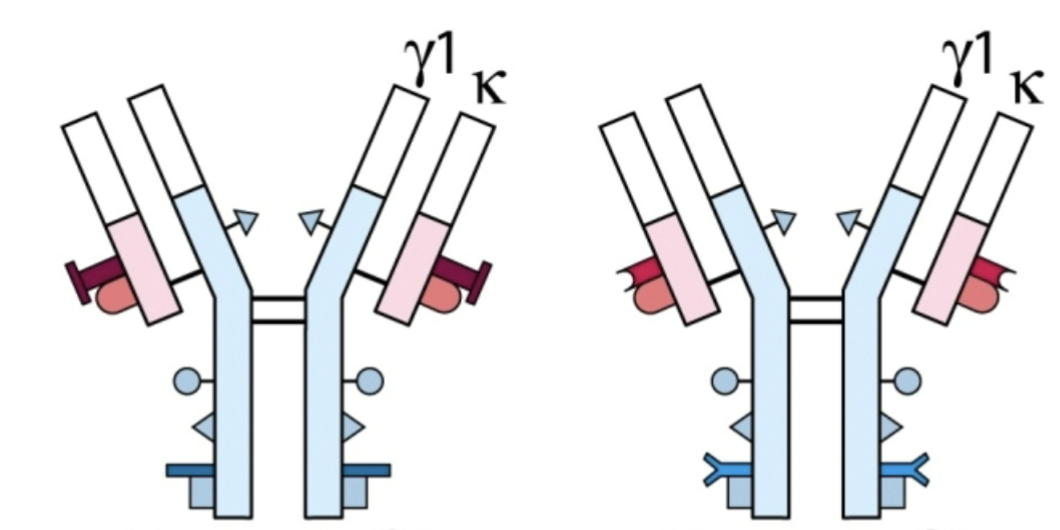
Allotypic determinants
Minor variations in amino acid difference in conserved portion of Ig molecules
Allotype
Allotypic determinants expressed by the Ig
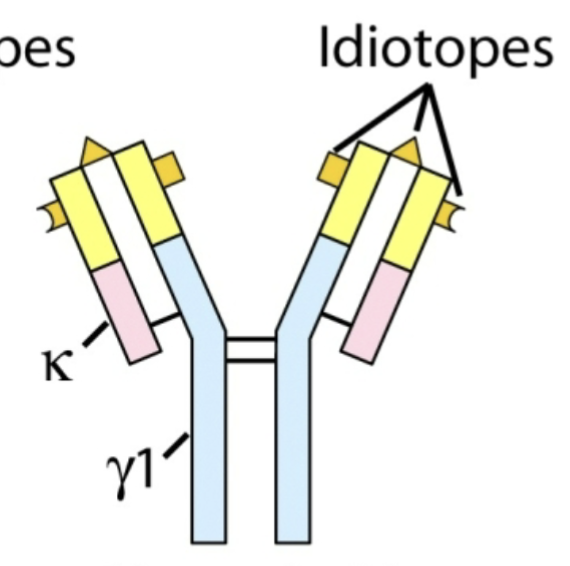
Idiotope
An antigenic determinant of the variable region
Idiotype
Antibody molecules that share an idiotope belong to the same
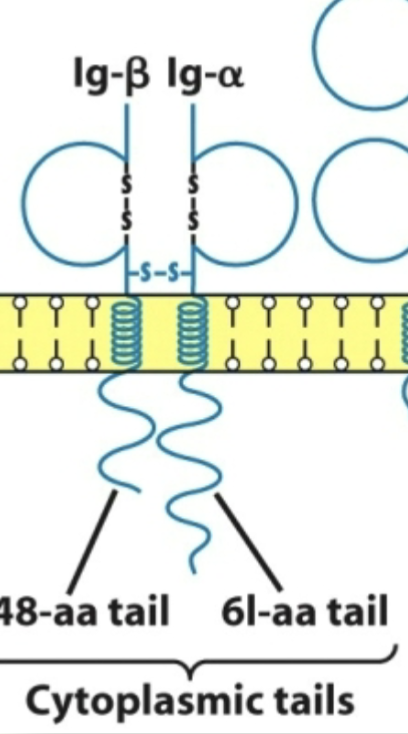
B-cell receptor
Comprises a membrane bound Ig molecule and its 2 associated signal-transducing molecules (Ig alpha-beta heterodimer)