LAB 8-Photosynthesis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is photosynthesis
the process of converting light energy into chemical energy
what used photosynthesis
plants, algae, some bacteria
what are the four essential components of photosynthesis
-sunlight
-carbon dioxide
-water
-chlorophyll
where is the chlorophyll located
in the chloroplast
what does the chloroplast contain
-inner membrane
-outermembrane
-grana: stacks of thylakoids from a third membrane layer
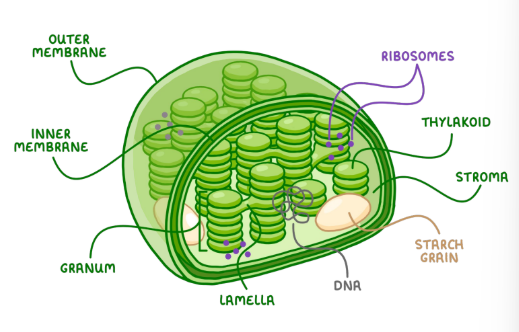
what is in the thylakoid membrane
-pigments (molecules that absorb light) responsible for the initial reaction between light and plant material
-numerous proteins that make up the electron transport chain
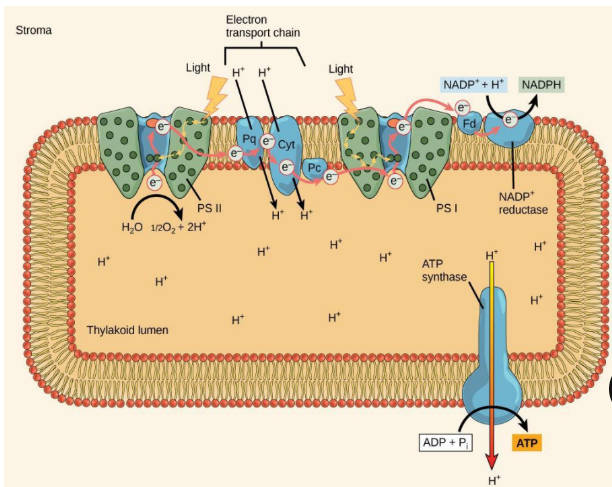
where does photosystem I and photosytem II get their energy from
light
where do the ETC electrons come from
they come from the water molecules (H2O) and are given to NADPH
what are the H+ from water used for
used to drive ATP synthase
Photosystem II
-energy from sunlight is used too extract electrons from water
-the electrons travel through the ETC to PSI which reduces NADP+ to NADPH
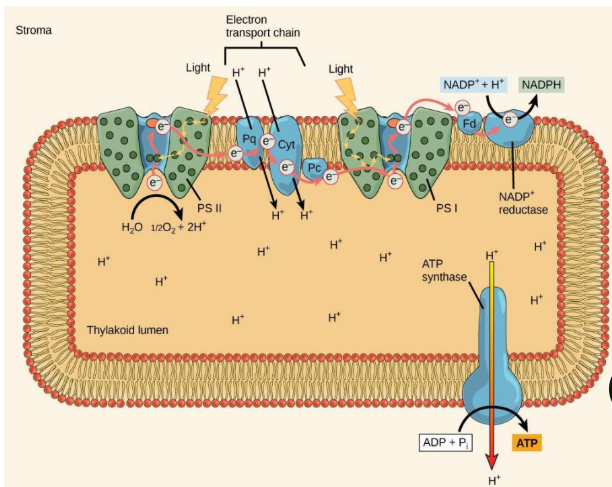
ETC
-moves protons across the thylakoid membrane into the lumen
- Splitting of water adds protons to the lumen and reduction of NADPH removes protons from the stroma
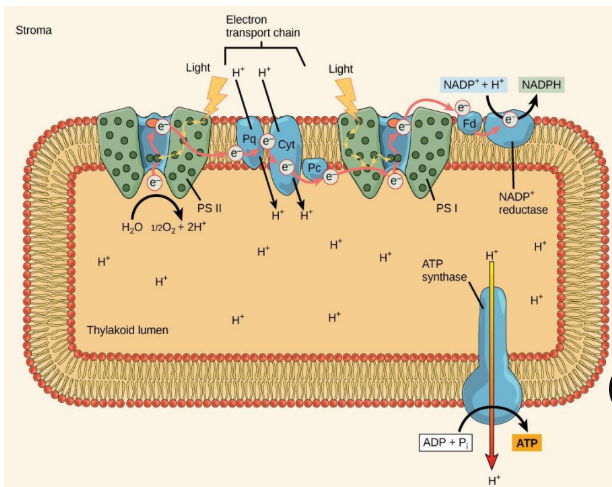
ATP synthase
-uses this electrochemical gradient to make ATP
plant pigments
-organic pigments found in the thylakoid membrane
- Light energy initiates the process of photosynthesis when pigments absorb specific wavelengths of visible light
blue wavelength
enhances production of chlorophyll
green
-least efficient
-plants relfect green light
red
yields more leaves when mixed with blue
chlamydomonas (chlamy)
-genus of green algae
-use flagella to “swim”
-they require ATP for movement
-use photosynthesis to get ATP
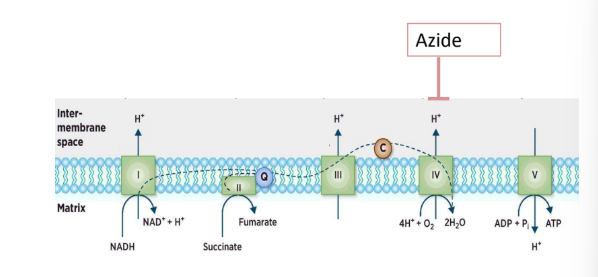
metabolic poisons
-sodium azide
-DCMU
sodium azide
-inhibits the ETC of the mitochondrion and therefore, respiration
-Chlamydomonas will not be able to make ATP through cellular respiration
-In light, it can still survive for a while because photosynthesis can produce ATP and NADPH in the chloroplast.
-In the dark, sodium azide is lethal because the cell relies entirely on mitochondrial respiration for ATP when no photosynthesis occurs.
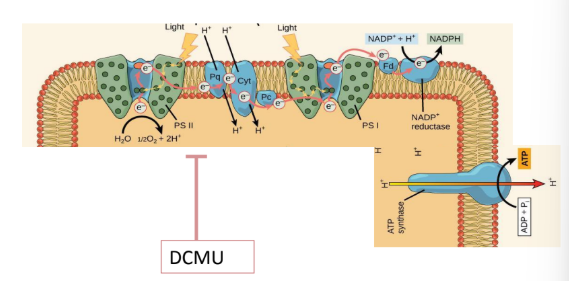
DCMU
-specifically inhibits the flow of electrons from PSII, thereby disrupting photosynthesis in the chloroplast
-Result:
No ATP or NADPH from photosynthesis.
No oxygen evolution.
The cell can still respire in mitochondria, so it can survive in the dark or in light using respiration, but overall growth slows since carbon fixation is impaired.