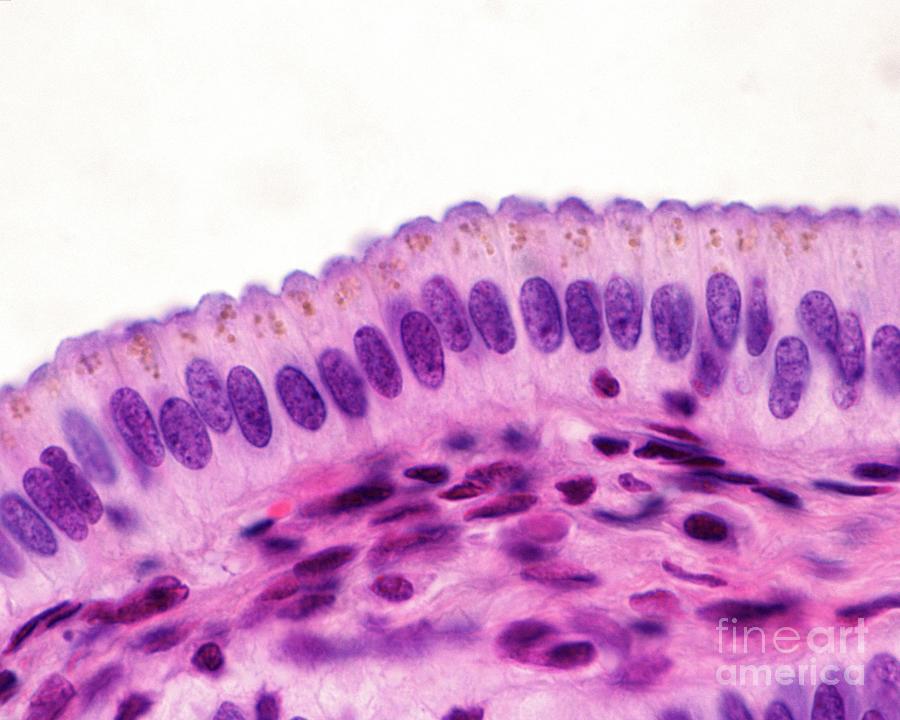
Epithelium
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Histology
The study of tissues.
Simple epithelium
Simple squamous 2. Simple cuboidal 3. Simple columnar 4. Pseudostratified columnar
Stratified epithelium
Stratified squamous 2. Stratified cuboidal 3. Stratified columnar 4. Transitional
Glands
Exocrine 2. Endocrine
Epithelium
Tissue that covers outer body surface OR lines a body cavity. (Often forms glands.)
Characteristics of epithelia
Cellularity, composed almost entirely of cells. 2. Cell junctions. 3. Polarity (the two sides are different.) Ex: Goblet cell-secrets mucus 4. Basement membrane (anchors epithelium to the underlying connective tissue.) 5. Ability to regenerate quickly
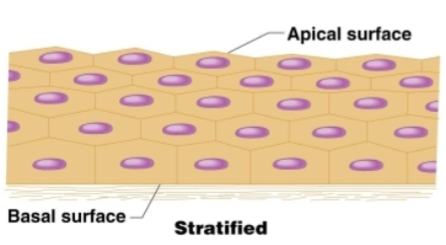
Apical
Toward space
Basal
Toward attachment
Avascular
Not associated with blood vessels
Innervated
Associated with nerve cell processes
Absorption
Active uptake of molecules (Active: USES CELL ENERGY)
Secretion
Active release of molecules (Active: USES CELL ENERGY)
Microvilli
Extensions to increase surface area
Diffusion
Molecules move down concentration gradient (Passive: NO ENERGY USED)
Filtration
Plasma (fluid component blood) leaks across capillary walls (Passive: NO ENERGY USED.)
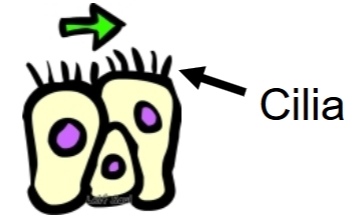
Propulsion
Cillia drive fluid along surface of epithelium
Sliding
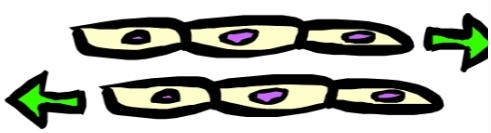
Protection

Sensory reception
Epithelial cell generates sensory signal
Classification: Simple
Each cell is attached to basement membrane
Classification: Stratified
Multiple layers; only the basal layer directly attached to basement membrane
Simple
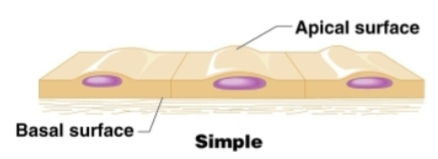
Stratified
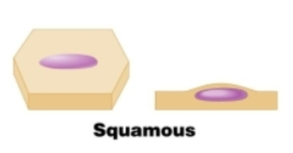
Squamous
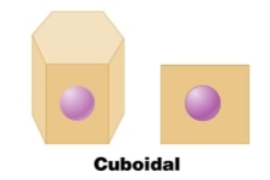
Cuboidal
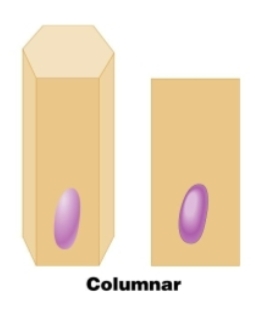
Columnar
Simple squamous
(Thinnest kind) No surface projections
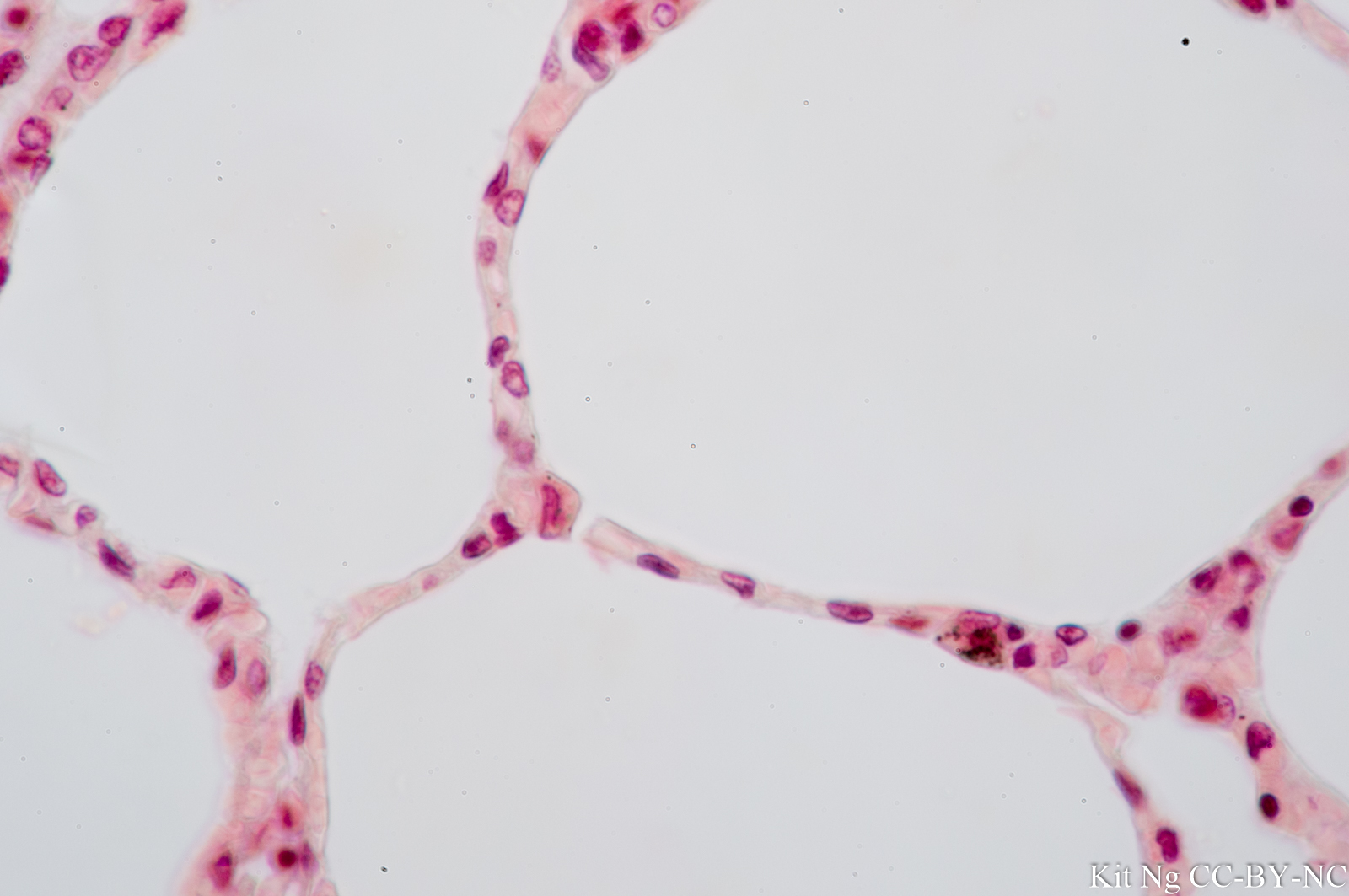
Alveoli
Lining of air sacs in lungs
Mesothelium
Lining of closed body cavities
Endothelium
Inner lining of heart & blood vessels
Glomerular
Capsule in kidney where filtration occurs.
Simple cuboidal
Glands (most), kidney tubules
Simple columnar