anatomy exam 3
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Arteries are defined as vessels that carry oxygenated blood
False
The____ is the sympathetic nerve responsible for increasing heart rate in response to situations like low blood pressure
Cardiac accelerator nerve
Starling’s law states that if tension increases so does the force of
Contraction
For blood to be pumped properly into arteries, the atria and ventricles must contract at different times from each other
True
Valves in the heart that have Cordae tendinae attached to them are called
Atrioventricular valves
The point of exchange of the circulatory system are tubes called
Capillaries
The heart is the first organ that is faded off of the aorta
True
Capers are only made above one layer of tissue
True
The thickest layer of the vein that is made of primarily of connective tissue is the
Tunica externa
Arteriosclerosis can be caused by many things, parent, including building up a plaque in the arteries) but is primarily a problem because of the loss of____ of the atrieal walls
elasticity
The term for blood pressure at the time that the ventricles are not contracting is called
Diastolic
The main portion of the circulatory system that is responsible for keeping blood flow to the capillaries constant even between heartbeat is the
Arteries
Most of your blood is located in what part of your circulatory system
Blood reservoir in the veins and venules
Arteries are highly elastic and poorly distensible(stretch)
true
Of the two blood pressure measurements taken the blank___ pressure is the most important in terms of the cardiovascular health
Diastolic
Both lymph vessels and blood vessels keep fluid from backflow by using___structures
valves
List one factor that can increase the per peripheral resistance (friction of blood on artery wall) of blood
Less Water
Cardiac muscle cells can accomplish spontaneous depolarization due to their inherent leaks to
Sodium
___ percent of cardiac fibers are self excitable fibers
1%
The volume of air that is brought in with an average breath is about 500 mL and is scientifically called the ____ volume
Tidal
The total air capacity of the average human lung is____ml
6000
Expiration of air from the lungs is normally an active phenomenon
False
The main way that air is brought into the lungs is by changing the_____ of a pulmonary cavity, which will change the pressure
Volume
____ is secreted by alveolar cell in order to decrease the surface tension and keep Alveoli from collapsing
Surfactant
The mass action principle states that any change of concentration on one side of an equation at equilibrium result in a change in the other side
True
____ is air that remains in the airway but it’s not used in respiratory exchange. It is particularly because of this year that we exhale. They are still rich in oxygen.
Dead space
most skeletal muscles are a mix of fast and slow twitch fibers
True
weak acids and bases have good/poor buffering ability in the body
good
___ is a protein which is red and color in store is oxygen in the muscles
myoglobin
one of the factors that contribute to muscle fatigue would be
build up of lactic acid
Compare the action potential of skeletal muscle cell with the action potential that occurs in a cardiac contractile muscle fiber. Explain the difference between them and why this is so important in cardiac tissue.
Skeletal muscle;
Normal depolarization
Action potential occurred before the contraction
Relative refractory period occurs before contraction to maintain longer contraction if needed
1 ms for the action potential and 5 ms for the contraction time
Cardiac:
Maintain depolarization to avoid tetanus
Prolonged contraction and relaxation
Contraction occur occurs before refractory. Period
300 ms to complete absolute refractory, action, potential, and for contraction
Describing detail the process of how capital is exchange nutrients and waste tissue cells do not focus on the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide specifically but the exchange of nutrients and waste in general they should include term such as hydrostatic, pressure, filtration, and osmosis. Be sure to adequately describe why each process works and where it works for full credit and include relative fluid pressure across the different spaces. You may use a diagram as well if you would like, but diagrams must have descriptions include.
At the arterial end of the capillary, hydrostatic pressure is higher than osmotic pressure, pushing fluid and nutrients out of the blood into the tissue (filtration).
At the venous end, osmotic pressure (mainly from plasma proteins) becomes greater than hydrostatic pressure, pulling water and wastes back into the capillary (osmosis).
This balance of pressures allows nutrients to leave the blood and wastes to return efficiently.
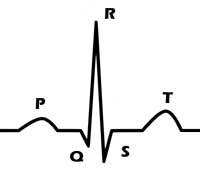
Name an identify what is happening during each wave of the EKG in the heart and what it is called on the graph
P wave: atrial depolarization
QRS: Ventricular depolarization
T: Ventricular repolarization
The 2 main ways that the body can overcome gravitational forces to return blood to the heart through the veins are due to which 2 pumps? Briefly explain how these pumps work, especially in relation to the special structure of veins. Finally explain how varicose veins occur and list at least one thing a person can do to help prevent varicose veins.
Skeletal muscle pump: Muscles squeeze veins when they contract, pushing blood upward. Vein valves stop blood from flowing backward.
Respiratory pump: Breathing changes pressure in the chest and abdomen, helping push blood toward the heart.
Varicose veins: Happen when vein valves weaken and blood pools.
Prevention: Exercise, avoid long standing/sitting, and elevate legs.
Describe the process of the conduction of electrical signals across the heart, including where the impulses should begin and where they will finish. Also describe what happens if each of these sections is damage. Lastly, explain how the normal heart rate is obtained, even though none of the sections have this right.
SA Node (Pacemaker): 90-100 per min Atria Contract
AV Node 40- 60 per min Atria
AV Balance of his
Land R Bundle Branches
Purkinje Fibers 20-40 per min
If part of the conduction system is damaged, the heartbeat can become slower and go to the next option
Compare fast, twitch and slow twitch muscle fibers include the type of respiration that they primarily use to make ATP and also for structural and or functional differences that distinguish them
Slow twitch:
aerobic respiratioon
slow contractions
more myoglobin
many mitochondria
less glycogen
Fast Twitch:
anaerobic respiration
fast contractions
a few mitochondria
less myoglobin (used at moment)
more glycogen
Describe two main factors that can change the dissociation curve of oxygen in the body. Next explain how these factors explain the difference between oxygen dissociation and a person who is exercising versus one who is at rest. It may help to draw a dissociation curve for your explanation.
Two main factors are PH and temperature
Two main factors that change the oxygen dissociation curve are pH and temperature.
pH: Low pH (more acidic) makes hemoglobin release oxygen more easily to tissues but hold less overall. High pH makes hemoglobin hold oxygen tightly and release less to tissues.
Temperature: High temperature makes hemoglobin release more oxygen to tissues, while low temperature makes it hold oxygen more tightly.
During exercise, lactic acid lowers pH and muscles are warmer, so hemoglobin releases more oxygen to active tissues. At rest, pH and temperature are normal, so oxygen delivery is steady.