Hazard management- disaster/risk management cycle and the park impact/response model
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
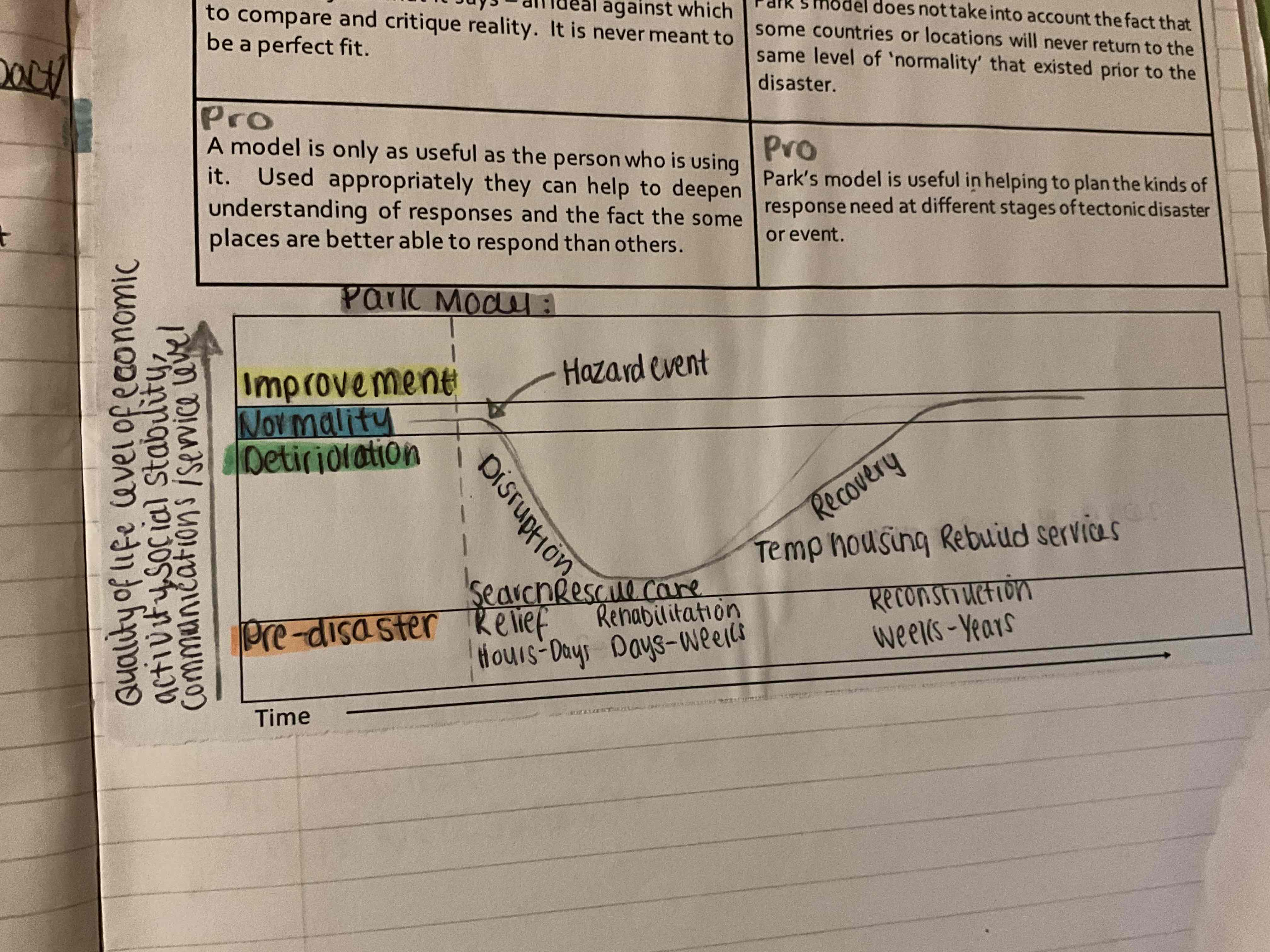
What is the park model?
describes a sequence of phases (3) following such event→ also known as the disaster response curve
Pros- usefulness of analysing human responses to hazards
it is a useful tool to analyse the different types of response and the sequence in which they happen
A model is only as useful as the person who is using it. Used appropriately they can deepen understanding of responses and the fact that some places are better able to respond than others
It is useful for pinpointing the different kinds of response needed at particular points in time
Parks model is useful in helping to plan the minds of response needed at different stages of tectonic disaster or event
Cons-usefulness of analysing human responses to hazards
the model takes no account in the varying capacity to respond and the fact that some places will take much longer to reach different stages of relief ,rehabilitation and reconstruction
Parks model is far to general and not specific enough about the different impacts of hazards of different magnitude and frequency and how these can influence the ability to respond
A model is just what it says- an ideal against which to compare and critique reality. It is never ment to be a perfect fit
The model takes no account of inequalities in development- it assumes that a level playing field between countries
The model does not critically examine the fact that some countries are in need of more help from outside than others
Parks model does not take into account the fact that some countries or locations will never return to the same level of ‘normality’ that existed prior to the disaster
What does the park model look like?
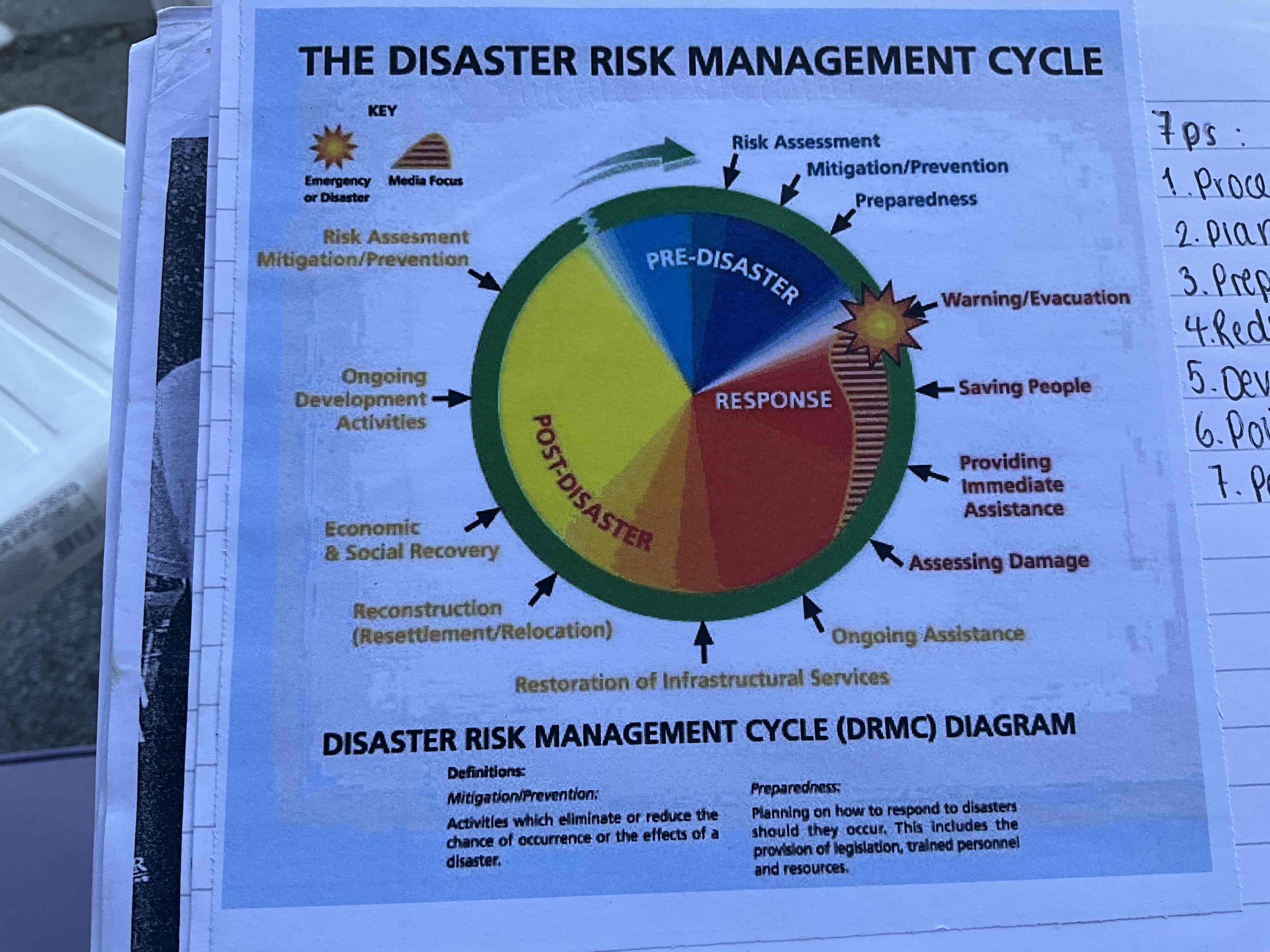
What is the disaster risk management cycle?
The Disaster management cycle illustrates the on-going process by which governments, businesses, and civil society plan for and reduce the impact of disasters, react during and immediately following a disaster, and take steps to recover after a disaster has occurred
Is a continuous loop which explains an approach to managing a known hazard
Preparedness- concerned with using evidence and data from previous events to plan for hazards associated with the event. Good preparation is the key to minimising impact apon the population
Response- concerned with deploying services and resources to save people and property from harm. Response is likely to involve emergency services e.g. fire and rescuer teams in an earthquake
Recovery- concerned with post disaster reconstruction and restoration of the local built and natural environment
Mitigation is an extension to recovery. This is the active steps taken to minimise the negative impacts associated with the hazard. Construcing earthquake proof buildings or flood protection systems are examples of mitigation
What are the 7ps in the disaster risk management cycle?
process
Plan
Preparedness
Reduce poverty
Develop policies
Politics
People first