Coronary angiography & angioplasty
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
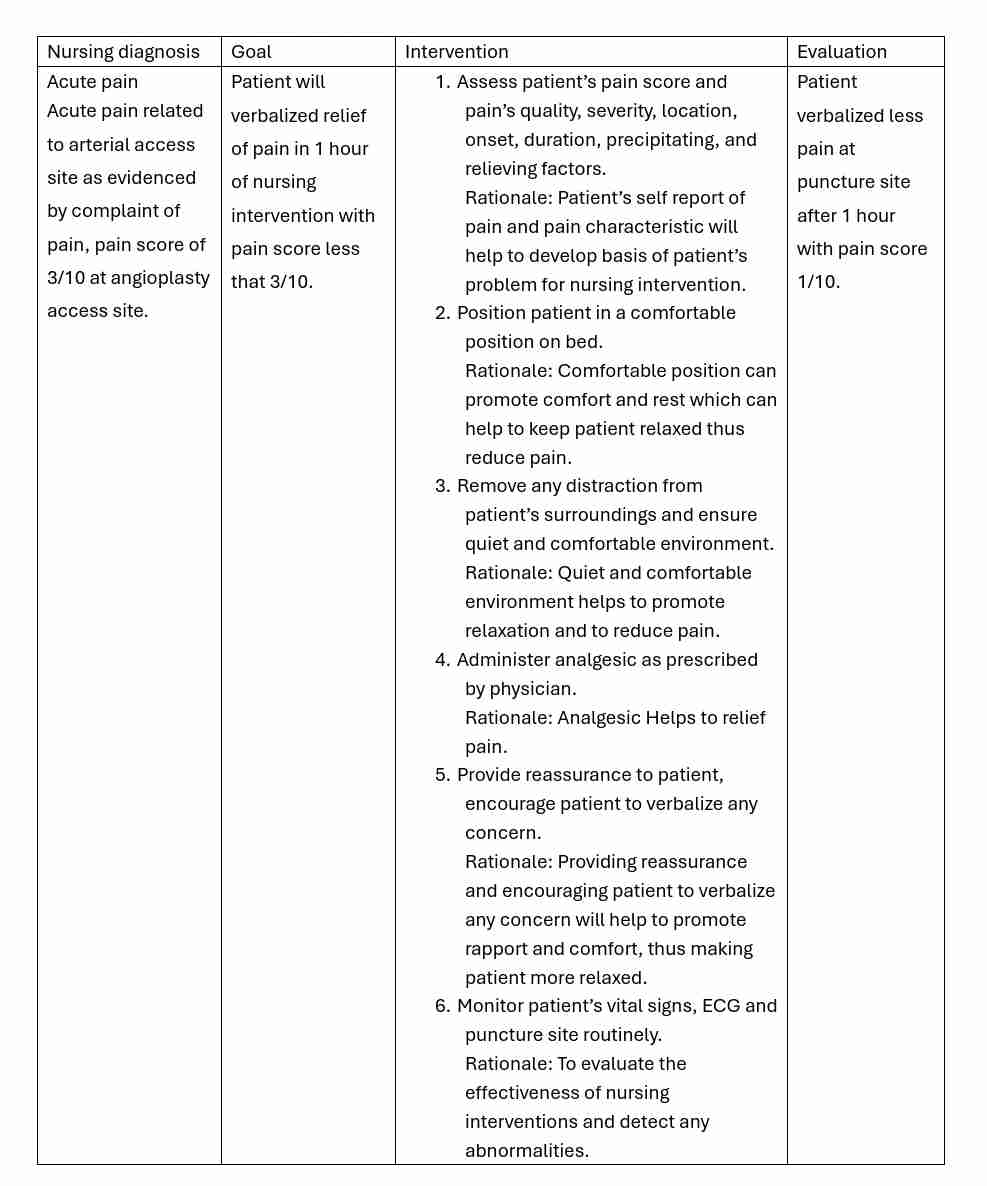
Angiography
Radiographic visualization of the coronary vessels after the injection of radiopaque contrast media.
Coronary Angiography can be done via:
i. X-ray Coronary Angiography or “Angiogram”/ “COROS”
ii. Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography (CCTA)/“CT Angiogram”
iii. Coronary Magnetic Resonance Angiography (CMRA)
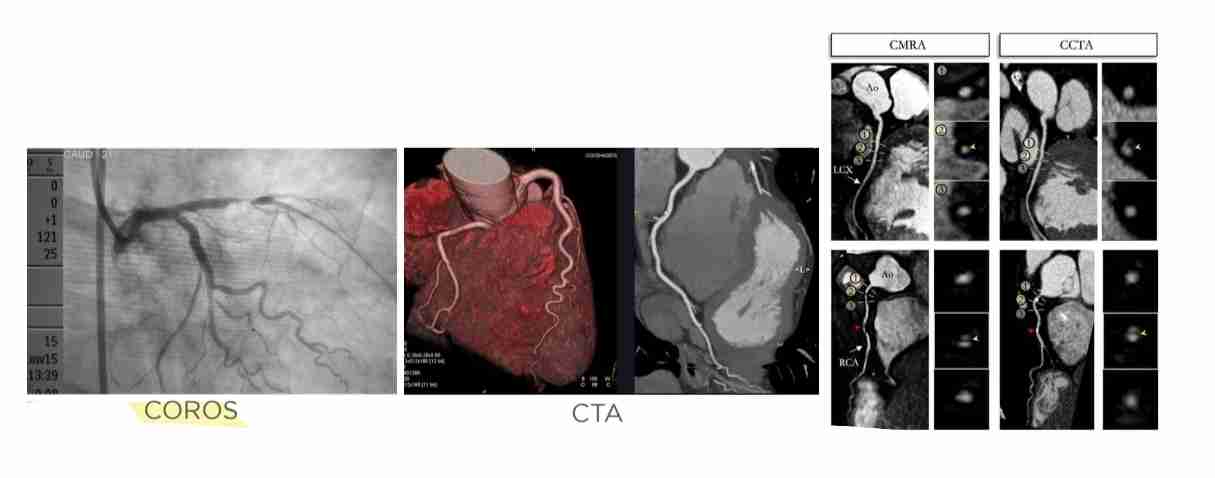
Angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty with or without stenting is a nonsurgical procedure used to open clogged or narrow coronary arteries due to underlying atherosclerosis.
Done with CT machine and injection of IV contrast medium to obtain images of blood vessels and to diagnose coronary artery disease.
However, calcium scores > 1000 prohibit CTA accurate interpretation.
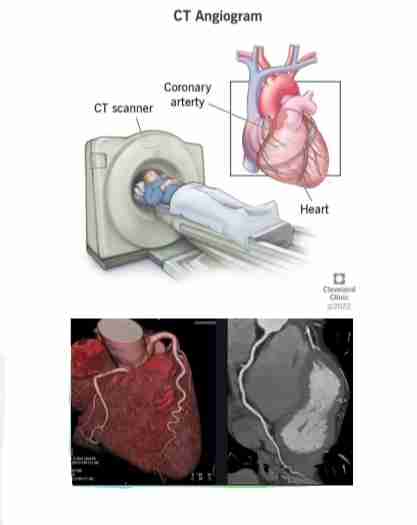
CT Angiography preparation
1. Explain procedure to patient. Gain consent.
2. Check for sensitivity to contrast media (Omnipaque or Visipaque) or any allergy history especially to iodine/seafood. Gain consent.
3. Obtain intravenous access for contrast injection. Preferably brachial, with large bore IV Cannula 18G. Gain consent.
4. Metal objects should be removed prior to examination.
5. Beta blocker may be prescribed to control heart rate – patient must have a regular heart rhythm for accurate testing.
X-ray angiography
Coronary angiography is an X-ray procedure where contrast dye is injected into the coronary arteries using a catheter. It helps assess artery blockages and blood flow. Additional procedures like intravascular ultrasound (IVUS), fractional flow reserve (FFR), and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) can be done during the same session.
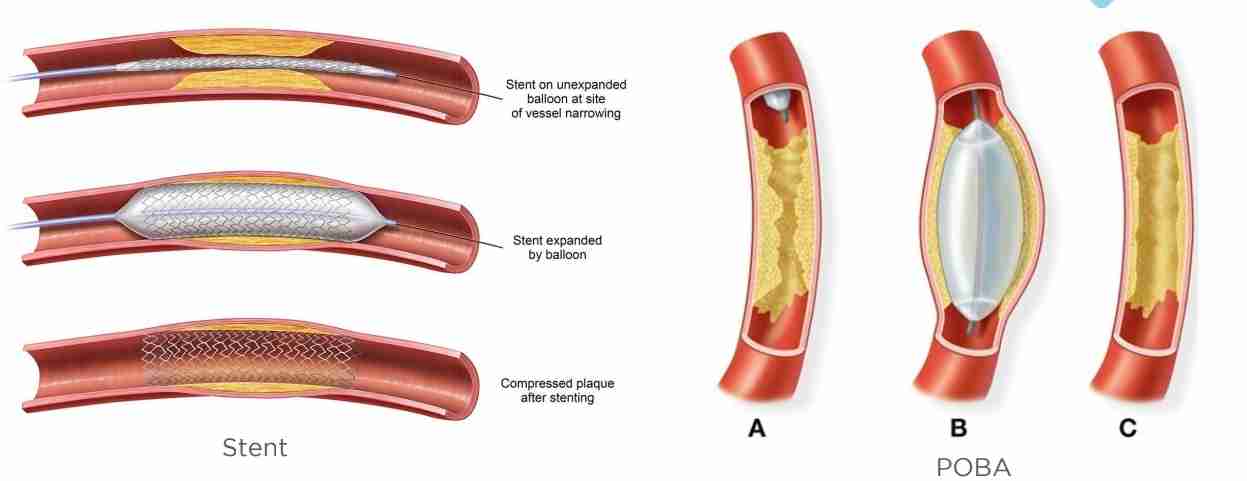
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Coronary angioplasty, also known as Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI), is a procedure used to treat coronary artery disease by opening blocked arteries and improving blood flow, often with stent placement.
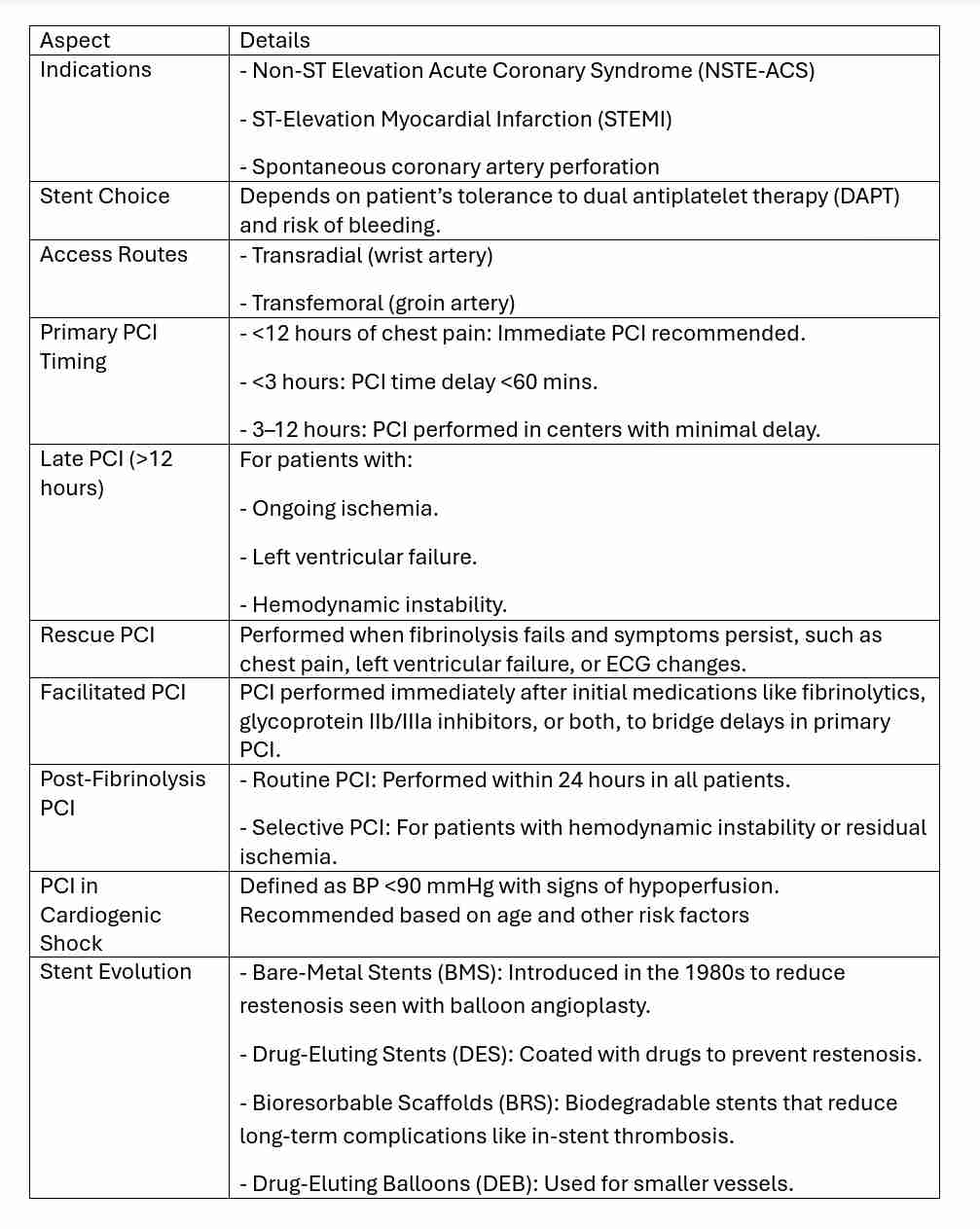
Complications
1. Abrupt closure from coronary artery dissection
2. Vascular injury at artery access site.
3. Acute MI.
4. Stent embolization.
5. Coronary spasm.
6. Dye allergy.
7. Renal Compromise.
8. Bleeding (Retroperitoneal)
9. Infection.
10. Stroke.
11. Emergent CABG surgery.
12. Dysrhythmias.
Nursing intervention
1.Acute pain
Acute pain related to arterial access site as evidenced by complain of pain, pain score of 3/10 at angioplasty access site.
2. Risk of bleeding
Risk of bleeding related to coronary angioplasty via transfemoral approach.
3. Anxiety
Anxiety related to the fear of impending death secondary to coronary angioplasty.
4. Deficient knowledge
Deficient knowledge related to coronary angiogram and angioplasty as evidenced by patient verbalized of inadequate knowledge regarding procedure preparation.
5. Readiness for enhanced knowledge
Readiness for enhanced knowledge related to coronary angiogram and angioplasty as evidenced by patient willingness to participate in health education and compliant to procedure preparation.