CCJ 2020 Test 2 - Bryan Holmes
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Shaw and Mckay's social Disorganization theory
- higher poverty
- higher resident mobility
- high rates of culture dissimilarity
All leading to culture weakened to crime
Location based thoery
cultural dissimilarity
When different cultures in an area aren't connecting
Merton's Strain theory
Theory that says crime is caused by goal blockage (money and status)
Societal strain
Adaptations to Merton's strain
-Conformity: accept societal goals
-innovation: accept societal goals, but reject legitimate means to reach those goals
-Ritualism: scale down goals to something more attainable
- Retreatism: reject all goals and all mean to get there
Agnew's General strain theory
Says people experience strain because they are striving for personal goals and fail to reach them
3 types of strain from Agnew's strain theory
- failure to achieve goals
-removal of positive stimuli
- presence of negative stimuli
Coping mechanisms for Agnew's strain theory
- minimize importance of goals
- minimize negative consequences
-accept responsibility
- behavioral and emotional coping
Sutherland's Differential Association theory
-crime is learned though interactions with signifigant others
- learned directly from friends/ observation and indirectly
Hirschi's Social bond theory
States that people do not commit crime because they are bonded to society.
4 Social Bond theory bonds
Attachment, commitment, involvement, belief in a common set of values
Labeling theory
Labeling a person as deviant will make them more likely to commit a crime
What was the primary goal of a sheriff in historical contexts?
To maintain law and order for the crown.
What is the modern role of a sheriff?
Typically in charge of rural or county crime control.
Who were the Justices of the Peace historically?
Wealthy landowners who acted as judges.
What does the term 'Justice of the Peace' refer to today?
It refers to lower-level court judges.
What was the role of watchmen in historical law enforcement?
They acted as police officers to assist but were not formally trained.
What is a 'posse comitatus'?
A group called by the sheriff to help carry out law enforcement duties.
What is the basic mission of police according to Sir Robert Peel?
To prevent crime and disorder as an alternative to military action.
What does the effectiveness of police depend on? (Peel)
Public approval.
How does the need for physical force relate to voluntary cooperation? (Peel)
As the need for physical force increases, voluntary cooperation decreases.
How should police preserve public favor? (Peel)
By being impartial to the law and not catering to public opinion.
When should physical force be used by police? (Peel)
As a last resort.
What is the relationship between police and the public according to Peel?
The police are the public, and the public are the police; they share best interests.
What is the test of police effectiveness? (Peel)
The absence of crime and disorder, not the presence of police action.
Political Era
Citizen run police forces, mayor picks officers from list of potential officers, ripe for corruption
Professional Era
Incentivizes police to move outside the jurisdiction they are policing. Merit- based civil system
August Vollmer's 4 Tactical advancements
- Increase number of police officers
- Police patrol on bikes instead of on- foot
- Light-based emergency system
- police eventually get radios
August Vollmer's other advancements
- Discovered modus operandi
- makes police go through police classes
- increasing hiring standards
Modus operandi
method of operation, "everyone has their own MO"
Community Era
Police are simply reacting to crime
Kansas City preventative patrol experiment
Determined that preventative patrol does not have a ton of effect in decreasing the fear of crime
Problem solving policing (crime triangle)
There will be 3 things about that crime that make it identifiable: suitable target, motivated offender, lack of a capable guardian
SARA Model (problem-solving policing)
Scan for problems, Analyze the problem, respond, get data on the problem before you respond
Federal law enforcement
Department of homeland security, department of justice
Screening methods: minimum requirement for police hires
Criminal record, driving record, psychological evaluation, physical agility, written essay
Education requirements
Only federal levels require some type of college education. You need the live in the town you are policing.
How would education improve policing?
Less authoritarian, take fewer leave days, heightened ability to analyze, less negligent firearm use.
What are some drawbacks to education being a requirement for police officers?
- less people to recruit, college is expensive, police may no longer represent the public
What does probationary status signify for a police officer?
The transition from academy training to becoming a full patrol officer.
What mental health statistic is concerning for police officers?
Police are more likely to commit suicide than die by homicide.
Police basic tasks on the job
crime fighting, order maintenance, service
What are the key subjects taught in the police academy
operations, use of force, self-improvement, legal education
Legalistic style of policing: the soldier
-Issue larger number of minor crimes
- detain large number of juvenile offenders
- assumes the purpose of the law is the punish
Legalistic style: the watchman
- handles minor offenses informally
- helps build a relationship of trust with community
- seen as a neighbor
Legalistic style: service style
- the teacher
-primary responsibility is protecting public order
- takes all orders seriously
- courteous and respectfult
on the job stressors
- organizational practices
- the criminal justice system
- the public
- trauma
preliminary investigation
Witnesses interviewed, descriptions gathered, information collected.
continuing investigation
Theorizing, conducting follow-up interviews.
reconstructing the crime
To seek a rational theory about the crime
focusing the investigations
Efforts are made to prove the suspect(s) guilty.
informants
Informants can be citizens who contact the police or individuals who have been previously arrested or convicted.
interrogations
involve a more accusatory approach and formal questioning of a suspect with the intent of gaining a confession.
types of police discretion
full enforcement, random enforcement, professional discretion
Police discretion
the power held by police officers to decide who is actually arrested
Discretion decisions
How and if to intervene
Factors that influence police discretion
Legally relevant criteria, situational factors
Liberation hypothesis
as legally relevant criteria increases, the predictive power of other factors will decrease
What are the two main concepts for police use of forse?
- All police brutality will be police use of force, but not all police use of force will be police brutality
- Complaints for police use of force are unevenly distributed
How do we asses whether the police use of force was reasonable?
objective reasonableness: would a similarly trained officer have done the same?
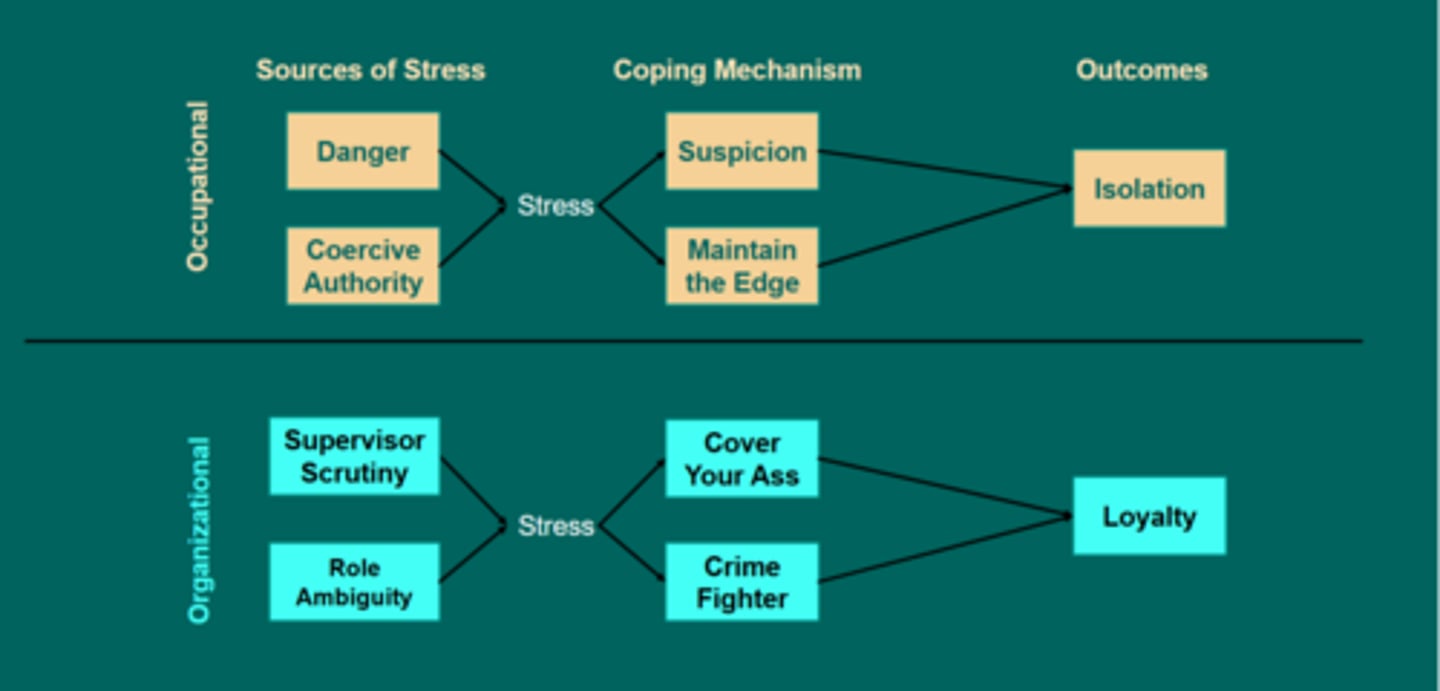
Police culture: monolithic model
- occupational stressors lead to social isolation
- organizational stressors lead to in-group loyalty
Police legitimacy
the extent to which community members perceive government action as fair, proper, and just
4 pillars of procedurally just policing
fairness to all, voice (make citizens feel heard), transparency with the encounter, unbiased decision making
4th amendment
protection against unreasonable searches and seizures
2 primary parts of the 4th amendment
warrant clause, reasonableness clause
When is 4th Amendment activity triggered?
people have a reasonable expectation to privacy, property rights in their home/papers/effects
What is not a 4th amendment activity?
consent search, public place, search done by private citizen, abandoned property
arrest warrant
an order signed by a judge naming the individual to be arrested for a specific crime
Anticipatory warrant
Gives police permission to search a location, but only upon a triggering event
search warrant
A court order allowing law enforcement officers to search a suspect's home or business and take specific items as evidence
Affaduit
a sworn oath in writing of probable cause