Biomechanics Study Guide
1/94
Earn XP
Description and Tags
from week 1 & 2 (assignment due 5/27/25)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Kinesiology is the science of _______ ________ and ________.
human movement ; performance
Biomechanics is the study of ______ of living things using the science of _______.
movement ; mechanics
Mechanics is the study of motion and how _____ influences motion.
forces
Kinematics are the study of characters in motion. What are the three main characters in motion?
displacement - how far something moves or changes location
velocity - the rate of change of position
acceleration - the rate of change of speed
Kinetics is the study of the forces that affect motion. What are some forces that affect motion?
momentum - object in motion wants to stay in motion
force and torque - applied push/pull, twisting force
energy and work - movement of atoms, force applied to resistance
Static is the study of objects in equilibrium. Why “equilibrium” and not “rest”?
because we are always moving (as long as the earth is turning)
ex: when you are is in cruise control, your actual body is static but you are still in motion
Static is the study of objects in ______ while dynamics is the study of objects in _____.
equilibrium ; motion
Displacement is a term in relation to motion that can be defined as?
the distance traveled of an object within a time frame
There are 3 types of motion. Rotary motion is what?
movement around a fixed axis in a curved path
ex: what we measure with goniometry
There are 3 types of motion. Translatory motion can be defined as movement in a _____ line.
straight
There are 3 types of motion. Curvilinear motion includes both rotary and translatory because it is defined as what?
movement of an object both around an axis and through space at the same time
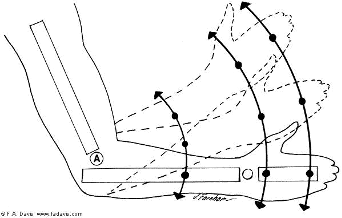
This is an example of what type of motion?
rotary
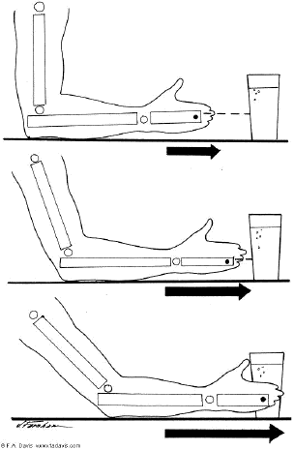
This is an example of what type of motion?
translatory
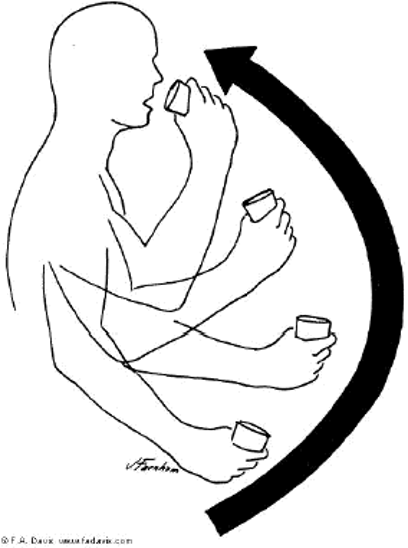
This is an example of what type of motion?
curvilinear
What are common movements associated with a rotatory motion?
flexion/extension
abduction/adduction
internal/external rotation
What are common movements associated with a translatory motion?
compression - pushing together
distraction - pulling apart
A force can either be a ____ or a _____.
push ; pull
True or false
Vectors posses both direction and magnitude.
True
What are the 4 characters of force?
point of application - where the force is being applied
line of application - the directional line going through the vector
direction - where the vector is pointing
magnitude - how long the vector is (harder push=longer line, lighter push=shorter line)
An internal force can be broken into 2 categories. What are they?
contractile - muscle contractions
non-contractile - passive tension from ligaments, joint capsules, intramuscular connective tissue
What are examples of an external force?
movement by an external force
friction
gravity
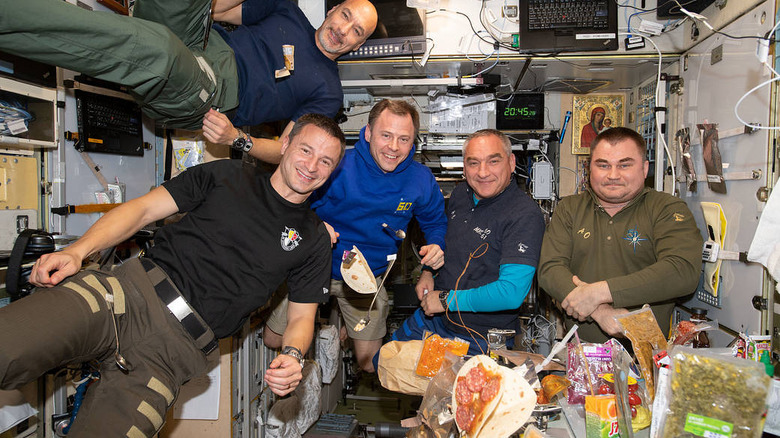

What is Newton’s 1st law?
an object in motion wants to stay in motion, an object in rest wants to stay in rest
What is Newton’s 2nd law?
the heavier something is, the more mass it has. the more mass it has, the more force is required to move the object.

What is Newton’s 3rd law?
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
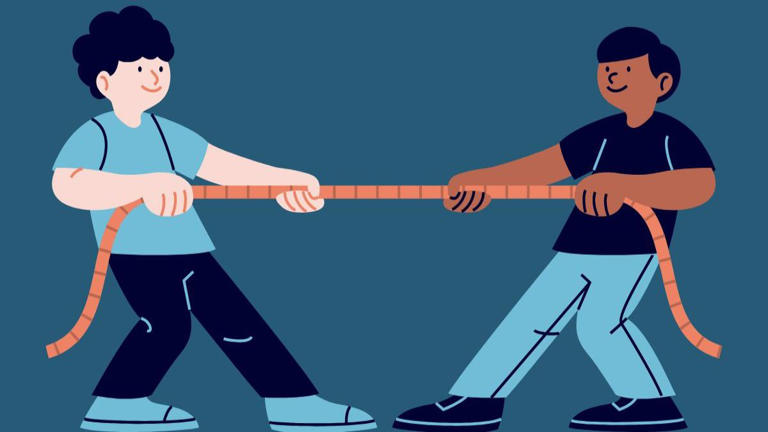

This is an example of what type of force?
tension
when something is pulled tight from both ends

Pushing this spring together would be an example of what type of force?
compressive
when an object is pushed together at both ends
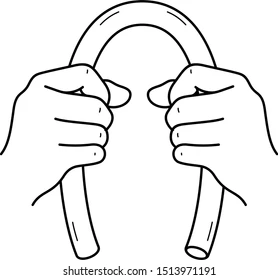
This is an example of what type of force?
bending
force is applied at both ends of something, causing it to bend
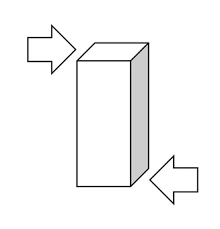
Applying force at both arrows would be an example of what type of force?
shear
when opposite forces are applied on two sides that causes it to shear
Katie is ringing the water out of her towel. What type of force is being applied to the towel?
torsion
twisting the opposite direction at both ends
A gravitational force is when there is force due to _____.
gravity
What is the difference between mass and weight?
mass is how much matter is in something and weight is the force related to gravity pulling on that mass
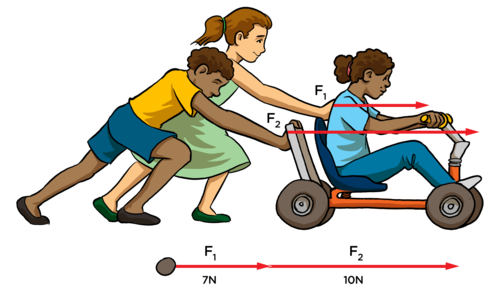
A contact force is when force is applied between 2 objects in ____ contact.
physical
A ________ force is a force that tends to push objects together while a ______ force tends to pull objects apart.
compressive ; distractive
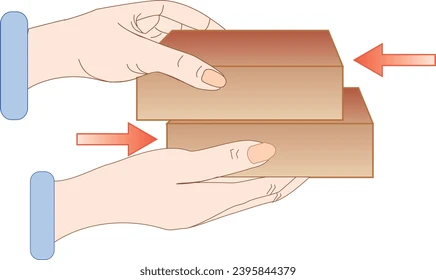
Jessie is rubbing these two blocks together in music class. This is an example of what type of force?
friction
forces due to interactions of 2 surfaces that are in contact
What type of force does a muscle develop when it contracts?
muscular force
True or false
Muscles can push and pull.
false
muscles can only contract meaning they CANNOT push
What type of force is required to start an object into motion or to resist an object that is already in motion?
inertial force
______ force is force due to an object deforming or stretching.
elastic
______ force is when there is upward force due to the object being in some kind of fluid like water.
buoyant
There are 3 types of force systems. Which force system is being applied in this image?
linear force system
2 or more forces act on the same object and in the same direction
A ______ force system is when 2 or more forces acting at a common point of application on an object but in divergent directions.
concurrent
A _____ force system is when 2 or more parallel forces act on the same lever but at some distance from each other and at some distance from the axis about which the lever will rotate.
parallel
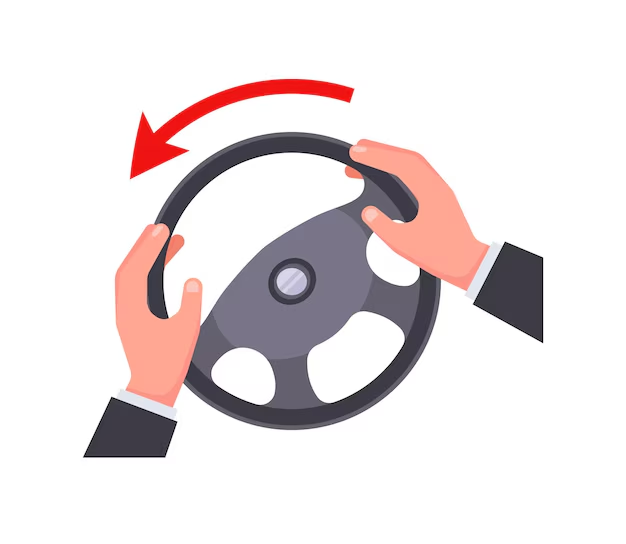

Turning your steering wheel while driving is an example of what?
force couples
when 2 or more parallel forces are working in opposite directions
_____ is a force that causes displacement of an object.
Work
_____ is the capacity to do work and is broken into two types: kinetic (due to motion) and potential (due to position).
energy
_____ is the rate of doing work and the rate of change of energy.
Power
Torque is when _____ ______ is applied to an object.
angular force
what are the 4 important parts of torque?
axis of rotation
magnitude of force applied (how hard your muscle is pulling)
distance from axis to applied force (moment arm)
angle (direction) or force
Twisting a long wrench is easier than twisting a short wrench because…
a long wrench has more leverage due to the longer length
What are the 2 ways you can calculate torque?
cross product (hard way)
moment arm (easy way)
What is a moment arm?
the straight-line distance to the point of application of the perpendicular force component
Anatomically, the angle of insertion is made up of what 2 components?
bone axis
tendon insertion
The greater the ______, the greater the torque. The longer the ______ _____, the greater the torque.
force ; moment arm
Effort force (EF) is the force causing what?
the rotation of the lever
Resistance force (RF) is the force that is doing what?
opposing the rotation of the lever
The ____ arm is the moment arm of effort force while the _____ arm is the moment arm of resistance force.
effort ; resistance
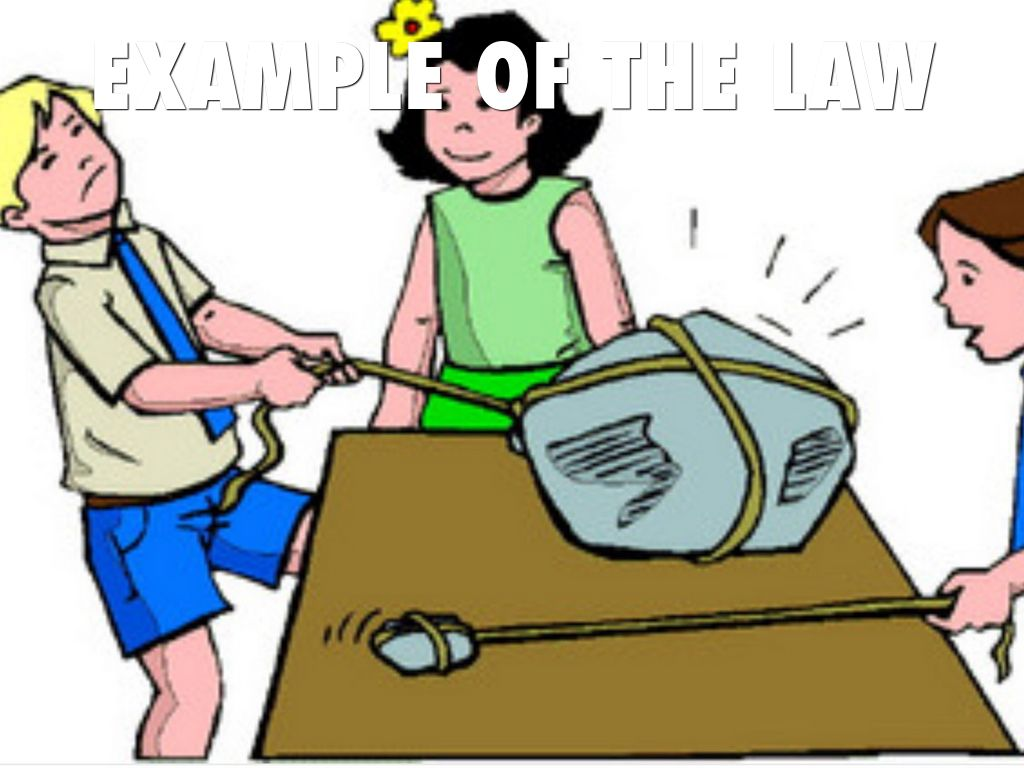
2 parallel forces applied on either side of an axis at some distance from that axis, creating rotation of the lever in opposite directions is what classification of levers?
first class lever
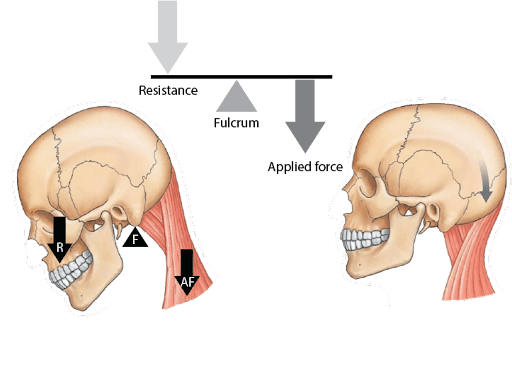
This is an example of what type of lever?
first class lever
When the resistance force is applied closer to the axis than the greater force, this is an example of what classification of levers?
second class lever
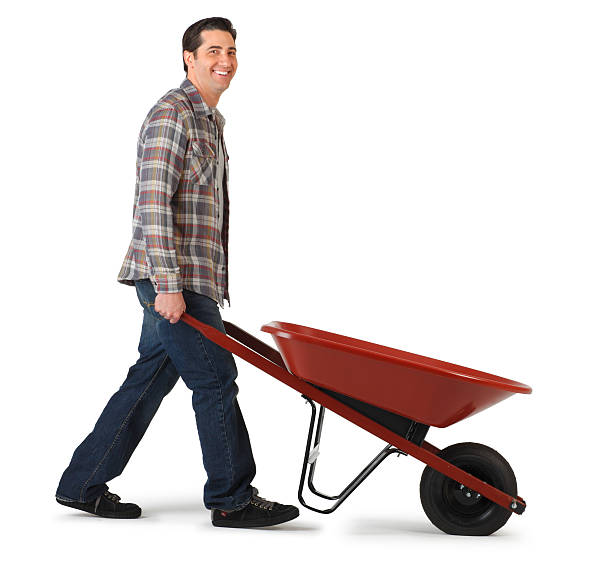

David is demonstrating what classification of levers?
second class lever
True or false
When talking about a second class lever, the effort arm is always greater than the resistance arm.
True
When the effort force is applied closer to the axis than the resistance force, this is an example of what classification of levers?
third class lever
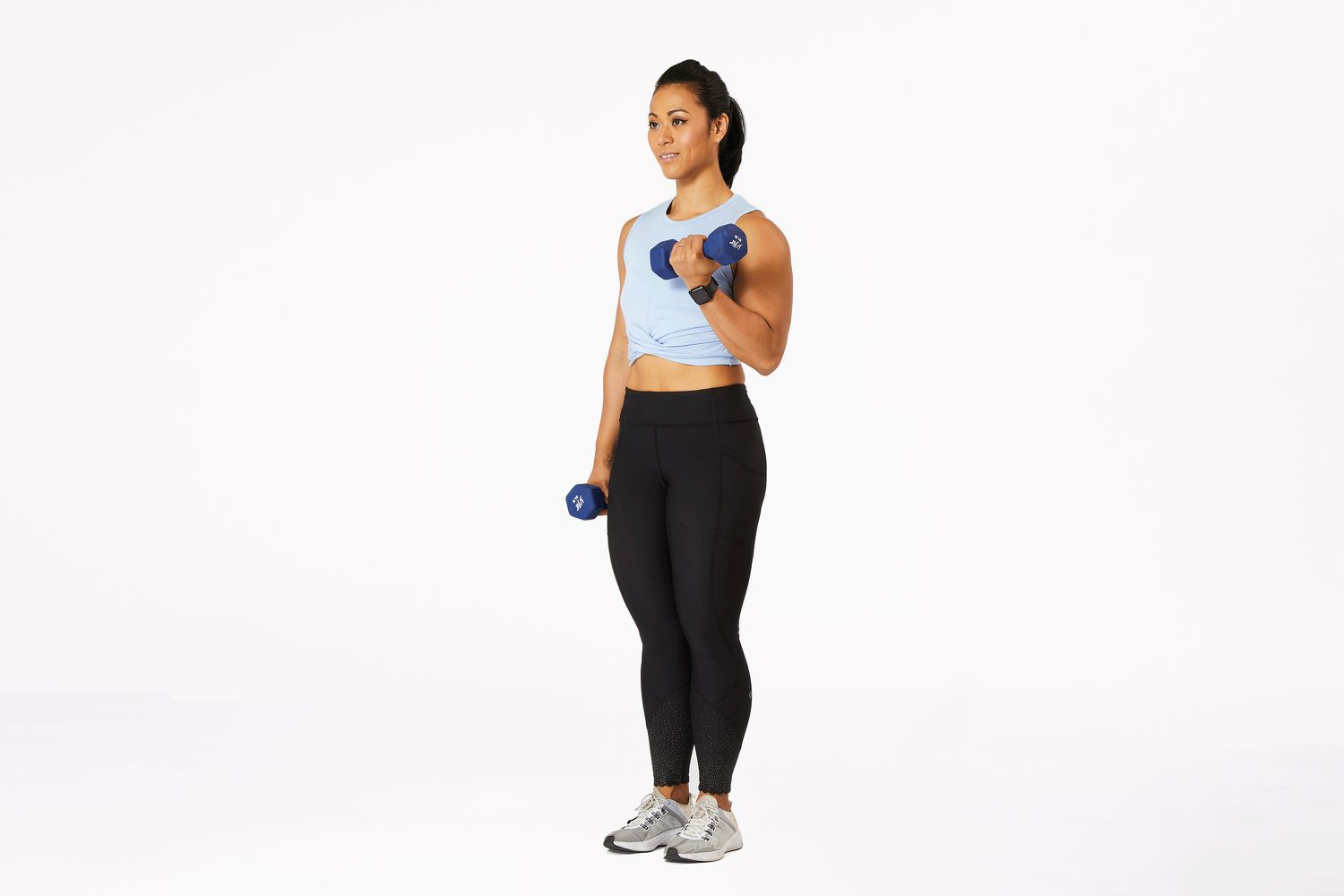

Brittany is demonstrating which lever class with this exercise move?
third class lever
True or false
When talking about a third class lever, the effort arm and the resistance arm are equal.
false
third class lever → resistance arm > effort arm
True or false
The third class lever is the most common type of lever used by humans.
true
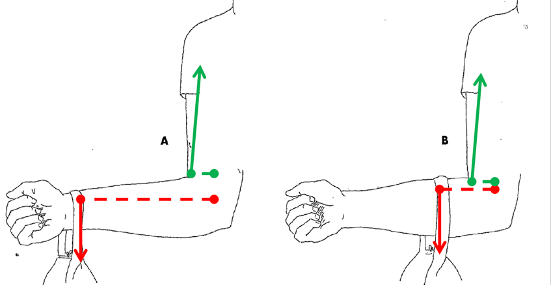
Austin is helping his mom carry in groceries from the car. Which position is easier to carry the groceries? why?
position B
the grocery bag (object) is closer to the axis point (elbow)
Mechanical advantage describes efficiency of a lever system. The more efficient the lever system, the ______ force needed to overcome a larger resistance.
less
Which lever class has more mechanical advantage?
second class
the load is always closer to the fulcrum than the effort
True or false
Anatomical pulleys change the magnitude of a muscle force
false
they change the direction of the muscle force
____ is force on an object that might cause it to deform.
stress
_____ is change in shape of an object due to stress.
strain
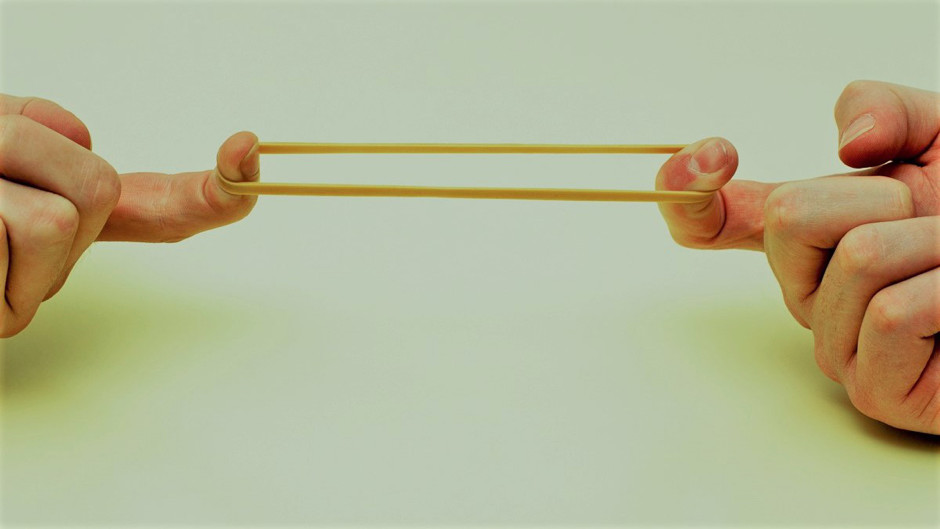
Pulling on a rubber band is an example of ______ strain.
tension

Mike got frustrated studying for his biomechanics exam and crushed this can against his forehead, causing it to collapse. What type of strain was applied to the can?
compression strain

Like Mike, Timmy also got frustrated studying for his biomechanics exam. He decided to cut his notes apart because he was so upset. What type of strain was applied to his paper by the scissors?
shearing strain
What are the 3 types of loading?
axial loads (tension and compression)
bending loads (bending)
torsional loads (twisting)
______ is when material is able to immediately return to its original size and shape when stress is removed.
elasticity
______ is when material remains some of its stressed size and shape when stress is removed.
plasticity
________ is when material does not deform instantaneously when loaded, but does not change overtime.
viscoelasticity
_____ law is when the BONES of the human body will adapt to loads under which they are placed overtime.
Wolff’s
_______ law is when TISSUES in the human body will be shaped by mechanical stresses placed upon them.
Davis’s
Biomechanics is defined as the:
a. physical laws of biology that relate to mammals
b. mechanical principles that directly relate to the body
c. mechanical aspects of biology and science
d. biological principles that involve human movement
b. mechanical principles that directly relate to the body
A force can occur in what ways?
a. direction, movement, and structure
b. direction, stability, and strength
c. stability, mobility, and function
d. movement, structure, and function
a. direction, movement, and structure
A rolling ball that meets no resistance and continues to travel is an example of:
a. mass
b. torque
c. inertia
d. gravity
c. inertia
A force that resists the relative motion of two surfaces is:
a. vector
b. friction
c. statics
d. dynamics
b. friction
Which of the following has the greatest effect on your physical movement?
a. flexibility
b. gravity
c. strength
d. time
b. gravity
Running into a brick wall illustrates which of Newton’s three laws of motion?
a. Law of Inertia
b. Law of Action
c. Law of Acceleration
d. Law of Mobility
a. Law of Inertia
Which of the following are critical factors of Newton’s second law of motion?
a. mass, vectors, and gravity
b. force, gravity, and light
c. vectors, gravity, and acceleration
d. force, mass, and acceleration
d. force, mass, and acceleration
Stepping off of a free-floating canoe and onto an unstable dock is an example of:
a. vector and force
b. action and reaction
c. acceleration and deceleration
d. force and stability
b. action and reaction
Force can be divided into which three systems?
a. circular, collateral, and striated
b. linear, perpendicular, and vector
c. linear, parallel, and concurrent
d. oblong, simultaneous and regional
c. linear, parallel, and concurrent
Turning a wrench is an example of:
a. torque
b. gravity
c. vector
d. force
a. torque
Building a lever requires an axis and a:
a. rigid bar
b. plane
c. triangle
d. ball
a. rigid bar
A can opener, scissors, and long bar are all examples of what type of lever?
a. first class
b. second class
c. third class
d. fourth class
a. first class
An example of a second-class lever is a:
a. crowbar
b. shovel
c. wheelbarrow
d. drill
c. wheelbarrow
Which of the following generates the necessary support for mobility?
a. eccentricity
b. extensibility
c. flexibility
d. stability
d. stability
Walking with crutches highlights the biomechanical principle of:
a. law of vector
b. base of support
c. frame of torsion
d. axes of gravity
b. base of support