Lecture 18: Minor Ailments & Responding to Symptoms in Community Pharmacy | Gastrointestinal Queries
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Common GI Queries
Dyspepsia/Idigestion
Gastro-Oesephogeal Reflux Disease (GORD)
Constipation
Diarrhoea
Nausea and Vomiting
Piles
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Common GI Queries - WWHAM
Define each condition Symptoms
Causes
Referral (red-flags)
Treatment/management (lifestyle changes)
Dyspepsia/indigestion
Refers to a group of symptoms, that are linked to eating and drinking - associated with excess acid
Symptoms:
Bloating
Burping
Stomach cramps
Flatulence
Causes:
Certain foods
Time of eating
Caffeine
Medication
GI tract problems (ulcer, cancer, infection)
Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD)
Reflux of gastric content into the oesophagus
Symptoms:
Gstric pain
Discomfort and wind
Nausea
Acidity (back of throat)
Abdominal pain
Causes:
Diet and lifestyle (overeating, drinking, obesity)
Pregnancy
Incompetence of oesophageal sphincter (hernia, drug induced)
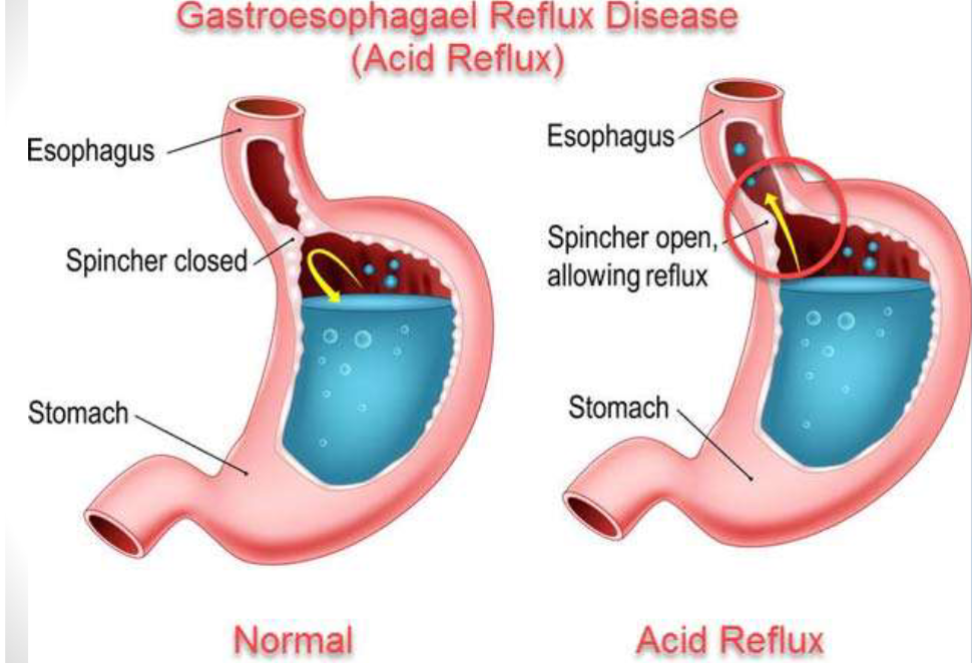
GORD - what is it?
Indigestion/heartburn/acid reflux
Heartburn (acid reflux) : occurs when the sphincter muscle between the stomach and oesophagus allows the stomach acid to leak back up into the oesophagus
Indigestion (dyspesia): occurs when acid from the stomach comes into contact with the lining of the digestive system
GORD is a more chronic severe form of acid reflux
Lifestyle advice
Diet changes: avoid large meals, fatty/hot spicy food, reducing alcohol consumption and stop smoking
Avoid aggravating factors
Raising the head of the bed and not lying down withing 3 hours of taking a meal
Losing weight if overweight
Antacids
Raise pH (neutralise excess acid) and provide rapid relief
Alter absorption of certain drugs and damage encentric coating of tablets
Sodium bicarbonate
Belching CO2, less suitable in flatulence
Sodium content
Aluminium and magnesium hydroxide
Aluminium causes constipation
Magnesium causes diarrhoea
Used in combination - counteract both problems

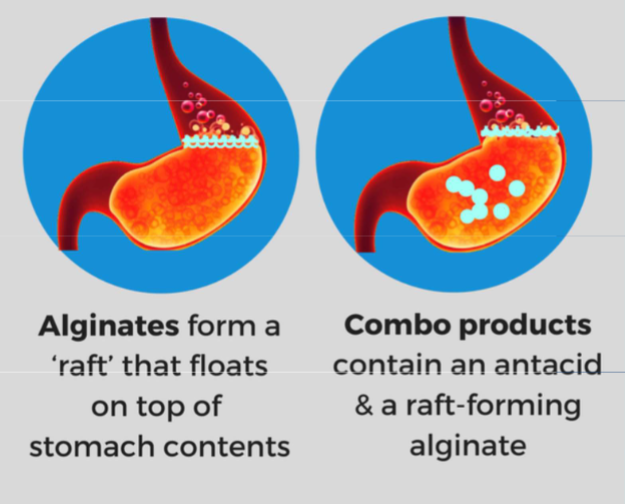
Alginates
Rafting agents
Could be mixed with antacids
Forms a raft/viscous foam
Protects oesophagus during reflux
Bismuth chelates
Absorbs pepsin
Increase prostaglandin production and bicarbonate secretion
Healing ulcers
Draken stool and tongue, taken on empty stomach
Misoprostol: analogue of prostaglandines, not recommended in child bearing age women
H2 receptor antagonist
Competitive antagonist of H2 receptor
Inhibit histamine-induced acid secretion
Effective at night
OTC: Rantidine (Zantac) no longer available OTC due to international recall - minimal amounts of NMDA (probable carcinogen) found
Slower acting than antacids
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)
Inhibit a chemical system - hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphate enzyme system (proton pump)
PPIs are converted to active drugs at acid pH
Regular use to be effective as they have preventative role rather than symptomatic
Inhibit certain drugs metabolism thus increase their concentration
When to refer?
Dysphagia
Hematemesis
Weight loss
Vomiting
Upper abdominal masses
Repetitive request for OTC supply
Onset of new symptoms
Upper epigastric pain
Hunger pain
Night pain relieved by eating
Drug induced
Diarrhoea
Passing soft or watery stool at an increased frequency
Common and debilitating condition
Can be life threatening due to dehydration
Symptoms:
Crampy stomach pains
Fever
Loss of appetite
Nausea and vomiting
Diarrhoea - causes
Bacterial or viral infection - food is culprit
Broad spectrum antibiotics - alter natural gut flora leading to superinfection
Medication: PPIs, magnesium salts, NSAIDs, metformin, iron salts, excessive use of laxatives
Change of climate and country - body not used to different water and food
Anxiety and too much alcohol
Diarrhoea - management
General advice - drink plenty of fluid, high carbohydrate food
Drug induced: review medication and counselling
Oral rehydration therapy
Antibiotics
Antimotility drugs
Signs of dehydration
Dry:
Mouth, lips cracked, eyes
Loose skin, lack of elasticity
Sunken features
Urine/GI:
Low output
Concentrated
Low abdominal pain, burning sensation in stomach, loss of apetite
Head:
Dizziness, light-headedness, tiredness, headaches
Clammy hands and feet
Confusion and irritability
Oral rehydration therapy
Dehydration causes electrolyte disturbance - with certain drugs e.g. diuretics
Specific mixture of electrolytes and glucose
Made up to correct osmolality - freshly boiled and cooled water
Number required depends on number of watery stools
Antimotility agents
Symptomatic but limited use
Reduce motility of the gut, allowing reabsorption or water and minerals
Allow control of diarrhoea - less disturbance to daily activities
Loperamide widely used - less central side effects
Antibiotics
Most cases are viral in nature
If bacterial infection confirmed by stool culture, then correct antibiotc prescribed
Traveller’s diarrhoea: need to ascertain any recent travel history
When to refer?
Length of diarrhoea > 3 days
Blood in stool
Moderate to severe dehydration - not properly self managed (elderly)
Drug induced (clindamycin, colchicine)
Recent travel - check
Regular purchase of codein based products
Constipation
Altered bowel habits, reduced frequency and passing hardened faeces
The Rome IV diagnostic criteria for constipation include spontaneous bowel movements occuring fewer than 3 times a week
Usually harmless but can indicate underlying serious disorders
What is important regularity not frequency
Constipation - causes
Lifesyle:
Diet lacking fibres/fluid lack of exercise
Hospital admission, depression, anxiety
Ignoring call to stool
Metabolic/drugs/neurological
Hypothyroidism, hypercalcemia, hypokalaemia, diabetes
Opiates, irons, antacids, antidepressants
Dementia, stroke, multiple sclerosis, parkinsonism
Bowel disorders
Anal pathology
Tumour
Diverticular disease
Constipation - management
Lifestyle changes
Balanced diet, high in fibre and non-starch polysaccharides
High fluid intake
Increased exercise
Laxatives
Medicines that increases the number of bowel movements
Osmotic/stimulant/bulk-forming/softeners
When to consider laxatives?
Straning to pass stool that might affect other conditions like haemorrhoids or angina
Temporary illness which causes constipations e.g. lack of movement or loss of appetite
Elderly person develop constipation due to low mobility
Drugs taken concomitantly
Before colonoscopy - not related to constipation
Bulf forming agents
Swell up in gut to increase faecal mass - stimulates peristalsis
Take a few days to work, should be taken with plenty of water and not immediately before bed - risk of bowel obstruction
Equivalent to high fibre diet
Can cause wind/bloating
Stimulant laxatives
Stimulate nerve endings in gut which causes muscle to contract - speeds up persistalsis
Taken at bedtime, takes 8-12 hours to work
Rapid relief of symptoms
Short term - risk of bowel nerve damage
Can cause cramps/gripping pain
Osmotic laxatives
Increase the flow of water into the intestines to produce softer and easier to pass stools
Variable onset of action: phosphate enema (within 1 hour), lactulose (2-3 days), macrogols (12-24 hours) and magnesium salts (2-4 hours)
Lactulose is broken down in the gut and increase volume of faeces and water content
Can cause abdominal ramp and wind
Faecal softeners
Lubricating and softening faeces making them easier to pass
Small quantites due to serious side effects
Include: paraffin seepage from faeces which irritate the anus
Absorption of paraffin from the gut can cause damage to the gut wall
Interferes with absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K)
Causes
Bacterial or viral infection - food is culprit
Broad spectrum antibiotics - alter natural gut flora leading to superinfection
Other drugs: PPIs, magnesium salts, NSAIDs, metformin, iron salts, excessive use of laxatives
Change of climate and country - body not used to different water and food
Anxiety and too much alcohol
When to refer
Drug induced when regular laxatives are needed
Sudden onset of symptoms with no apparent reason especially in elderly
Blood in faeces (haemorrhoids and straning)
Overuse - slimming purposes
Severe abdominal pain
Nausea and vomiting
Common occurrence
Could following exposure to bacterial toxin
May reflect serious underlying pathology
Focus on GI related nausea and vomiting for OTC supply
Causes
Alcohol
Bacterial and viral infection
Motion sickness
Drugs (anticancer, NSAIDs, iron salts, erythromycin, SSRIs)
Peptic ulceration, migraine, pregnancy, head trauma
Meniere’s disease, renal failure
When to refer
Blood in vomit
Duration > 2 days
Weight loss
Severe abdominal pain
Treatment:
Manage the symptoms
Oral rehydration therapy
Preventative measures (diet)
Haemorrhoids (piles)
Swollen veins in the lining of the anus and rectum
External at the anus or internal at the rectum
Occur because of the increased pressure on haemorrhoidal vein
Made worse by straning and constipation
Pregnant women are particularly prone
Haemorrhoids - symptoms
Common bleeing after going to the toilet
Itching and irritation
Sense of not fully emptying rectum when going to the toilet
Sense of fullness around the anus
Haemorrhoids - management
Eat plenty of fibre - fruit, vegetables, wholemeal bread
Drink plenty of water - alcoholic drinks can be dehydrating
Fibre supplements: bulk forming/agents/bran
Toileting: respond to the call to toilet/not postpone, resist straning
Treating and managing constipation
Choice of preparation depends on location
Creams/ointments more suitale for external use
Suppositories for internal use
Topical corsticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Ages 20-30, more common in women
Abnormal contractions of the muscles in the large intestine and increased sensitivity of bowel to the presence of gas and movement
Causes are poorly understood - may be related to anxiety and depression or certain food types
IBS symptoms
Gripy, colicky pain acorss lower abdomen
Wind and bloating
Fatigue and disturbed bowel habits
Diarrhoea and constipation
OTC supply will be based on whether the patient has confimed IBS
IBS - management
Diary of diet, activity - define aggravating factors and avoid
Diarrhoea and constipation management as didiscussed in previous flashcard
Non-medical treatment
Cognitive behavioural therapy
Hypnotherapy
Acupuncture
Antispasmodics
Work by relaxing the intestine muscle so relieve muscle spasms