Enterprise Architecture Midterm
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Business process integration
the sharing and coordination of key processes between companies in a supply chain
Business process standardization
a business process is applied in a consistent manner across all of an organization's work units
Enterprise Architecture
The design framework for how an organization develops, employs, and supervises information technology
a coherent whole of principles, methods and models that are used in the design and realization of an enterprise's organizational structure, business processes, information
An aligned information infrastructure:
is an engine for operational excellence
• To deliver customer satisfaction, products, and services efficiently and cost effectively.
• provides a strong basis for seizing new opportunities and achieving strategic advantage
An operating model
defining how you will do business
Better foundation for execution
have embedded technology in the process to efficiently and reliably execute the core operations of the company
What benefits do
companies that digitize
the core business
operations see?
• Higher profitability
• Faster time to market
• More benefits/return on IT investments
• Better access/sharing of customer data across the company
• Fewer mission-critical systems failures
• 80% more senior executive satisfaction with IT
• 25% lower IT costs
These companies are positioned to move further
and further ahead of their competition.
Reasons That A Foundation for Execution Makes
A Difference
By automating core operations, errors are reduced or eliminated.
• Reducing/eliminating errors gives executives and managers more time to focus on buildingbusiness success.
• Core operations become reliable and predictable.
Cloud Computing
the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.
Signs that a Company Does Not Have
Foundation for Execution for Its Strategy
Different parts of our company give different answers to the same customer questions.
• Meeting a new regulatory or reporting requirement is a major effort for us, requiring a
concerted push from the top and significant infrastructure investment.
• Our business lacks agility—every new strategic initiative is like starting from scratch.
• IT is consistently a bottleneck.
• There are different business processes completing the same activity across the company,
each with a different system.
• Information needed to make key product and customer decisions is not available.
• A significant part of people's jobs is to take data from one set of systems, manipulate it, and
enter it into other systems.
• Senior management dreads discussing IT agenda items.
• We don't know whether our company gets good value from IT.
What's the traditional approach to IT-Business Alignment that results in
an infrastructure that looks like this picture?
Individually (a set of silos), the applications
work fine. But:
• Building IT solutions rather than IT
capabilities
• A separate IT solution, each implemented
on a different technology
• IT becomes a bottleneck instead of an
asset
Problems with this Infrastructure
• Rigidity
• Excessive cost
• Inability to adapt to new channels
like social media
• Higher risk of failure
• Little to no reuse
• Strategic disadvantage
• More vulnerable to competitive and
regulatory threats
Operating Model Examples:
Definition: An operating model is the necessary level of business process integration and standardization for delivering goods and services to customers.
Examples of Business Strategies:
Target markets
Positioning in each target market
Capabilities a business wants to
leverage/build
Guidance for IT investments
What's the relationship between an operating
model and a strategic initiative?
• The operating model constrains
which strategic initiatives are
viable. The strategic initiative
must fit in with the business
capabilities in the operating
model (existing or planned).
• Existing capabilities can provide
low-cost, fast implementation of
an initiative.
Standardization
(defining exactly how aprocess will be executed regardless of who is performing the process or where it is completed)
• Example - using a standard process for selling products or buying supplies
What are the benefits?
• Efficiency
• Measurability (Enables tracking metrics)
• Predictability
What are the challenges?
• Limits local innovation
• Resistance when good systems are replaced
Integration
(links the efforts of organizational units through shared data)
• Example - loan officer’s access to customer’s checking, savings, and brokerage accounts for better information about the customer’s financial situation
What are the benefits?
• Efficiency
• Coordination
• Transparency
• Agility
What are the challenges?
• Data integration – creating and using one data format
Two Levels of Each Dimension Gives Us Four Operating Models
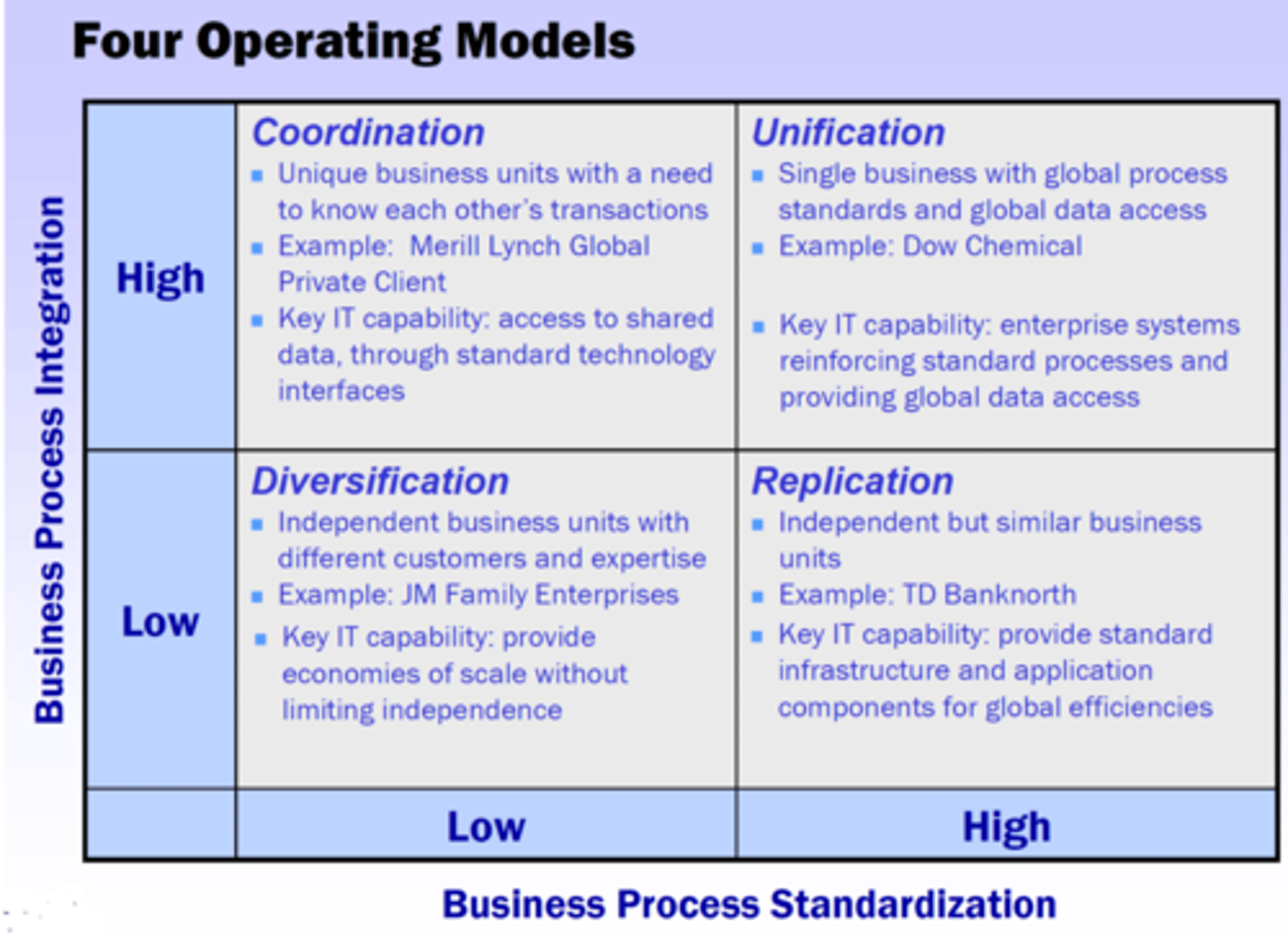
Integration requirement:
To what extent is the completion of one business unit's transactions dependent on the timeliness of other business units' data?
Standardization requirement:
To what extent does the company benefit by having business units run their operations in the same way?
Coordination - Seamless Access to Shared Data
• Unique business units with a need to know
each other's transactions
• Shared customers, products, or suppliers
• Impact on other business unit transactions
• Autonomous business management
• Business unit control over business process
design
• Shared customer/supplier/product data
• Consensus processes for designing IT
infrastructure services: IT application
decisions made in business units
Replication
• Independent but similar business units
• Few, if any, shared customers
• Independent transactions aggregated at a
high level
• Operationally similar business units
• Autonomous business unit leaders with
limited discretion over processes
• Centralized (or federated) control over
business process design
• Standardized data definitions but data locally
owned with some aggregation at corporate
• Centrally mandated IT services
Unification
• Single business with global process standards and
global data access
• Customers and suppliers may be local or global
• Globally integrated business processes often with
support of enterprise systems
• Business units with similar or over-lapping operations
• Centralized management often applying
functional/process/business unit matrices
• High-level process owners design standardized
processes
• Centrally mandated databases
• IT decisions made centrally
Analog Data
Historically, data was mostly analog,
encoded as continuous variations on various physical
media. Ex: Audio was recorded as vibrations
impressed on vinyl disks. Images were recorded as
chemicals on celluloid tapes.
Digital Data:
oday, data is mostly digital, encoded as
zeros and ones on electronic and magnetic media.
• The shift from analog to digital data facilitated the
rise of large computer databases.
database
is a collection of data in a structured format. The database structure ensures that similar
data is stored in a standardized manner.
database system
also known as a database management system or DBMS, is software that reads
and writes data in a database.
query
is a request (or a command) to retrieve or change data in a database.
query language
is a specialized programming language, designed specifically for database systems.
Query languages read and write data efficiently, and differ significantly from general-purpose
languages such as Python, Java, and C++.
database application
is software that helps business users interact with database systems.
Database Architecture

Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
All of the costs associated with the design, development, testing, implementation, documentation, training and maintenance of a software system.

Why use TCO?
• To compare the costs of running an entire infrastructure
environment or specific workload on-premises versus on AWS
• To budget and build the business case for moving to the cloud
Coordination Core Diagram (process)
Senior managers take the lead:
the template for the core diagram of the
operating model is a good starting point:
• Identifying key customers, core business process, shared data,
standardizing and integrating technologies
• Implementing strategies around the core business
• Build IT capabilities
➢ IT leaders taking the lead (two strategies):
IT facilitates senior management discussions –
• Start from IT capability
• Senior management provides leadership
• Map out the operating model and the enterprise architecture
core diagram
• Example: Delta Airlines
IT Leaders Design the core diagram
• IT develops the core diagram from IT perspective
• With senior management supporting the vision of what IT can
deliver
• Example: MetLife
Universal digital representation of information
• Sampling to represent analog experience, e.g., to take a digital photographs, to create an mp4 audio file.
• Everything becomes a number, a binary number.
Universal digital processor
The capabilities of all computers are the same.
EDVAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator)
• Proposed by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert
• Design team joined by John Von Neumann
• Von Neumann's, "First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC," proposed the stored
program concept
• Delivered in 1949
• Binary rather than decimal
Computer architecture
is the discipline that deals with designing the processor and its
connections to the rest of the machine: Computer science + Electrical engineering.
Processor
are very fast, performing an instruction in
well under a nanosecond.
(historically been called the CPU or central processing unit):
• Brain of the computer
• Processor speed is measured by GHz or MHz (number of operations or instructions
performed/second).
• 1Hz =1 beat per second
The primary memory:
By comparison, memory is excruciatingly
slow—fetching data or an instruction from memory
might take 10 to 20 nanoseconds.
• RAM or random-access memory
• Stores the data that the processor is currently working on
• Stores the instructions that tell the processor what to do with that data (run a word processor,
surf the web, a spreadsheet, etc.)
Secondary storage is often disk (or drive)
• Store much more information than the primary memory
• Two kinds of secondary storage:
• Magnetic disk, called the hard disk or hard drive (old). Uses rotating machinery
• Solid State Drive or SSD (new) - uses flash memory instead of rotating machinery
• Flash memory is faster, lighter, more reliable, won't break if dropped, requires less power. used
in cell phones, cameras, and lap-topes
Caches
a small high-speed memory between the
processor and the memory to hold recently used
instructions and data.
Primary memory
has a large but limited capacity to store information
and contents disappear when the power is turned off. S
Secondary memory
holds information even when the power is off.
Moore's Law
The logical structure of computers has not changed much since the 1940s, but the physical
construction has changed enormously.
• Moore's Law - describes an exponential decrease in the size and price of individual components
and an exponential increase in computational power for a given amount of space and money.
How does the processor work? What does it
process and how?
do arithmetic—add, subtract, multiply and divide numbers, like a calculator.
• fetch data from the memory
• store results back into the memory,
• controls the rest of the computer - coordinate input/output for devices, including mouse, keyboard,
display.
• make simple decisions – compare numbers (“<“, “>” , “=“) or compare information
• decide what to do next based on the outcome
Turing Test
One method of determining the strength of artificial intelligence, in which a human tries to decide if the intelligence at the other end of a text chat is human.
Memory Hierarchy
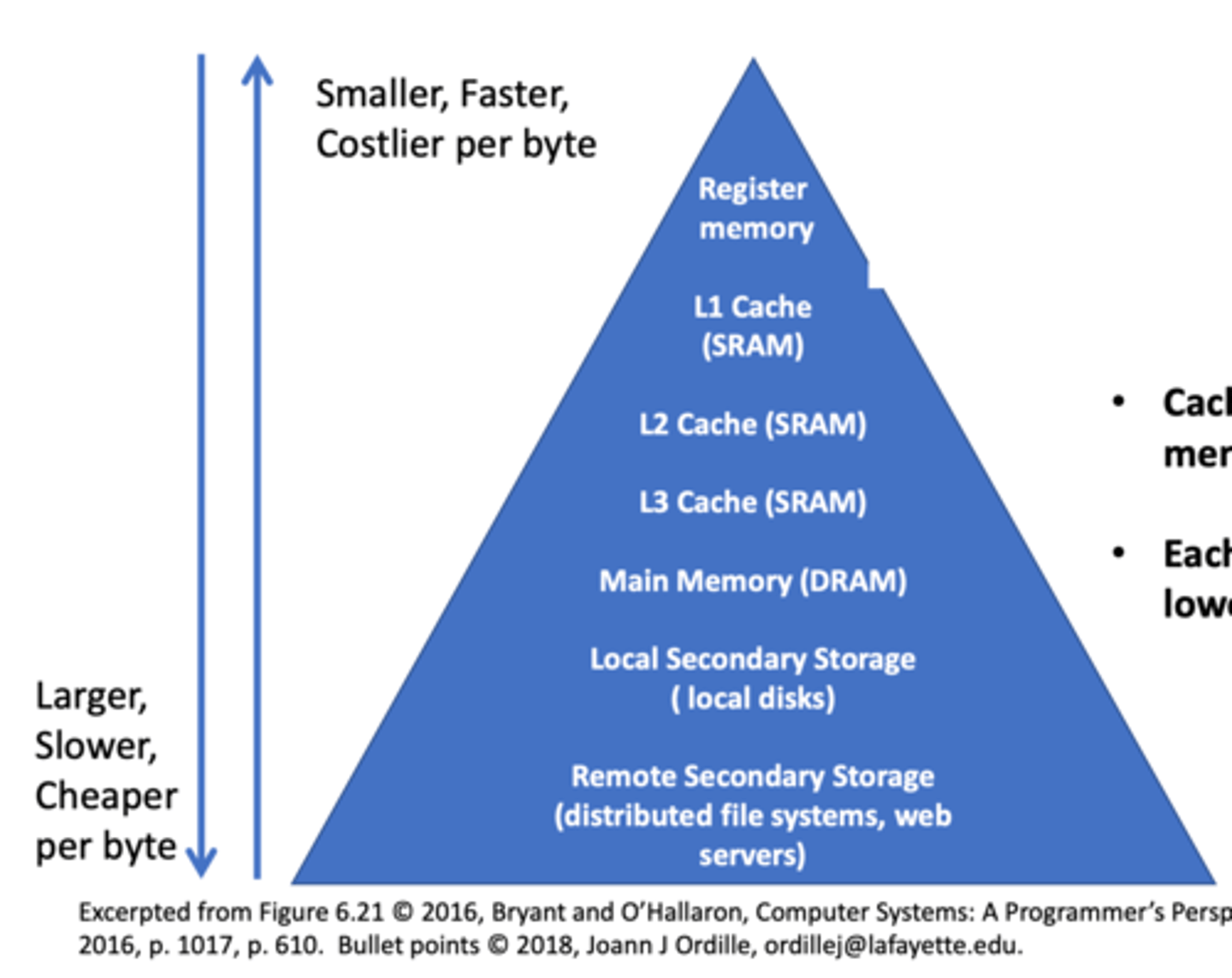
Memory levels
• hold programs and information the processor is
currently using.
• fast and flexible and are typically based on
semiconductor technology.
Storage levels
• preserve data and programs for future use.
• have to be big, permanent, and affordable and
predominantly employ magnetic technology.
Caches work because of spatial and temporal
locality in programs
• Temporal locality: locations that are referenced are
likely to be referenced again
• Spatial locality: locations near a referenced location
are also likely to be referenced
• "Programs with good locality run faster than
programs with bad locality."
Supercomputers:
Computers that are among the fastest of any in the world at the time of their introduction.
A Graphics Processing Unit or GPU
-A special-purpose CPU chip whose hardware is specially designed for fast graphics and video processing.
-Many computers, laptop, tablets, and smartphones today come with built-in graphics processors.
Distributed computing
• Refers to computers that are more independent—they don't share
memory, they may be physically more spread out, even located in
different parts of the world.
• Large-scale web services used for online shopping, social networks, and
cloud computing (e.g. Amazon, Google search engine)