NCEA Level 3 Biology - Human Evolution
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Broca's area
Brain area for speech development
Cerebellum
Part of brain for Balance and coordination
Teeth/Jaw shape in quadrupedes
U shape
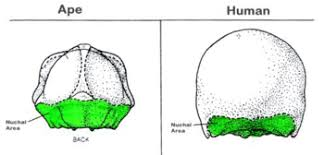
Nuchal crest and it’s differences
Bony ridge across back of skull where muscles supporting head are attached. Well defined in quadrupeds. Reduces in bipeds
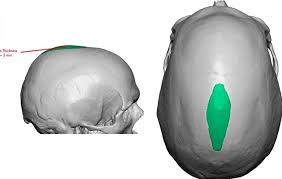
Sagittal crest and differences
Ridge running lengthwise along top of skull where jaw muscles are attached. Well defined in quadrupeds. Reduced in bipeds.
Spine shape in quadrupeds
C-shaped
Valgus angle in bipeds
Angle formed by the femur with pelvis allowing knees to be closer than hip joints. Allows to have knees under centre of gravity
Arched foot
Shock absorbing property
Non-divergent big toe purppose
Gives thrust in walking
A. afarensis
“Lucy”
4-3.0 mya
Chimpanzee-like skull
more human-like teeth
human-like pelvis and thigh bones
stood 1.5m
385-450cc brain size
Occipital bun
Bulge at lower rear of skull
Diastema
Gap between incisors and canines
Upper palaeolithic
Made by H. sapiens, finely worked stone, bone carved into needles and hooks, carved wood, used more than one material in a tool (composite)
Oldowan
Produced by H. habilis, small flakes knocked off stone cobbles, used for hammering, chopping, digging. Flakes used as knives
Acheulean
Made by H. ergaster and H. erectus, symmetrical teardrop shapes, bifacial (flakes detached from both surfaces) digging roots, chopping wood, butchering animals, hand-axes
Mousterian
Made by H. neanderthalensis,
finely-worked, sharp edged flakes.
Made using Levalloi method
Cooperative hunting
Levallois method
refers to a strategy of stone-tool production, specifically a means of taking a block of stone (core) and producing sharp - edged flake tools through percussive application of a stone hammer
Biological evolution
Passing down of genetic information
Multiregional theory
H. erectus migrated out of Africa, into Europe and Asia. Each population evolved in parallel with some interbreeding. Evidence: Fossils with transitional forms
Out of Africa theory (Replacement theory)
H. erectus migrated into Europe and Asia.H. sapiens who evolved in Africa migrated and replaced H. erectus. Evidence: analysis of mtDNA and y-chromosome, H. sapiens skull found in Africa
mtDNA
DNA passed from mother to child, mutations occur at a steady rate
Foramen magnum
The name for the hole in the base of the skull, through which the spinal cord passes
Hominin
Living and fossil species belonging to human and bipedal ancestors
Wernicke's area
The brain centre responsible for interpreting speech
Cultural evolution
The type of evolution where things are taught/learned between and within generations, and not passed on in the DNA
Tools better, use of shelter, abstract thought, imagination, domestication of plants/animals
Positive feedback between biological and cultural evolution
Shape of pelvis in bipedal organisms
Bowl shaped
larger for glute muscles to lift leg
Holds organs while upright
Lower Palaeolithic
The name for the culture that included the Oldowan and Acheulian together
Upper Palaeolithic
The later phase of the Old Stone Age
Brow ridge and differences
Heavy bone over the eye which reduces the stresses in the skull and lower jaw involved with chewing. Large in quadrupeds. Small in bipeds
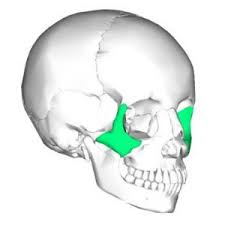
Zygomatic arch and differences
Gap through which large jaw muscles pass through, also known as cheekbone. Large in quadrupeds. Reduced in bipeds.
Mitochondrial DNA
mtDNA passed on from mother to daughter only.
Effect of cooking
Kills bacteria, softens food, supports change in jaw structure.
Effect of H.erectus discovering fire
Cooks food
hardens tools
lengthens day
kept warm
keeps predators away
Sexual dimorphism
Name for the differences observed between male and female skeletons
Bipedal feet characteristics.
Forward facing big toe, arched, big toe attached
Power grip
Type of grip used by all primates
Precision grip
Type of grip used by humans only
Shorter pelvic advantages
Stronger, able to tilt and rotate during walking
Arboreal
Living in trees
Shape/dental arcade of jaw of bipedes
V- shaped Jaw
Middle Palaeolithic tools
Mousterian and scrapers axe heads
Domestication
Deliberately managing the reproduction of a species of plant or animal to make use of it for human benefit
Nomadic
A population with no fixed home.
Knuckle Walking
A form of quadrupedal locomotion in which the body weight of the individual pushed down on the ground with its knuckles
Brachiating
Locomotion accomplished by swinging by the arms from one hold to another
Cranium
The part of the skull the encompasses the brain
Mandible
The lower Jaw or jawbone
Hunter-gatherer
Populations who were nomadic who would forage wild plants foods and actively hunt animals
Early Farmer
Populations who would live in settled societies, these groups cultivated crops and domesticated animals
Effect of Art
Imagination
Other ways of communication
Better mental wellbeing
Showed some spirituality
Hominids
A group term referring humans and great apes
Spine shape in bipeds
S-shaped
Rib cage shape in quadrupeds
Flattened side to side, wide rib cage
Rib cage shape in bipeds
Flattened back to front, narrow rib cage
Shape of pelvis/ pelvic girdle in quadrupeds
long and narrow
Valgus angle in quadrupeds
No valgus angle, femur is straight under hip joint. “swagging” motion when walking bipedal
Femur size in quadrupeds
short and thick
Femur size in bipeds
Long
Arms in quadrupeds
longer for walking on all fours and swinging
Arms in bipeds
shorter - no tree swinging
Knee joint in quadrupeds
No buttress
Knee joint in bipeds
Buttresses that prevents sideways sliding of joint
Hands in quadrupeds
Larger fingers
Short thumbs
Curved fingers
Power grip
Hands in bipeds
Shorter fingers
Long thumb
Straight fingers
Precision grip
Feet in quadrupeds
Opposable big toe - tree swinging
Flat feet
Feet in bipeds
Forward facing big toe
Arched feet
What does larger cerebrum mean
memory and decision making
Neolithic tools
hunter-gatherer to domestication of plants and animals
Effect of making shelters
Safety, warmth, protection
Stay in one place, therefore allows farming
Effect of making clothes
Enables to live in different conditions
Effect of communication
learn from others
cooperation during hunting
Positive effects of domestication
Easy food source
Allows for trade
Allows permanent settlement
More time available as less time hunting/gathering
use animals for hard labour
negative effects of domestication
restricted to “what” available “when”
Attracts insects and rodents, therefore disease
Conflicts
weather dependent
OAMUPN mnemonic
For tool cultures
Olodowan
Achulean
Mousterian
Upper Paleolithic
Neolithic
HEENS mnemonic
for Homo groups
Habilis
Ergaster
Erectus
Neanderthalensis
Sapien