labour at risk
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
complications during labour
increases chances of mother and baby dead
may be excepted or happen unexpectedly
what does caring for high risk clients
understand the normal birth process
prevent and detect deviations from north labour and birth
implement nursing measures if complications arise
what happens in preterm labour
cervical changes with uterine contractions occuring between 20-37 weeks
which age group has higher risk of preterm labour
pt. younger than 18
younger adolescents still developing and premature
pt older than 35
elasticity of collagen impacts cervical dilation and cervix opens too early
prevent this by cervical curettage
what is preterm birth?
any birth occuring before 37 weeks completion of pregnancy regardless of weight
what are some risk factors
history of previous spontaneous preterm birth between 16 and 36 weeks of gestation
family history of preterm labour
africian descent
genitial tract infection
uterine anomaly
womens uterus develops abnormally at birth
use of assisted human reproduction
cigar smoking, substance misuse
peridontal disease
gum infection
bleeding of uncertain origin in pregnancy
low prepregnancy weight
low socioeconomic status
lack of access to prenatal care
high levels of personal stress in one or more domains in life
what causes preterm labour?
infections
vaginal bleeding
hormone changes
stretching of the uterus
signs and symptoms of preterm labour?
uterine activity
discomfort
vaginal discharge
what does uterine activity refer to
contractions more often than every 10 mins, lasting an hour
painful or painless
what type of discomfort
Lower abdominal cramping similar to gas pains; may be accompanied by
diarrhea
dull, intermittent low back pain
painful, menstrual like cramps
suprapubic (lower part of belly) pain or pressure
what changes do you see in vaginal discharge
any change in vaginal discharge
thicker and thinner
bloody, brown, clear, watery
unusual smell
come in larger amount than usual
how to predict preterm labour and birth
fetal fibronectin test
cervical length less than 30mm risk for preterm labour
combination of both better
what are the three main signs used to diagnose preterm labour?
gestational age between 20 and 36 6/7 weeks
regular contractions with cervical change
regular contractions and cervical dilation of 2cm or greater
what is the main goal of nursing care for preterm labour
prevention from starting labour too early
what is preconception counselling ?
talking to women before pregnancy about ways to stay healthy and lower the risk of preterm birth.
what should be done during prenatal care to prevent preterm labour
Manage risk factors (like infections, alcohol smoking, stress).
Promote good nutrition and regular exercise.
Encourage stress management and healthy habits
what can be given to decrease the rate of preterm birth and labour?
prophylactic progesterone- daily vaginal suppositories or creams and weekly intramuscular injections
why give progesterone?
preserve excitement/contractions of uterus to get it to relax
what is used to supress uterine activity?
tocolytics
used to supress labour
what are some common types of tocolytics?
nifedipine
indomethacon
magnesium sulphate
nitroglycerin
contraindications of tocolytics - maternal
severe pre-eclampsia or severe gestational diabetes
significant vaginal bleeding
intrauterine infection (chorioamnionitis- infection of amnotic sac)
cardiac disease
medical or obsterical condition that contraindicates continuation of pregnancy
contradindications of tocolytics- fetal
gestational age of 37 weeks or more
fetal demise
stillbirth
lethal fetal anomaly
birth defect that results in baby no surviving after birth
acute or chronic fetal compromise
not getting enough oxygen in womb
what is given to promote fetal lung maturity before preterm birth?
antenatal glucocorticoids
how do antenatal glucocorticoids help the baby?
speed up fetal lung development by stimulating surfactant production
why is surfactant production important
keeps the baby air sac open after birth, helping the baby breathe
why is magnesium sulphate used in inevitable preterm birth?
to protect baby brain and reduce risk of neuro problems such as cerebal palsy
what should be explained to pt. and family when giving tocolytic therapy?
purpose is to stop/slow contractions and the possible adverse effects
what postion should the pt be in when giving tocolytic therapy
lateral position to enhance improve blood flow to placenta and reduce pressure on cervix
what should be assessed during this time
vital signs
lung sounds
resp effort
fetal HR
pattern
labour status
frequency and strength of contractions
assess labour pt. and fetus for signs of adverse reactions
measure intake and output
provide pyschosocial support to pt and family
what to do with early symptoms for preterm labour
bedrest
empty bladder
drink 2-3 glasses of water or jucie
enhance blood supply
lie on side for 1 hour
palpate contractions
what to do if your symptoms still continue?
call HCP and go to hospital
what to do if symptoms go away
resume light activity but not what you were doing before symptoms arised
what to do if symptoms return?
call HCP or go to hospital
for what symptoms should u call HCP or go to the hospital immediiatley?
uterine contractions every 10 mins for 1+ hour
vaginal bleeding
leakage of amnotic fluid
what is PROM?
spontaneous rupture of amniotic sac and leakage of amniotic fluid that starts before labour at any gestational age
what is pPROM
rupture of membranes before the complication of 37 weeks of gestations
what are the risk factors for PROM
history of prior preterm birth, esp if associated w/ preterm PROM
history of cervical surgery or cerclage
urinary or gential tract infection
short ( less than 25mm) cervical length (noted on transvaginal ultrasound)
preterm laboyr or symptomatic contractions in current pregnancy
uterine overdistension
overstretched
second and third trimester bleeding
pulmonary bleeding
connective tissue disorder
low socioeconomic status
low body mass index
nutritional deficiency
smoking
what two nutritional deficiencies
copper
ascorbic acid
what does care depend on
based on risk of maternal, fetal and newborn complications
what to do for term pregnancy?
induction of labour
how is PROM managed at 34-36 weeks?
conservative management (watch and wait) if low risk for intrauterine infection
how is PROM managed before 32 weeks
Expectant/conservative management to allow fetal lung maturity and reduce preterm complications, unless contraindicated.
when is expectant/conservative management NOT recommended
if is there
intrauterine infection
significant vaginal bleeding
placental abruption
advanced labour
atypical or abnormal fetal assessment
how is fetal health assessed in preterm PROM
using NST, BPP to check fetal wellbeing and amniotic fluid volume
what meds are given for preterm PROM?
Antenatal corticosteroids
24–34+6 weeks) → accelerate fetal lung maturity
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
7-day course to prevent infection
(e.g., ampicillin/amoxicillin + erythromycin)
Magnesium sulphate
(<34 weeks) → fetal neuroprotection
how should fetal movement be monitored?
Patient should count fetal movements daily.
Expect 6 movements in 2 hours.
If fewer, further testing (NST, BPP, or both) is needed.
what infection sign should be reported to HCP immediatly?
foul smelling vaginal discharge
maternal and fetal tachycardia
what hygiene instructions should be given to pt.
Keep the genital area clean
Nothing should be introduced into the vagina
maternal complications of PROM?
chorioamnitoitis-bacterial infection of the amniotic cavity
placental abruption
retained placenta and hemorrhage sepsis and death
How is chorioamnionitis diagnosed
maternal fever
maternal and fetal tachycardia
uterine tenderness
foul odour of amnitiotic fluid
what factors increases the risk of chorioamniotiis?
prolonged membrane rupture
multiple vaginal exams
use of internal FHR and contraction monitoring modes
young maternal age
low socioeconomic status
no to minimal prenatal care
nulliparity
pre-exisiting infections of the lower genital tract
what is the management for chorioamniotiis?
IV broad spectrum antibotics (ampicillin or penicillin and gentamicin)
What additional antibiotics may be given after cesarean section?
Clindamycin or metronidazole (Flagyl)
what are the fetal complications of PROM?
intrauterine infection
cord prolapse and umbilical cord compression associated with oligohydramnios
cord comes out faster than babys head
pressure on umblical cord, does not get enough blood supply, end up with hypoxemia
what is post term pregnancy?
pregnancy that goes beyond the end of week 42 of gestation or more than 294 days from the first day of the LMP
what are the risk factors for post term preganancy?
first pregnancy
prior post term
male fetus
obesity
genetic predispostion
what are maternal risks for post-term pregnancy?
labour dystocia
severe perineal injuries
chorioamnionitis
endomyometritis
inflammation of outer layer, muscular uterus d/t infection
postpartum hemorrhage
ceasarean birth
anxiety
risk of morbidity during intrapartum period
fetal risks of post term pregnancy?
macrosomia
risk w/ mothers w/ GDM
small for gestational age
shoulder dystocia
birth tramua
aphyxia
deprieved of oxygen
oligohydramnios
cord compression
abnormal HR
aging placenta
can apply support until 42 weeks, then worse supply
stillbirth
meconium-stained amniotic fluid, meconium aspiration
baby stool in amnotic fluid, baby breathes of causing resp problems
low apgar scores
convlusion in newborn
seziures
when does antepartum fetal assessment begin for post-term preganancy?
beginning at 41 weeks of gestation
what tests are included in antepartum fetal assessment
Daily fetal movement counts
Nonstress tests (NSTs)
Amniotic fluid volume (AFV) assessments
Contraction stress tests
Biophysical profiles (BPPs)
Doppler flow measurements
what should patients do for daily fetal monitoring at home?
Count fetal movements daily
Watch for signs of labour
Call healthcare provider if:
Membranes rupture
Fetal movements decrease or stop
Why are appointments for fetal assessment and cervical checks important?
To monitor fetal well-being and detect complications early.
when is birth reccomeneded for post-term preganancies
By 42 weeks and no later than 42 + 6 weeks
This reduces risk of perinatal morbidity and mortality
what is dystocia
abnormally slow progress of labour
difficult, does not follow normal delivery
how slow is the progress of labour for dystocia?
greater than 4 hours of less than 0.5 cm per hour of cervical dilation in active labour OR
greater than 1 hour of active pushing with no descent
how does powers affect dystocia?
ineffective uterine contractions or bearing-down efforts(pushing effects of mother)
most common cause
how does passageway affect dystocia?
CHANGE IN SHAPE OF PELVIS
changes in pelvic structure, abnormalities of labouring patient’s bony pelvis or soft tissue abnormalities of reproductive tract
how does passanger affect dystocia?
fetal causes, abnormal presentation or position, anomalies (abnormalities or defects in baby),
transverse/oblique/breech → not good
cephallic→ good
how does position affect dystocia?
postion of patient during labour or birth
supine, standing, squatting?
how does psychological reponse affect dystocia?
past experiences, prep, culture, heritage, support system
supportive care for dystocia?
supportive care by nurse
health care team approach
electronic fetal monitoring
ultrasonography to identify potential labour complications related to fetus
abnormal fetal position
pelvis of pregnant patient
risk assessment is continous process to identify dysfunctional labour
prevention
interventions for dystocia
external cephalic vision
move pt. from breech to cephaliac
cervical ripening
put foley in vagina with balloon, if cervix dilates, it will fall out
induction or augmentation of labour
operative procedures
c-section
what are complications of labour dystocia?
fetal distress
risk of maternal and neonatal infections
postpartum hemorrhage
uterine rupture
increased risk of pelvic floor, gential, perineal tramua
increased risk of uterine or pelvic organ prolapse
increased risk obsterical fistula (vesico-vaginal or rectovaginal fistula) and incontinence
abnormal opening, feces or urine comes through vagina
sacroiliac joint dislocation
connects pelvis to spine
prolapsed umbilical cord?
descending part of baby puts pressure on cord → lack of blood supply and o2
cord sneaks out before baby
how do u know of a cord prolapse when doing a vag exam?
feel the skull pulsating
umbilical cord prolapse patho
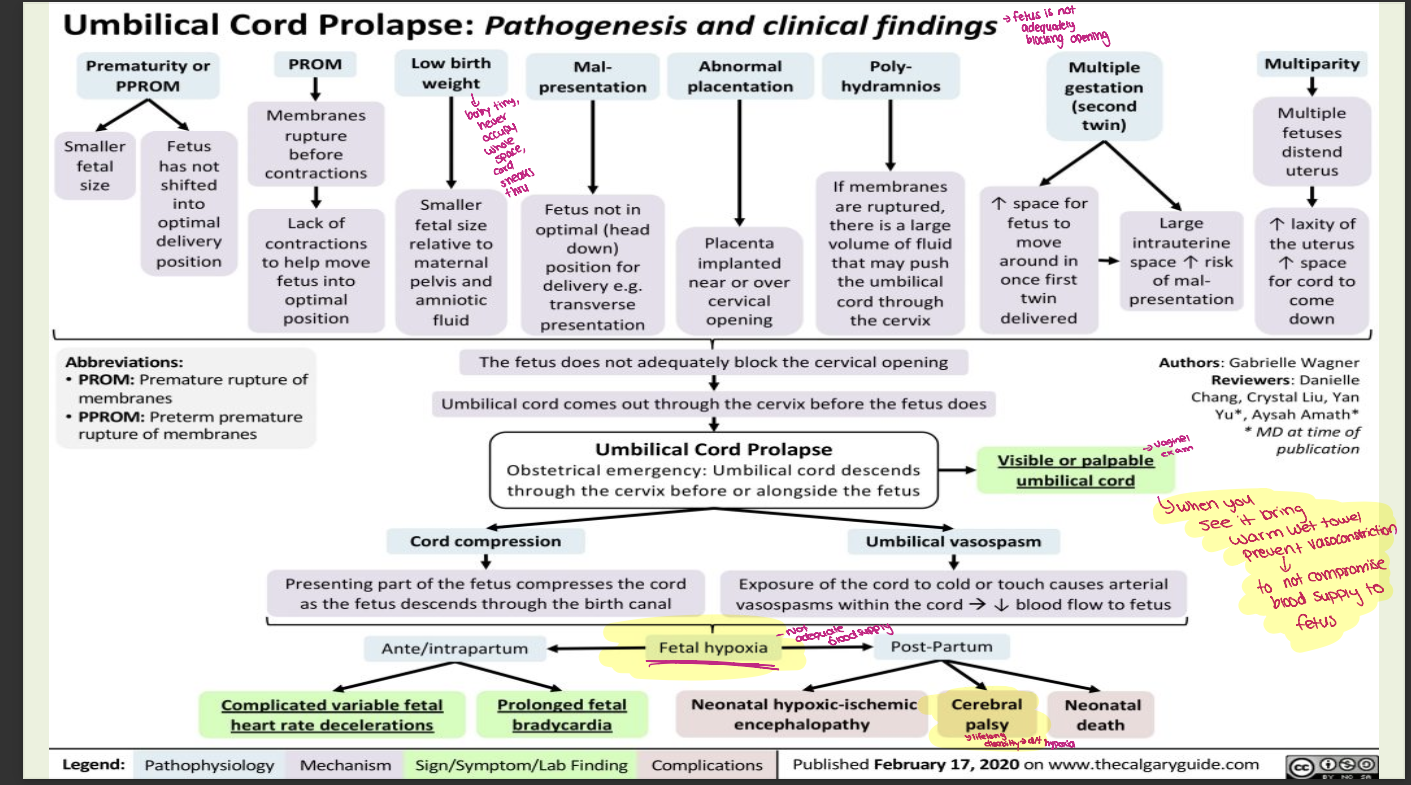
What is the main goal in managing umbilical cord prolapse
To relieve pressure on the umbilical cord and maintain fetal oxygenation until delivery (usually by C-section).
What immediate position should the client assume to relieve cord compression?
Knee-to-chest position or Trendelenburg position to use gravity to lift the presenting part off the cord.
What manual intervention can be done by the healthcare provider?
Manual decompression
using a gloved hand to gently elevate the presenting fetal part off the cord until proper cervical dilation.
What should be done if the umbilical cord is protruding from the vagina?
Keep the cord warm and moist (using sterile saline-soaked gauze) to prevent vasospasm and further compromise of blood flow.
warm wet towel?
What medication may be used to reduce uterine contractions?
A tocolytic (e.g., terbutaline) can be administered to slow contractions and reduce pressure on the cord.
What are warning signs that may indicate a cord prolapse
A sudden gush of fluid followed by a feeling of vaginal pressure or fullness.
What should the patient do if they suspect a cord prolapse before help arrives?
Immediately assume a knee-chest position and call for emergency assistance—do not attempt to push the cord back in.
Why is maintaining pressure off the cord critical?
Compression of the cord decreases fetal blood flow and oxygen supply, risking fetal hypoxia and death.
what do u do if if cervix is not fully dilated or risk of
fetal compromise is high?
c-section
what is shoulder dystocia?
head is born but anterior shoulder cant pass under pubic arch
what causes shoulder dystocia?
fetopelvic disproportion caused by excessive fetal size
more than 4000g
macrosomia
pelvic abnormailities
mother has small pelvis
prolonged second stgae of labour
history of shoulder dystocia with previous birth
what are the two first-line interventions for shoulder dystocia?
McRoberts maneuver
suprapubic pressure
gaskin manoeuvre
what is McRoberts maneuver
legs are hyperflexed on abdomen
legs to chest
suprapubic pressure-applied over anterior shoulder
fundal pressure should be avoided
apply pressure to pelvis not the uterus
what is the gaskin manoeuvre?
place patient in all positions with hands and knees postion
what are the complications of shoulder dystocia
brachial plexus (erb palsy), phrenic nerve injuries
fracture of humerus or clavicle
asphyxia
baby not getting enough oxygen
what is amniotic fluid embolism (AFE)
amniotic fluid leaks into the circulation(bloodstream) of labouring patient during labour, during birth, within 30 mins after birth,
what 3 things happen when AFE happens?
resp distress
circulatory collapse
hemorrhage
what happens in resp distress?
restlessness
dyspnea
cyanosis
pulmonary edema
resp arrest
what happens in circulatory collapse?
hypotension
tachycardia
shock
cardiac arrest
what happens with hemmorhage
Coagulation failure
DIC
Uterine atony
uterus fails to contract after delivery
mortality rate is 61% or higher
what are the risk factors?
advanced age
non-White race
placenta previa
pre-eclampsia,
forceps-assisted or Caesarean birth
what to do for AFE?
oxygenate
maintain cardiac output and replace fluid loss
adminster IV fliods
adminster blood; packed cells, fresh frozen plasma
insert cathether and measure hourly urine
correct cogulation failute
monitor fetal and maternal status
prepare for emergency birth once patiennt condition has stabilized
provide emotional support
how should the patient be oxygenated
non-breather face mask 10L.min or resuscitation bag delivering 100% oxygen
prepare for intubation and mechanical ventilation
intiate or assist CPR
tilt pregnant patient 30 degrees to side to displace uterus
how should the patient be position
on their side