ECON Unit 2 Microeconomics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Microeconomics
Branch of economics that deals with behavior and decision making by individuals, businesses, and household
Demand
The amount of a product that consumers desire and are willing and able to buy at certain prices
Demand involves the relationship between price and quantity
Law of demand
All other things being equal
An increase in price causes a decrease in the quantity demanded
Decrease in price causes an increase in the quantity demand
Inverse relationship between price (P) and quantity (Q).
Demand schedule
Table that lists the quantity of a product that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices
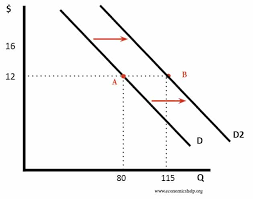
Demand curve
Plots information from demand schedule
Change in Quantity Demand
Caused only by change in price of product
Prices of products changes, but still using original demand schedule
Income effect (Change in Quantity Demand)
When price of produce decreases, people demand more because we can afford to buy more without giving up something else, feels like our income is giving farther, even if it hasn’t change,
Purchasing power (Change in Quantity Demand)
Amount of money we have available to spend on products (decline in prices increases purchasing power)
Substitution effect (Change in Quantity Demand)
When price increases, people buy less of that product in favor of a cheaper substitute
Change in demand (itself)
Price stays the same, but something happens that creates a whole new demand schedule (and causes) at every price (something other than price that caused the change)
Income (Change in Demand)
More income = more demand (and vice versa)
Number of consumers (Change in Demand)
Larger market = more demand (and vice versa)
Expectations (Change in Demand)
Our expectation of a price change in future, or something new coming out in the future
Price of related goods (Change in Demand)
Substitutes: Similar good replacing higher price goods (substitute price decrease, demand for our product increases, vice versa)
Complements: Goods commonly used with each other (competition product price increases, demand for competition decreases, vice versa)
Taste (Change in Demand)
What consumers like and dislike
Affected by ads, trends, news, holidays, seasons, etc
Elasticity of demand
Degree to which a change in price affect the quantity demand
Elastic (Elasticity of demand)
When small change in price causes major, opposite change in amount of demand (wants)
Inelastic
When change in price has little impact on amount demanded (needs)
Diminishing Marginal Utility
The last item consumed will be less satisfying than the 1 before.