CompTIA A+ 220-1201 (4.1 - Virtualization Services)
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
The hypervisor
• Virtual Machine Manager
- Manages the virtual platform and guest operating systems
• May require a CPU that supports virtualization
- Can improve performance
• Hardware management - CPU, networking, security
Virtualization
• Run many different operating systems on the same hardware
• Each application instance has its own operating system
- Adds overhead and complexity
- Virtualization is relatively expensive
Hypervisor types
• Type 1: Bare metal
- The hypervisor is the primary operating system
- VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, Xen Project
• Type 2: Hosted
- Hypervisor runs in the existing OS
(Windows, Linux, macOS, etc.)
- Virtual machines run on top of the current OS
- VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox,
Parallels Desktop

Resource requirements
• CPU Processor Support
- Intel: Virtualization Technology (VT)
- AMD: AMD-V
• Memory - Above and beyond host OS requirements
• Disk space - Each guest OS has it's own image
• Network
- Configurable on each guest OS - Virtual switch
Network requirements
• Most client-side virtual machine managers have
their own virtual (internal) networks
• Shared network address
- The virtual machine shares the same IP address as the physical host
- Uses a private IP address internally
- Uses NAT to convert to the physical host IP
• Bridged network address
- The VM is a device on the physical network
• Private address
- The VM does not communicate outside of
the virtual network
Hypervisor security
• Hypervisor is a sweet spot for the bad guys
- No significant vulnerabilities yet
• VM escaping
- Malware recognizes it's on a virtual machine
- Malware compromises the hypervisor
- Malware jumps from one guest OS to another
• Many hosted services are virtual environments
- Malware on one customer's server can gather information from another
Guest operating system security
• Every guest is self-contained - Like a real computer
• Use traditional security controls
- Host-based firewall, Anti-virus, anti-spyware
• Watch out for rogue virtual machines (VMs)
- The bad guys try to install their own system
- You're in big trouble
• Self-contained VMs provided by 3rd parties
can be dangerous
- You have no idea what's running on there
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
• Basic application usage
- Applications actually run on a remote server
- Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
• Minimal operating system on the client
- No huge memory or CPU needs
• Network connectivity - Big network requirement
- Everything happens across the wire
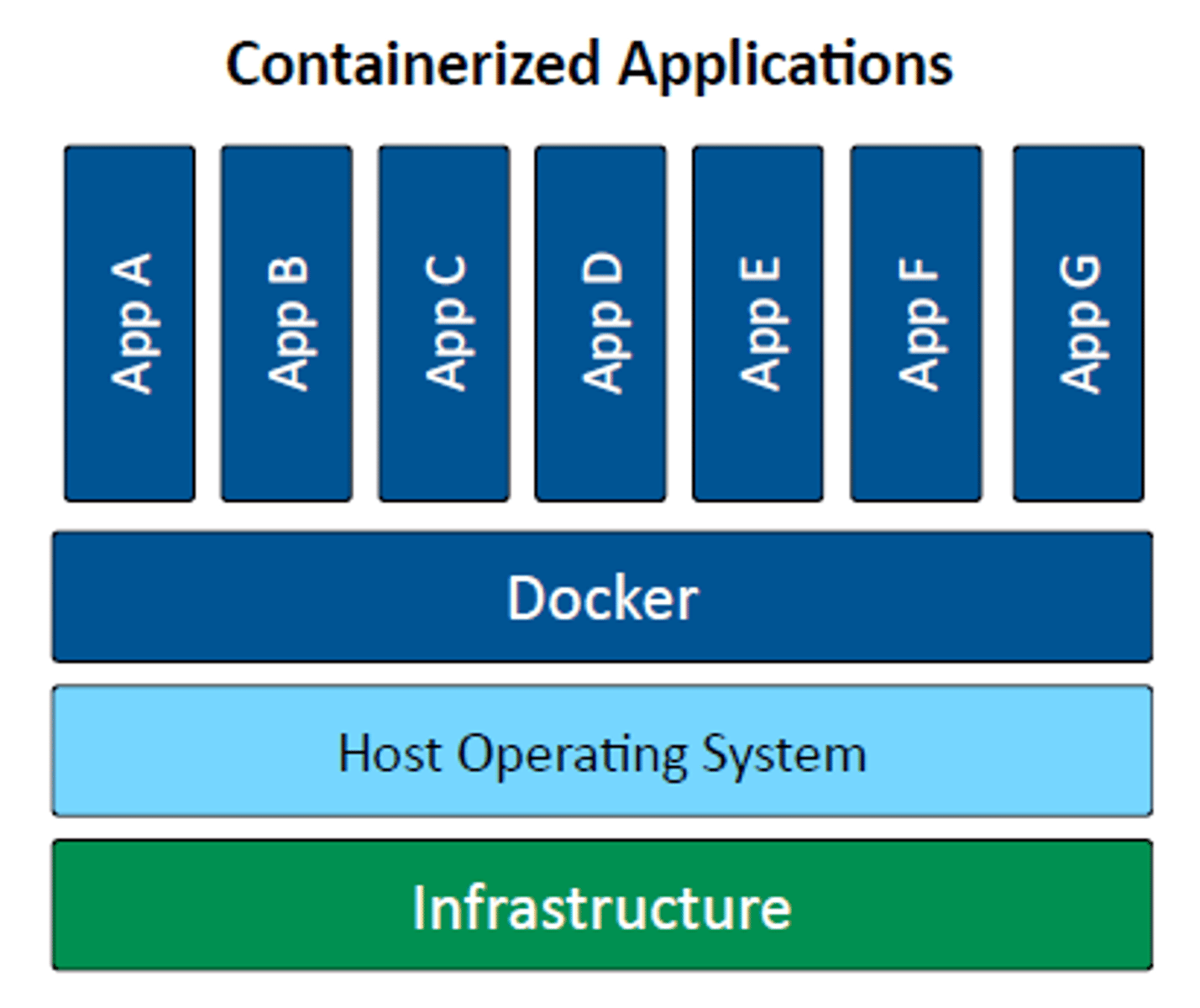
Application containerization
• Container
- Contains everything you need to run an application
- Code and dependencies
- Standardized unit of software
• Isolated process in a sandbox
- Self-contained
- Apps can't interact with each other
• Container image
- A standard for portability
- Lightweight, uses the host kernel
- Secure separation between applications