Bio 111 lecture 15
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Translation is when info in a(n) ____ is translated into a(n) _______.
mRNA, protein
what are the three components necessary for protein synthesis/translation?
mRNA that contains a genetic code
ribosomes
transfer RNAs(tRNAs)
what is the genetic code?
a series of codons on an mRNA
what is a codon?
a sequence of 3 nucleotides
what are the possible functions of a codon?
specify an amino acid
signal translation start/stop
why is it important for codons to signal start and stop of translation?
because mRNAs have 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions
how many different codons are there?
64
is the genetic code universal in all organisms?
yes nearly
why is the genetic code degenerate/redundant?
because it has 64 codons and only 20 amino acids, so some amino acids have more than one codon
how many start codons does the genetic code have?
one
how many stop codons does the genetic code have?
three
what is the start codon?
AUG → Met
what are ribosomes?
enzyme complexes that translate info in mRNAs into proteins(carry out protein synthesis/translation)
what are the two subunits of a ribosome?
large ribosomal subunit
small ribosomal subunit
what is each subunit of a ribosome made up of?
ribosomal proteins and ribosomal RNAs
which subunit is responsible for positioning of the mRNA?
small
what subunit is responsible for binding tRNAs
both large and small
what subunit is responsible for peptide bond formation?
large
what subunit is responsible for recognition of stop codon and protein release?
large
what does release factor signal to release?
the end protein of translation
what are ribozymes(rRNAs)?
RNA molecules that catalyze reactions
what do tRNA molecules do?
carry amino acids to the ribosome
does an uncharged tRNA molecule have an amino acid attached?
no
does a charged tRNA molecule have an amino acid attached?
yes
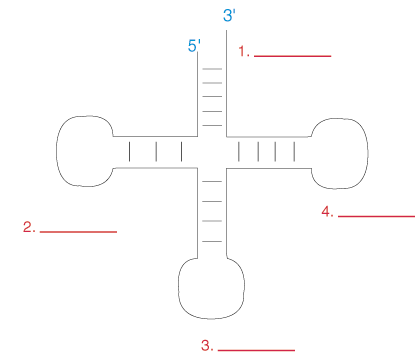
what is number one?
acceptor stem
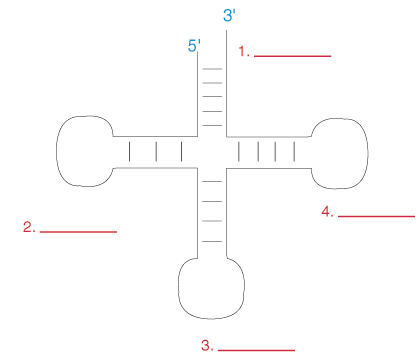
what is this a picture of?
tRNA
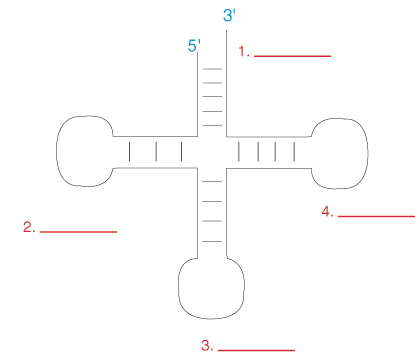
what is number three?
anticodon loop
what binds to the acceptor stem of tRNA?
amino acid
the anticodon associates with the codon through __________?
complementary base pairing
what type of bond is formed between the acceptor stem and amino acid?
aminoacyl
what do aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS) enzymes bind to?
an amino acid
an ATP
an uncharged tRNA
how many different aaRS enzymes are there?
20(one for each AA)
what are the three phases of translation?
initiation
elongation
termination
what happens during initiation?
assembly of the ribosome/mRNA/initiator-tRNA
what happens during elongation?
starts at the start codon, AAs are added until the stop codon
what happens during termination?
the new protein is released and the ribosome complex dissolves
what are the steps of prokaryotic initiation?
initiator and tRNA bind to the start codon
large subunit joins
what are the steps of eukaryotic initiation?
small subunit and initiator tRNA bind to mRNA 5’ cap
complex scans for start codon on the mRNA
large subunit joins