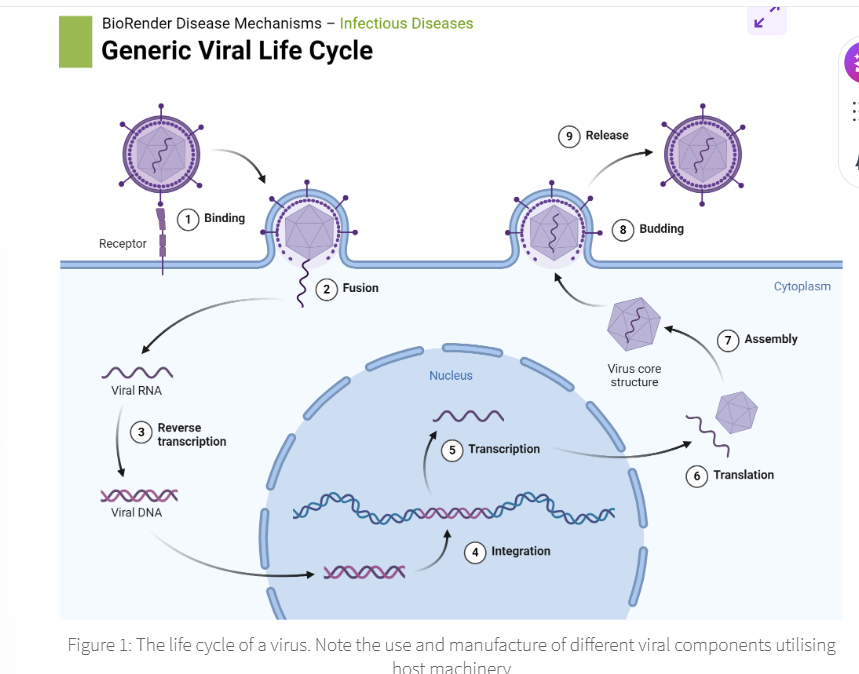
4.0 Virology: structure, function and classification into RNA/DNA viruses
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
viruses
small obligate intracellular parasites which contain nucleic material surrounded by a protective virus coded protein coat
viruses are simple acellular and present with a distinct pattern of multiplication
viruses may be viewed as mobile genetic elements
viruses are dependent on a cellular host such as mammalian, plant or bacterial cells
for propagation with host cells supplying the complex metabolic and biosynthetic machinery required
viruses are specific to a particular cell type
with different viruses requiring different specialised cellular machinery
virion
complete virus particle
main function of a virion
to deliver its genome into the host cell so that the genome can be expressed (transcribed and translated) by the host cell
the viral genome often associated with basic proteins
is packaged inside a symmetric protein capsid
nucleoprotein
the nucleic acid associated protein
nuceleoprotein + genome
→ nucleocapsid
in elveloped viruses the nucleocapsid is surrounded by a lipid bilayer
derived from the modified host cell membrane and studded with an outer layer of virus envelope glycoproteins
viruses are inert outside the host cell
small virruses (polio/ tobacco mosaic virus) can be crystalized
as obligate intracellular parasites
they fully depend on the machinery of their host cells for replication
therefore the main function of a virus is to
deliver its genome into the host cell to allow its expression (transcription + translation) by host cells
virion
fully assembled virus
basic components of a virion
nucleic acid
capsid
envelope
nucleic acid
single/ double stranded RNA/DNA
capsid protein coat
coded for by the viral genome which functions as a shell to protect the viral genome form nuclease
during infection the capsid protein coat…
…attaches the virion to specific receptors exposed on the protective host cell
envelope, not univeersal to all viruses
consists of a lipid bilayer that closely surrounds a shell of virus envoded membrane associated proteins
the exterior envelope bilayer is studded with virus coded glycosylated (trans) membrane proteins
therefore enveloped viruses often exhibit a fringe of glycoprotein spikes or knobs AKA poplomers
in viruses that acquire their envelope by budding through the plasma or another intracellular cell membrane
the lipid composition of the viral envelope closely reflects that of the particular host membrane
The outer capsid and the envelope proteins of viruses are glycosylated
this is important in determining the host range and antigenic composition of the virion.