Anatomy & Physiology: Chapter 3 - The Cell
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Cell Metabolism
all the chemical reactions a cell does to stay alive; includes anabolic, catabolic, and oxidation-reduction reactions
Anabolic Reactions (cell metabolism)
build bigger molecules using energy
Catabolic Reactions (cell metabolism)
break molecules down to release energy
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (cell metabolism)
transfer energy by moving electrons between molecules
Substance Transport
moving compounds into, out of, or within a cell
Communication
cells communicate with themselves, with their surrounding environment, and with other cells in the body
Cell Reproduction
many cells undergo cell divison
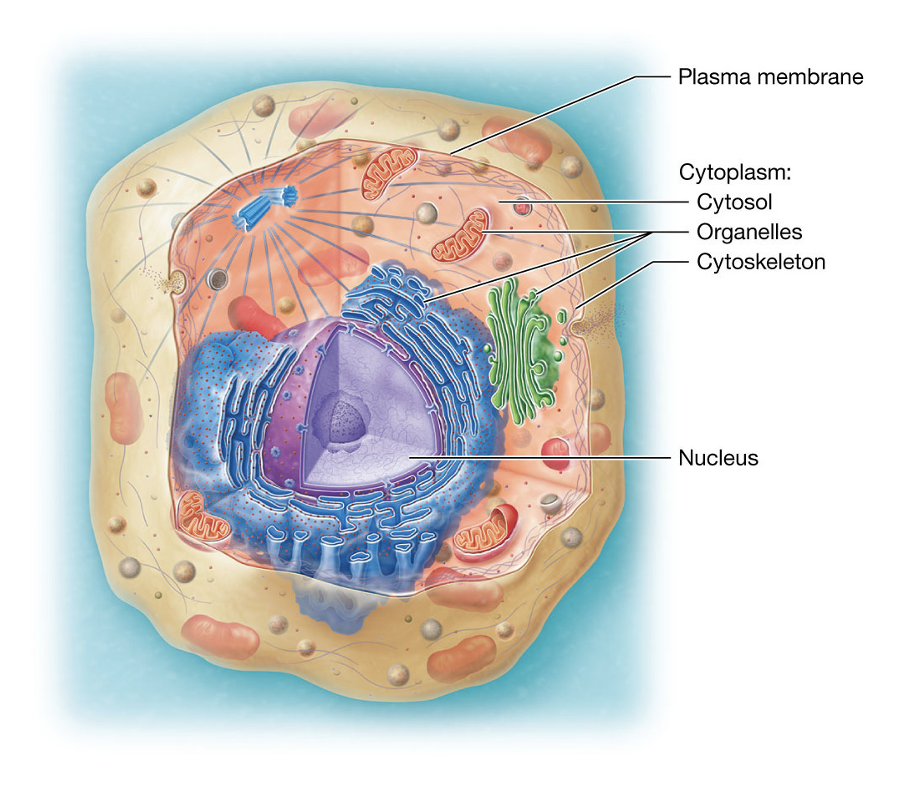
Plasma Membrane
the cell’s outer layer that keep it separate from its surroundings (like a fence), supports its structure, communicates with other cells, and controls what enters and leaves.
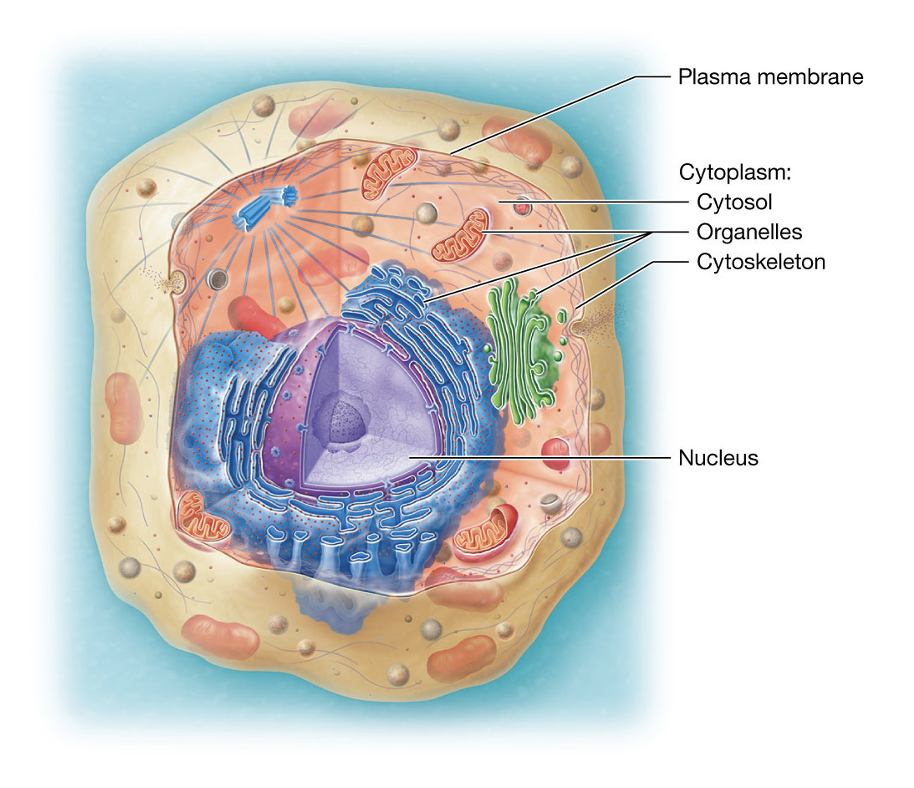
Cytoplasm
contains cytosol, organelles, cytoskeleton, nucleus
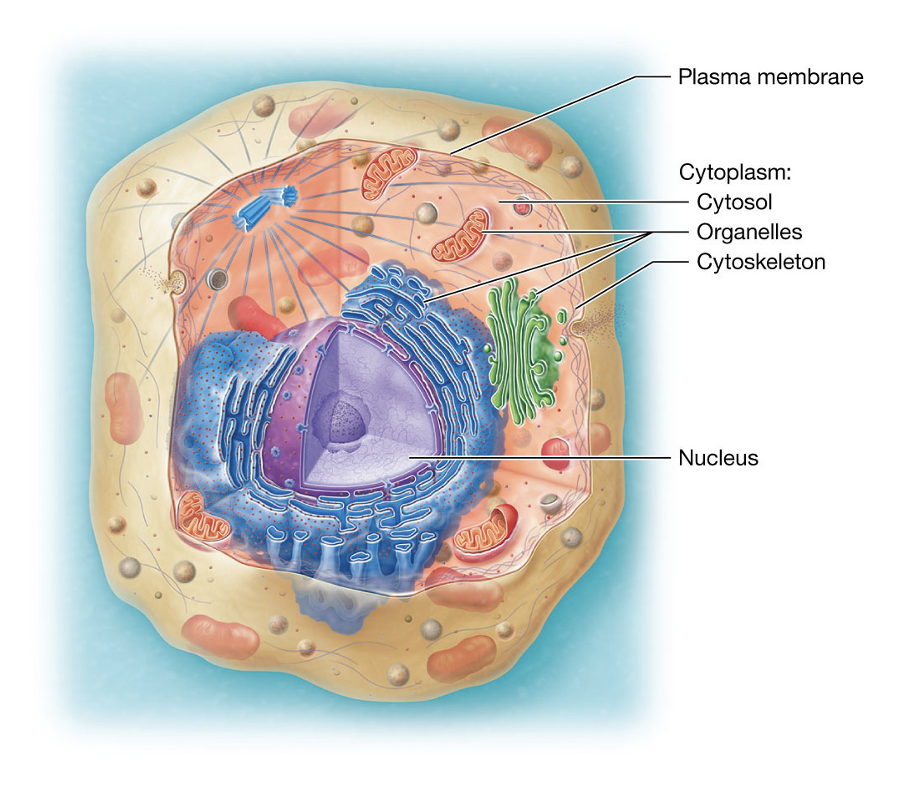
Cytosol
fluid inside the cell where organelles float
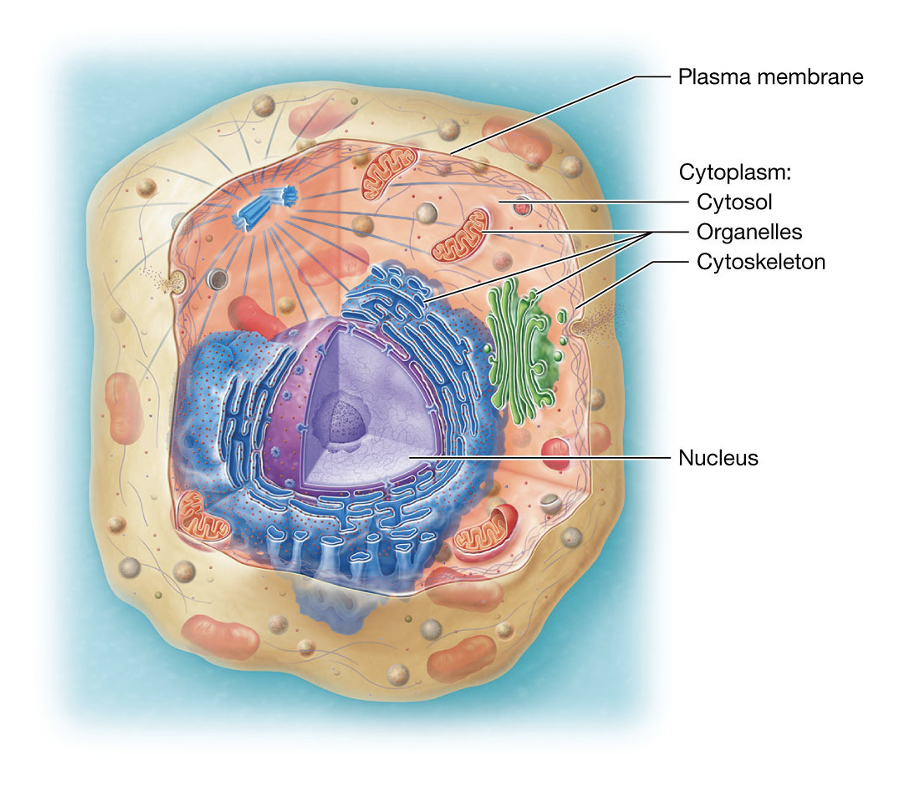
Organelles
specialized “mini organs” inside the cell that do specific jobs
(like mitochondria making energy)
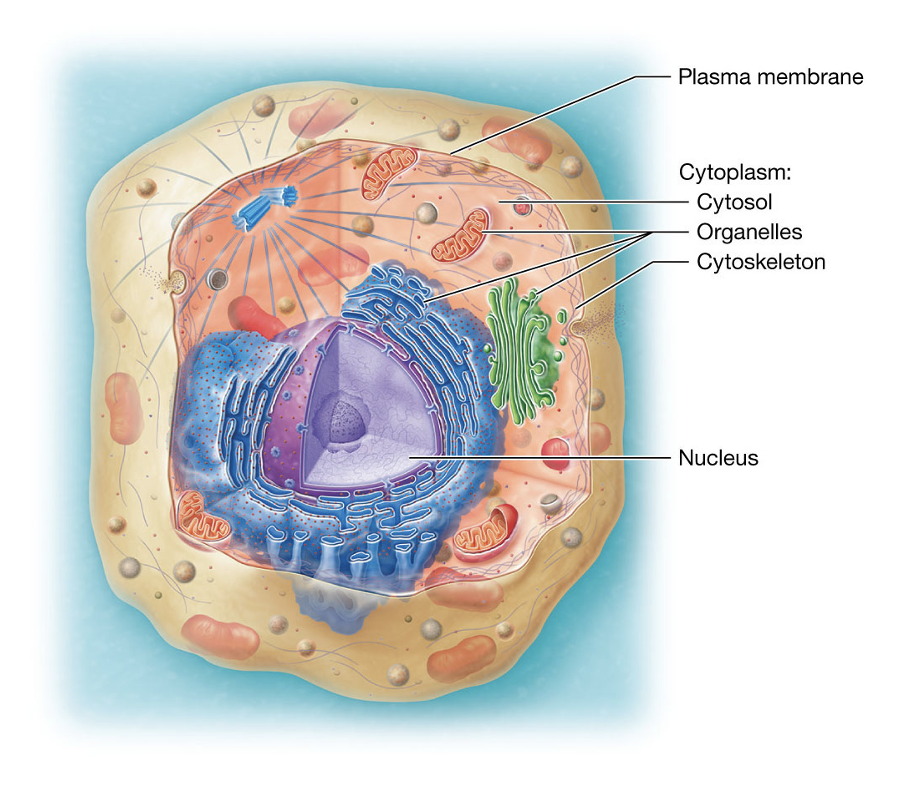
Cytoskeleton
gives the cell shape and support
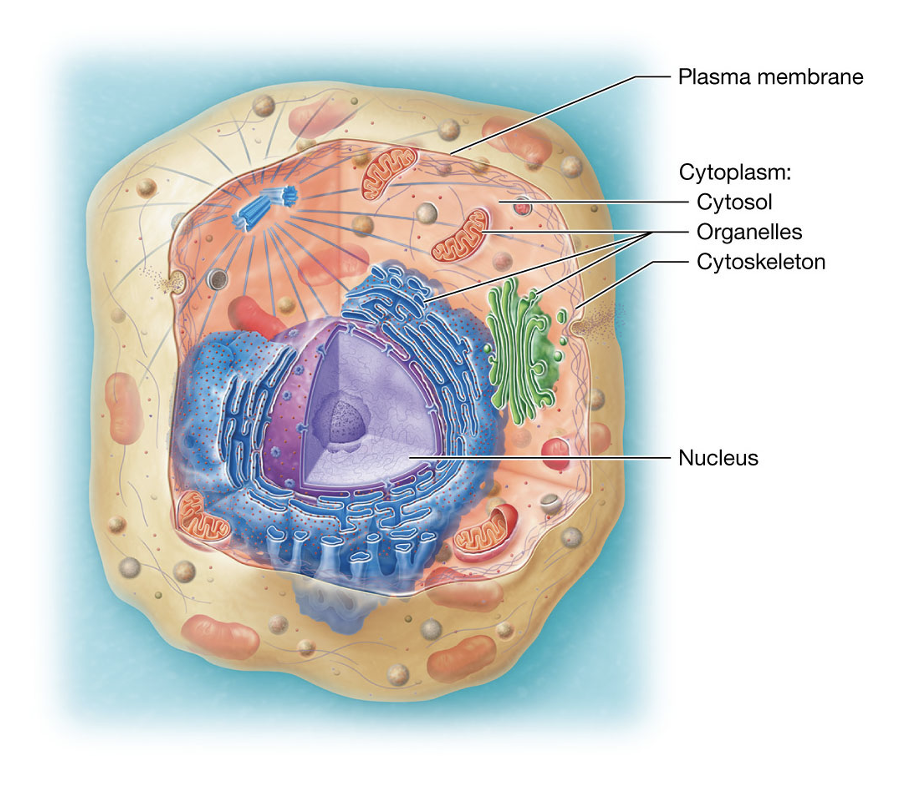
Nucleus
cell’s control center, holds DNA
Eukaryotic
contrains a nucleus
Prokaryotic
contains no nucleus (bacteria)
Intracellular Space (plasma membrane)
space within the cells that contains cytosol
Extracellular Space (plasma membrane)
space outside the cells that contains extracellular fluid (ECF)
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
the fluid inside cells, a watery gel containing proteins, dissolved solutes, and RNA
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
the fluid outside cells

Phosopholipid Bilayer
forms an effective barrier between the ECF and cytosol

Polar phosphate “heads”
hydrophilic (water loving) head of a phosopholipid
Nonpolar fatty acid “tails”
hydrophobic
plasma membrane
“fence” or “skin” of cell
Mosaic: lipids, phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates; this diversity of what’s able to move around within plasma membrane
Fluidity: plasma membrane is not a rigid wall; membrane changes constantly as things in the bilayer move around in different directions
Membrane proteins
carry out plasma membrane’s functions and give different cell types unique properties.
integral proteins
span entire width of membrane; type of membrane protein
transmembrane proteins
span entire width of the membrane; type of membrane protein
peripheral proteins
found on only 1 side of membrane, type of membrane protein
(can be anchored in place by cytoskeleton or floating freely in phospholipid bilayer)
Channel membrane proteins
substances pass through the membrane
Carrier membrane proteins
substances are transported through the membrane
Receptor membrane proteins
ligands bind to the receptor to trigger a change in the cell
Enzyme membrane proteins
catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions while staying in membrane
Structural support membrane proteins
provide cell shape and structural support
Linker membrane proteins
hold adjacent cells in a tissue together
cholesterol
keeps structure of the plasma membrane in tact when temperature changes
diffusion
solute high to low concentration
simple diffusion
nonpolar solutes and gases pass straight through the phospholipid bilayer without the need for a membrane protein
facilitated diffusion
charged or polar solutes cross the phospholipid bilayer through a channel or carrier protein
osmosis
solvent (water) moves low to high concentration
water can cross the plasma membrane:
through aquaporins (water channels)
between phospholipids in membrane due to water’s small size
two pressures cause water movement to stop:
osmotic pressure
hydrostatic pressure
osmotic pressure
the pressure that must be applied to a solution to prevent water from moving into it by osmosis
hydrostatic pressure
force that water exerts on the walls of the container
when both sides have equal volume: hydrostatic pressure is equal
when water level rises: hydrostatic pressure increases
osmotic gradient
difference between the osmotic pressures in sides with unequal volume
osmosis stops when the hydrostatic pressure in the side with more volume reaches the value of osmotic gradient
Isotonic ECF vs. cytosol ability to cause osmosis?
same, so no water movement
hypertonic ECF vs. cytosol ability to cause osmosis?
greater, so cell loses water (can crenate)
hypotonic ECF vs. cytosol ability to cause osmosis?
lesser, so cell gains water and swells (can rupture/lyse)
active transport
requires energy (ATP) because solutes go low to high
transport vesicles
transport large particles into or out of cell
vestibular transport
transport using vesicles that REQUIRES ATP to fuel the process
endocytosis
brings substances into the cell
phagocytosis
cells eat big particles (bacteria, dead cells, or parts of cells)
pinocytosis
bring nutrients and other substances into the cell
receptor-mediated endocytosis
type of pinocytosis that results in transport vesicles containing a high concentration of a specific substance
exocytosis
moves substances out of the cell
transcytosis
moving molecules across a cell in from one side to the other, then releasing from cell’s other side
primary active transport
movement of solute against concentration gradient using ATP
secondary active transport
RER
makes and folds proteins that are usually secreted out of the cell or sent to the membrane, RIBOSOMES
SER
makes lipids, detoxifies chemicals, stores calcium
Cystic Fibrosis
RER’s ability to dispose of misfolded proteins is detrimental
free ribosomes
float in cytoplasm, make proteins that stay in cell
bound ribosomes
attached to RER and make proteins that are exported out or put in membranes
golgi apparatus
modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids produced by ER for transport
“post office”
lysosomes
break down/digest unwanted materials (worn out organelles, bacteria, cellular waste)
“digestive system”
Gaucher’s Disease
missing enzyme that breaks down glycolipids which accumulate in cells of blood, spleen, liver, lungs, bone, and sometimes brain. fatal in infancy/early childhood
Tay-Sachs Disease
missing enzyme that degrades glycolipid in the BRAIN, fatal by 4-5 yrs old
Hurler Syndrome
missing an enzyme that digests certain large