cranial nerve nuclei in the medulla and pons
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
somatic motor nuceli
located at the midline
somatic sensory nuclei
located laterally
visceral motor and visceral sensory nuceli
located in between somatic motor and somatic sensory nuceli
cranial nerves 3,4,6,12
somatic motor nuceli
cranial nerves 5,7,9,10
branchial motor nuceli
cranial nerves 3,7,9,10
visceral motor nuceli
cranial nerves 7,9,10
visceral sensory nuceli
cranial nerves 5,7,8,9,10
general/special sensory nuceli
tegmentum
area on the dorsal surface of the medulla where cranial nerve nuceli are located
dorsal rostral medulla
fourth ventricle is evident in its cross-section; begin to see the first cranial nerve nuceli at this location
hypoglossal nucleus
dorsal visceral motor vagal nucleus
nucelus ambiguus
nuceli seen on dorsal rostral medulla:
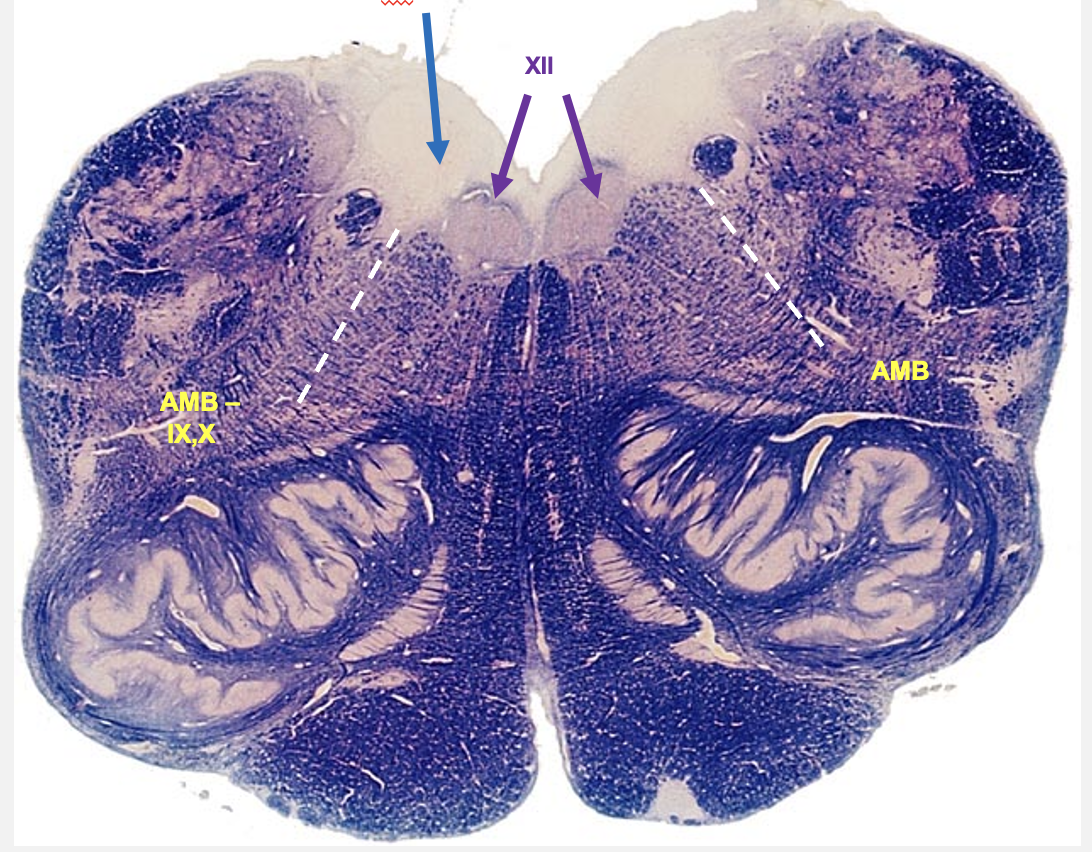
hypoglossol nucleus
nucleus of origin for axons of cranial nerve 12 (somatic motor)
dorsal visceral motor vagal nucelus
contain pre-ganglionic parasympathetic neurons that give rise to axons in cranial nerve 10 that innervate smooth muscle (visceral motor)
nucleus ambiguus
contain neurons that contain axons that innervate larynx and one pharynx muscle (cranial nerves 9 and 10 - branchial motor)
tract
collection of afferent/sensory axons that surround the nucleus in which they terminate
nucleus and tract solitarius
primary visceral sensory nucleus of the brainstem
cranial nerves 7,9,10
rostral portion of nucelus/tract solitarius
receives taste information from cranial nerves 7 (anterior), 9 (posterior) and 10 (epiglottis)
caudal portion of nucleus/tract solitarius
receives visceral information from GI tract (cranial nerve 10)
vestibular nuclei
cochlear nuceli
associated with cranial nerve 8; special sensory nuceli of brainstem
rostral medulla
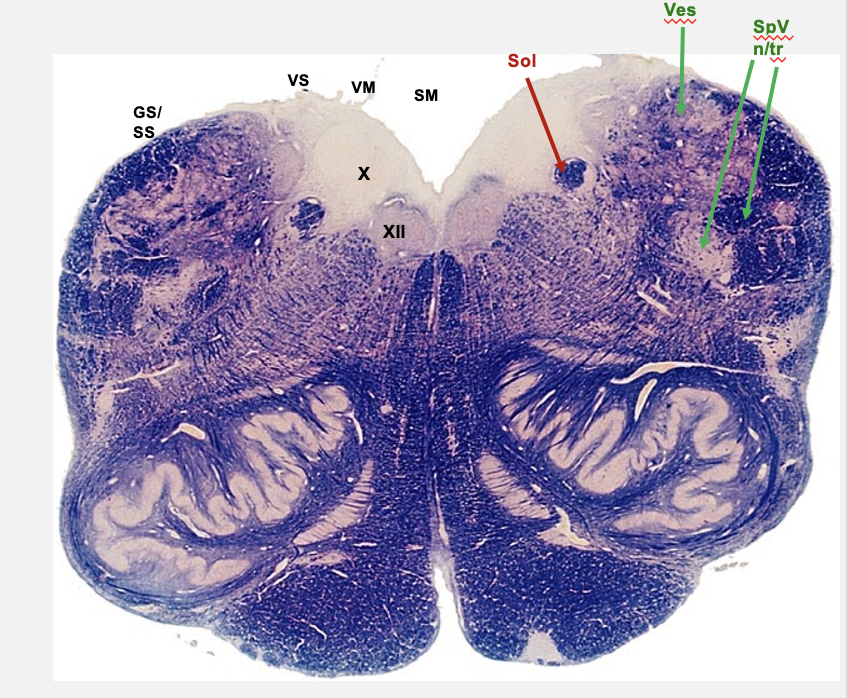
hypoglossal nucleus
dorsal visceral motor vagal nucelus
nucleus solitarius
vestibular nucelus
nucleus and tract of V
rostral medulla cross section cranial nerve nuclei
cochlear nucleus
pontomeduallary junction cross section cranial nerve nucelus
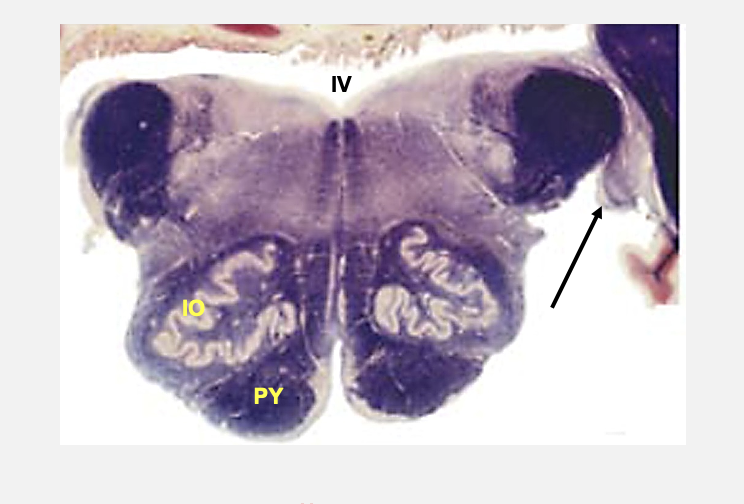
basilar pons
characterized by transverse oriented bands that coalesce to form middle cerebellar peduncles
pontocerebellar axons
axons that transverse the basilar pons to form the middle cerebellar peduncle
pontine nucleus
collection of neurons in basilar pon; neurons here give rise to pontocerebellar axons
caudal pons
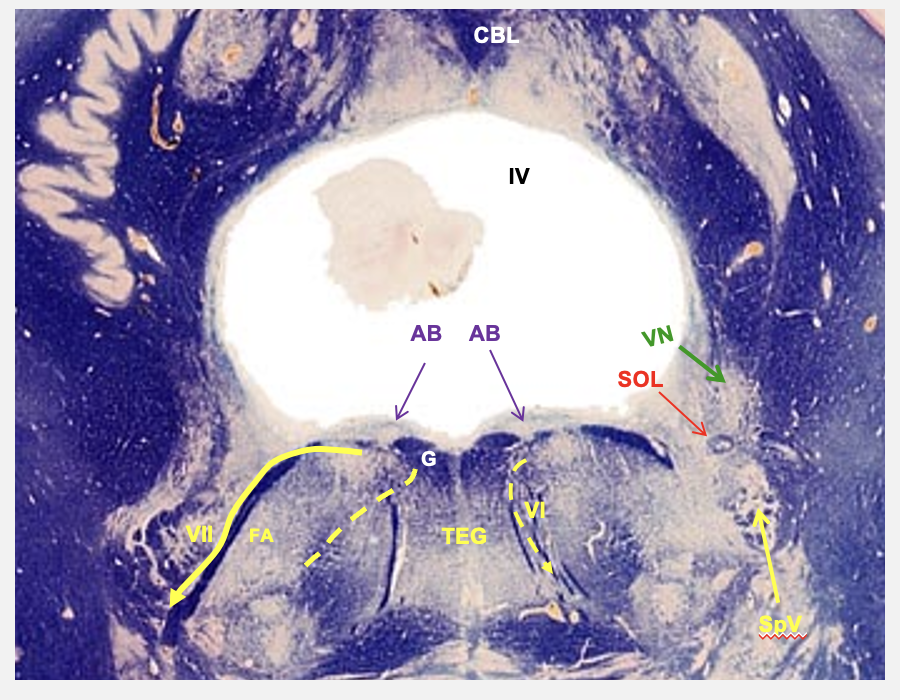
abudecens nucleus
cranial nerve 6; somatic motor - neurons here given rise to axons that leave the brain and innervate lateral rectus of the eye
facial nucleus
cranial nerve 7; branchial motor - neurons in this nucleus innervate muscles that control facial movements
dorsally
medially
internal genu
laterally
ventrally
pathway of facial nucleus
axons leave the nucleus and course BLANK and BLANK toward abducens nucleus, on reaching the dorsal surface of pons, they curve around abducens nerves and form the BLANK BLANK, then they go back BLANK and BLANK to exit the lateral side of the brainstem
abducens nucleus
facial nucleus
nucleus solitarius
vestibular nucelus
spinal and tract of V
cranial nerve nuceli seen in the cross-section of dorsal caudal pons
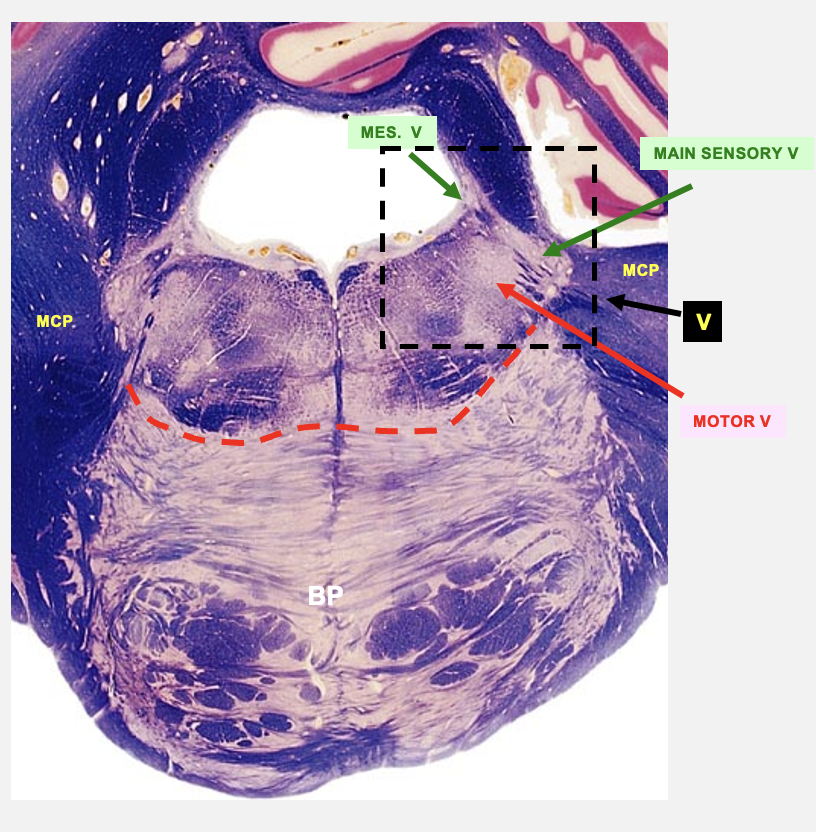
trigeminal nucleus
cranial nerve 5; general/somatic sensory conveying information on touch, pain, propioception from the face
composed of three nuceli
main sensory nucleus
spinal nucleus
mesencephalic nucleus
three nuceli that make up the trigeminal nucleus
main sensory nucleus
touch and pressure from all three divisons of CN 5
spinal nucleus
pain and temperature from all divisions of CN 5
mesencephalic nucleus
proprioceptioin from muscles of mastication and mechanoreceptors in teeth and jaw
motor V
cranial nerve 5; branchial motor - nucleus that gives rise to axons that innervate muscles of mastication
motor nucleus of V
main sensory nucleus of V
mesencephalic nucleus of V
rostral pons cross-section structures
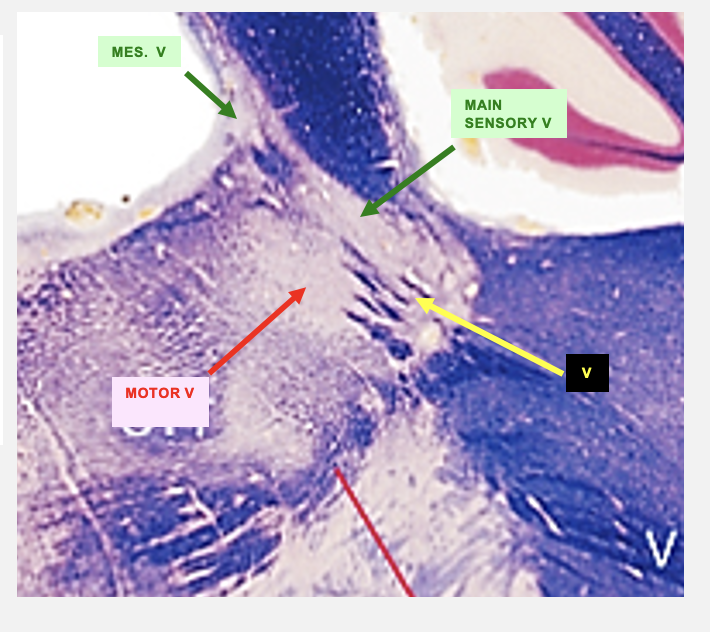
trigeminal nerve
main sensory nucleus
motor trigeminal nucleus
the axons of the BLANK BLANK separate the BLANK BLANK BLANK from the BLANK BLANK BLANK
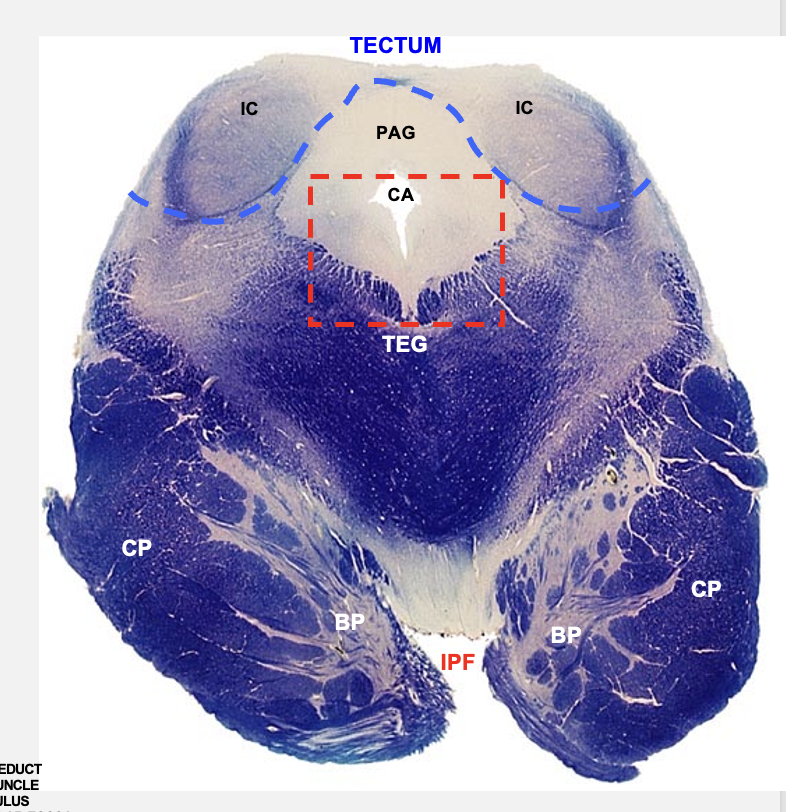
basilar pons
cerebral peduncles
troclear nucleus
cerebral aqueduct
periaqueductal gray
inferior colliculus
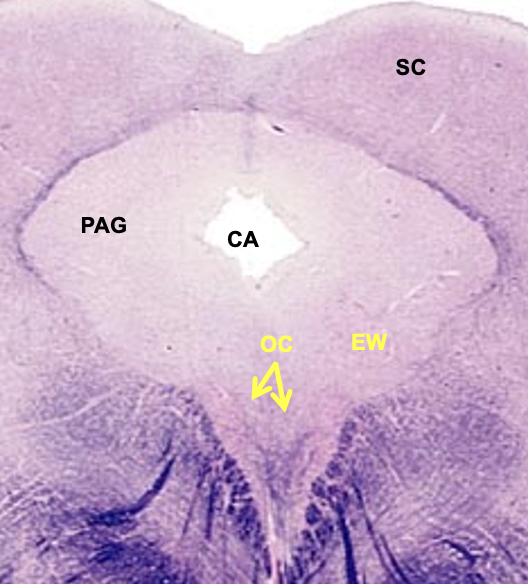
caudal midbrain cross section structures
troclear nucleus
CN#4; somatic motor - axons leaving this nucleus course dorsally where they cross on the midline, axons innervate the superior oblique muscle in the orbit
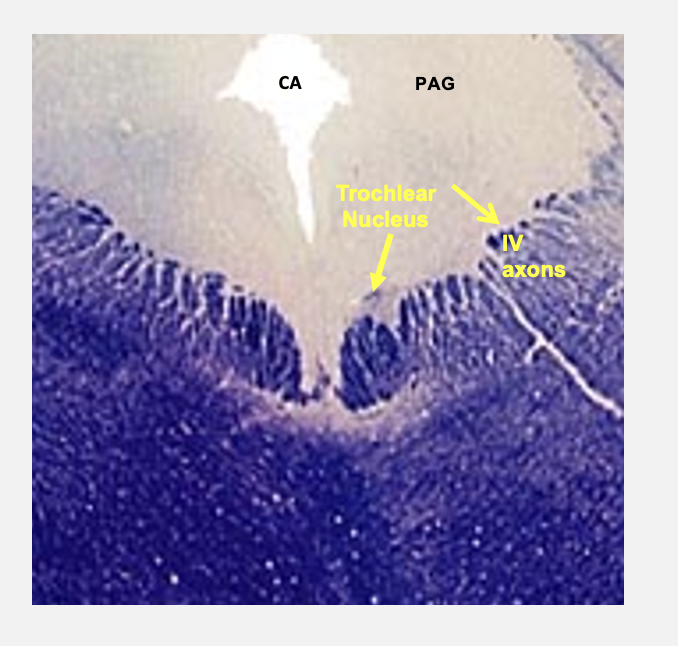
periaqueductal gray
contains neurons that give rise to descending pain-control pathway
cerebral peduncle
substantia nigra
oculomotor nucleus
periaqueductal gray
cerebral aqueduct
superior colliculus
middle midbrain cross-section features
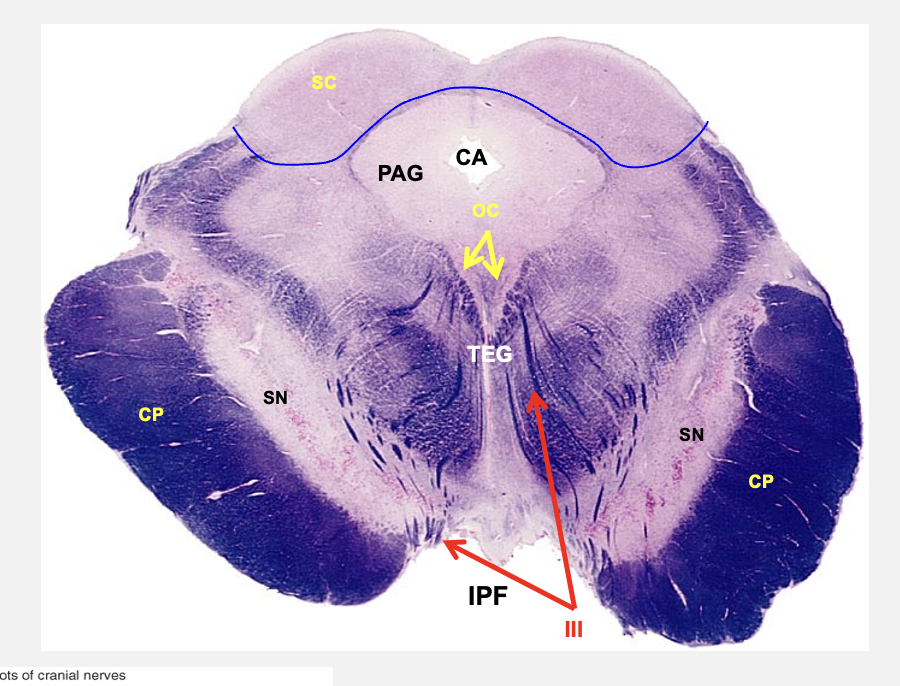
oculomotor nucleus
CN3; somatic motor - neurons here give rise to axons in oculomotor nerve that innervate eye muscles