NPB101: Membrane Potentials Part 4
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Getting that AP to Move; Signaling Between Neurons and Targets
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
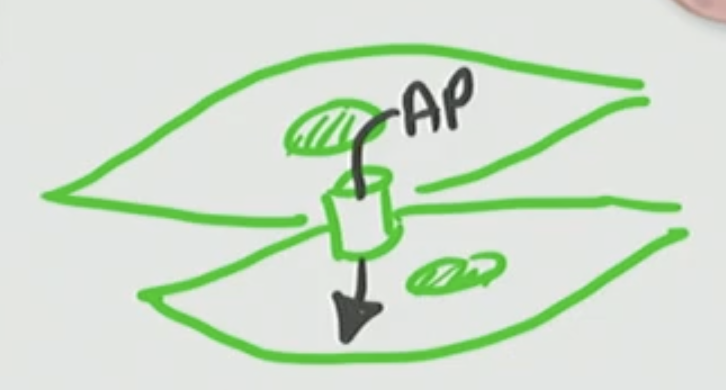
An AP drives a current to the ____.
neuron
T/F: An AP creates a local current
True an AP does create a local current (depolarization)
Distance matters when eliciting an AP because?
current can die out over time (length)
AP
It creates a current, and then that current depolarizes the adjacent region, and we regenerate the action potential.
T/F: Does the AP travel?
False, it regenerates not travels
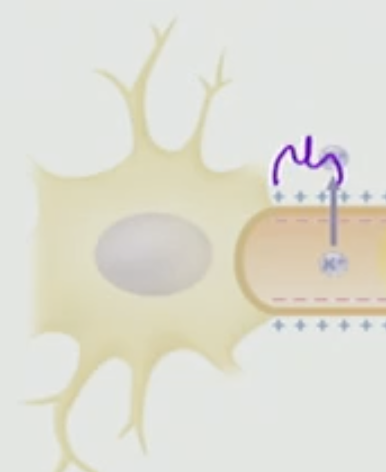
What is this region called
Axon Hillock
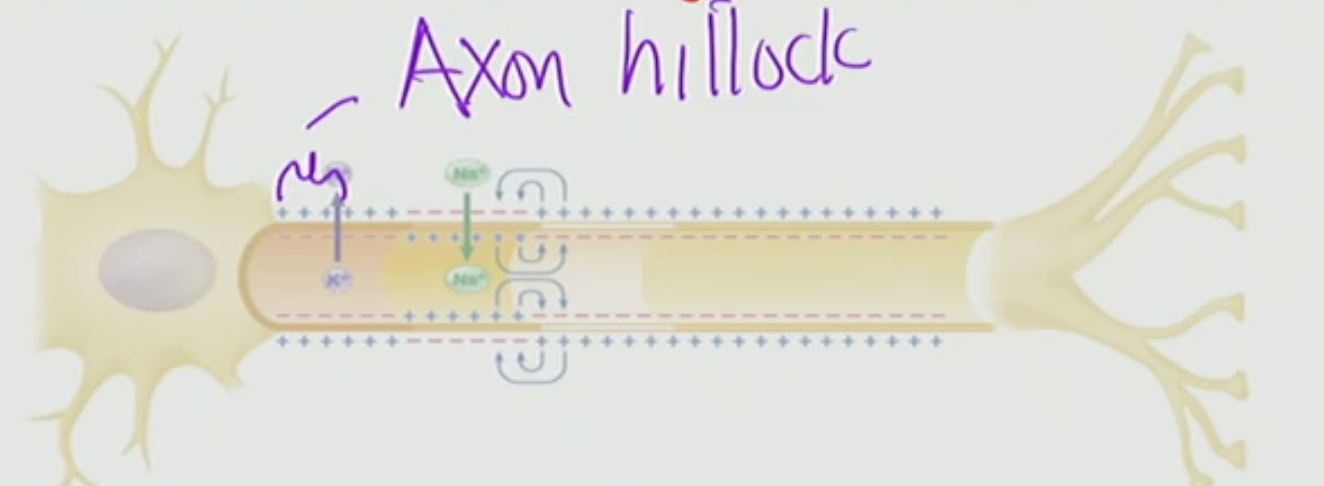
What is occurring at the Axon Hillock?
at the Axon Hillock is where the AP starts off (elicits & sum)
In vivo, why don’t APs travel backwards/upstream (antidromic direction)?
a) The upstream region’s V-gated Na + channels are inactivated and cannot open to induce an AP
b) The upstream region’s V-gated K + channels are inactivated and cannot open to induce an AP
c) The upstream region runs out of extracellular Na+, so no Na+ can flow to induce an AP
d) The upstream region needs to regrow new channels before it can conduct an AP
a) The upstream region’s V-gated Na + channels are inactivated and cannot open to induce an AP, because imagine eliciting an AP on your finger and it travels backwards and forwards OUCH
T/F: AP travel backwards
False, AP do NOT travel backwards, only forwards because Na+ channel would be inactivated
AP in a neuron called unmyelinated (naked axon)
An axon with a bunch of stuff wrapped around it is what?
The stuff wrapped around an axon is called myelin that supports the cell
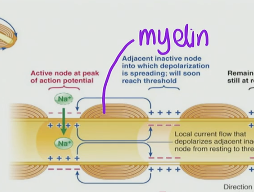
Myelin can be formed on?
oligodendrocytes (central neurons) and Schwann cells (peripheral neurons)
Myelin creates very specific region on the axon called _____
Nodes of Ranvier
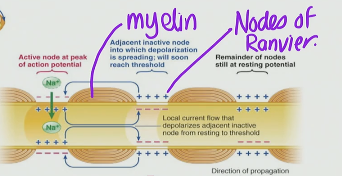
In the Nodes is the only place you have ____ and ____ channels
V-Gated Na+ and K+ channels
Saltatory
“jumping”
What is Saltatory Conduction in Neurons?
Saltatory Conduction in neurons is when an AP is being elicited through the neuron at the axon region where it takes “big steps” and does the AP at the Nodes of Ranvier
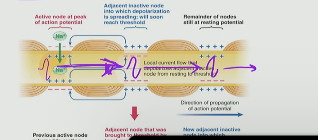
What happens to motors that get demyelinated?
When motors get demyelinated, they cannot conduct fast AP
T/F: AP occur at Nodes of Ranvier
True they occur at Node of Ranvier as it goes through the neuron at the axon
The neuron is the communication cell of the _____
body
Electrical current is traveling through the ____
Neuron
T/F: Is the electrical current that travels through the neuron which is the signal?
True, the electrical current that travels through the neuron is the signal, the info traveling through the neuron
How does the current get to the target?
The current gets to the target by the synaptic cleft (the space between the axon terminus and the target. This is because it cannot jump to the target
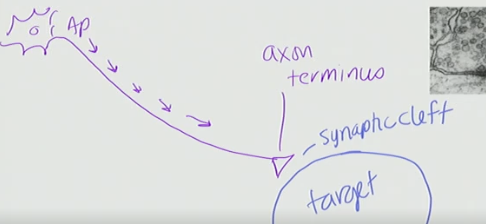
Vesicles contain _____.
neurotransmitters

Neurotransmitters are stored in ______
vesicles
The AP travels down the ____.
axon
The AP and ____ current cause _____ at the ____ terminus.
electrical, depolarization, axon
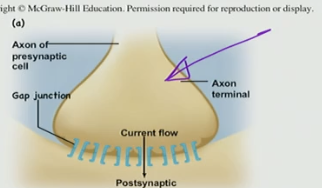
T/F: V-Gated Ca2+ channel responds to hyperpolarization
False V-Gated Ca2+ channel responds to depolarization bc it opens in response to it
When a V-Gated Ca2+ channel responds to depolarization what happens?
V-Gated Ca2+ channel will be activated
Depolarization at the ____ activates V-Gated Ca2+ channel and (opens/closes) ____ with an influx of ____
terminus, opens, Ca2+
When Ca2+ comes into the terminus it causes the ____ to fuse
vesicles
What do the vesicles fuse to?
Presynaptic membrane (end of axon terminus)
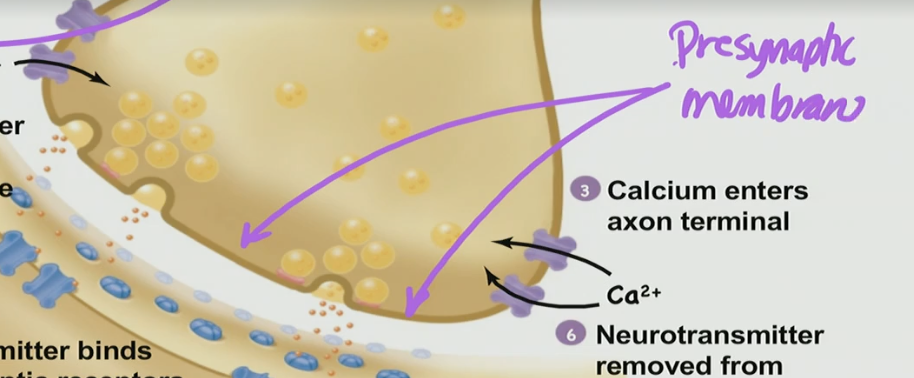
Neurotransmitters get released into the _____ cleft
synaptic
Neurotransmitter has a ___ distance to travel
short
The neurotransmitter will manage to ___ to the ____ on the target
bind, receptor
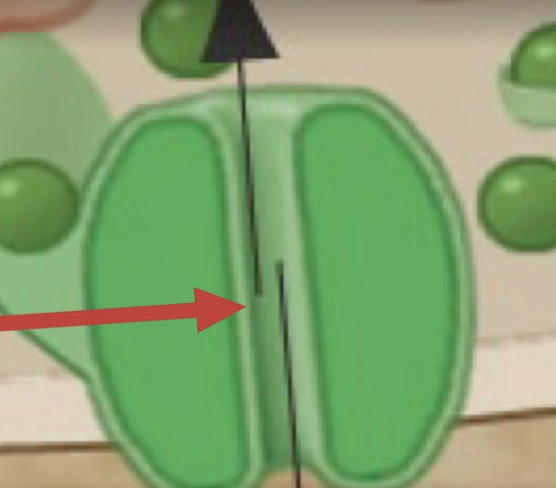
What is this? What does it look like?
This is the receptor for the neurotransmitter and it looks like a channel and can act like one
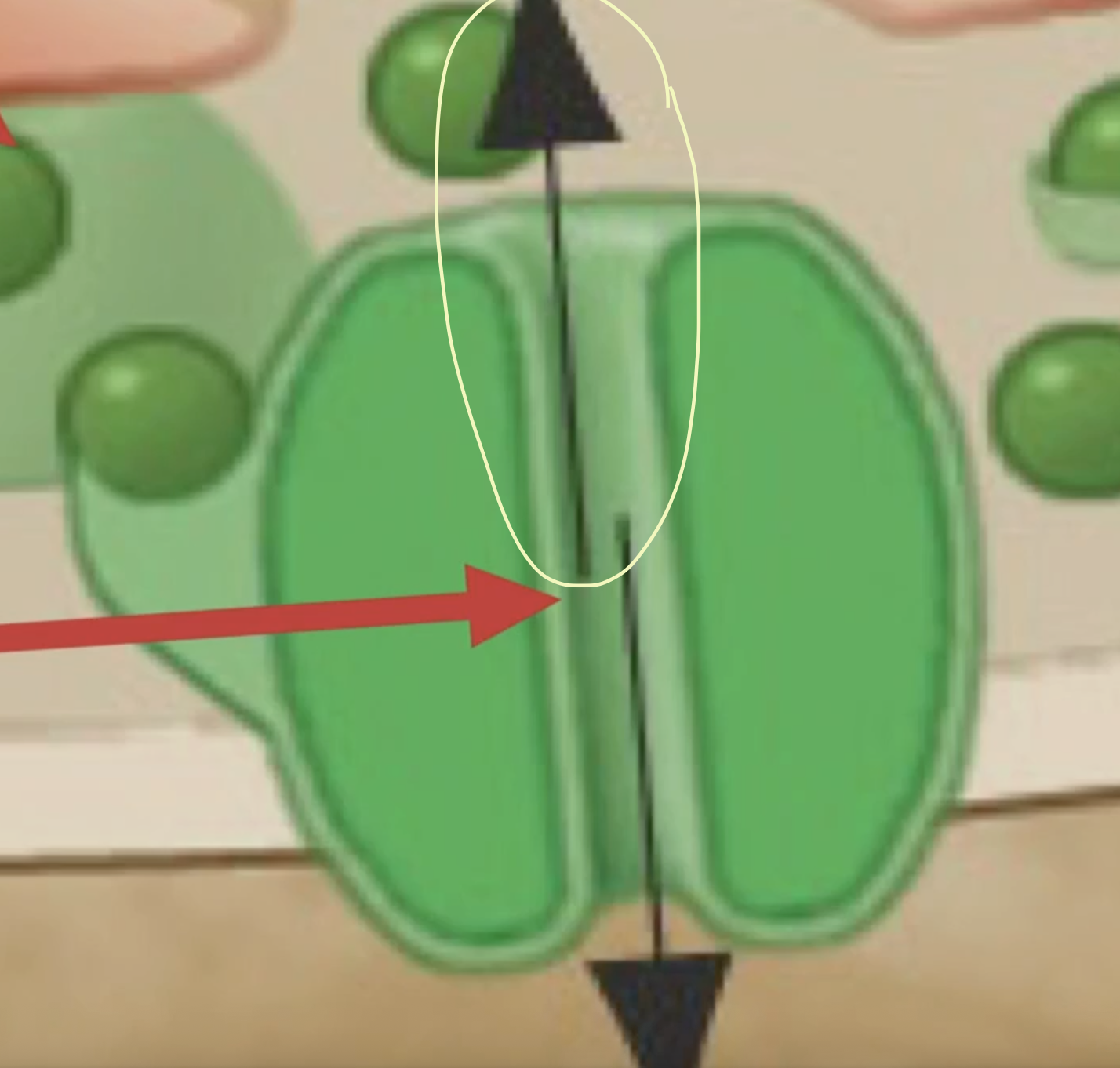
What does this arrow of the receptor do?
allows an influx of Na+ to flow through causing depolarization and passes threshold creating an AP
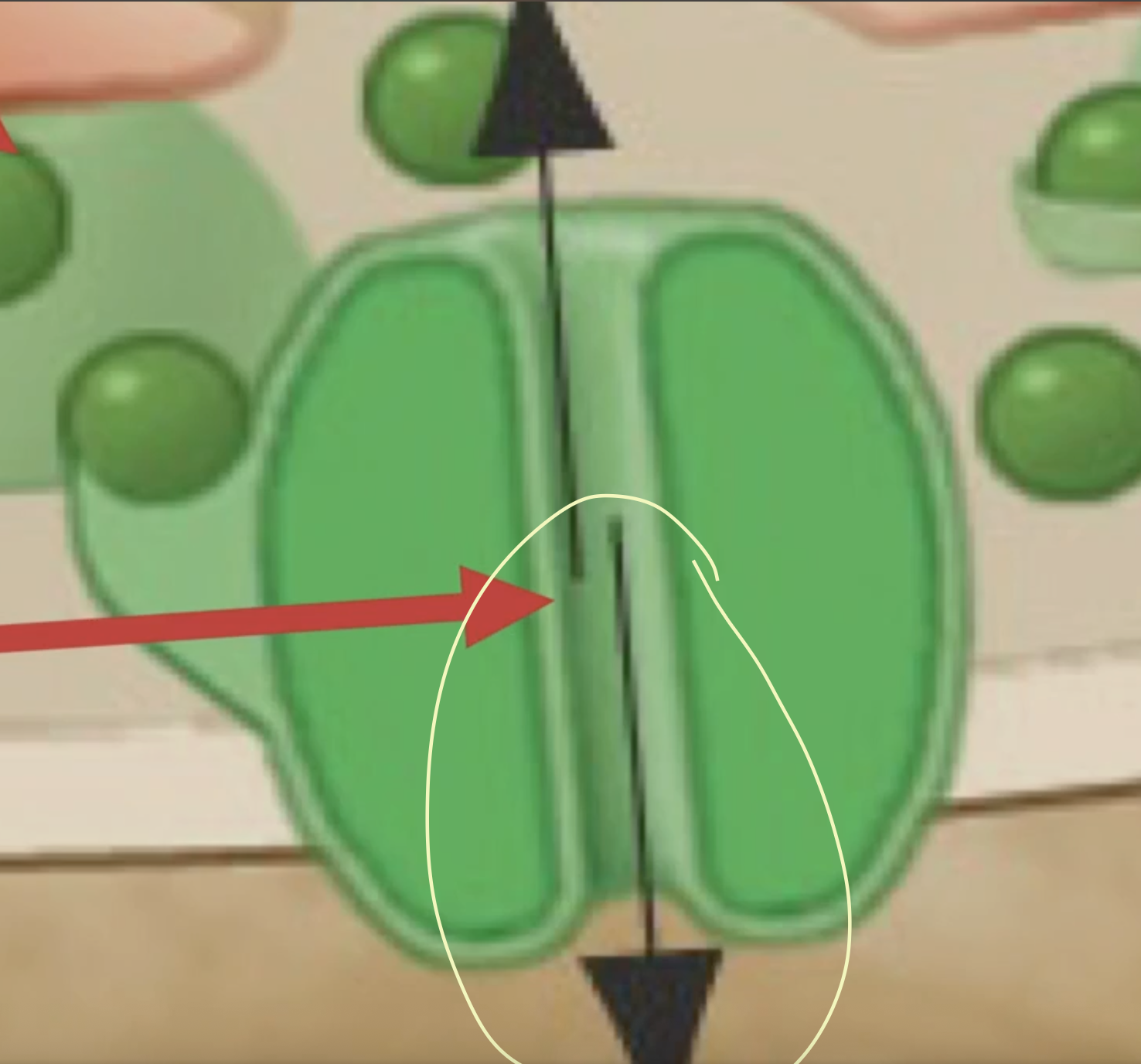
What does this arrow of the receptor do?
It allows an efflux of K+ to flow out the cell creating hyperpolarizing not firing an AP
Neurotransmitters that depolarize the cell are called?
excitatory neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters that cause ion, particularly K+(leave the cell) or even Cl-(into the cell) is called?
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
When K+ leaves the cell or Cl- going into the cell this is?
hyperpolarization
During hyperpolarization K+ ___ the cell and Cl- ____ the cell
leaves, enters
T/F: Excitatory causes hyperpolarization
False, Excitatory causes depolarization
What ions flow with an influx due to Excitatory/Depolarization? Choose 1 or more
Na+
K+
Cl-
Ca2+
Na+ and Ca2+ flow in with an influx
T/F: Inhibitory causes hyperpolarization
True
What ions flow with an influx due to Inhibitory/Hyperpolarization? Choose 1 or more
Na+
K+
Cl-
Ca2+
Cl- flows with an influx
What ions flow with an efflux due to Inhibitory/Hyperpolarization? Choose 1 or more
Na+
K+
Cl-
Ca2+
K+ flows with an efflux
If you have a lot of excitatory neurotransmitter, the neurotransmitter’s would cause a ____ depolarization
big
If you have a tiny amount of excitatory neurotransmitters the depolarization would be ___
small
If you have a lot of excitatory neurotransmitter, the neurotransmitter’s would cause a big depolarization & If you have a tiny amount of excitatory neurotransmitters the depolarization would be small. What is this called?
Graded Potential
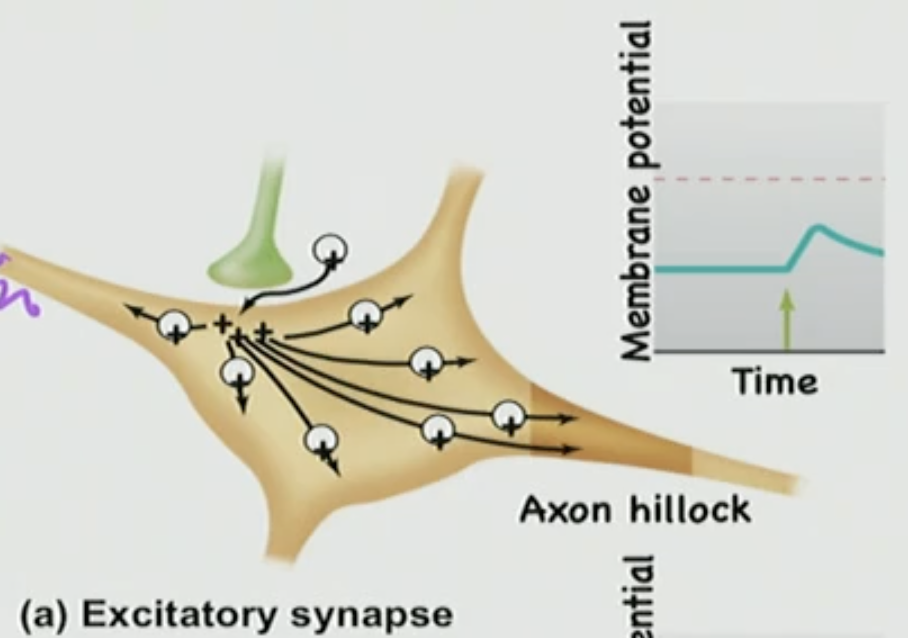
For those that cause depolarization/excitatory (Na+ & Ca2+) this is called?
Excitatory(Depolarize) Post-Synaptic (occurring on the target tissue post-synaptic cell) Potential: EPSP
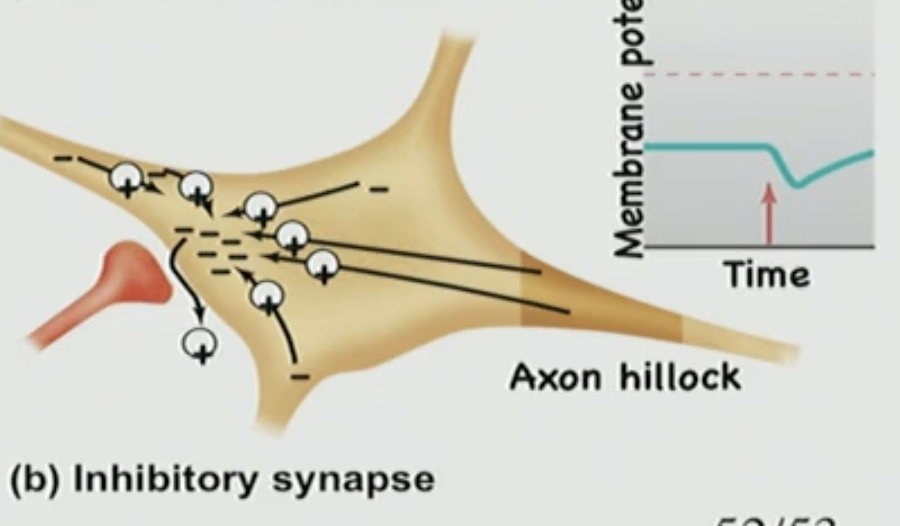
For those that cause hyperpolarization/inhibitory (K+ & Cl-) this is called?
Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential: IPSP
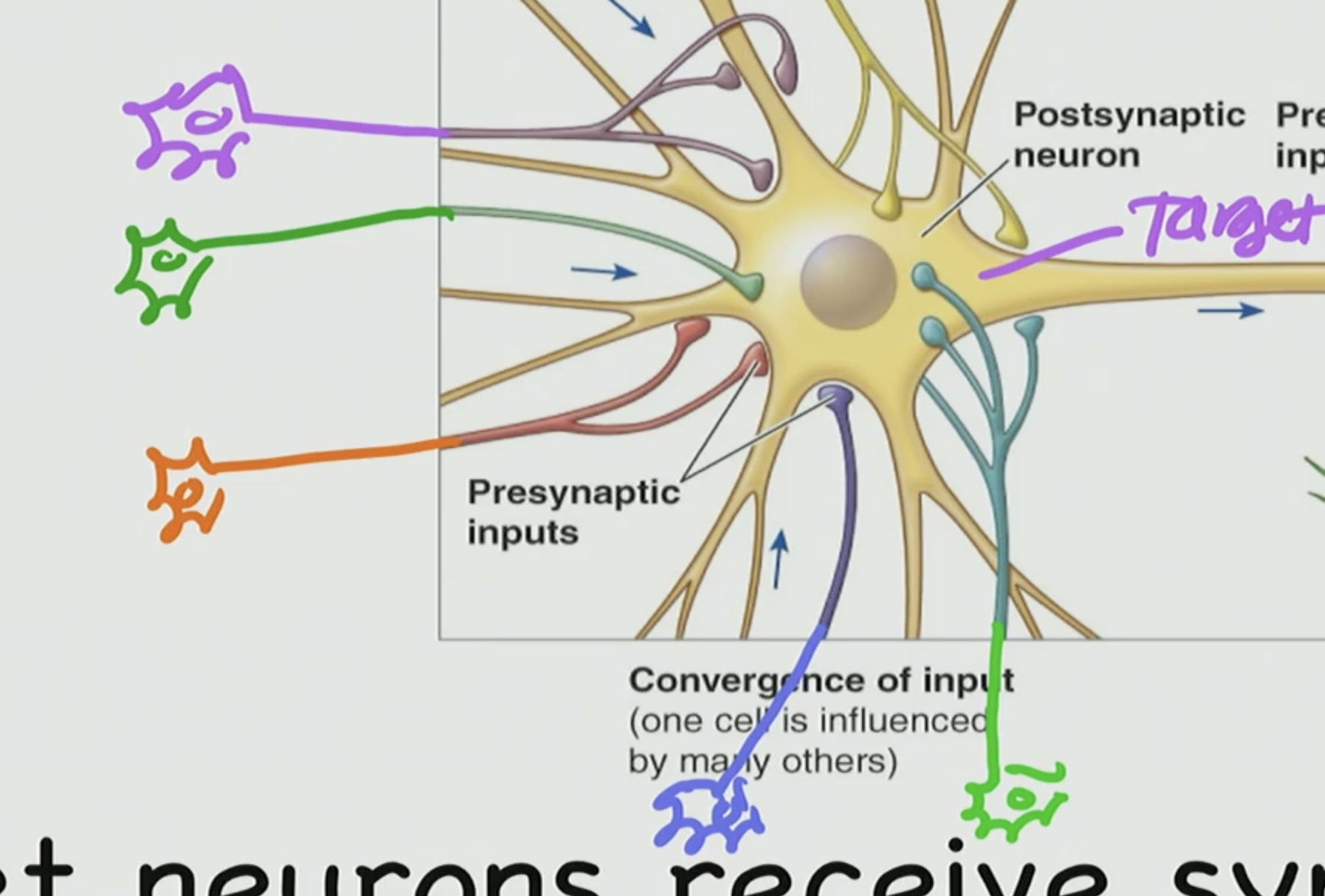
This is basically a ____ of information thats going to ___ this neuron
convergence, control
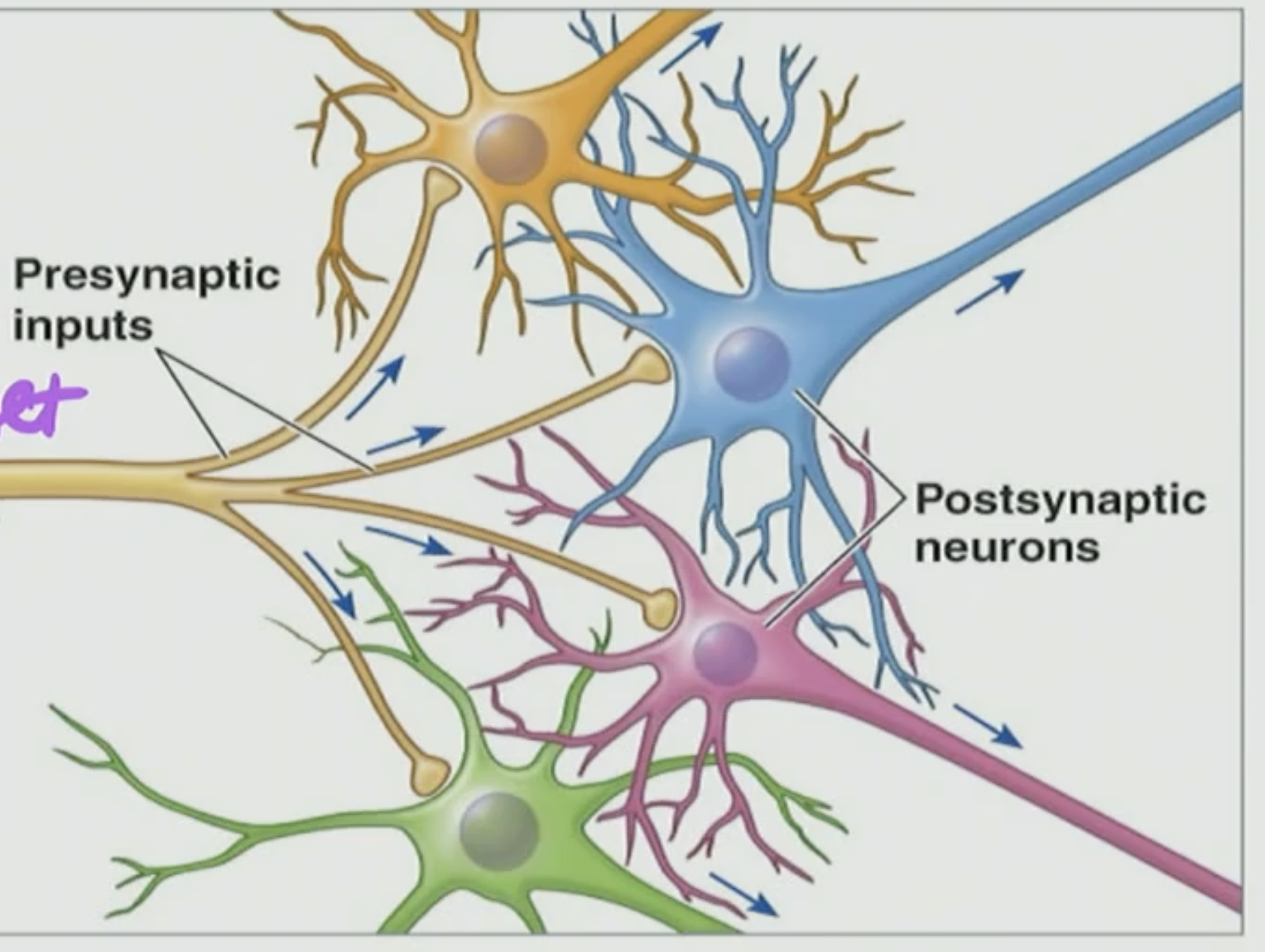
This is a ____ of information to talk to ____ targets
divergence, multiple
T/F: a Divergence output is when one postsynaptic neuron communicates with one presynaptic neuron
no a divergence output is when one presynaptic cleft from one axon communicates with many postsynaptic cleft bodies
T/F: a Convergence output communicates with a synapse at one target
False this doesn’t exist
T/F: a COnvergence
Target neurons receive ___ input from __#__ to __#__ of other neurons
synaptic, hundreds to thousands
T/F: this is Convergence: One cell influences many others
False this would be Divergence as it influences many others
T/F: this is Convergence: One cell influences many others. If not, explain what convergence is.
False, Convergence is one cell that is influenced by many others because it receives synaptic input from hundreds to thousands of neurons
T/F: this is Divergence: One cell influences many others
True, Divergency influences many others because its a single neuron that can communicate with a synapse upon many targets
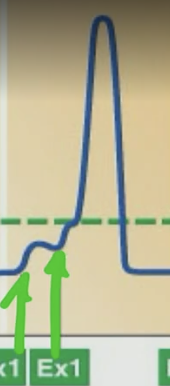
What is summation?
PSP coming together (summing) to form an AP as it passes threshold and depolarizes
To get an AP you want ____ to summate
PSP
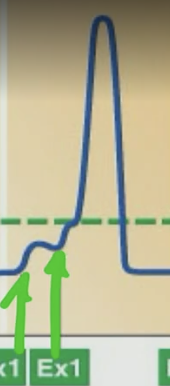
What is Temporal Summation?
The increase of frequency of input (coming from a given neuron)
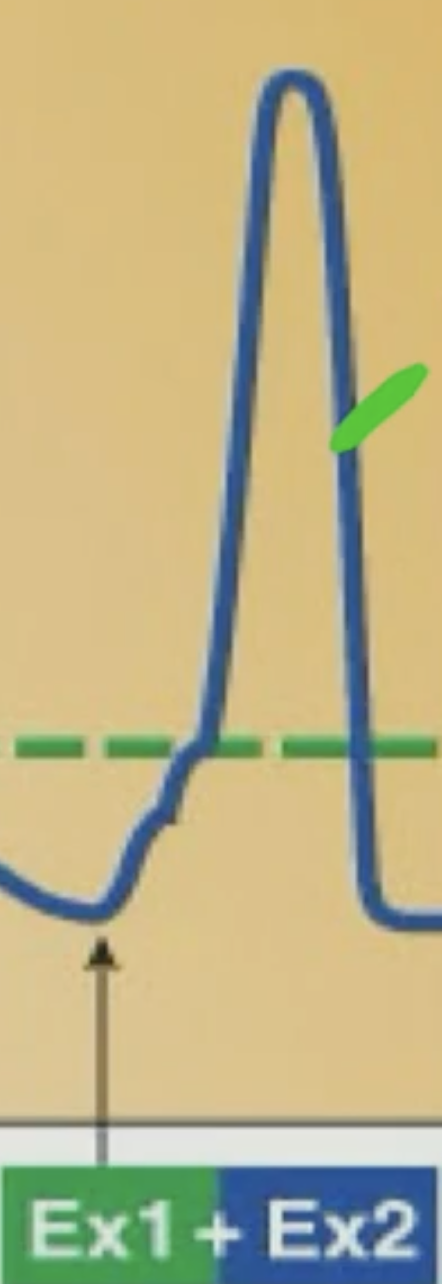
What is Spatial Summation?
Input from 2 or more presynaptic neurons (to induce the response)
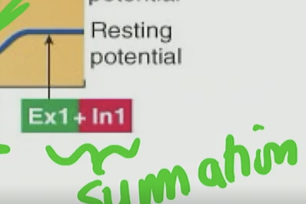
Is this summation bad? (Excitatory & Inhibitory)
No this is not bad, there are times we want to inhibit postsynaptic targets
DON’T REALLY NEED TO KNOW: Why do we want to inhibit postsynaptic targets?
To quiet down the target like in Parkisons
Neurotransmitters
chemical thats released by neurons this chemical can be norepinephrine, glycine, dopamine, etc.
T/F: The Electrical Synapse requires neurotransmitters
No the Electrical Synapse does not require neurotransmitters
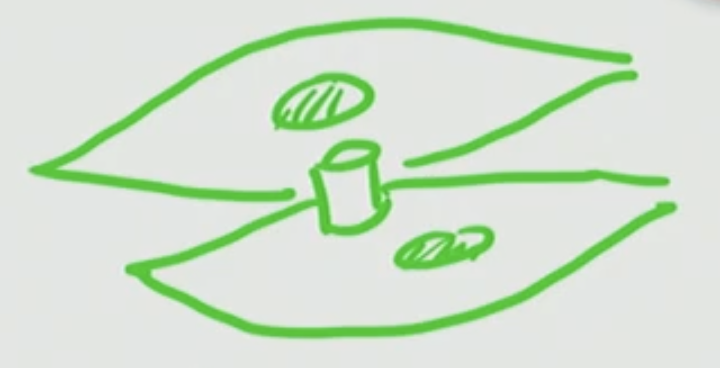
Gap Junction
Allows the signal to travel from one cell to the other cell
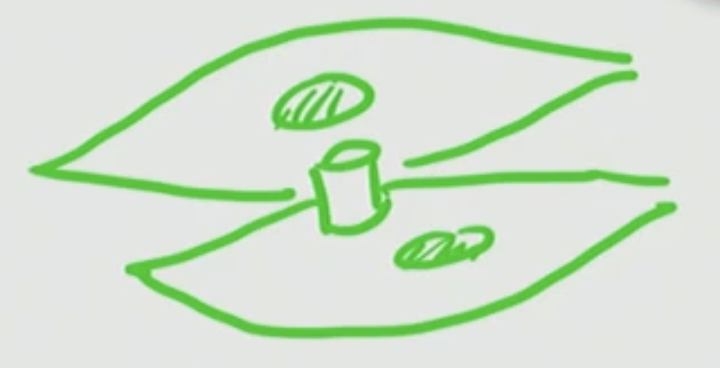
What can pass through gap junctions?
AP pass through gap junctions, as an AP can occur in one cell and travel to the adjacent cell and cause that cell to fire off an AP