Chapter 15: Lecture: Part 1
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
pathogenicity
the ability to cause disease
virulence
the degree of pathogenicity
portal of entry
mucous membranes (eyes, nose, mouth, sexual contact
skin/wound
parenteral route
deposited directly into tissues when barriers are penetrated
True or False: Most pathogens have a preferred portal of entry
true
Define ID50 and what does it measure?
infectious dose for 50% of sample population (or tissue or cell)
measures virulence of a microbe
LD50 and what does it measure ?
lethal dose for 50% of sample population (or tissue or cell)
measures potency of a toxin
Almost all pathogens attach to host tissues in a process known as what ?
Adherence or adhesion
an accessory in a pathogen that helps it bind to receptors in the host cells
adhesins (ligand)
Where can you find adhesins ?
in glycocalyx (biofilm, capsules)
fimbriae
pili
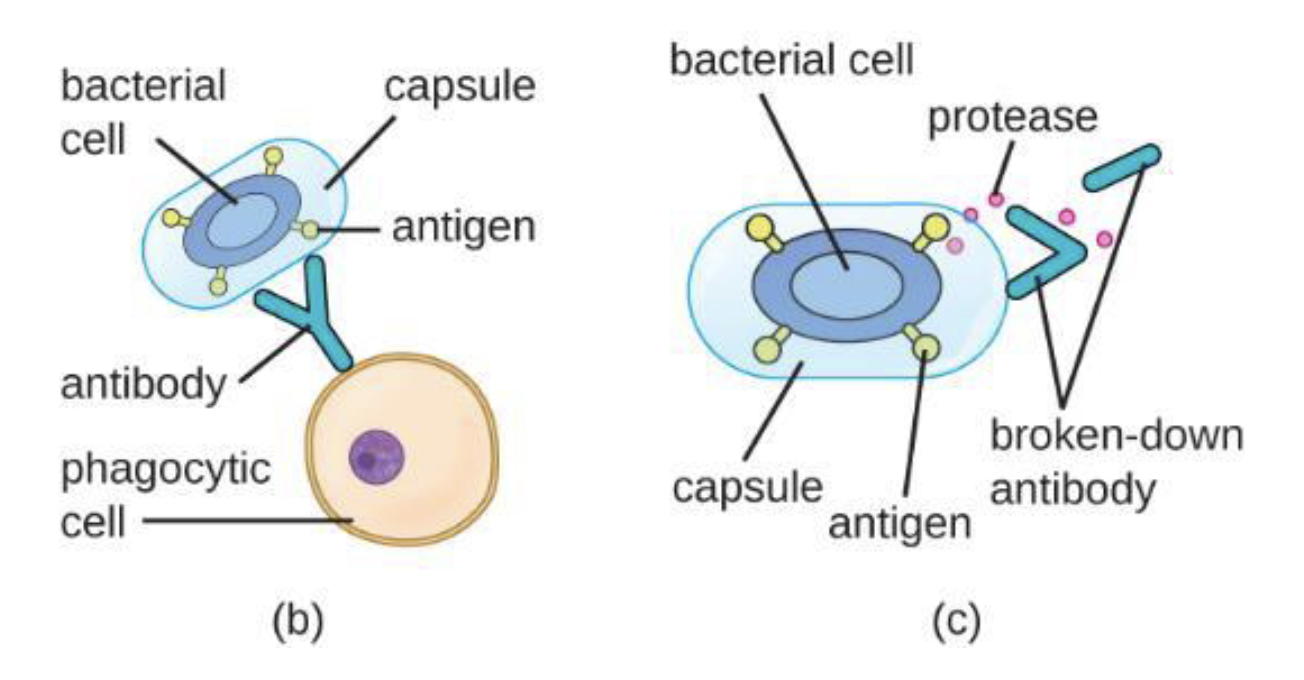
What does b) and c) depict ?
b) antibodies normally function by binding to antigens, molecules on the surface of pathogenic bacteria. Phagocytes then bind to the antibody, initiating phagocytosis
c) some bacteria also produce proteases, virulence factors that break down host antibodies to evade phagocytosis
Name bacteria with capsules
Yes,- Yersinia pestis
Some- Streptococcus pneumoniae
Killers- Klebsiella pneumoniae
Have- Haemophilus influenza
Pretty- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Nice- Neisseria meningitidis
Capsule- Cryptococcus neoformans
Cell Wall Components
M Protein resists phagocytosis
Opa protein allows attachment to host calls
Waxy lipid (mycolic acid) resist digestion
Give an example of an organism that contains an M protein
Streptococcus Pygoenes
Give an example of an organism that contains an opa protein
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Give an example of an organism that contains waxy lipid
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Coagulase
coagulate fibrinogen
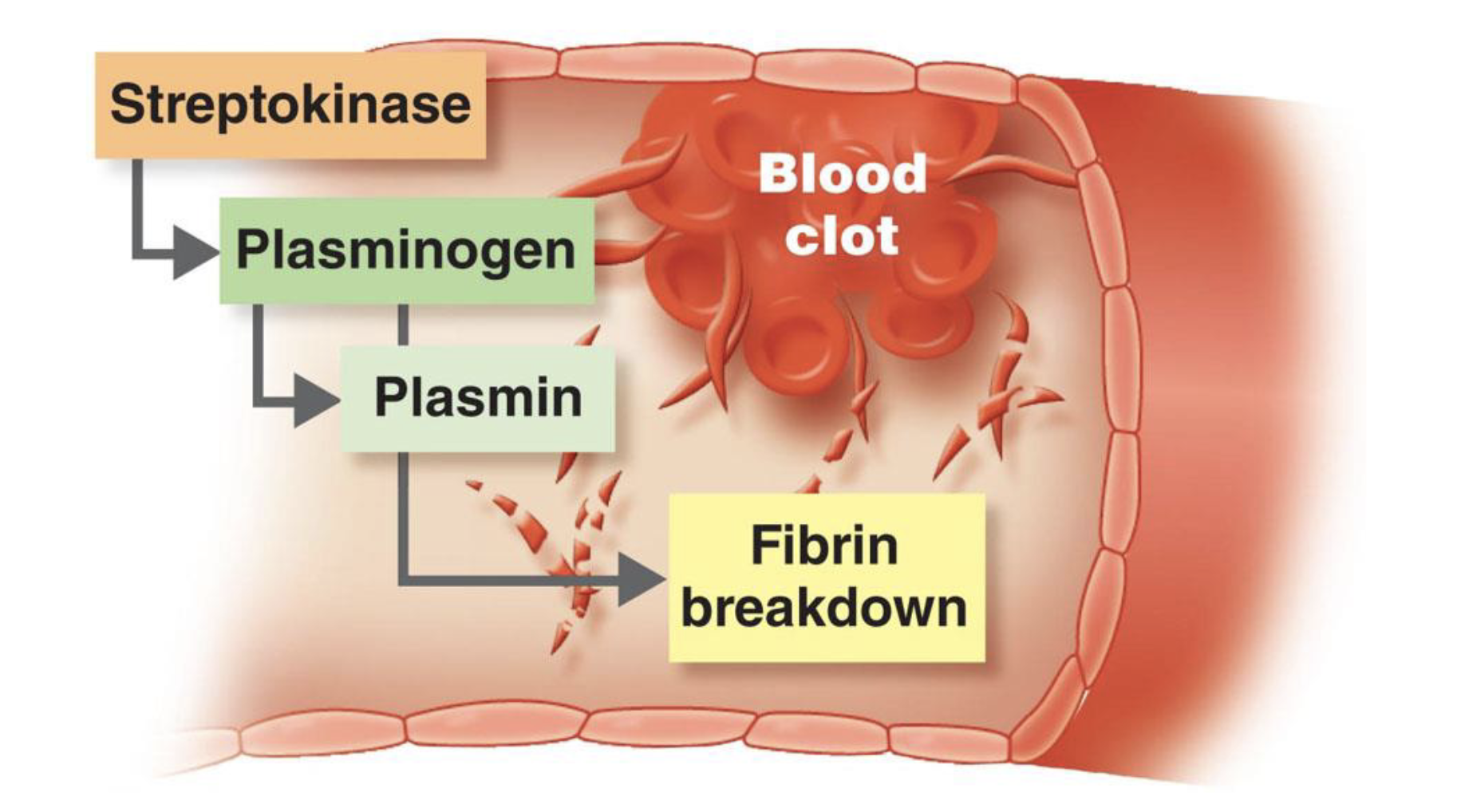
Kinases
digest fibrin clots
Hyaluronidase
digests polysaccharides that hold cells together
Collagenase
breaks down collagen
IgA protease
destroy IgA antibodies
Streptokinase
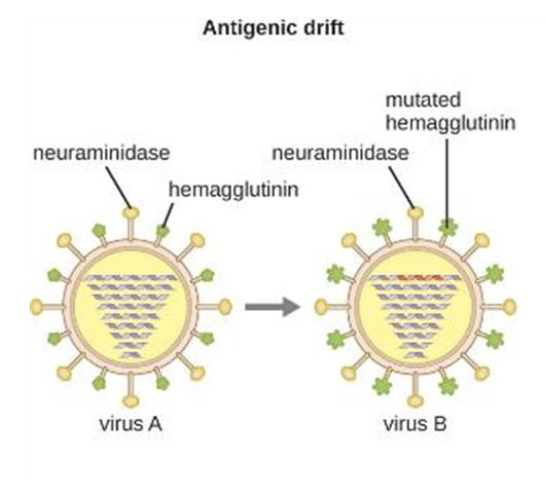
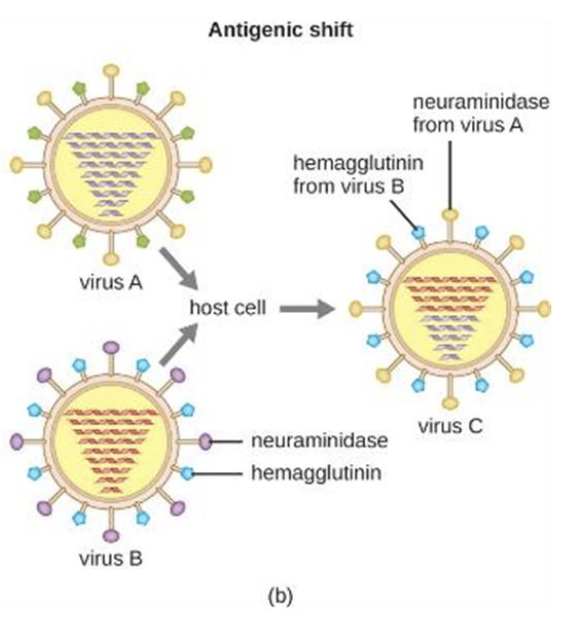
How does Antigenic Variation work?
Pathogens alter their surface antigens
Antibodies are rendered ineffective
Vaccines are less effective
Give examples of species that demonstrate antigenic variation
Trypanosoma sp.
Influenza
Covid-19
Antigenic drift
Antigenic shift
Penetration into the Host Cell Cytoskeleton
Invasins
Surface proteins produced by bacteria that rearrange actin filaments of the cytoskeleton
cause membrane ruffling
Give examples of species that use actin to move from one cell to the next
Shigella sp.
Listeria sp.