Spectroscopy Recall
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
de Broglie relationship
λ=h/p h= planck constant
speed of light frequeny and wavelength
Co = νλ.
energy of photon
E=hv=hco/λ =hcv~ v~ =wavenumber
Relationship between energy and quantity of material
E=kBT (molecular)
E=RT (molar)
Boltzmann distribution
N1/N0 = e^(- ΔE /k BT)
Beer Lambert Law
A=-log10 (It/Io)=εcl
Chromophore
colour bringer e.g. a carbonyl group that undergoes electronic transitions between bonding and antibonding orbitals. They usually have a carbonyl of conjugated pi system.
Conjugation
alternating pi bonds, the more conjugation the greater the absorbtion maximum difference between HOMO and LUMO decreased.
Frequency of vibration
ve=1/2pi sqrt (k/m) m=μ for 2 connected particles
Potential energy
V(r) = ½ k (r-re)2
Molecular potential enegry curve
lowest is not at minimum only certain values of energy allowed
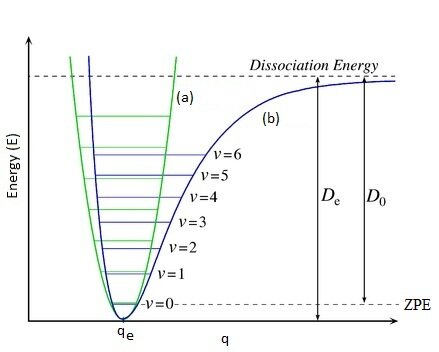
Energy of molecular vibration
E(v) = hνe(v +½) v=vibrational quantum number
What molecules are IR active
if there is a molecular dipole e.g. must be diatomic, electron density not equally shared, assymetric
Vibrational modes
n atoms in molecule 3n-6 vibrational modes (3n-5) if linear
O-H vibrational frequency
3500
C-H vibrational frequency
3000
C≡N vibrational frequency
2250
C=C aromatic vibrational frequency
1500 and 1600
C=O vibrational frequency
1750
C=C vibrational frequency
1630
NMR theory
Nucleus with magnetic dipole put into applied magnetic field
Electrons in nucleus shield from applied magnetic field
Causes electrons to move => current
Current generates an induced magnetic field
Effective magnetif cield = applies x (1xS) S = shielding constant
Chemical shift also affected by aromatic rings and pi bonding —> causes ring current which has a shielding effecr hence absorbs at higher frequencies
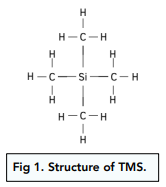
Standards in NMR
TMS has lots of electron density, inert, hard to measure meagnetic field in NMR machine so measure frequency relative to TMS instead
R=OH chemical shift
9.0-9.8
aromatics chemical shift
6.2-8.0
amide chemical shift
5-8
C=CH2 chemical shift
4.6-5.4
HOCH alcohol chemical shift
3.2-4.1
ester RCO2CH chemical shift
3.3-5.0
halide Cl/Br-CH chemical shift
2.9-4.0
R=COCH ester chemical shift
2-3.7
Coupling
If magnetic field of HA is affected by that of HB it will be split into 2 equal lines and vice versa. This depends on wether HA sees Hb in +1/2 or -1/2 spinn state this leads to spin spin coupling (peak heights follow pascals triangle)