Storms 3: Tornadoes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Visible tornadoes
1) recognizable from funnel cloud (most tornadoes)
2) dust and debris from ground (where the tornado hits)
3) some are invisible
Shapes for torndaoes
cones, v-shapes, wedge, cylinder, hour class, rope
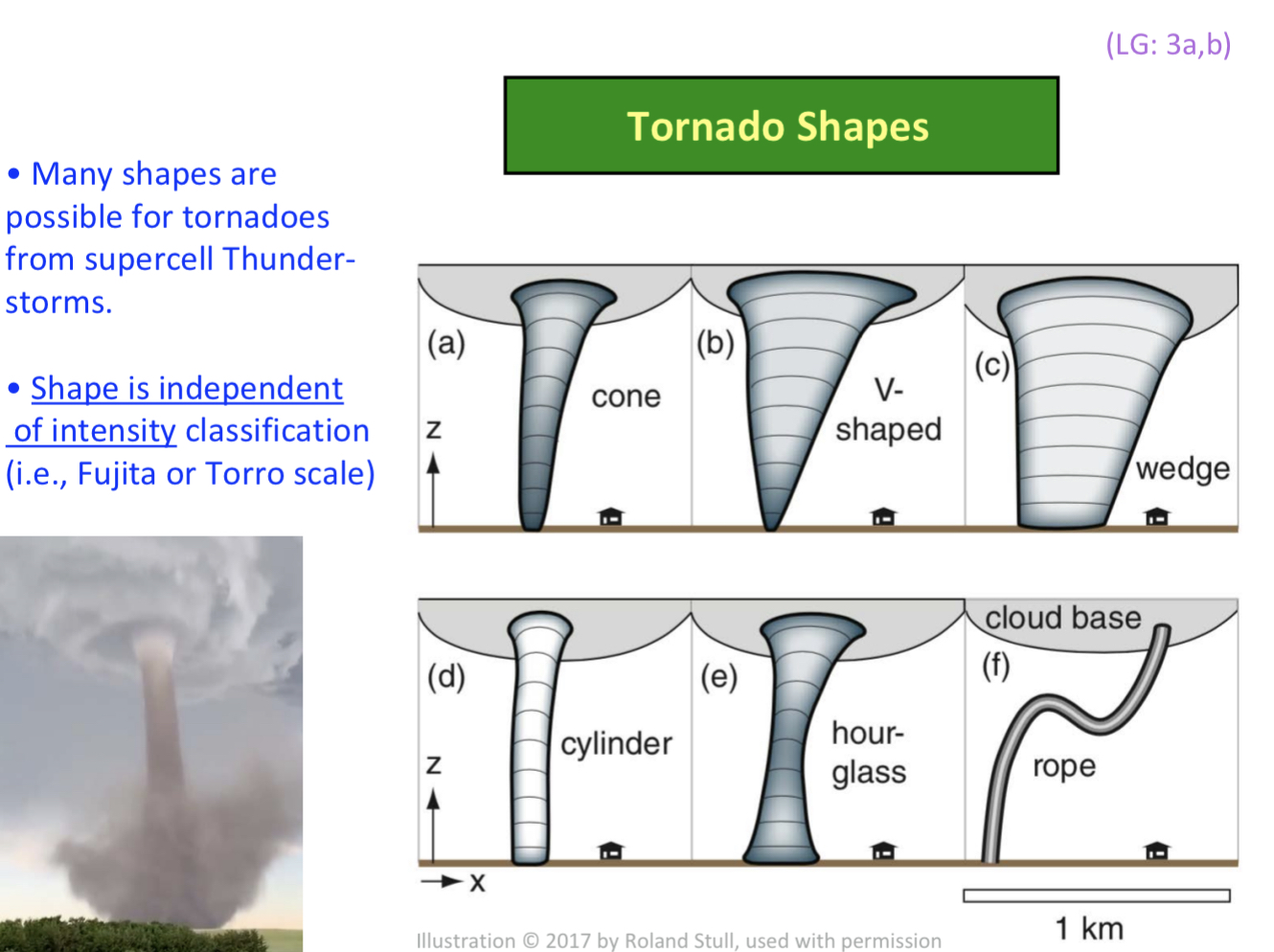
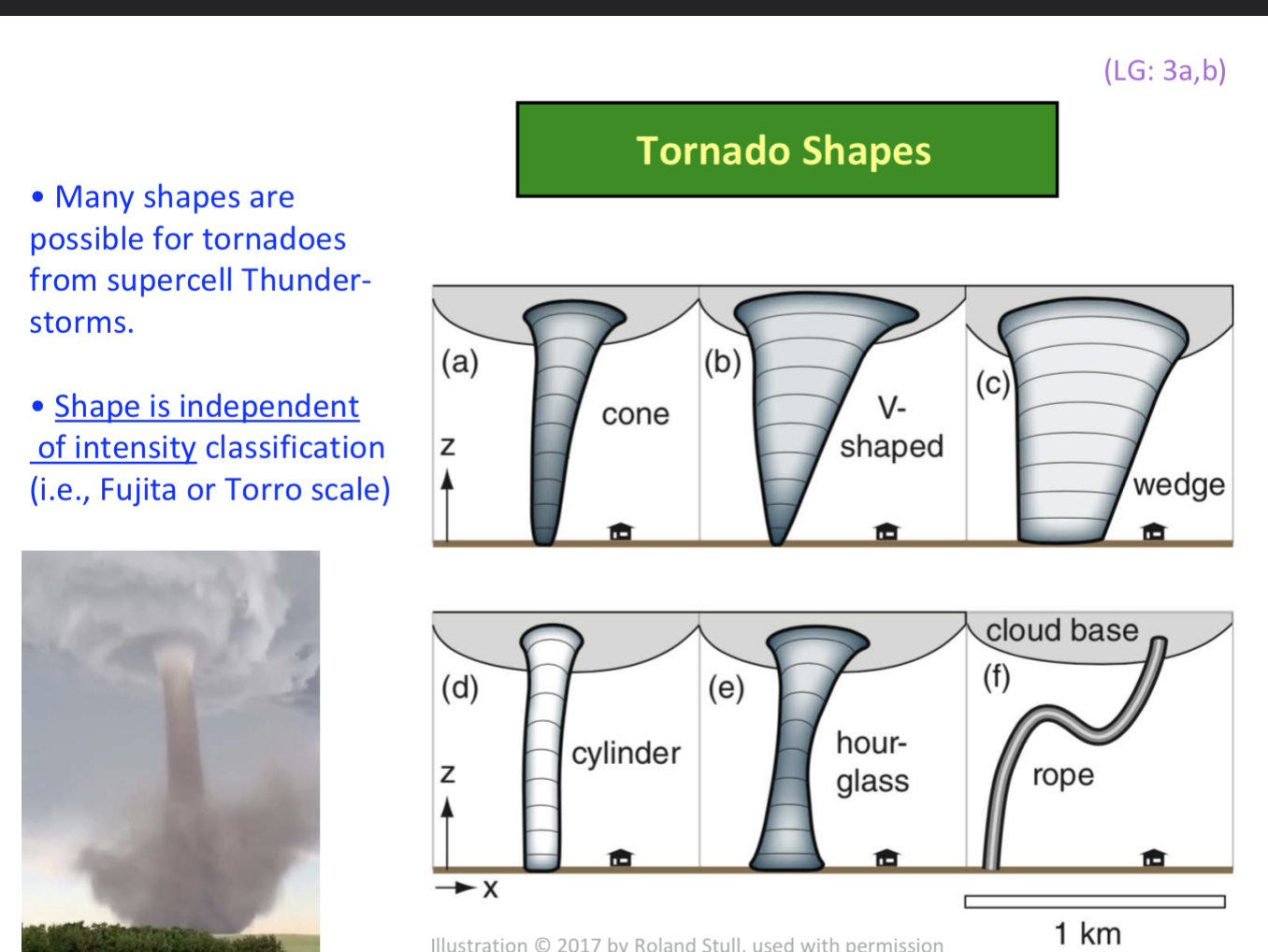
Is the shape of the tornado dependent or independent of intensity classification (fujita or torro)?
its independent
Relationship between tornado and thunderstorms
tornadoes are attached to thunderstorm
only 20-30 percent Supercell thunderstorms produce tornadoes
in North. Amer. T storms move SW to NE
supercell storms
strongest
most commonly associated w/ tornadoes
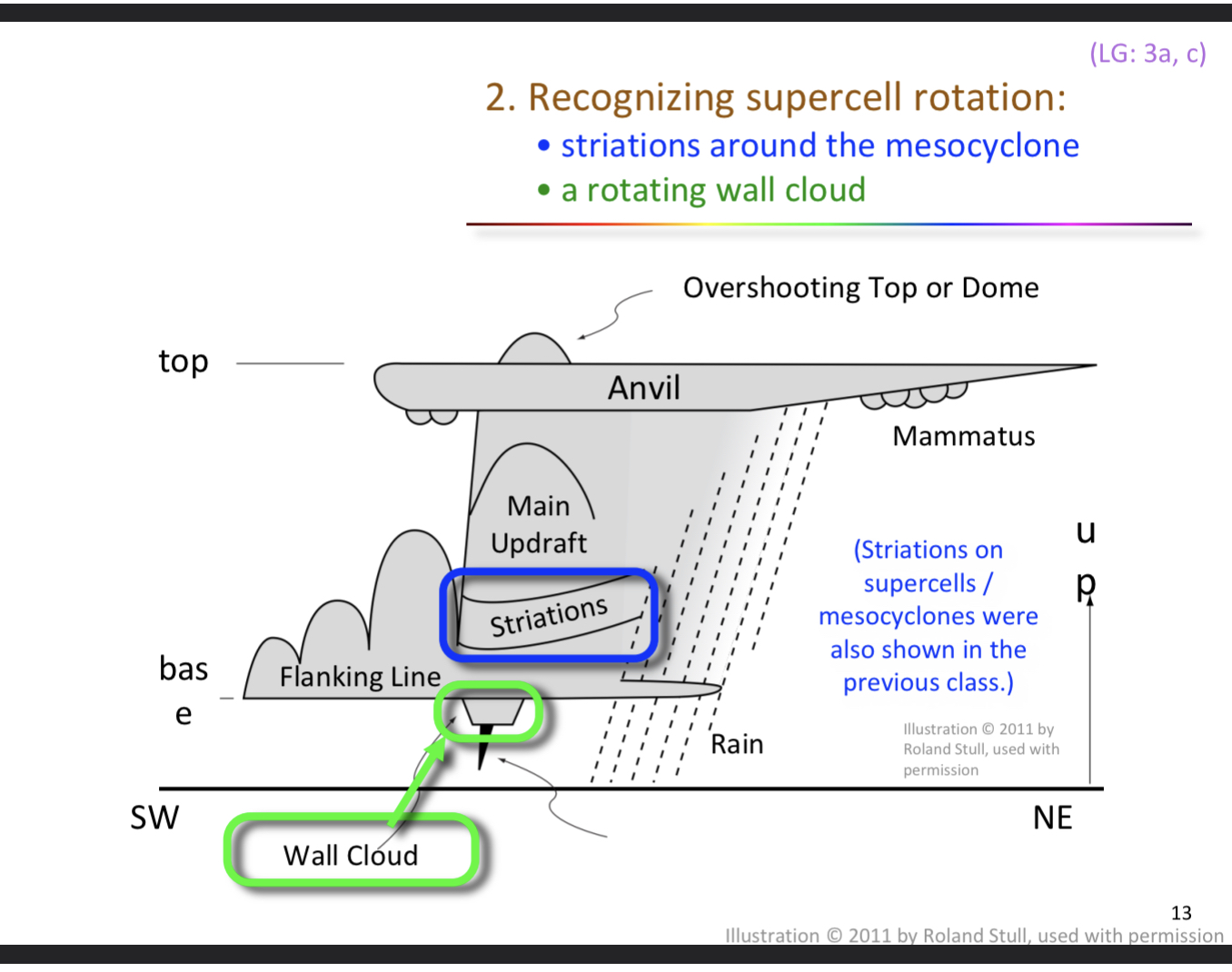
recognizing supercell rotation
striation around mesocylone
rotating wall cloud
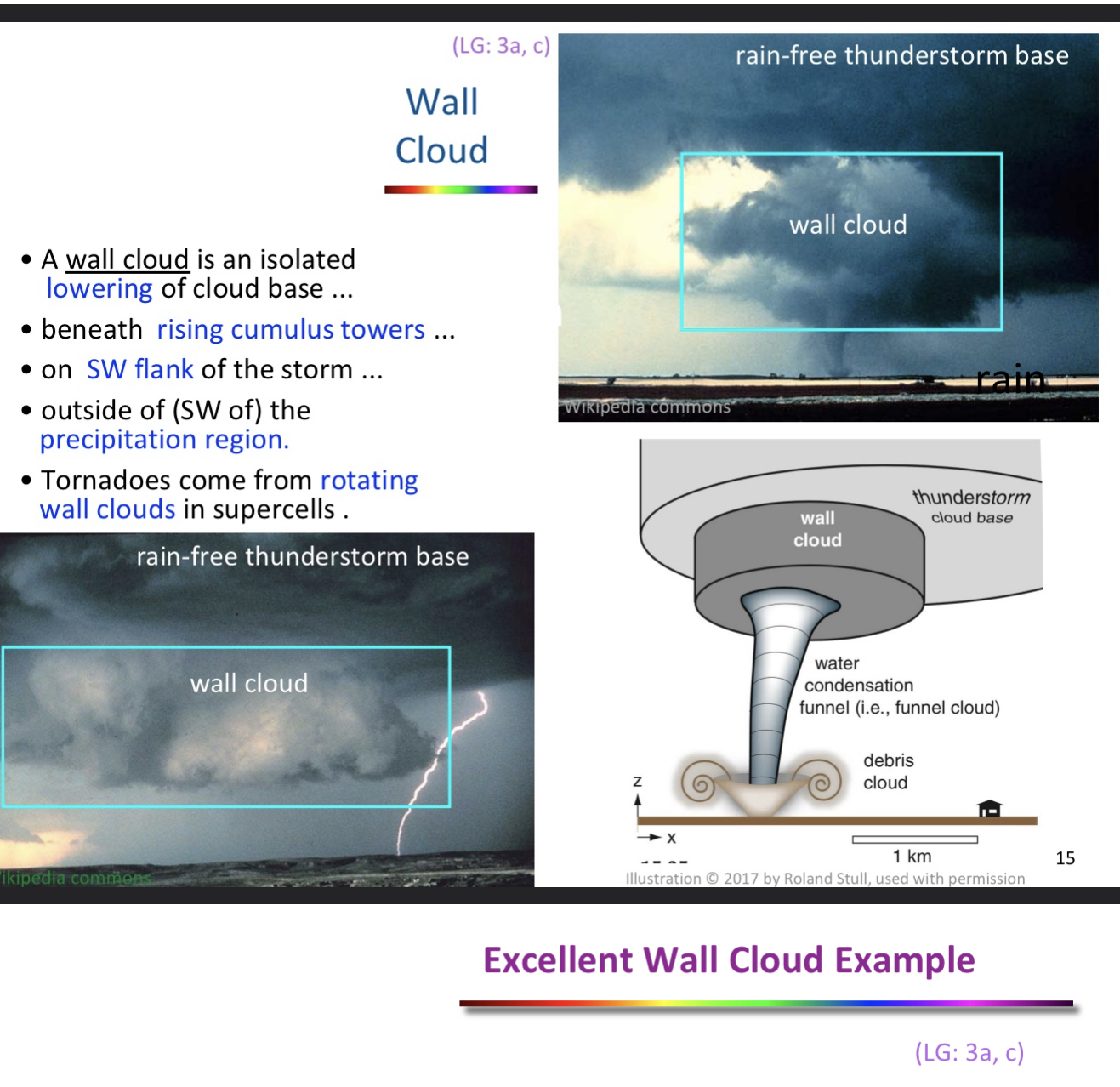
wall cloud
isolated lowering of cloud base
above funnel
on SW of storm
tornadoes come from rotating wall clouds in supercells
Horizontal movement (translation) of the center of tornado
usually SW —> NE in north America
translation speed 0-100km
if in car, drive perpendicular to tornado path
Rotational (tangential) speeds
rotational speeds around the center are much faster than translation speeds.
Cause damage!
classified by enhanced Fujita and torro
Enhanced Fujita scale (N.America)
determined by amount of damage to buildings
EF0- very weak
EF5- exceptionally strong
Torro Scale
determined by wind speed
Tornado safety
If indoors:
below ground (basement)
get out of mobile homes
if outdoors on foot
get into a ditch/hole
place body below “line of fire”
If in car
drive away from tornado
drive preferably to right or left of translation direction of tornado
do NOT hide under highway bridge/ overpass
tornado outbreak
6 tornadoes in one day and one region, or many tornadoes during about a week
ASSOCIATED w/ SQUALL LINES (which form along cold fronts)
many tornado outbreaks
squall lines and tornados
tornado outbreaks associated with squall lines
squall lines for along cold fronts
as cold front moves towards SE, thunderstorm along the front move NE
5 stages tornado evolution
1) thunderstorm // small dust whirl
2) funnel cloud
3) mature tornado
4) decaying “rope” stage
5) dissipating
Doppler radar
sees tornado vortex signature (TVS)
tornado nowcast warning tells you
where its is
where its moving
which towns/ countries
sirens activated
(warning 15 min or less). immediately react
hook echo
when there a little hook shape in storm formation (reflectivity) radar
In North America, thunderstorms move in which direction?
South West —> North East
What are 2 things you can look for when trying to recognize supercell rotation?
1) striation around the mesoclyne
2) a rotating wall cloud
How long can a tornado last and how much damage can they cause?
Rarely last for hours
Rarely have damage path 1km wide, or 100 km long
Where go Tornados occur the most?
Midwest-south of America and South of Canada (South of Alberta, Sasketchwan, Manitoba, Ontario, and Quebec -which has the most)
What is Graupel?
small hail
Waterspout
A tornado on the water
As cold front moves SE, the thunderstorms move..
NE North East
When will you recieve a tornado warning?
15 minutes prior to a tornado hitting you b/c very hard to detect