Biology test 2
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where do the light-dependent reactions take place?
within the thylakoid membranes
Where do the dark reactions take place?
stroma of the chloroplast
photosystems
light-collecting units of the chloroplast; protein+chlorophyll
Photosystem II
First; makes ATP
Photosystem I
Second; makes NADPH
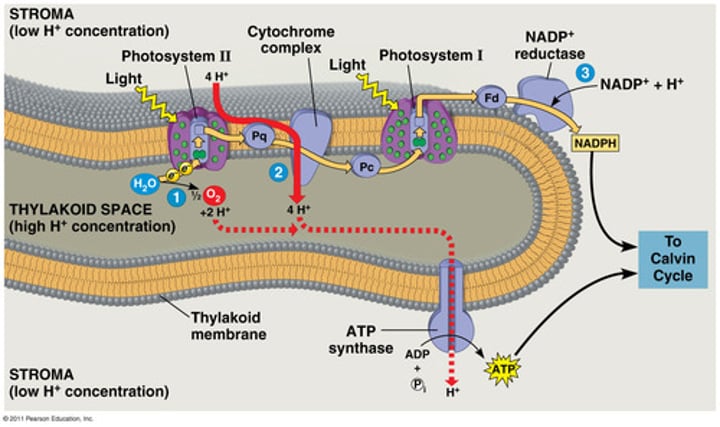
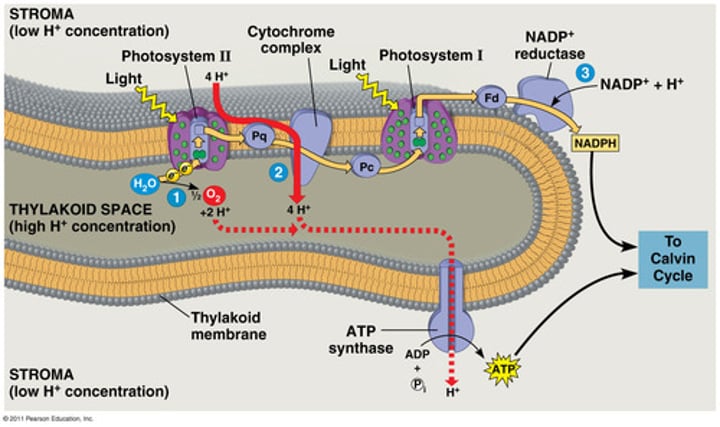
light-dependent reactions
reactions of photosynthesis that use energy from light and water to produce ATP and NADPH
-happens in the thylakoid membrane
1.) Light enters through photosystem II and then I by photon being absorbed by chloroplasts within.
2.) Light excites H2O particles which makes them split into in electrons and Hydrogen protons ;O in H2O leaves. (Only happens in photosystem II)
3.) Light also excited these electrons, and causes them to leave and pass through integral proteins; Electrons from H2O replenish this.
4.) Photosystem I receives these electrons and also uses P2 generated supply, and sunlight causes it to work with NADP+ reductase to make NADPH.
5.) Hydrogen protons also split by P1 and light flow to ATP synthase to generate ATP.
Creates Energy- "photo"
NADPH vs NADH
NADPH: only in photosynthesis
NADH: cellular respiration: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain
light-dependent reactions
Calvin-Benson cycle;
1.) Carbon Fixation: 6 CO2 (◉ each)combine with 6 RuBP (◉◉◉◉◉) with RuBisCo to make 12 PGA (◉◉◉)
2.) Reduction: 12 ATP (2 per CO2 invested) and 12 NADPH turn into 12 ADP and 12 NAD+; this powers the 12 PGA (◉◉◉) to turn into 12 G3P (◉◉◉)
3) Regeneration: of 12 G3P (◉◉◉), 2 G3Ps (has 6 C total) are used to make 1 glucose; other 10 G3P (30 C total) use half of previous ATP (6 in this case) to regenerate 6 RuBP to start cycle again. (◉◉◉◉◉)
synthesis part; uses energy from light reaction plus CO2 to make glucose.
Combustion Reaction
Fuel+O2--->CO2+H2O
cellular respiration formula
C6H12O2 + 6O2 ------> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP)
carbs and oil can be fuel because
they are made of hydrocarbons
aerobic respiration equation
small energy inversion+glucose + oxygen --> carbon dioxide + water + more energy
aerobic respiration
breakdown of glucose ,using oxygen, to energy
-makes 32-38 ATP
3-4 Steps: Glycolysis; intermediate/ Link reaction step; Krebs cycle; ETC.
Anaerobic vs. Aerobic
anaerobic: no oxygen, 2 ATP
aerobic: oxygen, 38 ATP
order or of aerobic respiration
Glycolysis, intermediate, krebs, ETC.
Glycolysis
TAKES PLACE IN CYTOPLASM; OUTSIDE OF MITOCHONDRIA
first step in releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvates.
1.) 2 ATPs invested to split molecule in half ; halves called G3P EACH LOOKS LIKE: P-⦿◎⦿⦿/⦿◉◉◉/⦿◎⦿◎
2.) 2 Phosphates are added to make
P-⦿◎⦿⦿/⦿◉◉◉/⦿◎⦿◎-P per half
3.) 2 NAD+ take 2 hydrogen atoms for electrons, becoming 2 NADH and leaving each pyruvate appearing as: P-⦿◎⦿/⦿◉◉◉/⦿◎⦿◎-P (removes 1 hydrogen per half)
4.) 4 ATPs are receive phosphates leaving a net gain of 2 ATP and: each half appearing as: ⦿◎⦿/⦿◉◉◉/⦿◎⦿◎
5.) molecules are ready to be modified for following steps.
⦿◎⦿/⦿◉◉◉/⦿◎⦿◎ + ⦿◎⦿/⦿◉◉◉/⦿◎⦿◎made
(two pyruvates, 2 NADH and 2 ATPs)
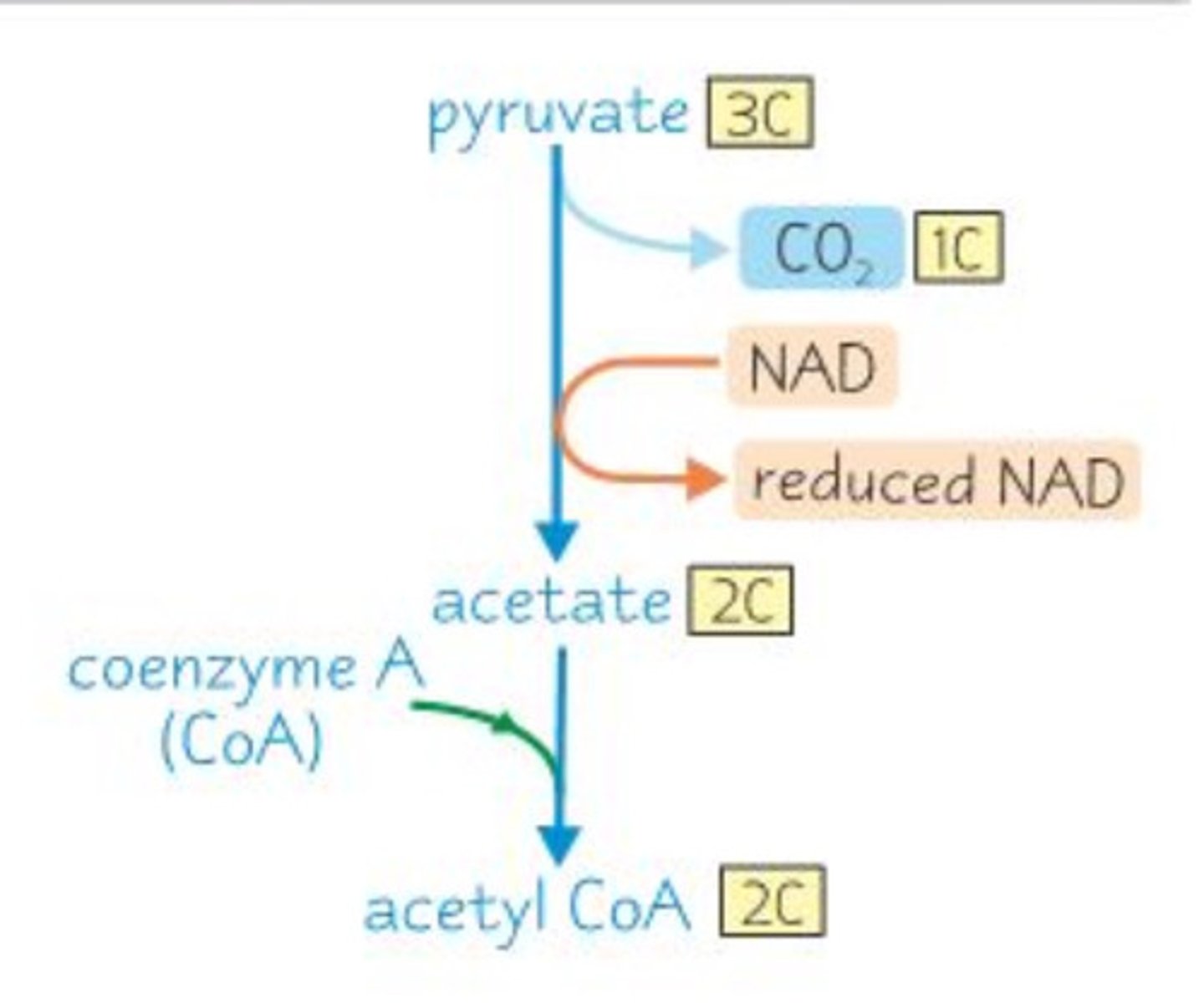
Intermediate/ Link reaction step
TAKES PLACE IN MATRIX (FLUID SPACE OF MITOCHONDRIA)
2nd; happens after Glycolysis:
1.) 1 Pyruvate (◉◉◉) enters and binds with 1 Coenzyme A (◘)
2.) Makes 1 Co2 (◉) leave and one NAD+ receives electrons from reaction to become 1 NADH
3.) This results in Acetyl-CoA, which is used to initiate Krebs cycle (◉◉-◘)
repeats twice, one per pyruvate in each glucose molecule. Net gain of 2 total NADH
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
TAKES PLACE IN MATRIX (FLUID SPACE OF MITOCHONDRIA)
3rd; happens after acetyl-CoA step
1.) 1 oxaloacetic acid (◉◉◉◉) combines with the acetyl-CoA (◉◉-◘) to form CITRIC ACID; co enzyme A leaves (-◘). =(◉◉◉◉◉◉)
2.) 1 NAD+ turns to NADH as electrons are stripped off it, causing 1 CO2 to leave (-◉) an resulting in: ◉◉◉◉◉
3.) another NAD+ turns to NADH causing another CO2 to leave (-◉), causing: ◉◉◉◉
4.) An ADP is turned to ATP
5.) FAD is turned to FADH2
6.) another NAD+ is turned to NADH, resulting in significant energy plus oxaloacetic acid regeneration.
products: 3 NADH, 1 ATP, FADH2, 2 CO2 waste and oxoacetic acid.
per two pyruvates: 6 NADH, 2 ATP, 2 FADH2, 4 CO2 waste and two oxoacetic acid.
HAPPENS TWICE PER GLUCOSE MOLECULE, 1 PER PYRUVATE
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
TAKES PLACE IN CRISTAE (INNER MEMBRANE.)
happens last
1.) NADH AND FADH2 donate protons and electrons to start process.
2.) electrons pass through membrane proteins until it binds with oxygen gas and other proton to form WATER
3.) Protons head out wards and go through ATP synthase to become ATP, created final product of about 32 ATP.
products 32 ATP plus water
anaerobic respiration
two types: Lactic Acid and Alcohol fermentation.
lactic acid fermentation
usually done by animals and humans when lack of oxygen and some bacteria.
1.) Glycolysis occurs, creating 2 ATP and 2 pyruvates
2.)1 Pyruvate (◉◉◉) is given protons and electrons, turning 1 NADH to NAD+.
3.) Pyruvate + (H+ & e-)= Lactic Acid (◉◉◉)
Net gain of only 2 ATP which is only given in Glycolysis
alcohol fermentation
usually done in yeasts; some bacteria.
1.) Glycolysis occurs, creating 2 ATP and 2 Pyruvates.
2.) 1 Pyruvate (◉◉◉) is given protons and electrons, turning 1 NADH to NAD+.
3.) 1 CO2 molecule leaves the pyruvate (-◉)
4.) 2-C pyruvate + (h+ & e-) = ETHANOL (◉◉)
Net gain of only 2 ATP which is only given in Glycolysis
obligate anaerobes
carry out fermentation or anaerobic respiration and cannot survive in the presence of O2 (ex. fungi, botulinum.)
obligate aerobes
organisms that must pretty much always be exposed to oxygen in order to survive. (ex. humans.)
*can sometimes do anaerobic but can not rely on it for long enough
facultative anaerobes
organisms that will do aerobic respiration is O2 is present but get by anaerobic respiration well. (ex. E Coli.)