Inheritance
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
What is the genome?
The entire DNA of an organism
What is a gene?
A section of DNA that codes for a specific protein
Genes are located on…
Chromosomes
What are chromosomes?
Long strands of DNA that are found in the nucleus
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Describe the structure of DNA
→ 2 polynucleotide strands coiled into a double helix
→ The strands are linked together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases
What are the 4 bases found in DNA?
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
A is complementary to…
T
C is complementary to…
G
How many bases code for an amino acid?
3
How many types of amino acid are there?
20
Describe DNA replication (unrelated to protein synthesis)
The polynucleotide strands of DNA separate when hydrogen bonds between bases are broken by enzyme helicase
Each strand acts as a template for the formation of a new strand of DNA
The enzyme DNA polymerase assembles nucleotides into two new strands according to the base-pairing rule.
Two identical DNA molecules are formed — each contains a strand from the parent DNA and a new complementary strand.
What does RNA stand for?
Ribonucleic acid
What are the differences between DNA & RNA?
DNA → Double stranded, has thymine as a base, sugar is deoxyribose
RNA → Single stranded, has uracil instead of thymine, sugar is ribose
What are the 3 types of RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
What is protein synthesis?
The process by which genetic information from DNA is copied & transported out the nucleus in order to make proteins
This happens because DNA is too large to leave the nucleus
What are the 2 stages of protein synthesis?
Transcription
Translation
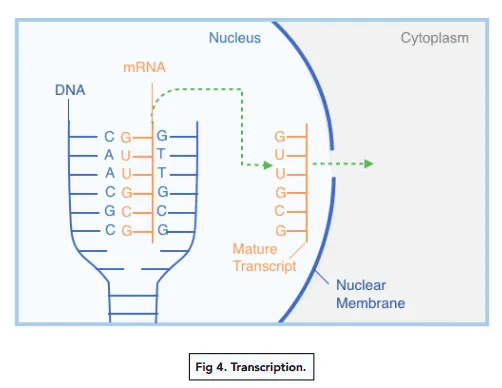
What happens in transcription?
The polynucleotide strands of DNA separate when hydrogen bonds between bases are broken by enzyme helicase
Complementary mRNA nucleotides in the nucleus line up to the bases on the template strand
The enzyme RNA polymerase bind those nucleotides to make the mRNA strand
mRNA detaches & leaves the nucleus
The DNA coils back up into a double helix
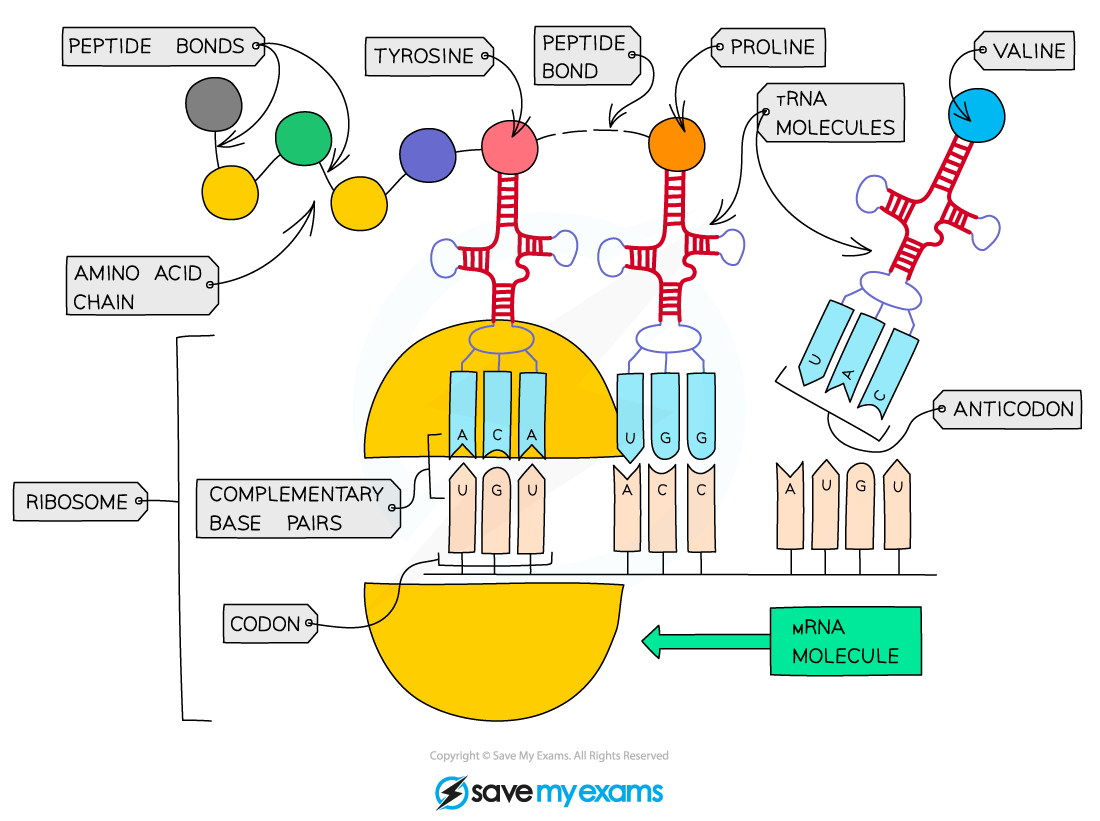
What happens in translation?
→ A mRNA molecule attaches to a ribosome
→ tRNA molecules in the cytoplasm have an anticodon that is complementary to the codon on mRNA
→ Each tRNA also carries a specific amino acid
→ The first anticondon binds to the start codon on mRNA & the the second anticodon binds to the next codon on mRNA
→ A peptide bond is formed between the first 2 amino acids
→ The first tRNA is then released & the ribosome moves along to the next codon.
→ More tRNA binds to the mRNA, adding amino acids to the growing chain
→ When the stop codon on the mRNA is reached, the protein is released from the ribosome
What is a codon?
3 bases that code for an amino acid
What is an anticodon?
3 bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to the codon on the mRNA molecule
What are alleles?
Different forms of the same gene that allow differences in inherited characteristics
(e.g. humans have 2 alleles for each gene as they inherit 1 from each parent)
What is the dominant allele?
The allele that only needs 1 copy for it to be expressed
What is the recessive allele?
The allele that needs 2 copies for it to be expressed
What is homozygous?
When both inherited alleles are the same
What is heterozygous?
When 1 of the inherited alleles is dominant & the other is recessive
What is the genotype?
The alleles an organism has for a certain characteristic
What is the phenotype?
The physical observable characteristic an organism has due to its genotype
What is codominance?
When both alleles are equal & therefore both are expressed in the phenotype
What is monohybrid inheritance?
The inheritance of 1 allele
What is a Punnett Square?
A table that shows all the possible outcomes for a genetic cross between 2 parents with known genotypes
Give a Punnett Square for a cross between a heterozygous blue eyed male (Bb) with a homozygous recessive green eyed female (bb)
50% blue eyed
50% green eyed

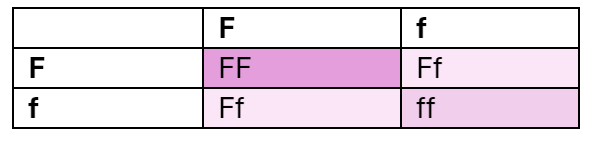
Give a Punnet Square for a cross between a homozygous dominant red flower (RR) with a homozygous recessive white flower (rr)
100% red flowers
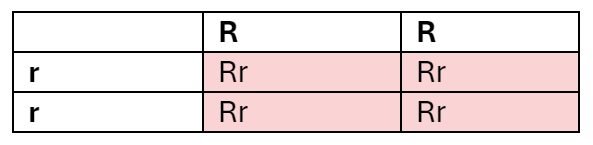
Give a Punnett Square for a cross between 2 heterozygous cystic fibrosis carries (Ff)
25% healthy
50% carriers
25% have CF
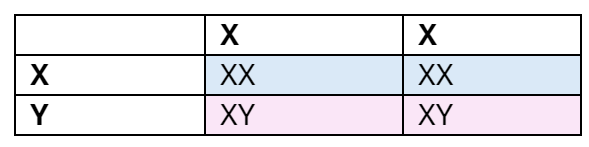
Give a Punnett Square to show how gender is determined
XY → 50% male
XX → 50% female
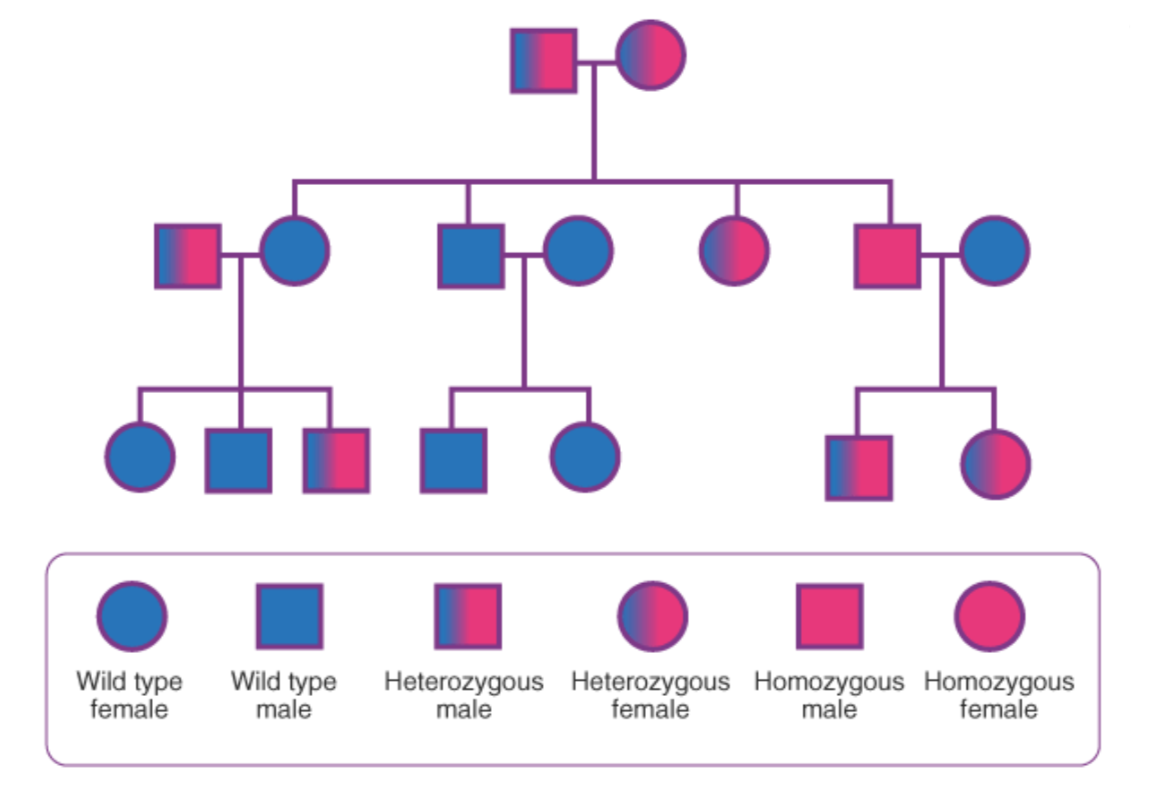
What are family pedigrees?
A diagram that shows the inheritance of an allele over generations
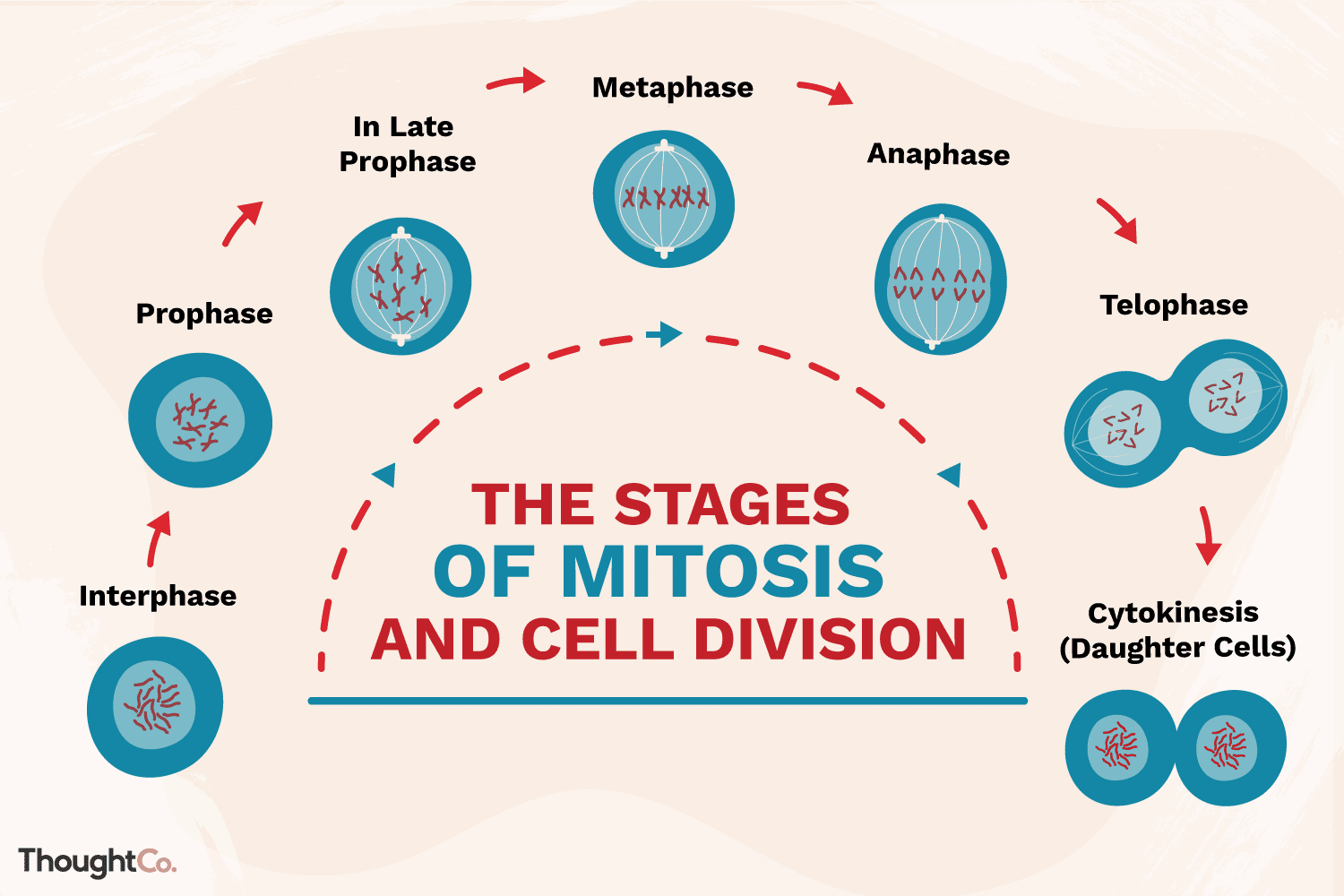
What is mitosis?
A type of cell division where a cell divides to form 2 genetically identical diploid daughter cells
What are the stages of mitosis?
Interphase → All 46 chromosomes are replicated
Prophase → The nuclear membrane breaks down
Metaphase → A spindle forms & the chromosomes line up against it, attached by their centromeres
Anaphase → Spindle fibres pull chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell
Telophase → 2 new nuclei form at the poles of the cell
Cytokinesis → The cell membrane divides into 2 daughter cells that are genetically identical to the original cell
Mitosis occurs during…
→ Growth
→ Repair
→ Cloning
→ Asexual reproduction
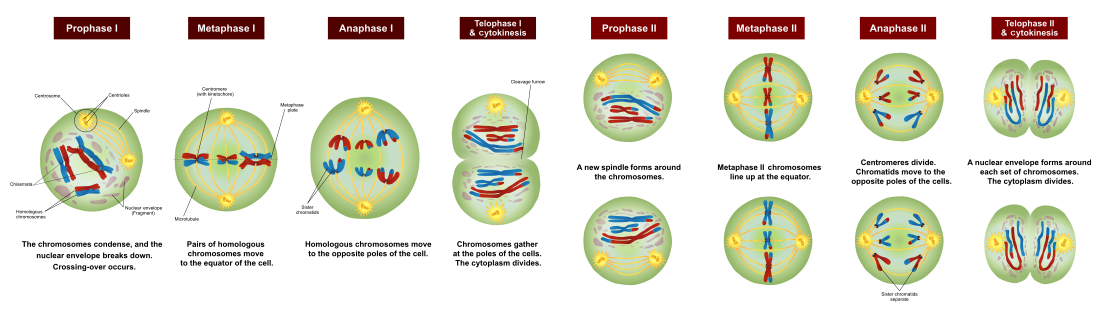
What is meiosis?
A type of cell division where a cell divides to form 4 genetically varied haploid daughter cells
What are the stages of meiosis?
→ Each chromosome in the parent cell forms a copy of itself & exists as a pair of chromatids joined at the centromere
→ Chromatids pair up in homologous pairs at the equator of the cell
→ The pairs are pulled apart to the opposite poles & the cell divides to form 2 daughter cells with 46 chromosomes
→ The chromatids in the 2 daughter cells line up at the equator & are pulled apart again to the opposite poles
→ Both cells divide to form 4 daughter cells with 23 chromosomes
Meiosis produces….
Gametes
What are the differences between mitosis & meiosis?
Mitosis → produces 2 diploid daughter cells that are genetically identical
Meiosis → produces 4 haploid daughter cells that have genetic variation
What does diploid mean?
2 complete sets of chromosomes, 1 from each parent
What does haploid mean?
A single set of chromosomes
What is the diploid number of chromosomes in humans?
46
What is the haploid number of chromosomes in humans?
23
What is random fertilisation?
The random chance of a specific male gamete fusing with a specific female gamete
This produces genetic variation in offspring
What are the different types of variation?
Genetic
Environmental
Genetic + environmental (both)
Give 2 examples of genetic variation
→ Eye colour
→ Blood type
Give 2 examples of environmental variation
→ White moths becoming darker in polluted areas
→ Polar bears have thick white fur which reduces heat loss & helps them camouflage
Give 2 examples of genetic + environmental variation
→ Height
→ Weight
What is mutation?
A rare & random change in genetic material
How do mutations affect the phenotype?
Mutations alter genetic material (DNA) which can cause it to code for a different sequence of amino acids
A different sequence of amino acids means that the protein will be different
This can either be beneficial, neutral or harmful
What factors increase the chance of mutations?
→ Ionising radiation
→ Certain chemicals (e.g. chemicals in cigarette smoke or tobacco)
What is the process of natural selection?
→ Populations are naturally varied due to random genetic mutations
→ Some of these mutations provide a selective advantage
→ Organisms with a selective advantage are more likely to survive & reproduce, passing on their successful genes
What is evolution?
A change in the inherited characteristics of a population overtime due to natural selection
Who came up with the theory of evolution by natural selection?
Charles Darwin
How does antibiotic resistance arise?
→ Random genetic mutations can cause some bacteria to become resistant to an antibiotic
→ When the antibiotic is used, the resistant bacteria survives & the non-resistant bacteria is destroyed
→ The resistant bacteria has a selective advantage & therefore quickly reproduces & continues to cause disease
Why does antibiotic resistance cause risks?
Because some disease causing bacteria cannot be treated with antibiotics as it is resistant, making the bacteria difficult to control
This can result in serious health issues & even death