Tonicity Regulation
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
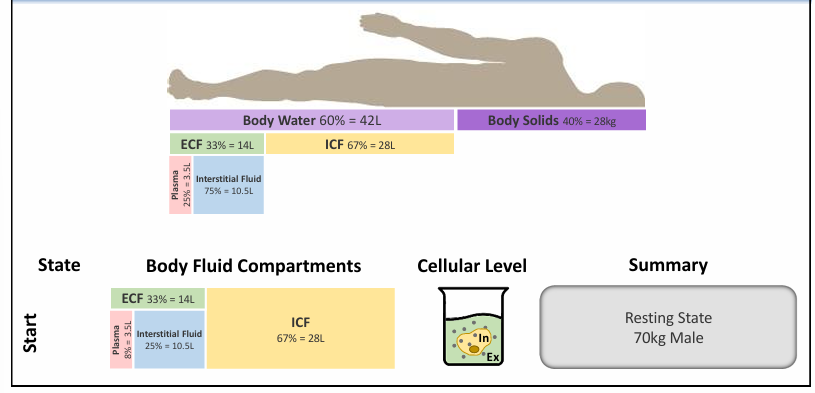
body compartments
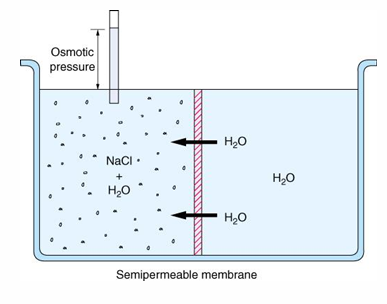
osmotic pressure (tonicity) v osmolality
-osmotic pressure = reflects the number of osmotically active particles in each compartment and determines fluid distribution
-osmolality = reflects the total number of particles in solution and is measured in the lab
-osmotic pressure is NOT the same as osmolality
-for a particle to exert osmotic pressure and be an effective osmole it must be restricted from movement across the 2 compartments (otherwise “ineffective osmole”- urea)

osmotic pressure (tonicity)
-proportional to the number of particles in a solution (not size, weight, or valence)
-units = osmole (osm)
-1 osm = 1mol of any substance represents the same number of particles (6.02×10^23)
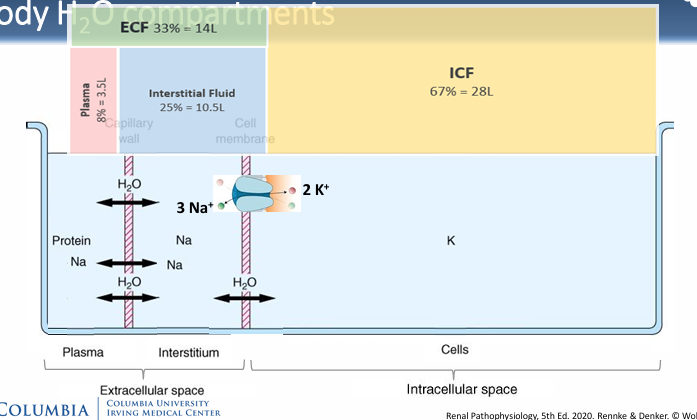
body water compartments
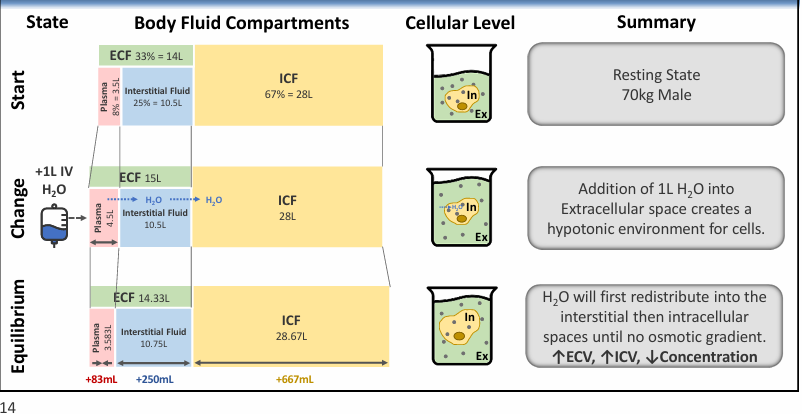
adding 1 L IV water (D5W)
losing 1L water (sweat)
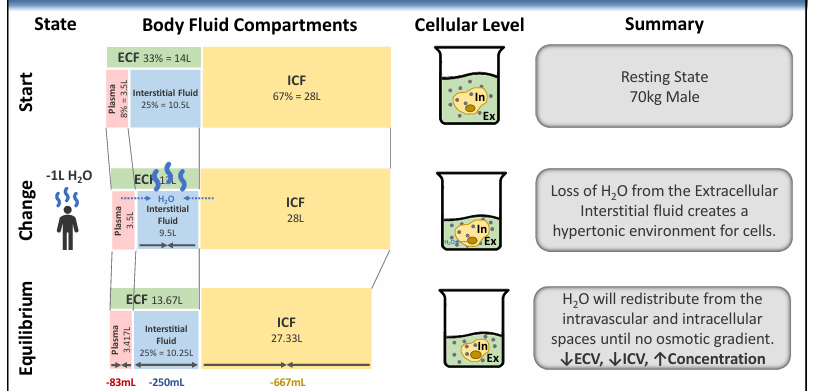
adding dietary salt (NaCl)
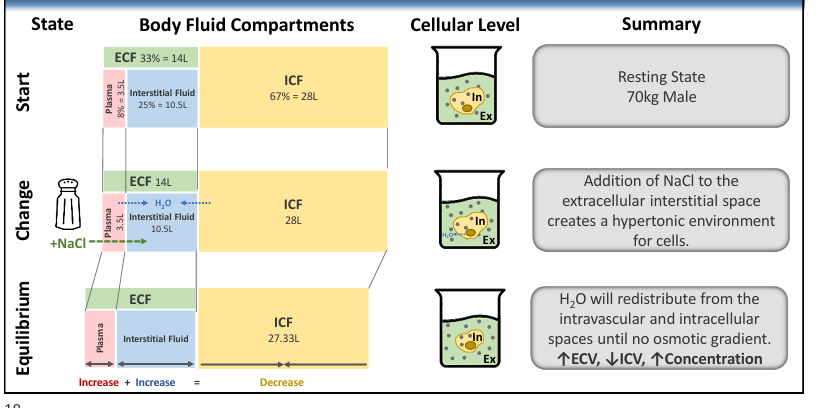
adding 1L IV isotonic fluid
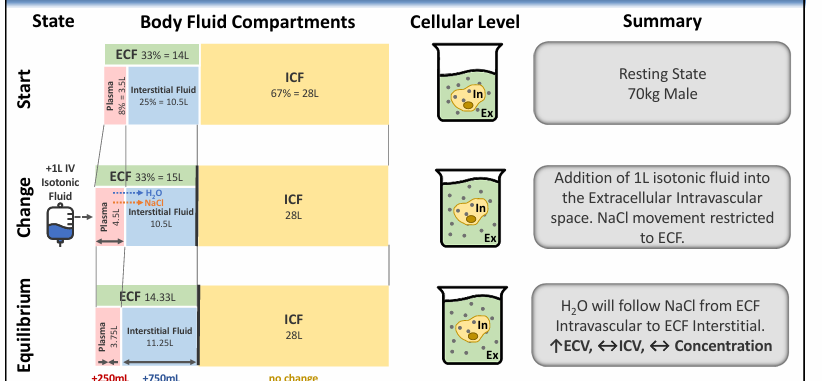
summary of body fluid compartment manipulations
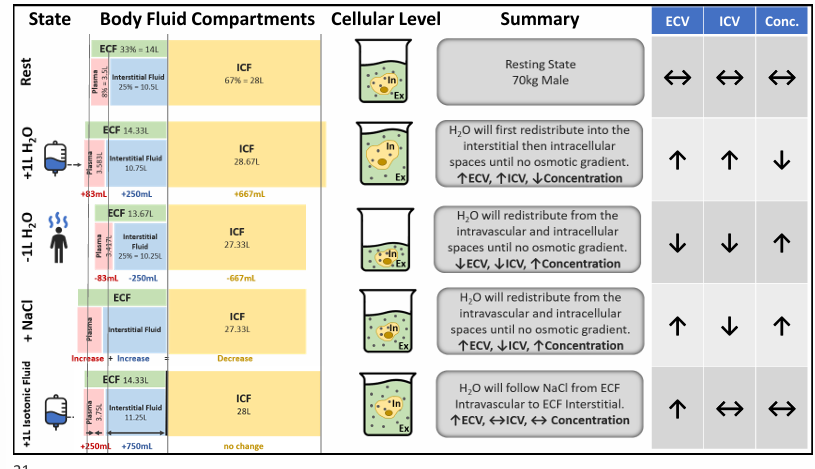
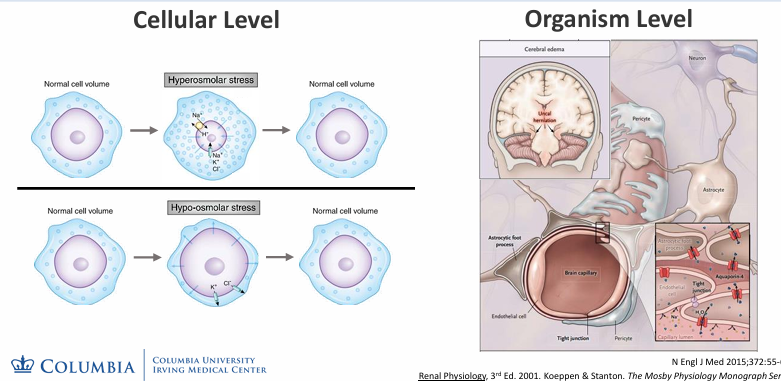
osmotic stresses at the cellular and organism levels
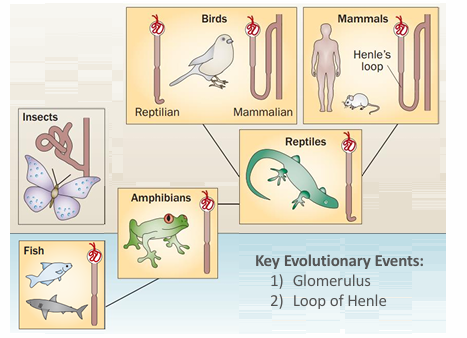
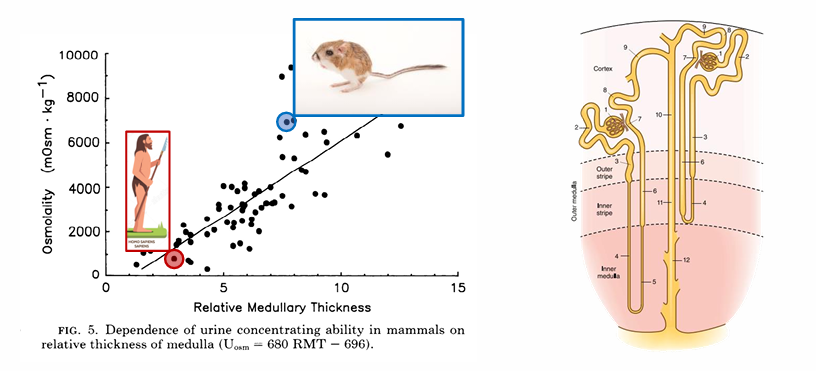
evolution and H2O conservation
H2O movement

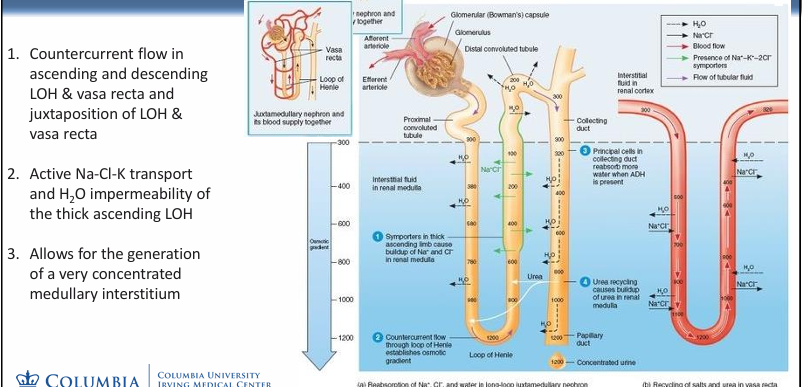
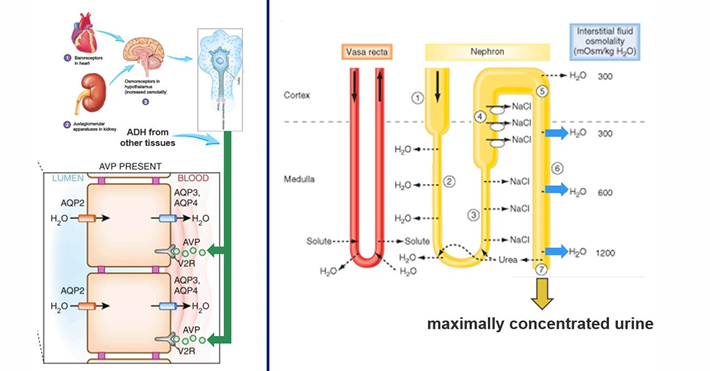
in order to form a maximally concentrated urine,
-need to establish an osmotic gradient in the medulla (electrolyte contribution from the thick ascending LOH countercurrent multiplier and vasa recta exchanger, urea contribution)
-need high H2O permeability in the distal nephron
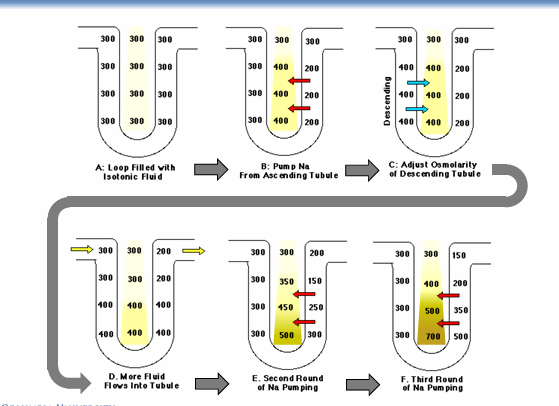
countercurrent multiplier and exchanger
countercurrent multiplier and exchanger procession
extreme H2O conservation
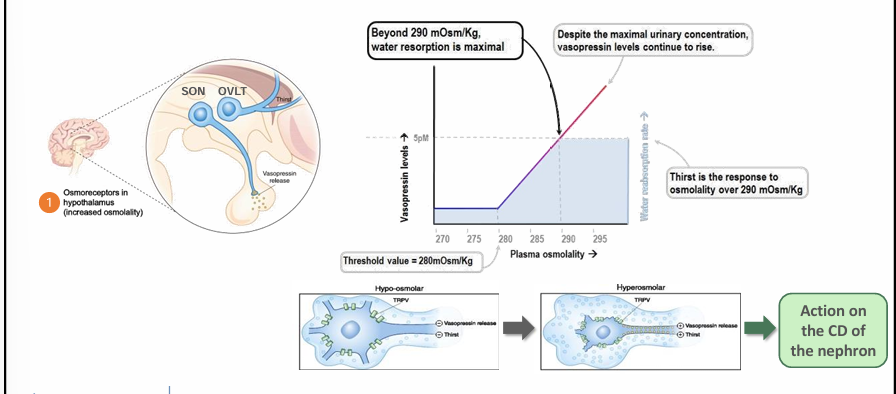
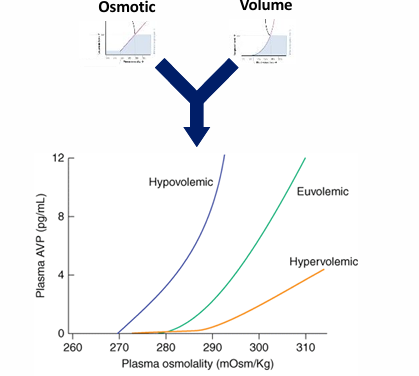
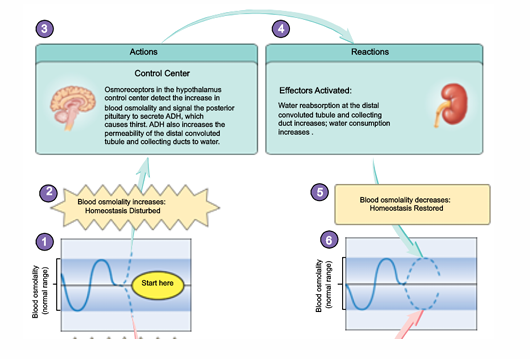
osmotic ADH release
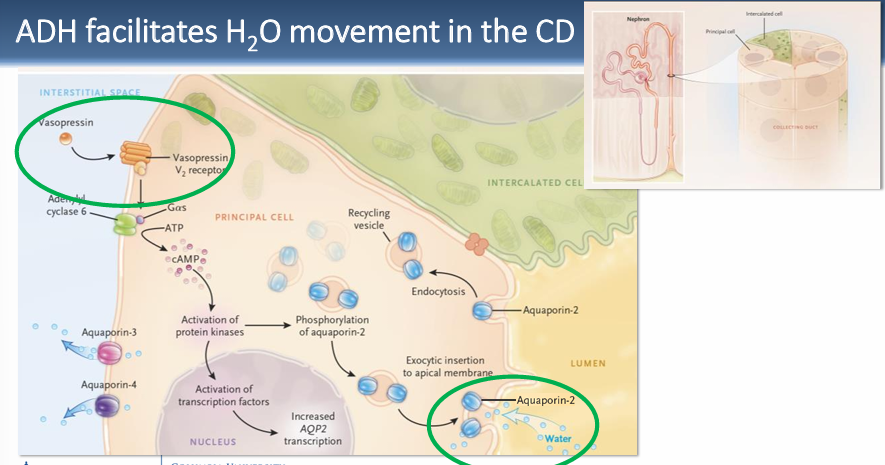
ADH facilitates H2O movement in
-the CD
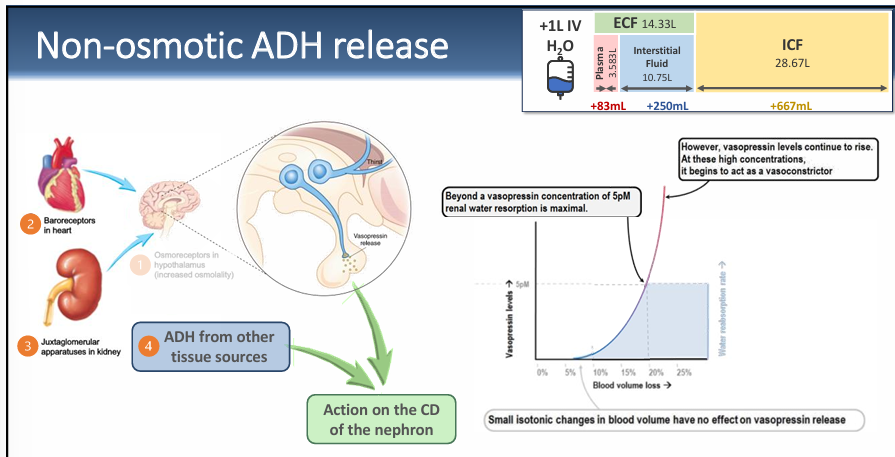
non-osmotic ADH release
integrated control of ADH release
in order to form a maximally concentrated urine (details)

water conservation
integrated water conservation
water excretion- in order to form a maximally dilute urine
1) ADH must be absent or gradient washed out
2) diluting segments of the nephron must be uninhibited
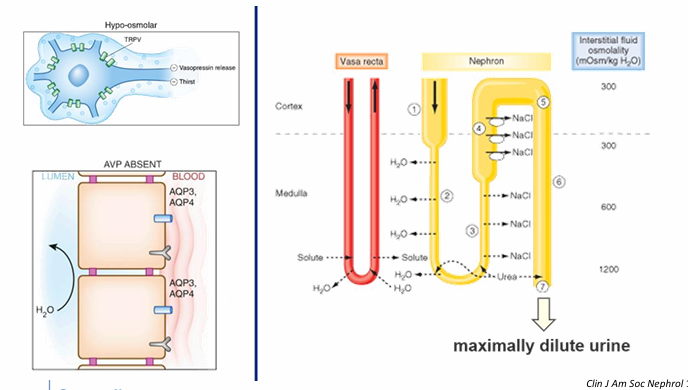
limits of urinary dilution determined by
1) filtered volume
2) daily osmolar intake that needs to be excreted
3) absence of vasopressin
integrated water excretion
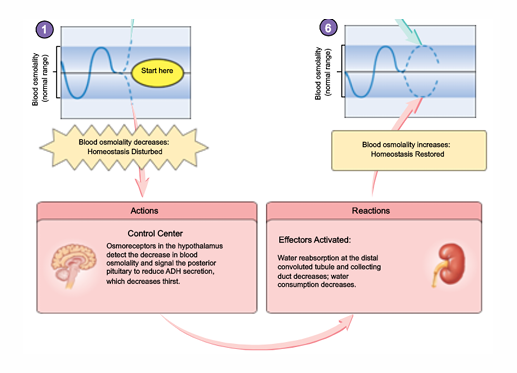
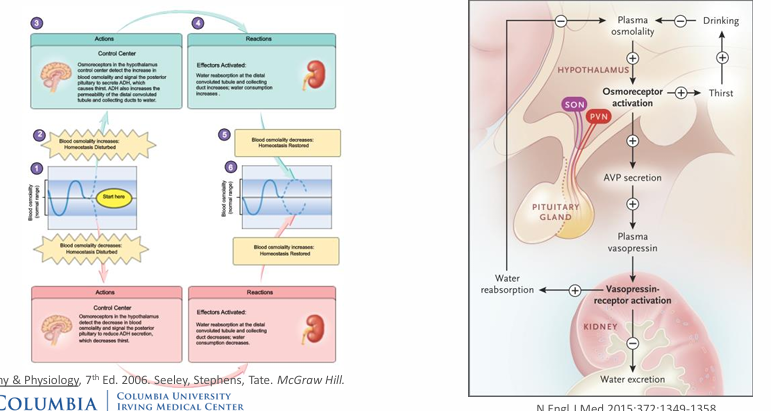
integrated H2O homeostatic control
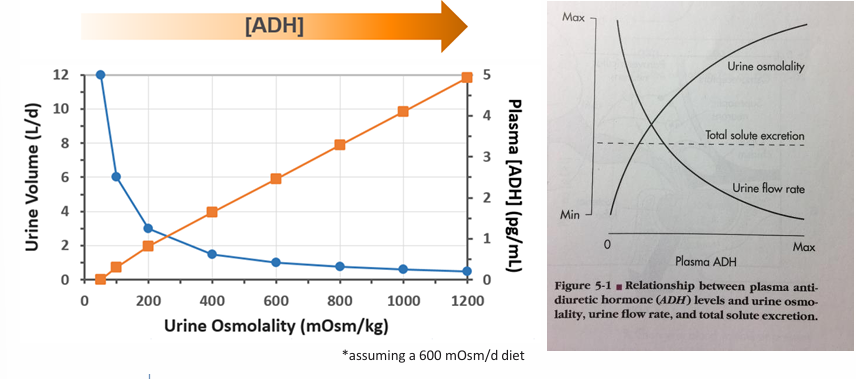
urine osmolality and volume
-proportional to ADH
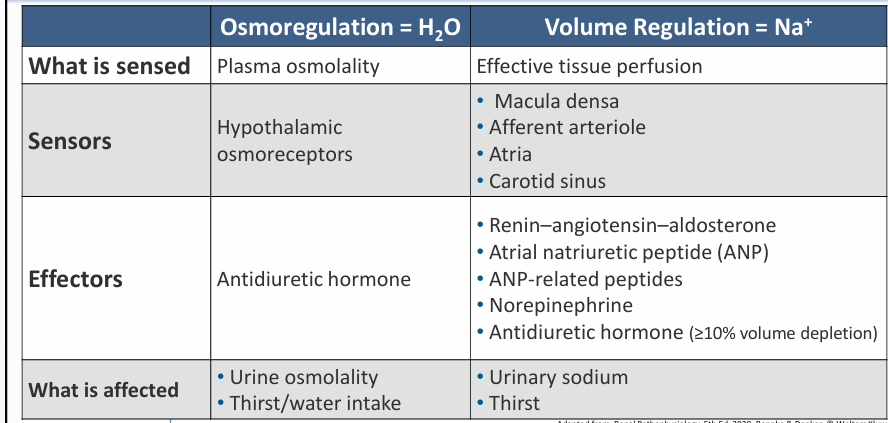
summary of sensors and effectors of osmoregulatory and volume regulatory pathways
key points
