Arterial Bypass Grafts, Hemodialysis Grafts, Fistula Questions
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes some answers to LM 2C practice quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What vein is used for an in-situ femoro-popliteal bypass graft?
great saphenous vein
Which of the following is NOT a potential complication of a reversed femoro-popliteal vein graft?
Graft stenosis
Graft aneurysm
Fistulas via non-ligated perforator veins
Graft kink
Fistulas via non-perforator veins
Graft entrapment typically occurs
at the popliteal
In which bypass graft procedure is a valvulatome used?
"in-situ" vein bypass
What type of bypass graft is being visualized in the image below?
PTFE
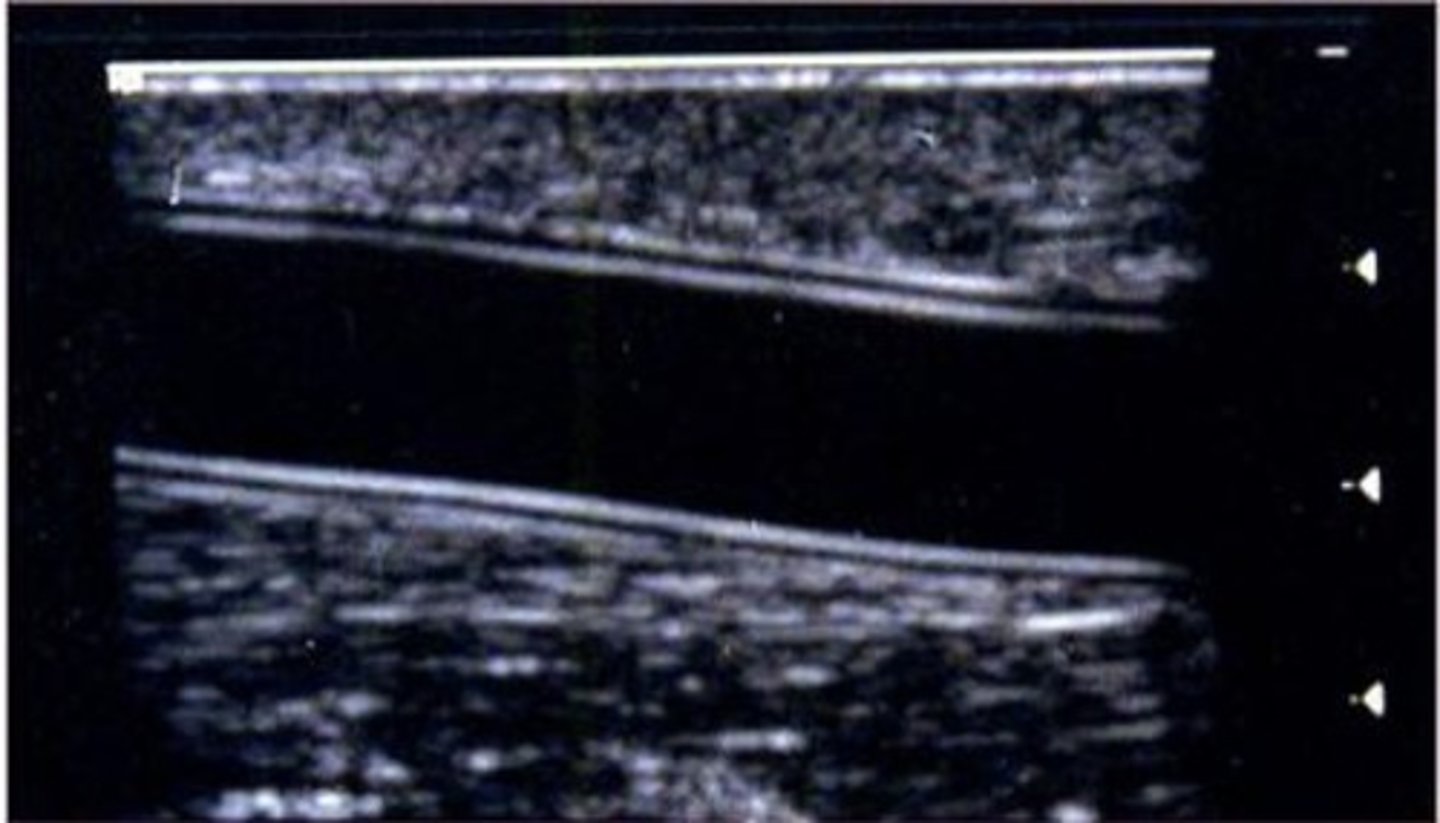
On serial follow-up of a bypass graft done 4 years ago, a new finding demonstrates a delay in systole in the Doppler spectrum at the mid-graft, what does this indicate?
atherosclerotic stenosis at the inflow
An abnormal increase in the number of cells: an increase in the number of smooth muscle cells within the intima in response to vessel injury
hyperplasia
During what period is endovascular intervention failure the highest?
within first 6 months post-op
In a patient with claudication, by how much should an initial ABI increase to demonstrate significant improvement in limb perfusion?
0.20
A patient presents to the vascular lab for follow-up of a superficial femoral artery stent. Upon duplex assessment of the stented area, the stent walls were noted to be sharply angled in the vessel lumen. Mosaic color flow pattern was noted in the area. What do these findings suggest?
Stent deformation or kinking
What is the minimum diameter of the great saphenous vein considered to be appropriate for a successful in-situ arterial bypass?
2.5 mm
Keep the visualized vein ___ of the ultrasound screen when placing a mark on the skin
To the center
Confirming that the exam room is warm and the patient is comfortable can decrease venous __ during venous mapping evaluations
constriction
All of the following are potentionally problematic for vein suitability during evaluation EXCEPT:
non-continuous segments
mobile venous valve
tortuosity
thrombosis
mobile venous valve
What is a vein that penetrates the muscular fascia of the leg and connects the superficial system to the deep system?
Perforating veins
How many common configurations does the thigh portion of the great saphenous vein have?
5
During a venous mapping procedure, the technologist notes a thin, echogenic line protruding into the vessel lumen that does not appear to be mobile. The patient does not have a history of previous superficial thrombophlebitis. What does this finding most likely represent?
Stenotic, frozen valve
When using color and spectral Doppler to evaluate the superficial venous system, which settings should be used?
High gain and low PRF/scale
To maximize venous pressure and distention, in what position should the patient's limbs be placed when mapping the superficial venous system?
Dependent
Because the superficial veins are under low pressure and just under the skin, what type of transducer pressure must the technologist use when performing diameter measurements?
Light
A patient is sent to your laboratory for a lower extremity arterial study with and without exercise for thigh claudication symptoms. Her baseline ankle pressures were 120mmHg on the right and 115mmHg on the left. Post exercise, her ankles pressures drop to 80mmHg on the right and 75mmHg on the left. They return to baseline values at 11 minutes. Based on these findings, what level of disease does this patient have?
Multilevel
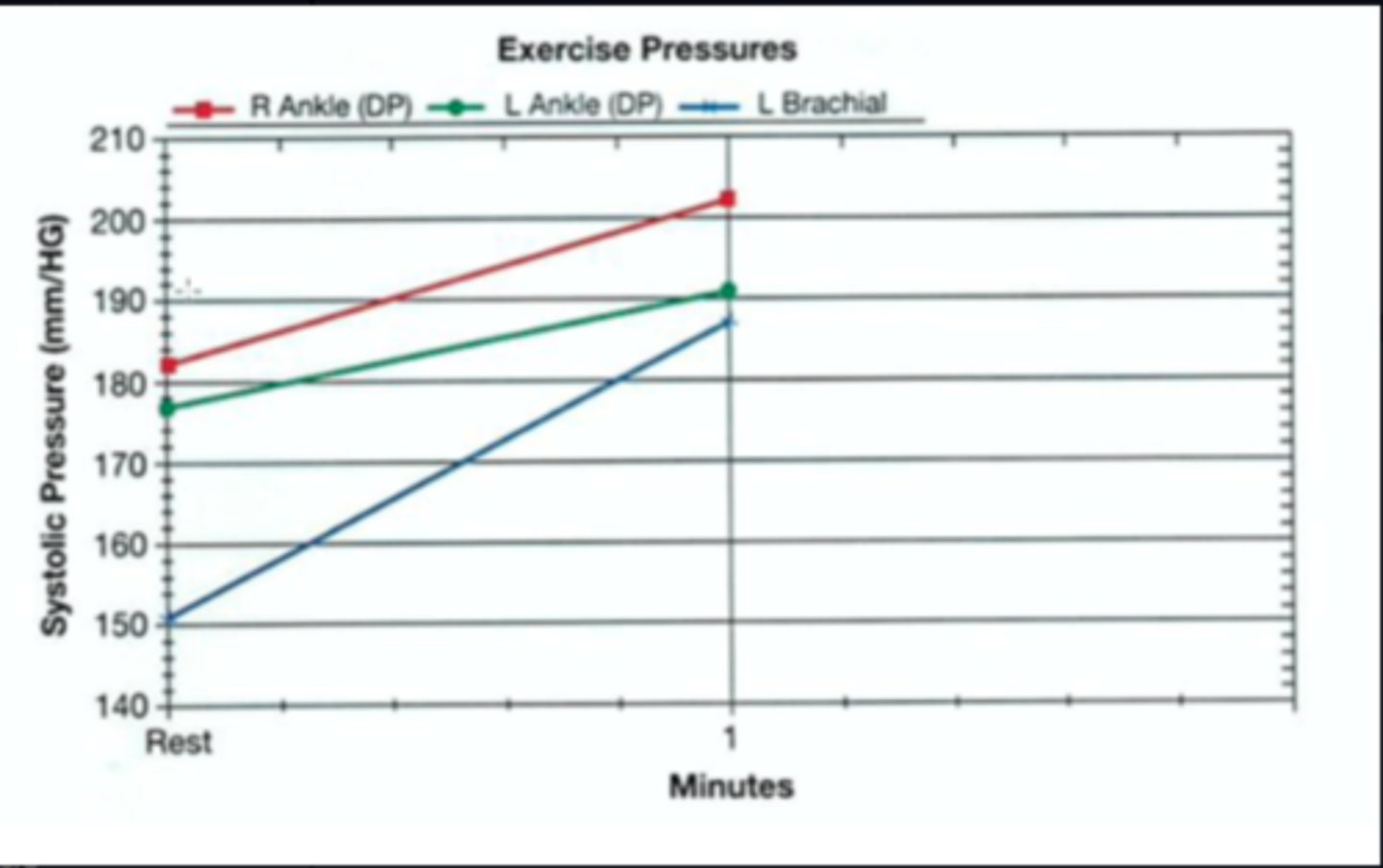
The below figure demonstrates the results of pre- and post systolic pressures during an exercise examination. What do these findings suggest?
Normal response to exercise
Most prominently, abnormal energy losses in the arterial system would result from pathologies such as obstruction and/or stenoses because of which of the following? (hint-Poiseuille law)
The decrease in the vessel's radius
Which of the following is NOT a contraindiction to treadmill exercise/stress testing?
ABI less than 0.5
Questionable cardiac status
Bilateral ABI of >1.0
Unsteadiness when walking
Bilateral ABI of >1.0
Which of the following would be an appropriate substitution for stress testing due to hypertension greater than 180 mmHg?
Post-occlusive reactive hyperemia
Hall walking
Stationary bike
Treadmill exercise
Post-occlusive reactive hyperemia
What is an essential evaluation to determine a proper diagnosis of thromboangitis obliterans (Buerger's disease)?
Digital evaluations with PPG waveforms
What term describes arterial embolization as a result of deep vein thrombosis in the presence of an intracardiac right to left shunt?
Paradoxic embolization
What condition is a congenital disorder of connective tissue often resulting in aneurysm formation?
Ehlers-danlos syndrome
A 32 yo Asian female presents to the vascular lab with weak radial pulses and several transient ischemic attacks. What should be suspected in this patient?
takayasu's arteritis
A 79-year old male present to the vascular lab with cool, pulseless limb shortly after catheterization through the right common femoral artery. Upon duplex assessment, echogenic material was noted in the common femoral artery with a staccato type waveform just proximal to this area. What do these findings suggest?
Acute arterial occlusion of the right common femoral artery
What is a dilated segment of the proximal descending aorta which may give rise to the takeoff of an aberrant subclavian artery?
Kommerell's diverticulum
You are scanning the origin of a patient's left subclavian artery and record high peak systolic velocity (247 cm/sec). You obtain a normal triphasic waveform at this patient's axillary artery with a peak systolic velocity of 119 cm/sec. What does this most likely indicate?
falsely elevated velocities
Injury of what artery may result in hypothenar hammer syndrome?
the ulnar artery at the wrist
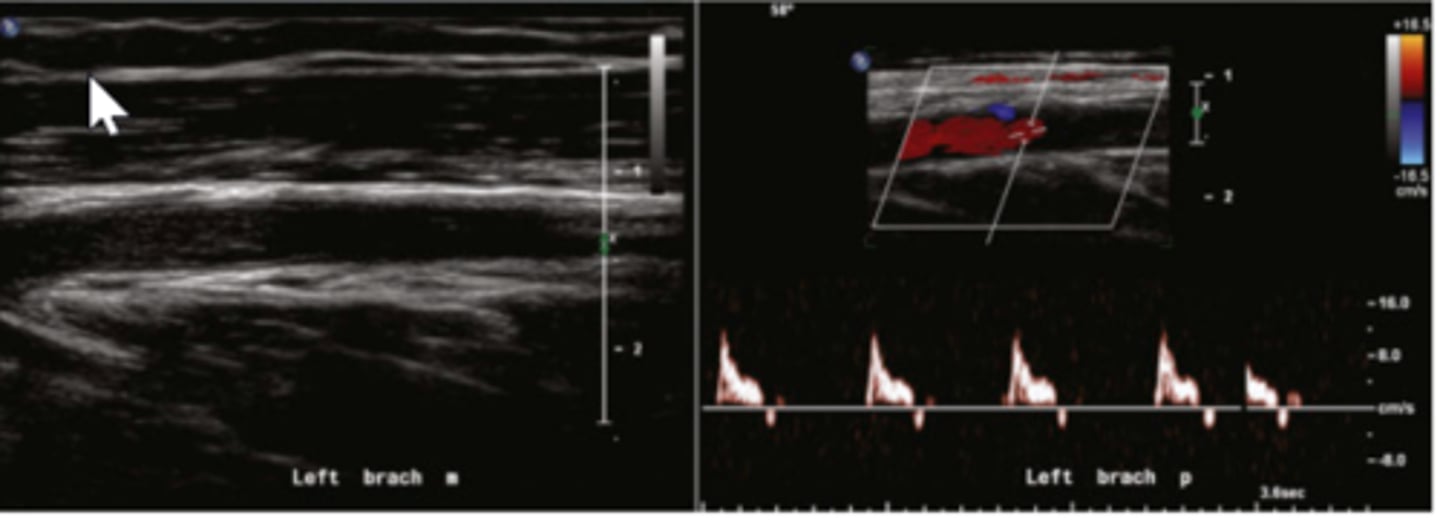
What do the below ultrasound images of the left brachial artery demonstrate? (ignore the mouse arrow on 2D image)
left brachial artery obstruction distal to the spectral Doppler sample site
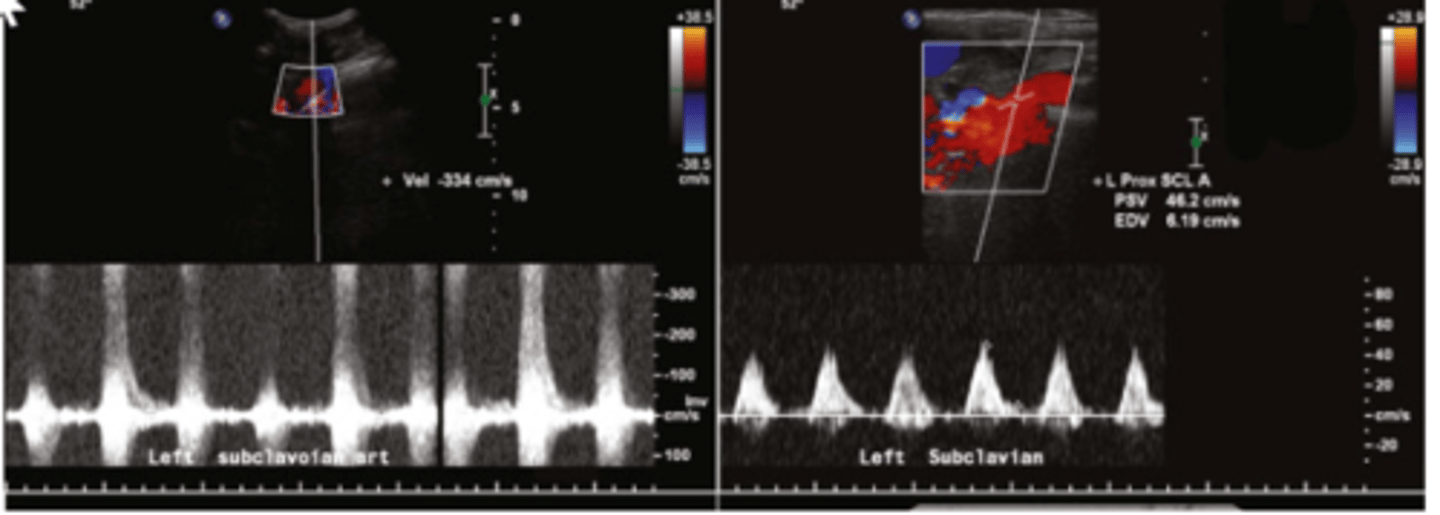
The ultrasound image with a velocity of 334 cm/sec was recorded at the proximal left subclavian artery, the ultrasound image with a velocity of 46/6 cm/sec was recorded at the mid left subclavian artery. What does this exam demonstrate?
>50% stenosis of the proximal subclavian artery
Buerger's disease is an arterial disorder involving which of the following vessels?
Digital arteries
Episodic, prolonged digital vasospasm brought on by cold exposure is what?
Raynaud's syndrome
While performing cold immersion testing; a persistent decrease in digital waveform amplitude of _____ minutes or longer (criteria threshold) confirms a vasospastic disorder or Raynaud's
10
Which of the following is the manual test for palmar arch patency?
PVR
Adson test
TOS test
Allen's test
Allen's test
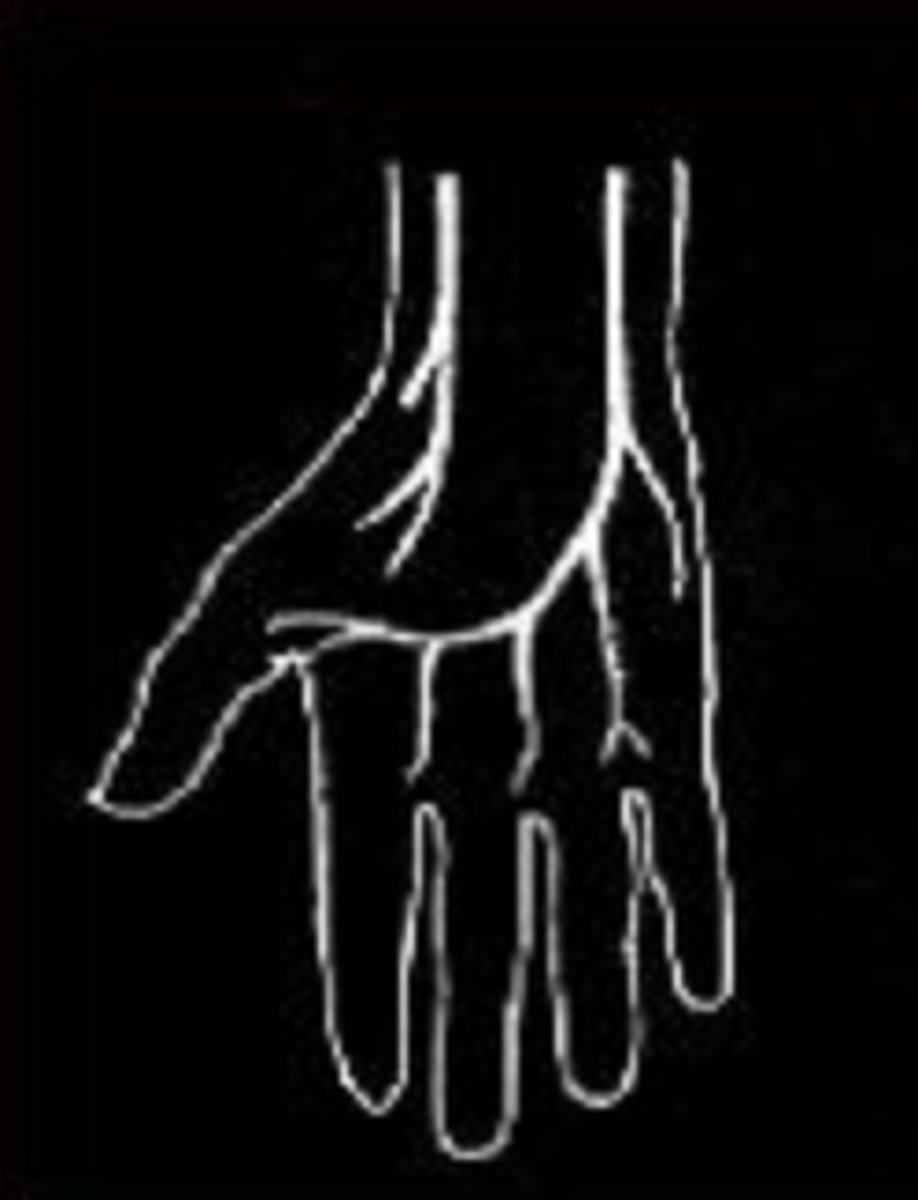
This diagram of the hand demonstrates a palmar arch that is:
ulnar dominant
The brachiocephalic vein is found:
On both the right and left sides of the neck
The cephalic vein and basilic vein are connected distally by what vein?
median cubital
With which vein does the brachial vein become the axillary vein at the confluence?
basilic vein
Which of the following is a sign of normalcy in a subclavian vein that is NOT normally present in the lower extremity veins?
Steady, continuous, non-phasic flow
Respiratory variation
Augmentation
Prominent cardiac pulsatility
Prominent cardiac pulsatility
What is the best ultrasound method for assessing the proximal central veins?
spectral Doppler flow pattern assessment
A patient presents to your vascular lab for upper extremity venous evaluation with face swelling and prominent veins on the chest and neck. What do these findings suggest?
superior vena cava thrombosis
Persistent retrograde flow in the internal or external jugular veins suggests:
innominate vein obstruction
A 23 year old male presents to your vascular lab with unilateral arm swelling. Upon taking his history you find out he has no history of venous puncture or cannulation and has recently started lifting weights. On duplex you discover acute subclavian vein and axillary vein thrombosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
Phlegmasia
Paget-Schroeder syndrome
Raynaud's syndrome
May-Thurner syndrome
Paget-Schroeder syndrome
A 78-year-old male presents to your vascular lab with right arm swelling for the past several days. The patient notes that he is currently being treated for cancer. During the upper extremity duplex examination, decreased pulsatility is noted in the right internal jugular and subclavian veins as well as rouleaux (slow) flow formation. What do these findings suggest?
a more proximal obstruction, likely in the brachiocephalic vein and superior vena cava
During upper extremity venous examination, the technologist has made the patient take a quick, deep breath through pursed lips while viewing the subclavian vein. What is the purpose of this action?
collapse/coapt the subclavian vein
Which of the following best describes the Brescia-Cimino procedure?
A radial artery to cephalic vein fistula
An indwelling hemodialysis catheter
A brachial artery to median cubital vein fistula
A straight Teflon graft from radial artery to the basilic vein
A radial artery to cephalic vein fistula
In a patient with a hemodialysis access forearm loop graft, digital ischemia can result from which of the following conditions?
Arterial steal
Which of the following veins does NOT have an accompanying artery?
Brachial vein
Axillary vein
Subclavian vein
Basilic vein
basilic vein
What is considered to be the lowest favorable vein diameter suitable for an arterial to venous hemodialysis fistula?
2.5 mm
Reverse flow detected in the distal radial artery of an ipsilateral proximal radial artery to basilic vein graft indicates which of the following conditions?
patent palmer arch
Antegrade, triphasic (high resistance) flow in a radial artery distal to a brachial artery to basilic vein loop hemodialysis access graft indicates which of the following?
normal radial artery flow
Which access graft does NOT require maturation time?
PTFE
Gore-tex
Polyurethane
Atrium
Polyurethane
Antegrade, triphasic flow in a brachial artery proximal to a radial artery to basilic vein hemodialysis access graft indicates which of the following?
Pseudoaneurysm at anastomosis
Venous outflow obstruction
Graft failure/Occlusion
Normal radial artery flow
Graft failure/Occlusion
All of these listed below are possible complications of a hemodialysis access grafts or fistula EXCEPT:
"Thrill"
Infection
Pseudoaneurysm
Arterial steal
"Thrill"
What can remaining valve leaflets that project into the lumen of a fistula become a source for?
stenosis devlopment
Graft aneurysm, neointimal hyperplasia, graft kink
What are potential complications of a reversed femora-popliteal vein graft?
Intimal hyperplasia.
What is the most common cause of in situ vein bypass graft stenosis?
Chronic vasodilation
A hyperemic waveform existing in the posterior tibial artery 3 weeks S/P a femoral to distal vein bypass is most likely due to which of these conditions?
Great saphenous vein
The most common vein used for "in situ" bypass grafts is:
Palmar arch
The radial artery terminates in which vessel?
Patient has radial artery dominance
A photoplethysmography (PPG) tracing on the 5th hand digit (small finger) that goes from normal to "flat-line with radial artery compression indicates which of the following?
2.5 mm
What is the minimum diameter of the great saphenous vein considered to be appropriate for a successful in situ vein bypass?
Determine if there is a calcified wall, measure the diameter of the radial a, and check for stenosis.
During arterial mapping of the radial artery, you should:
In situ vein bypass
In which bypass graft procedure is a valvulatome used?
There is air in the graft material
It appears that ultrasound cannot penetrate a newly placed PTFE lower extremity bypass graft. Which of the following is the most likely cause.
It can be used in the contralateral leg
What is an advantage of a reversed vein bypass in the legs?
Brachial vein
Which of the following vessels is not usually used hemodialysis access grafts of fistulas?
Basilic
Which of the following veins does not have an accompanying artery?
Incomplete palmar arch
In a patient with a hemodialysis access forearm loop graft, digital ischemia can result from which of the following conditions?
Graft failure
Normal, triphasic flow in a brachial artery in a patient with a radial artery to basilic vein hemodialysis access graft indicates:
Vectra (polyurethane)
Which access graft material or type does not require maturation time?
Vectra
Which of the following grafts is impenetrable by ultrasound?
Patent palmar arch
Reverse flow in the distal radial artery of an ipsilateral radial artery to basilic vein graft indicates which of the following conditions?
2.5 mm
What is considered to be the lowest vein diameter suitable for an arterial to venous hemodialysis fistula?
A radial artery to cephalic vein fistula
Which of the following best describes the Brescia-Cimino procedure?
Inflow artery, distal to the anastomosis
When interrogating for steal syndrome in a fistula, where should the sample volume be placed?
It does not require maturation, can be used sooner
Which of the following is an advantage of an arteriovenous graft (AVG) over an arteriovenous fistula (AVF).