PHYSICS Unit 3 Test
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Projectile Motion
Motion described by horizontal and vertical components.
Vectors
Quantities with both direction and magnitude.
Magnitude
Size or quantity of a measurement.
Scalar Quantities
Measurements with only magnitude, no direction.
Vector Quantity
Includes both magnitude and direction.
Velocity Vectors
Represent speed and direction of motion.
Scale for Velocity
1 cm = 20 km/h in vector representation.
Parallelogram Rule
Method to find resultant of nonparallel vectors.
Resultant Vector
Diagonal of the parallelogram formed by vectors.
Right Angle Vectors
Vectors at right angles form a rectangle.
Resultant Force Magnitude
Combined effect of two or more forces.
Crosswind Effect
Wind at right angle affects airplane speed.
Velocity Relative to Ground
Depends on airplane and wind velocities.
Component Vectors
Two perpendicular vectors that represent one vector.
Independent Components
Perpendicular components of a vector do not affect each other.
Vector Addition Order
Order of addition does not affect the result.
80 km/h Airplane
Speed of airplane relative to surrounding air.
Tailwind
Wind that assists forward motion of an object.
Crosswind
Wind blowing perpendicular to the direction of motion.
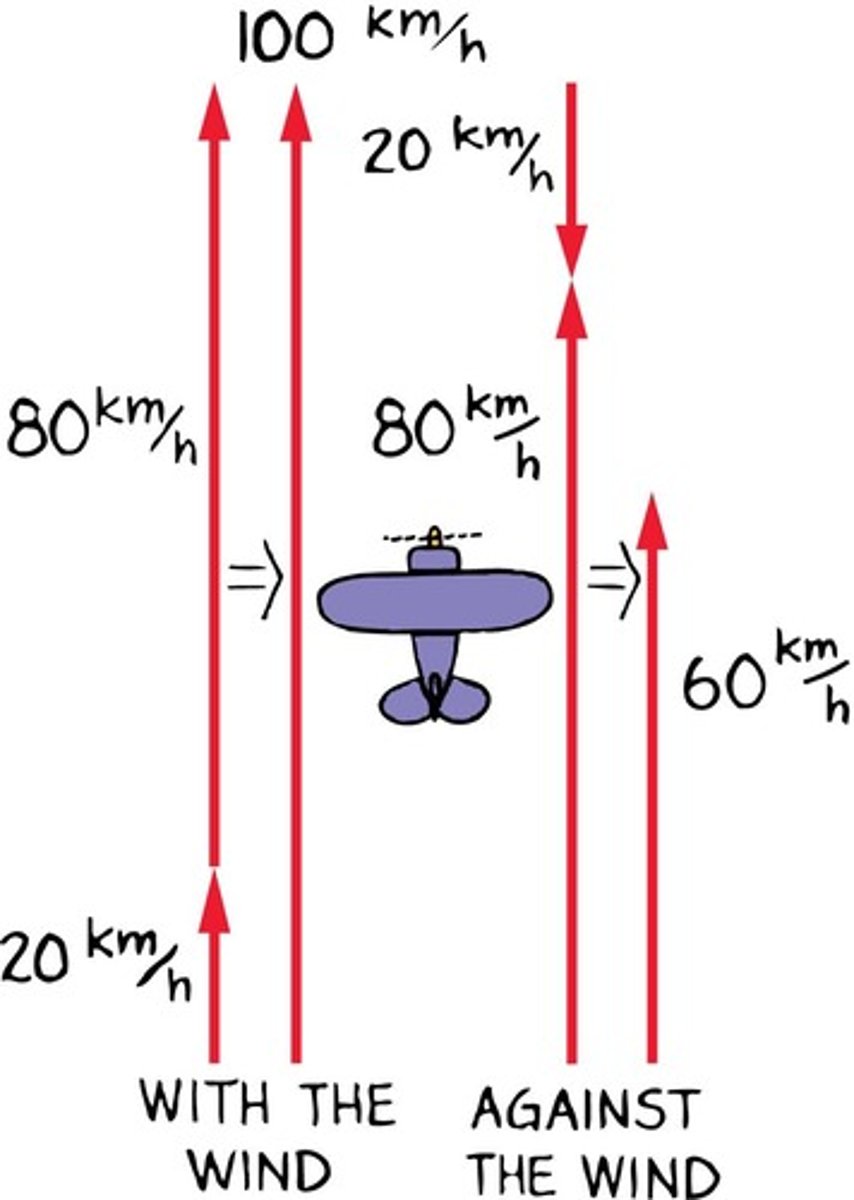
Resultant Speed Calculation
Combining velocities gives total speed relative to ground.
3-4-5 Triangle
Right triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5 units.
Diagonal of Rectangle
Represents resultant of two perpendicular vectors.
Vector Resolution
Breaking down a vector into components.
Velocity Combination
Result of combining multiple velocity vectors.
Airplane Speed in Wind
Speed changes based on wind direction.
Vector Representation
Visual depiction of magnitude and direction.
Vector Movement
Vectors can be repositioned without changing properties.
Components of a Vector
Two perpendicular vectors that sum to a given vector.
Resolution
Process of determining a vector's components.
Linear Motion
Motion along a straight path.
Nonlinear Motion
Motion along a curved path.
Projectile
Object moving under gravity's influence.
Examples of Projectiles
Cannonball, stone, ball, spacecraft.
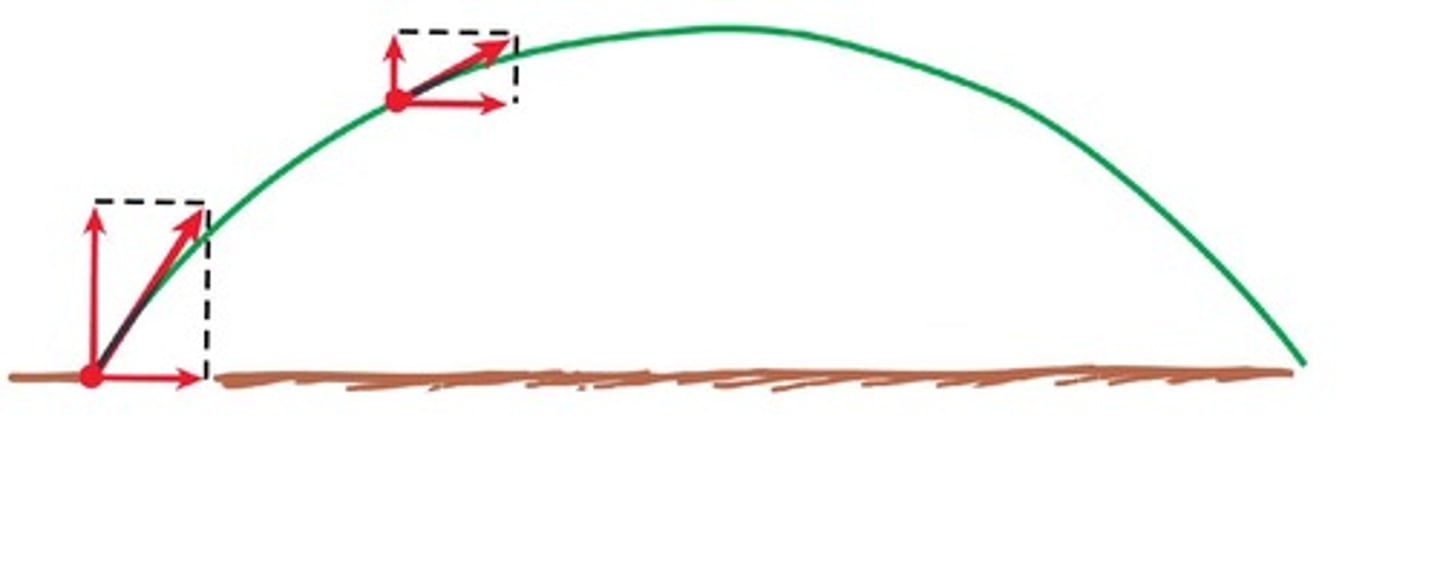
Curved Path of Projectiles
Path resulting from horizontal and vertical components.
Horizontal Component
Motion along the x-axis, constant velocity.
Instantaneous Velocity Formula
Vx = Dx/t, where Dx is displacement.
Displacement Formula
Dx = Vx * t, for horizontal motion.
Vertical Velocity Formula
Vy = -gt, for falling projectiles.
Independence of Components
Horizontal and vertical motions do not affect each other.
R = Curved Paths of Projectiles
Result from combined horizontal and vertical motions.
Projectile Motion Separation
Analyzing horizontal and vertical components separately.
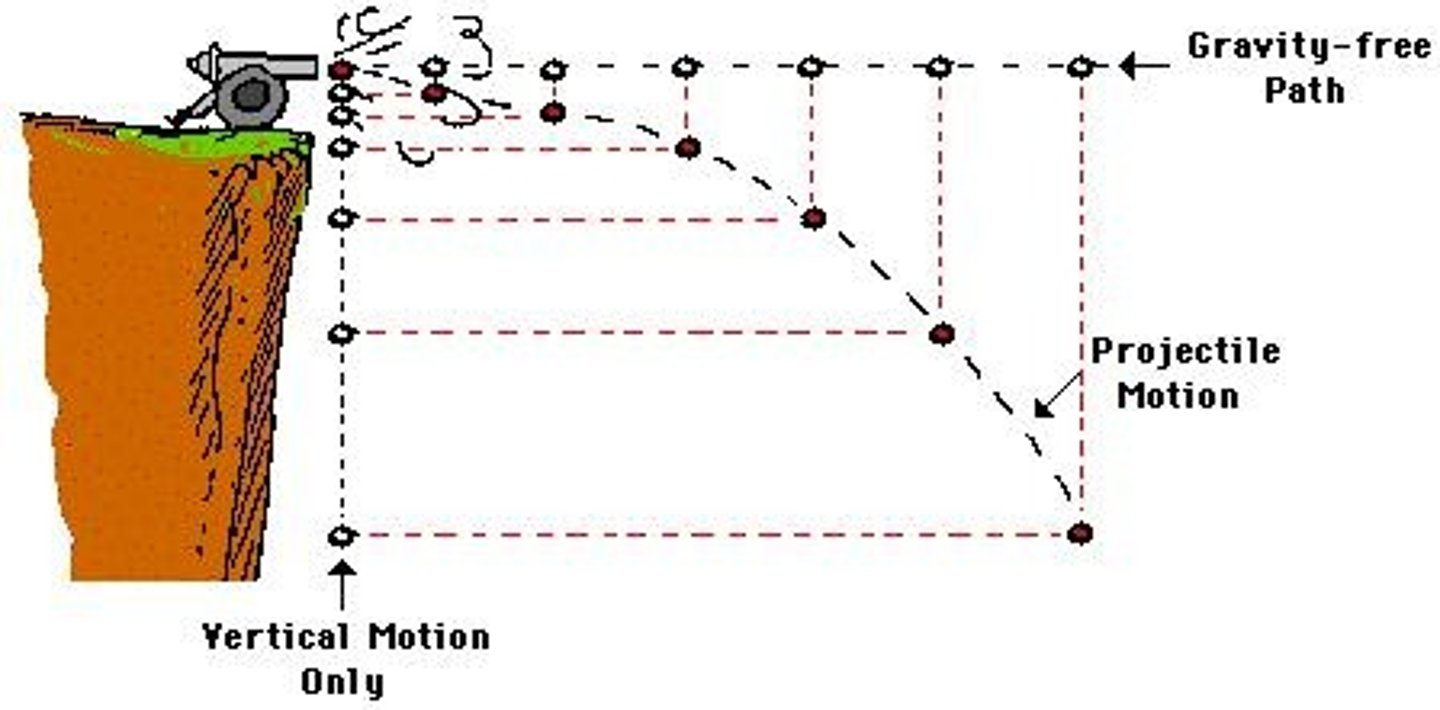
Cannonball Drop Experiment
Both cannonballs hit the ground simultaneously.
Free Fall
Motion affected only by gravity's acceleration.
Horizontal Launch
Projectile motion resembles level surface motion.
Vertical Launch
Projectile motion resembles free fall motion.
Constant Horizontal Velocity
No gravitational force acts horizontally.
Acceleration Due to Gravity
Denoted as 'g', approximately 9.81 m/s².
Projectile Motion Characteristics
Curved paths with independent motion components.
Horizontal Motion in Projectiles
Constant speed, unaffected by vertical motion.
Vertical Motion in Projectiles
Accelerated motion due to gravitational force.
Vertical Distance
Distance fallen vertically during projectile motion.
Horizontal Range
Horizontal distance traveled by a projectile.
Vertical Velocity at Impact
Velocity of a projectile just before hitting the ground.
Resultant Velocity
Combined velocity from horizontal and vertical components.
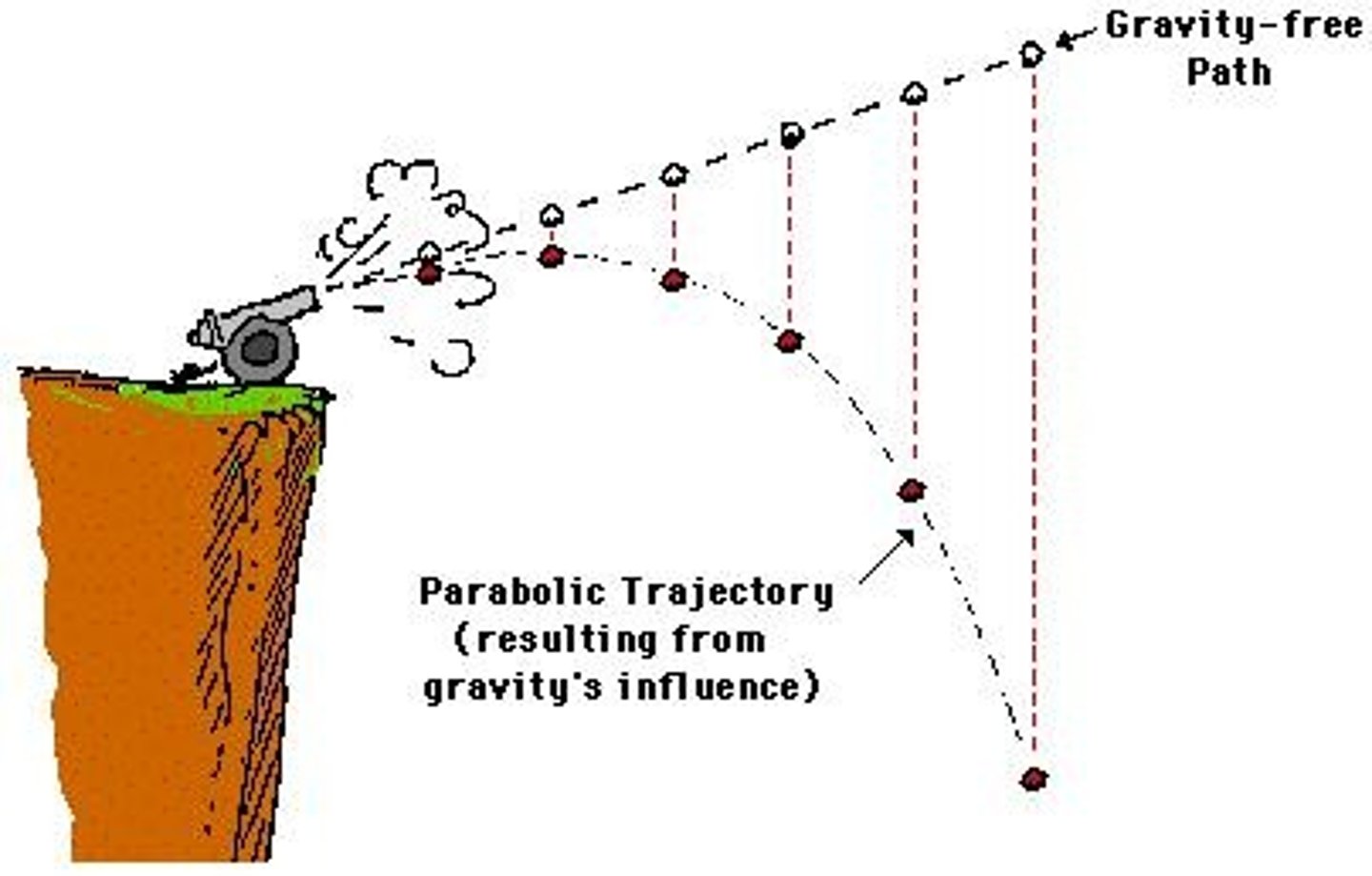
Parabolic Path
Curved trajectory of a projectile under gravity.
Initial Horizontal Velocity
Starting velocity in the horizontal direction.
Vertical Acceleration
Acceleration due to gravity acting downward, -9.8 m/s².
Time of Flight
Duration a projectile remains in the air.
Initial Vertical Velocity
Starting velocity in the vertical direction.
Maximum Altitude
Highest point reached by a projectile.
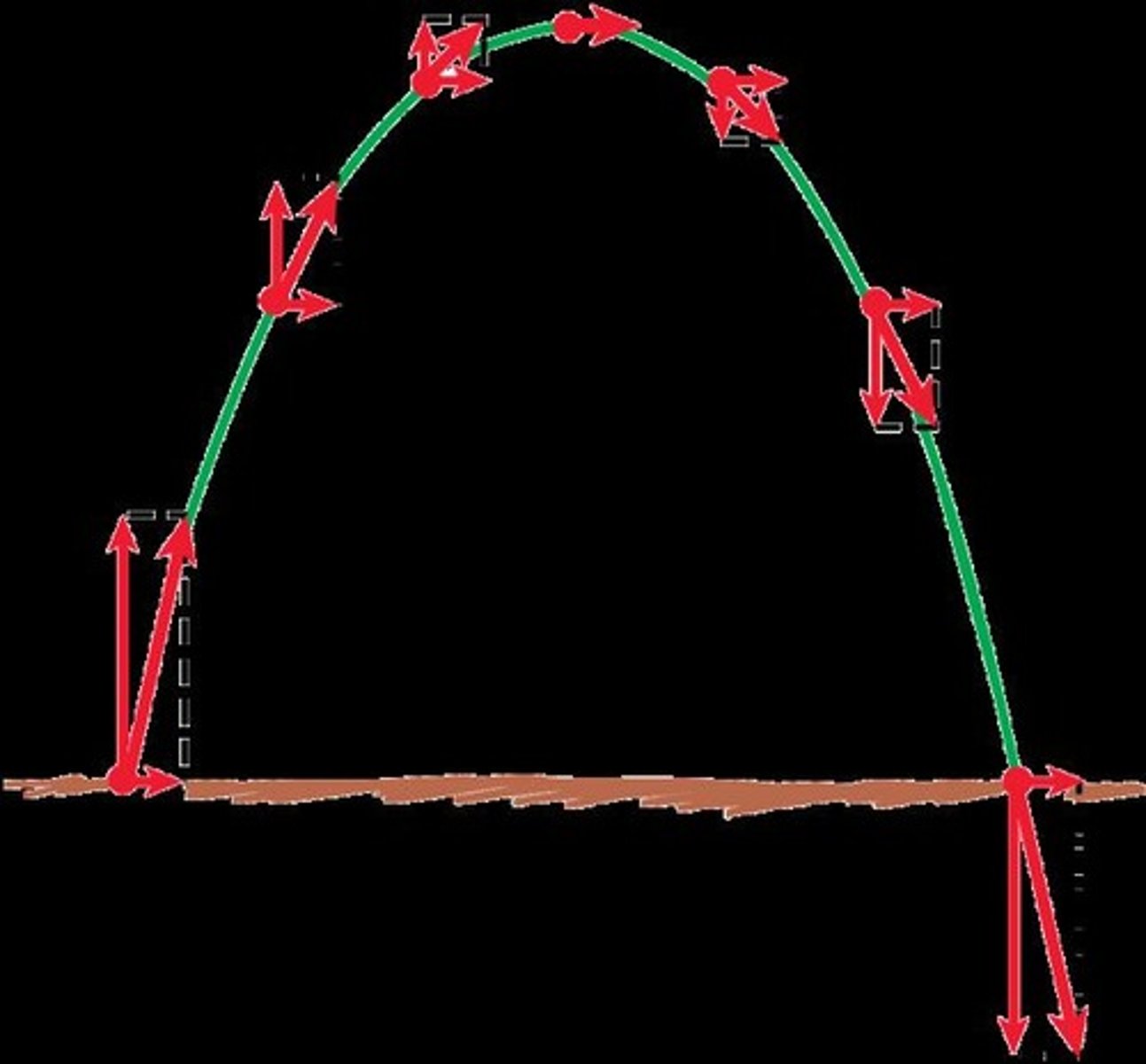
Velocity at Maximum Altitude
Vertical velocity is zero, horizontal remains constant.
Height of the Cliff
Vertical distance from top to bottom of a cliff.
Magnitude of Resultant Velocity
Overall speed of a projectile at impact.
Horizontal Acceleration
Change in horizontal velocity, typically zero.
Vertical Component of Velocity
Velocity directed downward just before impact.
Time of Fall Calculation
Determining time based on height and gravity.
Range Calculation
Determining horizontal distance based on time and velocity.
Vertical Distance Calculation
Using time and gravity to find height fallen.
Horizontal Distance Calculation
Using time and horizontal velocity to find range.
Initial Conditions
Starting parameters for projectile motion analysis.
Vertical Displacement
Distance fallen below ideal path, increases over time.
Ideal Trajectory
Path a projectile would follow without gravity.
Vertical Distance Formula
dy = 1/2 gt² for vertical fall.
What remains constant throughout projectile's motion.
horizontal component
Vertical Component
Changes due to gravitational acceleration, moving along the x axis
Instantaneous Velocity
Velocity at a specific point in projectile's path.
Cannonball Motion
Describes projectile motion with constant horizontal velocity.
Top of Path Velocity
Vertical component is zero; equals horizontal component.
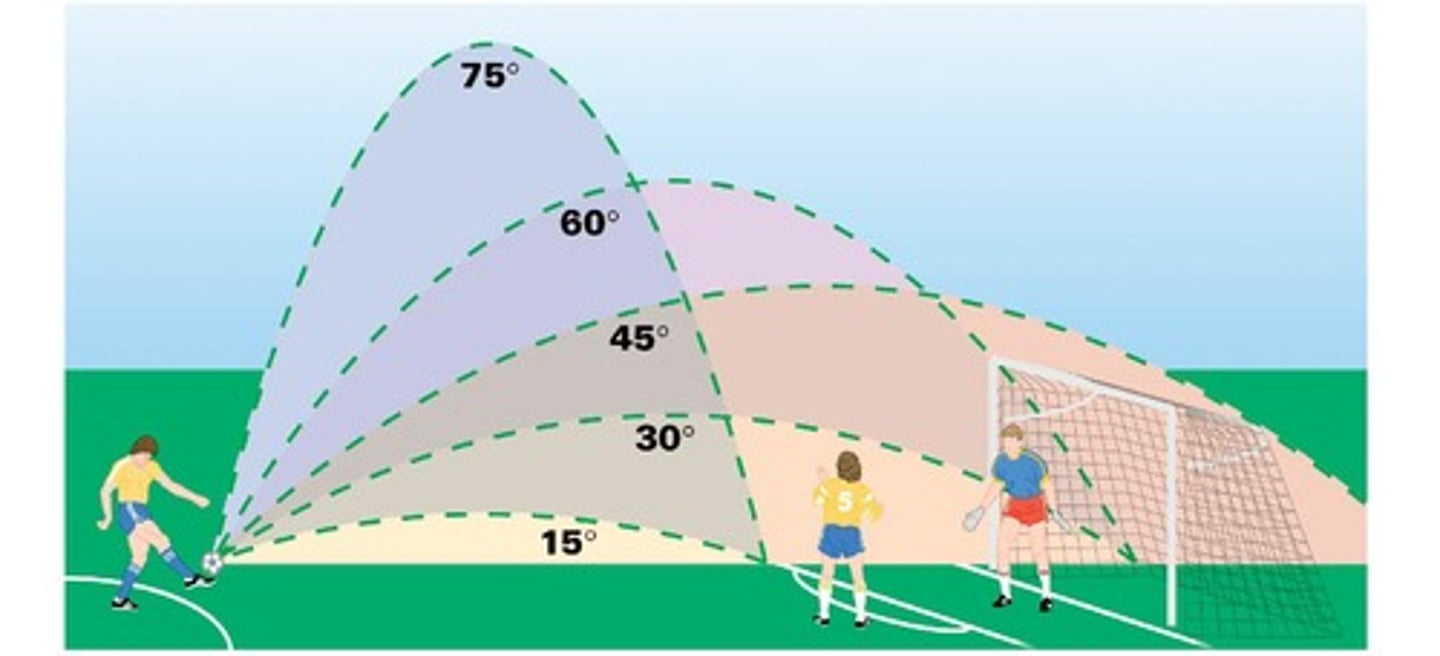
Launching Angle
Angle affects the range and height of projectile.
Range of Projectile
Distance traveled horizontally before landing.
Equal Time Principle
Vertical fall distance is same for equal time intervals.
Release from Rest
Projectile falls same distance as if dropped.
Velocity Magnitude
Greater at diagonal than horizontal or vertical components.
Projectile Path
Curved trajectory influenced by gravity and launch angle following an object in motion
Vertical Distance Increase
Continues with time due to constant acceleration.
Trajectory Comparison
Different angles yield different horizontal distances.
Motion Analysis
Examines changes in velocity components during flight.
Projectile Launch Speed
Initial speed affects maximum height and range.
Vertical Component Changes
Varies while horizontal component remains constant.
Gravity's Role
Essential for determining projectile's vertical motion.
Idealized Straight-Line Path
Represents motion without the influence of gravity.
Initial Velocity Vector
Velocity at launch, includes direction and magnitude.
Projection Angle
Angle at which a projectile is launched.
Altitude
Height of the projectile above the ground.
Flight Time
Total duration of the projectile's motion.
Maximum Height
Highest point reached by the projectile.
Angle of Launch
Initial angle determining projectile's trajectory.
45 Degrees
Angle for maximum range on level ground.
90 Degrees
Angle for maximum height but zero range.
Air Resistance
Force opposing projectile's motion through air.