Ecology
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Define community
A group of inderpendent lving organisms in an ecosystem
Define population
All the organisms of 1 species who live in the same place at the same time
Define ecosystem
The interaction of living organisms and their environment
Order the levels of organism
Producer → 1st trophic level
Primary consumer → 2nd trophic level
Secondary consumer → third trophic level
Tertiary consumer → 4th trophic level
What does interdependence mean?
All organisms in an ecosytem depend on eachother
↳ if the population of 1 organism fluctuates, it will also affect the rest of the ecosystem
What do plants compete for in an ecosytem?
Light
Space
Water and minerals from the soil
what do animals compete for in an ecosystem?
Food
Territory
Mates
What is a stable community?
Where all the species and environmental factors are in balance so that population sizes remain fairly constant.
Define abiotic
Non-living factors which affects an ecosystem
Give examples of abiotic factors
Light intensity
Temperature
Moisture levels
Wind intensity and direction
Soil pH and mineral content
CO2 concentration (plants)
O2 levels (aquatic animals)
Define biotic
Living factors which affects an ecosystem
Give examples of biotic factors
Food availability
New predators
Disease (new pathogens)
Competition
What are the different groups of adaptations called?
Structural → what you can see
Functional → What is on the inside
Behavioural → what is learnt
How are polar bears adapted for the cold?
Small ears → reduce heat loss
Big paws → easier to walk through snow
Thick fur → Insulates their body from the cold
Long nose → can hunt prey easier
White fur → camouflage in the snow
How are camels adapted for the desert?
Ears lined with fur → prevents sand and dust from entering
Varied diet → limited food supply
Nostrils can close → protect from sandstorms
Brown coat → camouflage
Fat stored in humps → no other body fat
What is an extremophile?
An organism that lives in an extreme environment
↳ e.g polar regions, deserts, deep ocean bed, geothermal springs, top of mountains, bacteria living in deep sea vents
What are decomposers? What do they do?
Bacteria and fungi
↳ break down dead organisms → decomposition or rotting
How do decomposers break down dead organisms?
They release enzymes onto the dead matter and then consumes the broken down substances
Define biomass
The mass of living organisms
How is biomass transferred?
- Producers → they use energy from the sun to make food by photosynthesis to increase biomass
↳ 1% of energy from the sun is transferred into biomass
When an organism eats another, the biomass and therefore energy is transferred
↳ 10% of the energy in a trophic level is transferred to the one above it
What processes are involved in the carbon cycle?
Photosynthesis → CO2 in the atmosphere is converted into glucose for plants
Respiration → CO2 is given out and into the atmosphere
Combustion → Fuels are burnt and releases CO2
Eating → animals feed on plants and pass the carbon compounds along the food chain
Decay → decomposers eat dead organisms and carbon in their bodies is returned to the atmosphere as CO2
What processes are involved in the water cycle?
Evapouration → energy from the sun turns the water from a liquid to a gas
Condensation → The evapourated water cools and turns back into a liquid, forming clouds
Transport → water in clouds can be blown away by strong winds and moved to a different area
Precipitation → rain, slow, or sleet
Surface runoff → water which is not absorbed by the ground, runs along the surface
Percolation → water trickles through gaps in soil and rock
Transpiration → loss of water vapour from plants
What conditions can increase the rate of decay?
Warm temperature
Moist conditions
Presence of bacteria
Lots of oxygen
How does compost and manure benefit new plants and the soil?
They recycle minerals for plant absorbtion
They increase aeration and water retention of the soil
What happpens if you overwater a plant?
The soil becomes water logged so the roots of the plant are flooded and anaerobic decay can occur and kill them
What are the products of anaerobic decay? What are the problem with these?
Methane and carbon dioxide
↳ Both gases are a greenhouse gas which contributes to global warming
What can the products of anaerobic decay be used for?
They can be used as fuel → the methane and CO2 is called biogas
↳ renewable energy
Define biodiversity
The variety of living organisms in a particular place
Why is our population increasing?
Better health care → people are living longer
New medicines
Farmers are able to produce more food
Some religions don't permit the use of contraception
What are the problems of overpopulation?
Overconsumption → not sustainable as many materials will soon run out
Water pollution → farmers use too much fertiliser which can pollute rivers leading to eutrophication and cause illness
Air pollution → combustion of fuels releases CO2 which is contributing to the greenhouse effect. It can also cause acid rain.
Land pollution → rubbish which is not recycled is thrown into landfill whcih is building up
Reduced biodiversity → land is cleared for houses/farms which leave fewer space and resources for other plants and animals
What are bogs?
Areas of land which are acidic and waterlogged
↳ They often have very low levels of nutrients so decomposition is very slow and peat is formed
Why is peat used? Why is this a problem?
For gardeners to add to their soil or to be burned as a fuel
↳ This reduces biodiversity since peat takes a while to form
It is also a non-renewable energy source
Why are peat bogs important?
They are a very important store of carbon
Why are draining peat bogs a problem?
They are drained so that the area can be used as farmland but this releases a lot of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
What is the greenhouse effect?
The retention of heat in the atmosphere caused by the build-up of greenhouse gases
Why is the greehouse effect good?
Without it, the Earth's temperature would be very cold and there would be little to no life
What is the problem with the enhanced greenhouse effect?
It is leading to global warming
What are the effects of global warming?
Melting polar ice caps → habitats are being lost, sea levels are rising which can flood cities
More severe weather → decreased crop production, more storm damage
Coral reefs are being bleached
More species are likely to become extinct
Define conservation
The preservation of ecosystems and the organisms that live within them
How can we maintain biodiversity?
Breeding programs for endangered species
Protecting and developing new endangered habitats
Replanting hedgerows
Reducing deforestation
Recycling
What do the arrows in a trophic level represent?
The transfer of biomass (energy) from one trophic level to the next
Why can biomass be lost between stages?
Not all matter is digested
↳ it can be excreted as: waste (faeces), carbon dioxide and water in respiration, water and urea in urine
What is the equation for percentage efficiency transfer?
Percentage efficiency transfer = biomass in higher trophic level/biomass in lower trophic level
Define food security
The measure of the availability of food → having enough food to feed a population
How is food security reduced?
Increase in human population
Changing diets
Crop failure/disease
The effects of climate change → famine
Economy → increases costs of farming
Wars
What is intensive farming?
The use of machines, natural and artificial fertilisers, and high yield crops to maximise food production
It can also include keeping livestock in smaller pens with regulated temperatures
↳ reduces the energy needed for movement
What are the advantages and disadvantages of intensive farming?
Advantages:
Higher yields
More efficient use of land
Disadvantages:
Ethical issues
Increase the risk of antibiotic resistance → animals are fed antibiotics to prevent disease
What is involved in organic farming?
They use natural fertilisers and rotate their crops to avoid monoculture
Why is the population of fish declining? What is the result?
Overfishing
↳ species disappearing in an area or going extinct
↳ Ocean food chains being disrupted
↳ Fewer fish for human consumption
What do sustainable fisheries need to do?
Ensure that the number of fish caught and killed dosen't exceed the number of fish being born
What has been put in place to ensure that we aren't overfishing?
Fishing quotas → controls how much fish can be fished and changes every 2 years depending on the stocks of fish
Increased net size → can only catch large fish so small fish can grow and reproduce to maintain biodiversity
What is biotechnology?
Using living systems to create/improve products
How has biotechnology increased food security?
Tomatoes has been genetically modified to produce bigger fruits
Golden rice has been genetically modified to contain beta-carotene → higher nutritional value
Crops can be genetically modified to be resistant to insects
Crops can be genetically modified to be resistant to pesticides
Increase yield
How is human insulin produced using bacteria?
Remove DNA plasmid from bacteria
Cut open the plasmid with an enzyme
Cut the gene responsible for insulin production from the chromosome
Insert the gene into the plasmid and seal it using enzymes
Put the plasmid back into the bacteria
Grow the bacteria which will reproduce and produce insulin
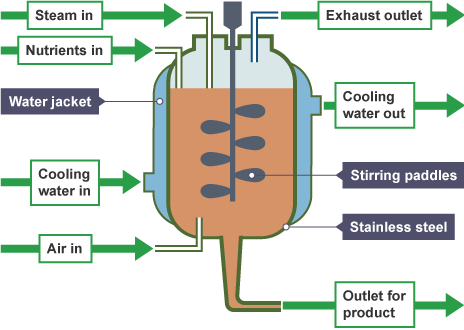
How are the conditions in a fermenter maintained to promote maximum growth?
pH and temperature are maintained at the optimum
Temperature is controlled by a water jacket
Sterile oxygen is added to ensure aerobic respiration occurs
A food source (glucose) is added
The mixture inside is stirred to ensure that all the oxygen and nutrients are equally distributed
What environmental changes affect the distribution of species in an ecosystem?
Temperatures
Availability of water
Composition of atmospheric gases
These changes may be seasonal, geographic, or caused by human intervention
What is used to produce mycoprotein
The fungus fusarium