Edexcel A Level Statistics
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Which dates does the Large Data Set cover?
May-October 1987
May-October 2015
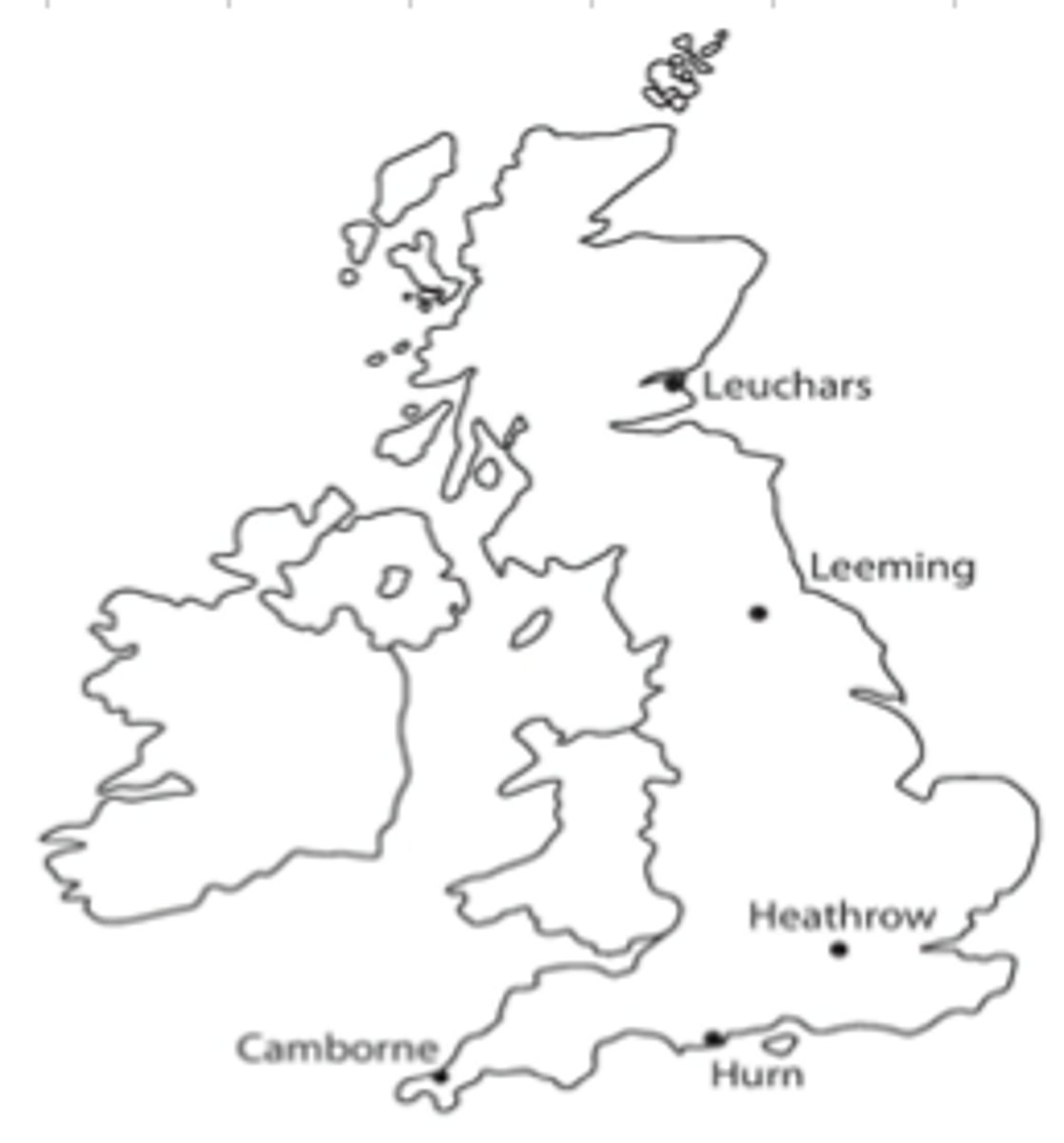
What are the 5 UK weather stations?
Camborne (Cornwall)
Heathrow (near London)
Hurn (Dorset - south coast)
Leeming (Yorkshire - North England)
Leuchars (Scotland)
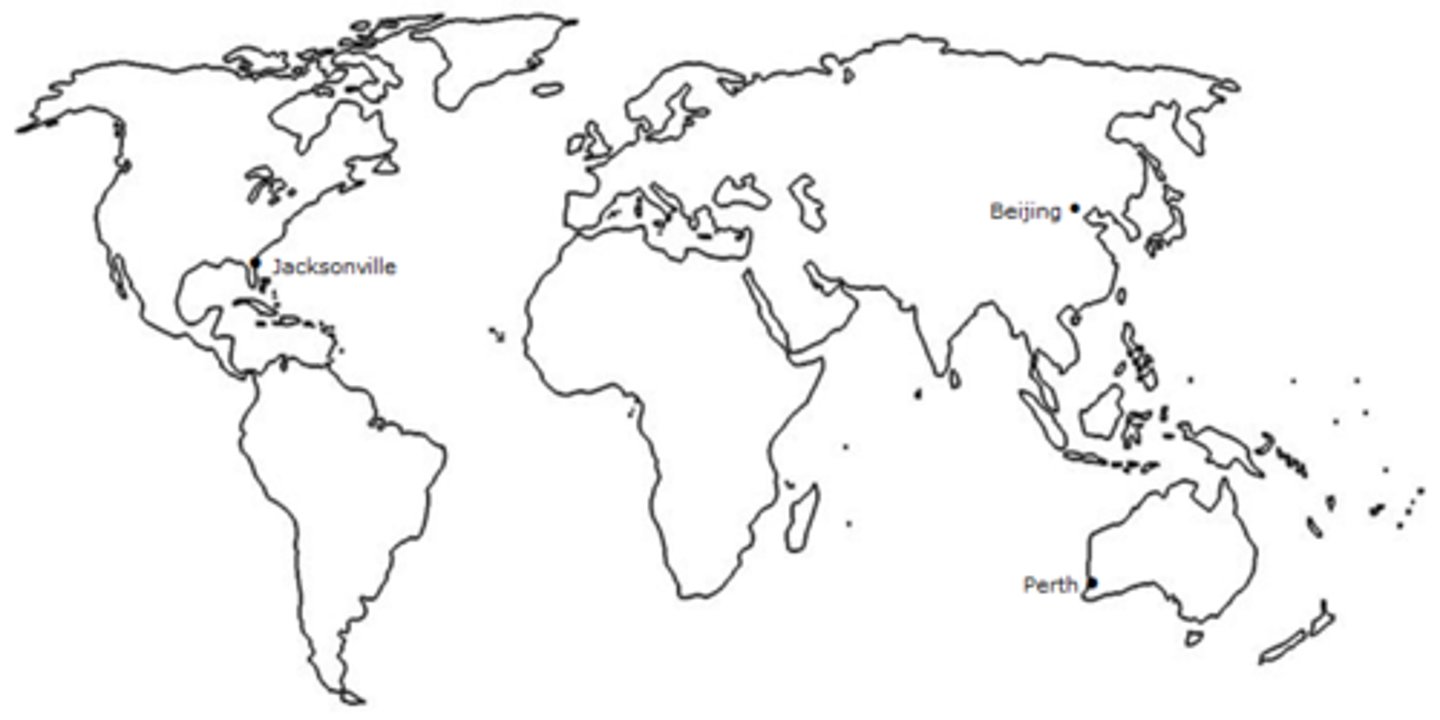
What are the 3 overseas weather stations?
Beijing (China)
Jacksonville (Florida, USA)
Perth (Australia)
What does tr mean?
trace - less than 0.05mm of rainfall
Histogram - frequency density equations
area of bar = k x frequency
frequency density = frequency / class width
Comparing data
Comment on:
- a measure of location
- a measure of spread
Conditions for Binomial distribution
- there are a fixed number of trials, n
- there are two possible outcomes (success and failure)
- there is a fixed probability of success, p
- the trials are independent of each other
Summary Statistic / Sₓₓ
Sₓₓ = Σ(x - x̄)²
Sₓₓ = Σx² - (Σx)² / n
Stratified sampling - Adv & Disadv
Adv
- Sample accurately reflects the population structure
- Guarantees proportional representation of groups within a population
Disadv
- Population must be clearly classified into distinct strata
- Selection within each stratum suffers from the same disadvantages as simple random sampling
Systematic sampling - Adv & Disadv
Adv
- Simple and quick to use
- Suitable for large samples and large populations
Disadv
- A sampling frame is needed
- It can introduce bias if the sampling frame is not random
Simple random sampling - Adv & Disadv
Adv
- Free of bias
- Easy & cheap to implement for small populations and small samples
- Each sampling unit has a known and equal chance of selection
Disadv
- Not suitable when the population size or the sample size is large
- A sampling frame is needed
Census - Adv & Disadv
Adv
- Completely accurate
Disadv
- Time consuming & expensive
- Cannot be used when the testing process destroys the item
- Hard to process large quantity of data
Census
Observes or measures every member of a population
State four properties of the normal distribution.
Symmetrical, bell-shaped, mean = median = mode, total area under curve = 1.
What is the standard normal distribution?
Z∼N(0,1) with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
How do you standardise a normal variable?
When can a binomial distribution be approximated by a normal distribution?
n is large
p is close to 0.5
State the formula for conditional probability.
What must you do when normal-approximating?
The mean and variance of a binomial distribution can be calculated by:
µ =np
σ = np(1-p)
Apply conituity correction (as binomial distribution is discrete and the normal distribution is continuous)
when does μ stay the same but σ gets divided by √n
Sample of another sample (typically normal)
what does Φ(a) mean
P ( Z score < a)
What is cloud coverage is measured in?
Measured in oktas which can be measured in integer values 0-8.