Business Studies GCSE- KEY TERMINOLOGY
Adding Value
The process of including an innovation or improving the perceived value of a product, in order to raise the price and value of it.
Aims in a business
Small achievements a business wants to reach while starting up, before achieving a larger objective.
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Adding Value
The process of including an innovation or improving the perceived value of a product, in order to raise the price and value of it.
Aims in a business
Small achievements a business wants to reach while starting up, before achieving a larger objective.
Apps
Usually used by firms to communicate with customers and provide information about the business. They can also be used to sell products and promote special offers.
Assets
Valuable items owned by the business, or money owed to the business.
Brand Images
The impression that customers have of the firm or the products sold by them. The business may have a reputation for cheaper prices.
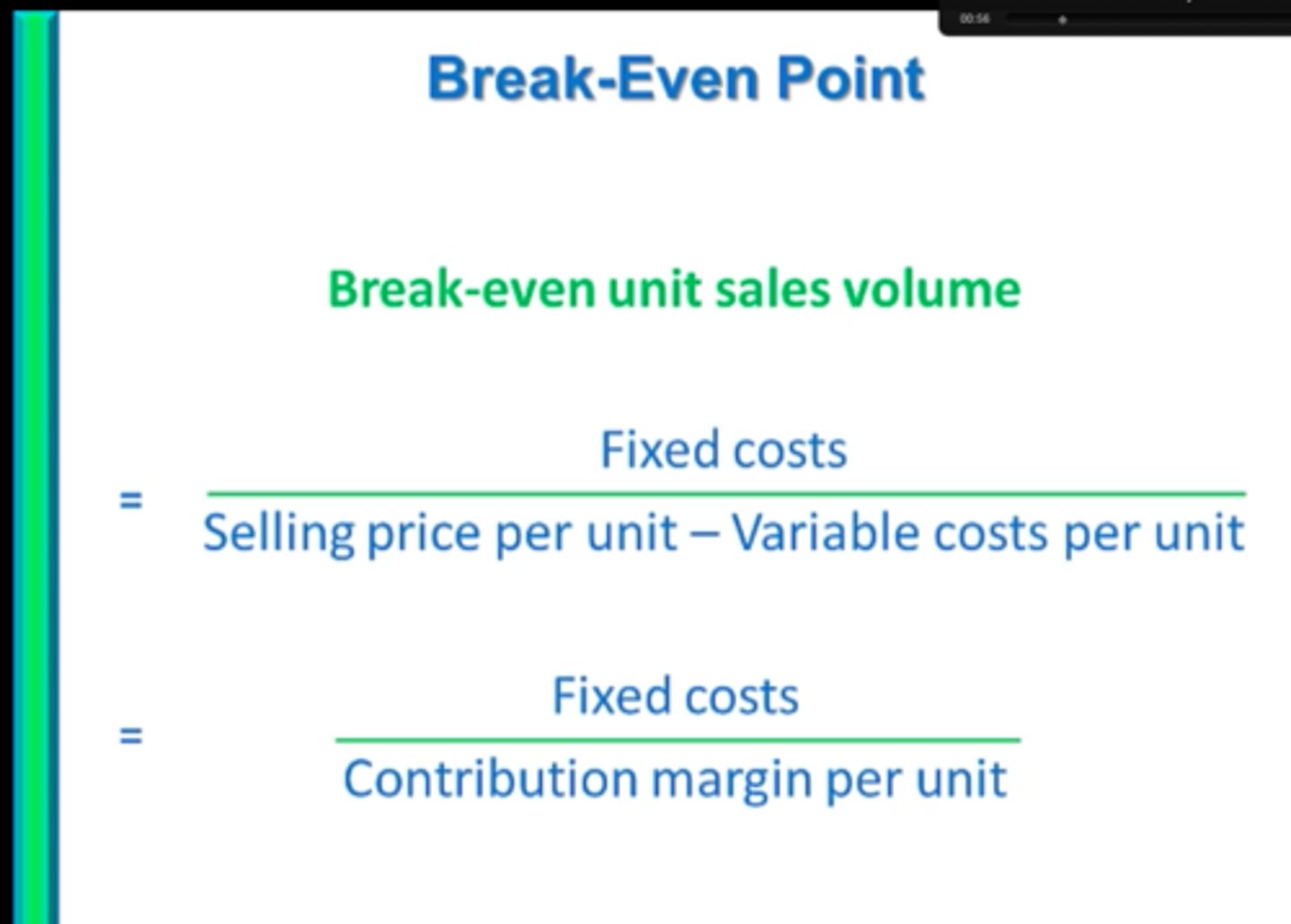
Break-even analysis
The level of sales (or output) a firm needs in order to just cover its costs. It can be measured by the number of units a firm needs to sell to break-even.
Business Ideas
The process of creating new and innovative concepts for a business due to the dynamic and ever-changing market.
Business Ownership Structures
Sole traders - A business with just one owner
Partnerships - A business with two or more sole traders
Private Limited Companies (Ltd) - An INCORPORATED business that is owned by shareholders.
Public Limited Companies (PLC) - An INCORPORATED business that is owned by anyone that anyone that invests in the business's shares on the stock market.
Business Plans
An outline of what a business will do in the future, and how it aims to do it. Anyone wanting to start up a business should have a plan.
Cash
The money a company can spend immediately.
Cash flow
The flow of all money into and out of the business. Net cash flow is equivalent to the total cash inflows subtracted by the total cash outflows for a given time.

Closing balances
The amount of money in the bank, at the end of a month.
Command words
The bit of the question that tells you what to do. (e.g give, state, define, identify, calculate, complete, and outline).
Competition
A situtation in which a business if trying to be more successful than another business in the same market.
Consumer laws
The laws restricitng how firms sell their products - the aim is to protect the consumer by giving complete honesty to them. The 'Consumer Rights Act 2015' covers how goods and services can be sold.
Convenience
Making a product/service generally more hassle-free for consumers
Costs
An amount that must be paid or spent by a business. This may be for manufacturing products and paying utilities, for example.
Credit
When a firm gives their customers longer to pay for products.
Crowd funding
When a large number of people contribute money towards starting up a business or funding a business idea.
Customer Needs
What customers want and may pay extra to have. Key examples are convenience, price, quality and customisation.
Demographics
A part of the market that is seperated by identifiable characteristics. E.g Age/Income.
Digital Communication
Conversing with consumers or shareholders through digital means, like emails or websites.
Discrimination
When employees are paid less for the same job or treated worse, laws like the Equality Act 2010 prevent these things happening.
Dividends
The payments that the shareholders get if the company makes a profit. The more shares a shareholder owns, the higher the dividend will be.
E-commerce
Using the internet to buy or sell products. It can be really convenient for consumers to use websites and apps.
Economic Climate
The overall health of the economic systems within which a firm operates. It includes many different economic conditions - like unemployment and taxes.
Emails
A message sent electronically on an 'email' app/website.
Employment Laws
Describes the many different laws associated with the relationship between employers and employees. The laws are generally about pay, recruitment, discrimination and health and safety.
Enterprise
The process of identifying new business opportunities, and then taking advantage of them.
Entrepeneur
Someone who takes on the risks of enterprise activity.
Exchange Rates
An economic condition that tells you how currencies compare in value and price. They're very important for firms that buy from or sell to other countries.
Financial security
To achieve a point where a business can depend on its own revenue to fund its activities.
Fixed costs
The costs that do not chnage with the quantity of output produced.
Focus groups
Where a small group of people (conducted by a business) discuss their attitudes towards a product.
Franchise
Where a company lets another firm sell its products or use its trademarks in return for a fee, for a percentage of the profits.
Gaps in the market
A customer need that isn't being met by other firms.
Globalisation
The process by which businesses and countries around the world become more connected.
Government taxes
Tax rates are set by the government. Changes occur every April 6th and these changes to tax rates can have a big impact on businesses.
Health and safety laws
Legislations that help to make sure that risks to people at work are properly controlled.
Income
The money received by someone, especially on a regular basis, for work or through investments.
Incorporated businesses
A business that has its own legal identity.
Inflation rate
The percentage of increase in the price of goods and services.
Insolvency
When a firm is unable to pay its debts.
Interest Rates
A value which shows the cost of borrowing money or the reward given for saving money.
Legislation
The act of making or enacting laws.
Limited liability
Where the owners of a business are not legally responsible for all the debts a business has.
Live chats
Customers can click a button at any time and have an instant messaging email or voice conversation with a customer service representative
Loans
A long-term source of money that must be paid back to the lender.
Location of a business
The consideration of where is suitable for the place a firm will locate. Some things to think about are where customers are, and where the raw materials needed are.
Loss (Negative Profit)
When the total costs for a business are MORE than the revenue made.
Margins of safety
The gap between current level of output and the break-even level of output.
Market
A place where goods are traded between customers and suppliers, trade in a particular type of product or the potential customers for a product.
Market maps
A diagram showing some of the features of a market.
Market research
Investigation of the features of a market and customer opinions within the market.
Market share
The proportion of total shares within a market that is controlled by a business.
Market size
The number of individuals within a market that are potential buyers and sellers of products, or the total value of products in the market.
Marketing Mix
The four elements that must be considered for good marketing: products, price, promotion, and place.
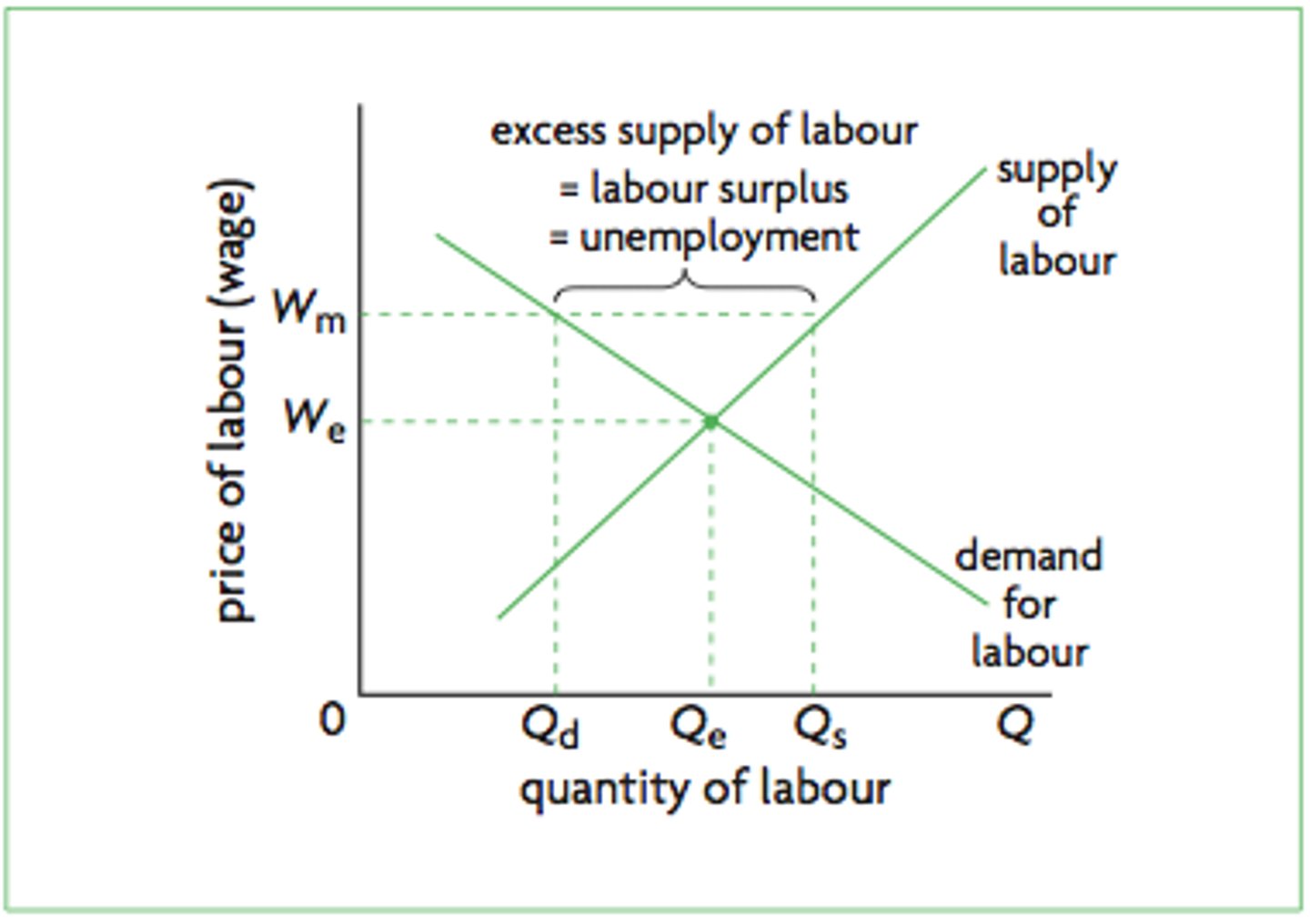
National Living Wage (NLW)
The minimum amount workers aged 23 and over must be paid - it is slightly more than the national minimum wage (NMW).
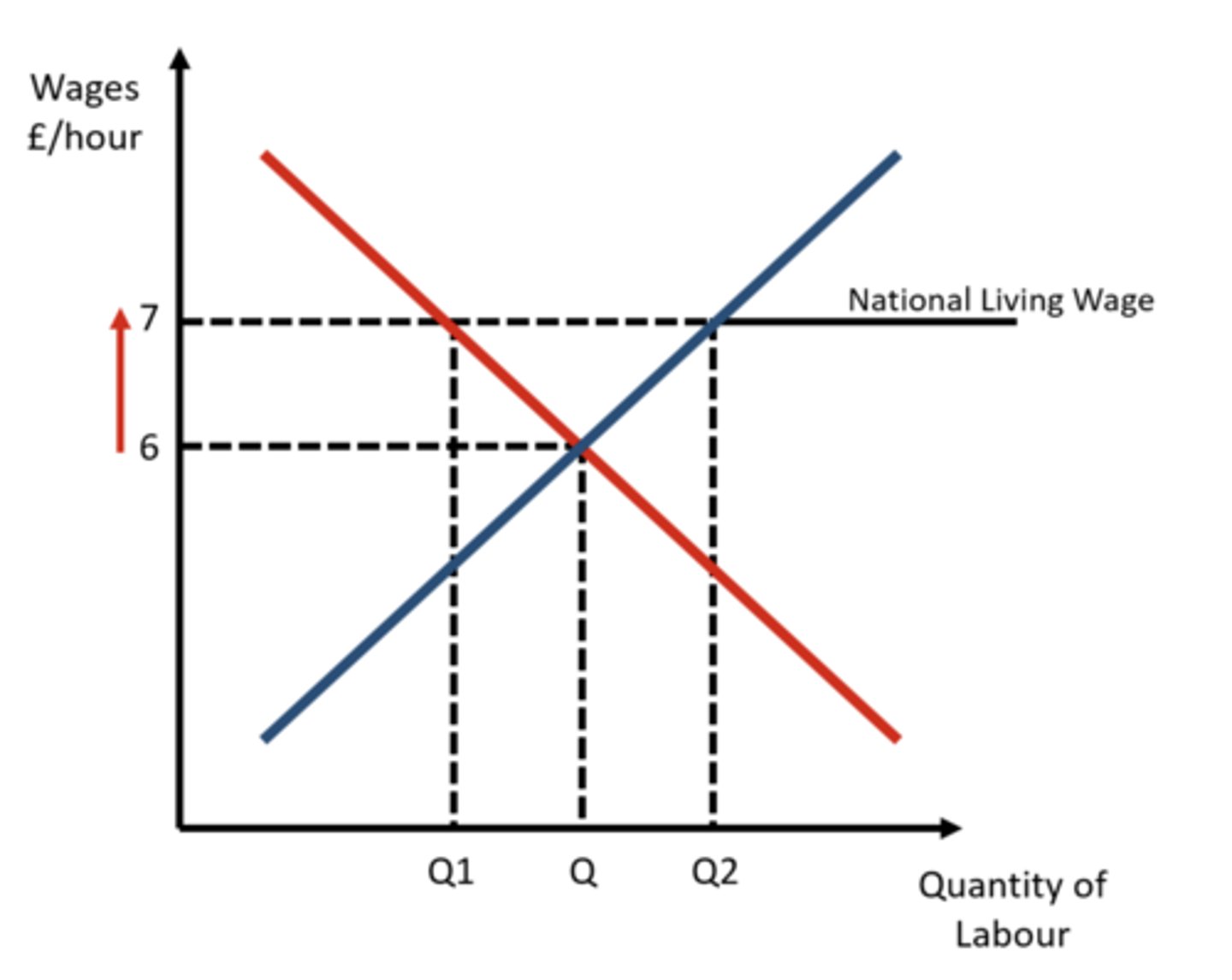
National Minimum Wage (NMW)
Workers aged 22 and under have to be paid the NMW - the exact amount depends on the age of the worker and the type of work.
Net cash flow
Total inflows - total outflows

Niche Market
A small and specialised group of potential customers for a product.
Objectives
A measurable step that business will set in order to work towards an aim.
Obsolete
When a product is no longer used, usually because it has become out-dated and has been replaced by something else.
Overdraft
When more money is taken out of a bank account than has been paid into it.
Partnerships
A business ownership structure in which a smaller number of people (usually between 2 or 20) own an unincorporated company.
Pay laws
- National Living wage £7.50 an hour
- Can be fines £20,000 per worker if they don't
- Employees seek to motivate staff
- Pass increase of staff costs to prices
- Some businesses employ younger staff to reduce staff costs
Payment systems
Ways to pay for products:
- Online payments
- Chip and PIN
- Contactless payments
Personal savings
Money that has been saved up by the owners of the business, for funding.
Place (marketing mix)
The method of distribution used to get a product from the company to the customer.
Pressure groups
A type of special interest group which consist of individuals with a common concern who seek to place demands on organisations to act in a particular way or to influence change in their behaviour (e.g. Greenpeace and PETA)
Price (marketing mix)
The price that a customer things is good value for money. (If the perceived value is high but the price is affordable)
Primary Market Research
Market research that involves getting information from customers or potential customers.
Private Limited Companies (LTDs)
A business ownership stucture that is incorporated and has shares, but the shares can only be sold with the agreement of all the shareholders.
Product (marketing mix)
The firm must furst identify customers' needs (or wants). Then it needs to come up with a product that will fulfil some of those needs.
Profits
The difference between revenue and costs over a period of time.
Promotion (marketing mix)
The product must be promoted so that potential customers are aware that it exists and will want to buy it.
Public Limited Companies (PLCs)
A business ownership structure that is incorporated and has shares that can be bought and sold by anyone.
Qualitative data
Information that involves people's feelings or opinions.
Quality and consumer laws
The legislation that products should be up to a certain standard for consumers.
Quantitative data
Information that can be measured or reduced to a number.
Recruitment laws
- must not discriminate (equality act 2010)
- make sure that new workers have legal right to work in the uk
Retained profits
Profits that are put back into the business.
Revenue
The value of all products sold in a given time period.
Reward in a business
The potential for success, profits and security when starting up a business.
Risk in a business
The potential for loss in entrepeneurial ventures.
Salary
A fixed payment that is made to employeed every month.
Secondary research
Market research that involves looking at data from outside the business, e.g market reports.
Segmentation
When people within a market are divided into different groups, in order to promote and advertise to an ideal audience.
Share capital
Money gained through issuing shares in the company.
Shareholders
Someone who owns stock and/or shares in a company.
Shares
A unit of ownership in a company. Owners of shares can share in the profits of the company.
Social media
Websites and applications that enable firms to promote a business and its products.
Sole trader
A business ownership structure where one person owns an unincorporated company.
Stakeholders
Any individual or group of people that is affected by a business.
Start-up capital
Finance needed by an entrepreneur to set up a business
Stock market
A market where shares of public limitied companies (PLCs) can be bought and sold.
Surveys
Collecting information from people, e.g directly over the phone or using questionnaires.
Target market
A set of buyers sharing common needs or characteristics that the company decides to serve.
Tariffs
A tax on goods that are being imported or exported.
Technology
Using the growing internet and development of computers to expand and communicate to customers.