Histology Laboratory Assessment 1
1/231
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
232 Terms
digital pad of dog; h&e
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
longitudinal section of lumbosacral nerve of dog; osmic acid
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
duodenum of dog (mucus-secreting goblet cells); periodic acid-schiff
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
cervix of sheep (epithelial cells); alcian blue/periodic acid-schiff
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
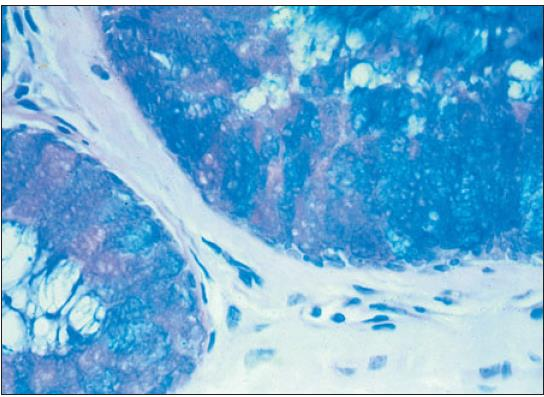
adrenal of horse (reticular fibers); gordon and sweet
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
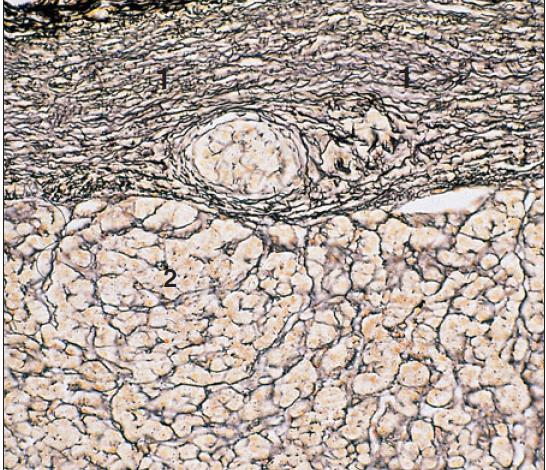
stellate cells in the cerebellum of cat; cajal’s uranium silver
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
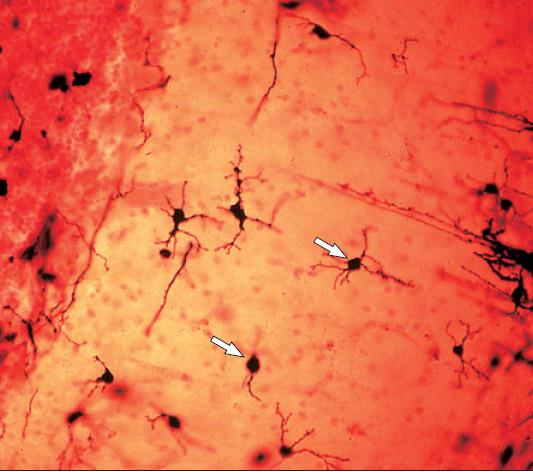
tongue of dog; masson’s trichrome
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
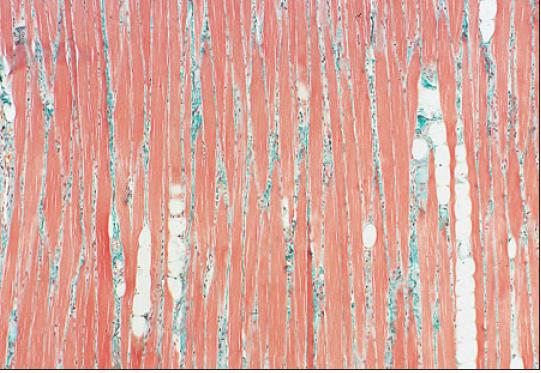
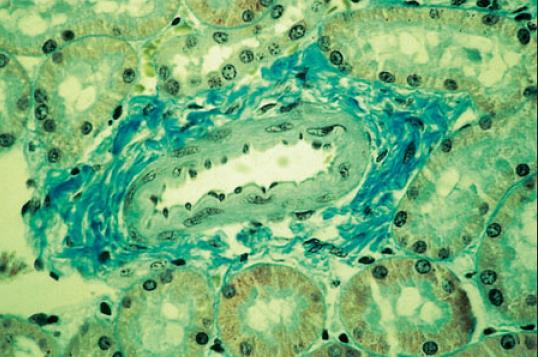
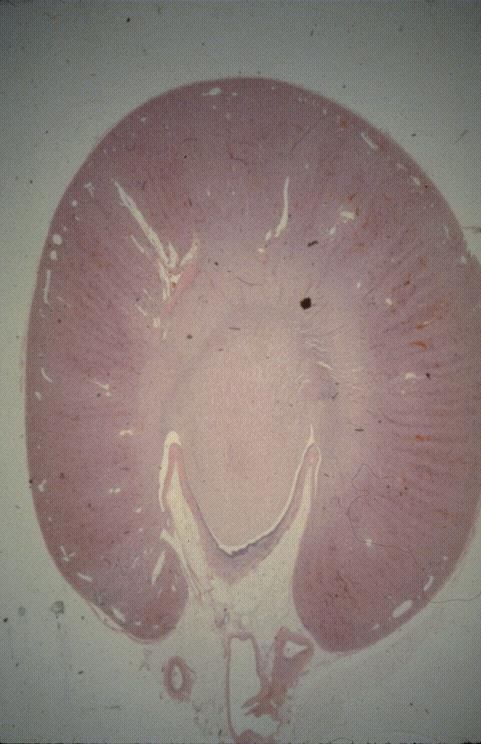
kidney of dog; gomori’s trichrome
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
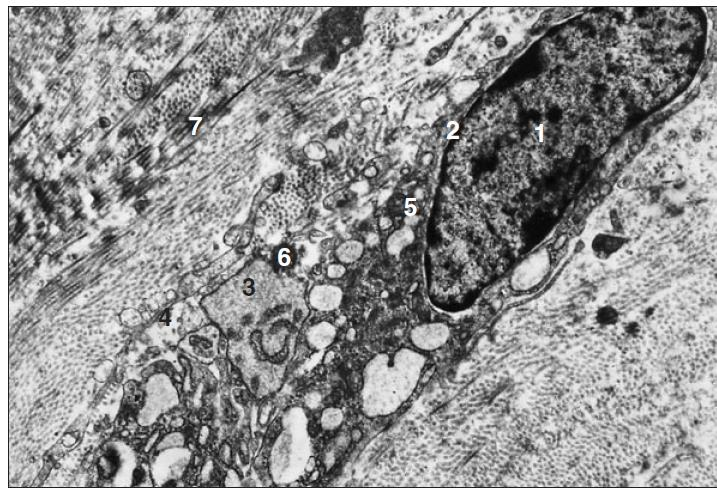
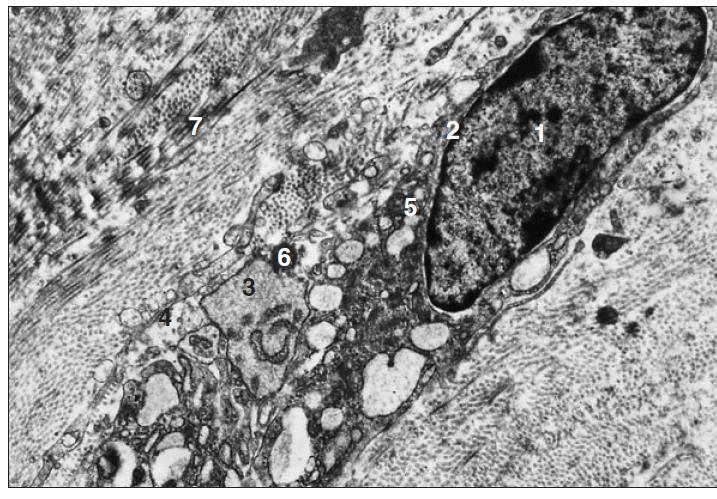
transmission electronic microscopy of a fibroblast of sheep
what is the specimen shown and microscopy technique used
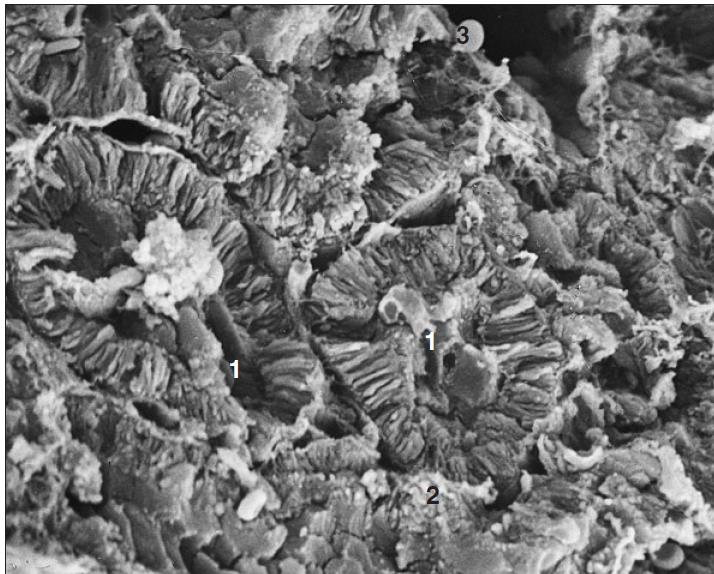
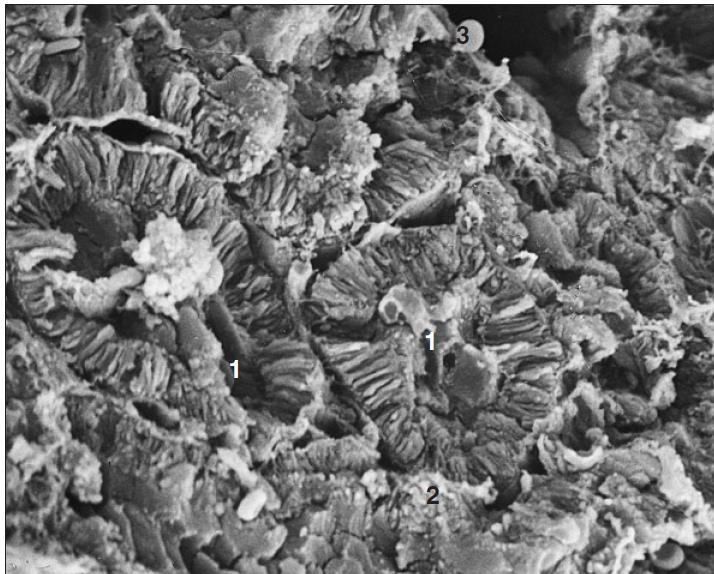
scanning electronic microscopy of a kidney of a dog
what is the specimen shown and microscopy technique used

nucleus
nuclear membrane
cisternae of RER
plasmalemma
mitochondria
fat droplet
collagen fibrils
identify the numbered parts of the specimen
renal tubule
intersitial connective tissue
free erythrocyte
identify the numbered parts of the specimen

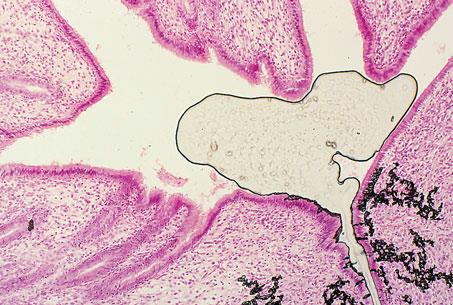
uterus of a cat; h&e; shrinkage
what is the specimen shown, staining technique used, and the artifact observed in the specimen
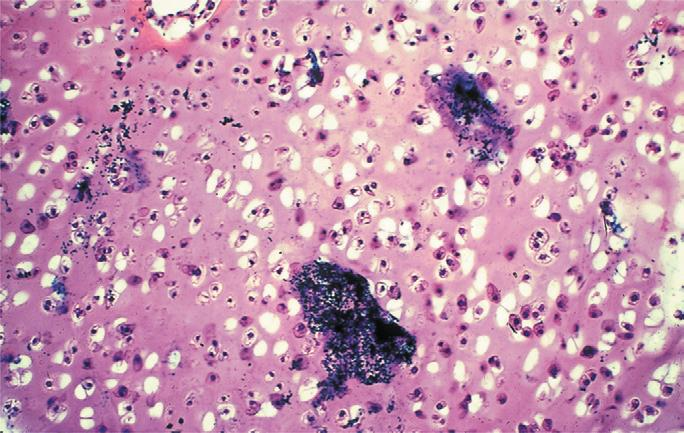
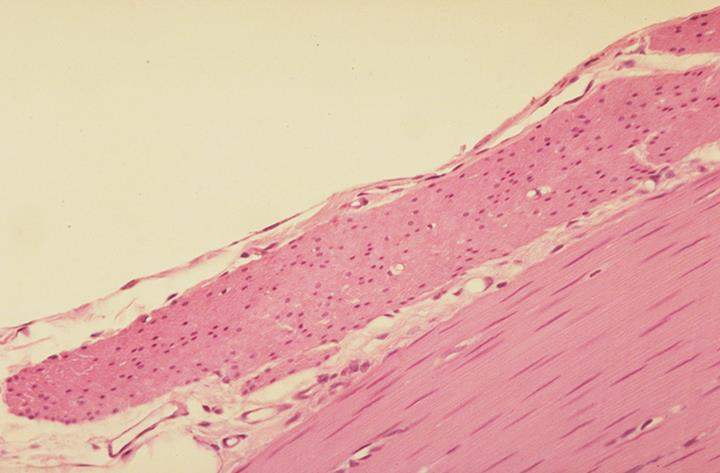
cartilage of dog; dark precipitates
what is the specimen shown and the artifact observed in the specimen
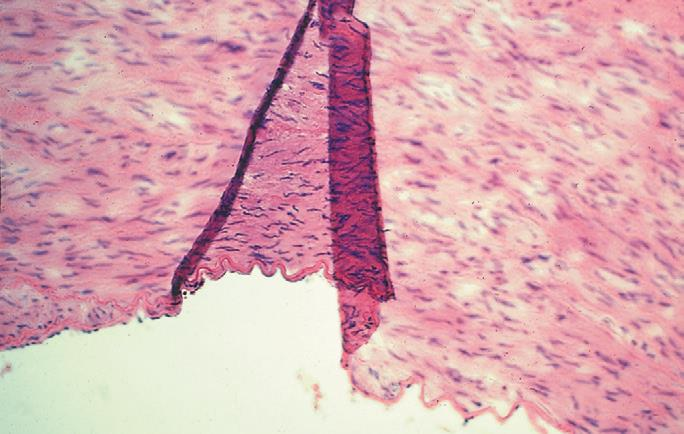
aorta of pig; fold and wrinkles
what is the specimen shown and the artifact observed in the specimen
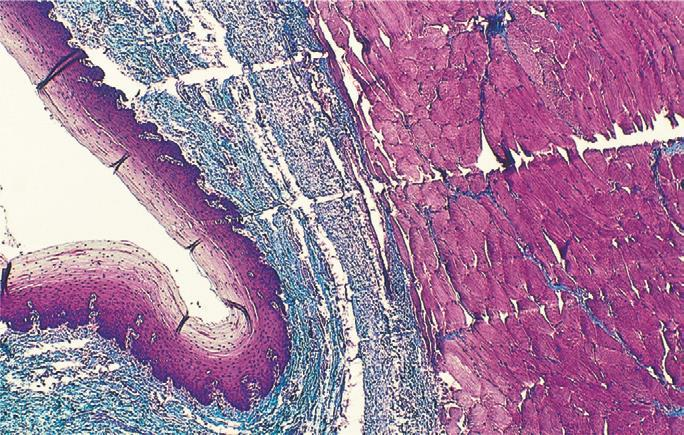
esophagus of horse; masson’s trichrome; knicks in the knife
what is the specimen shown, staining technique used, and the artifact observed in the specimen
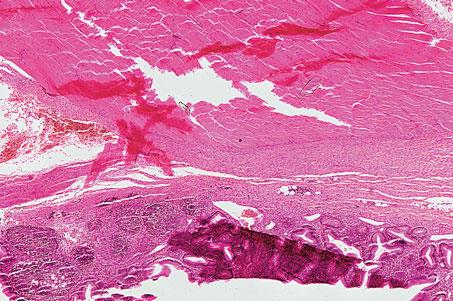
cloacal bursa or bird; h&e; pinching of tissue
what is the specimen shown, staining technique used, and the artifact observed in the specimen
spleen of dog; h&e; pinching of tissue
what is the specimen shown, staining technique used, and the artifact observed in the specimen
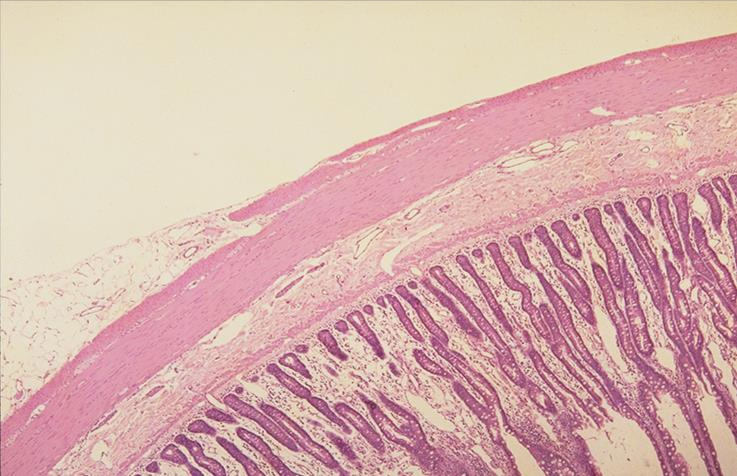
wall of jejunum; simple squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
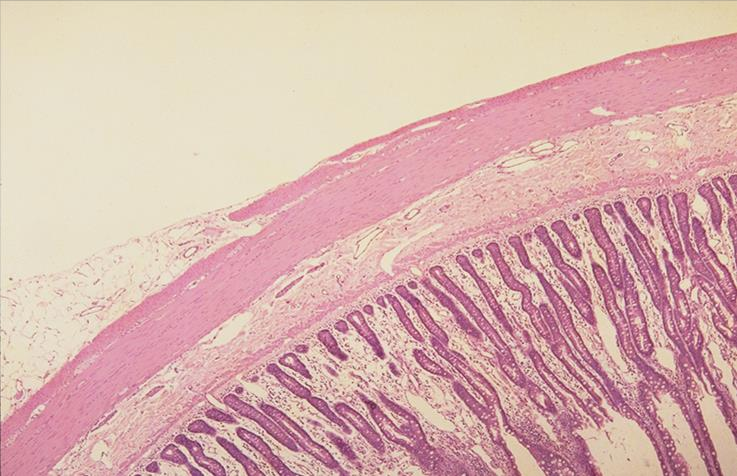
outer wall of the jejunum; simple squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
tunica serosa
tunica muscularis
identify the specific parts
muscle layer and serous membrane of small intestine:
mesothelium
tunica serosa
tunica muscularis (outer layer)
tunica muscularis (inner layer)
identify the specific parts
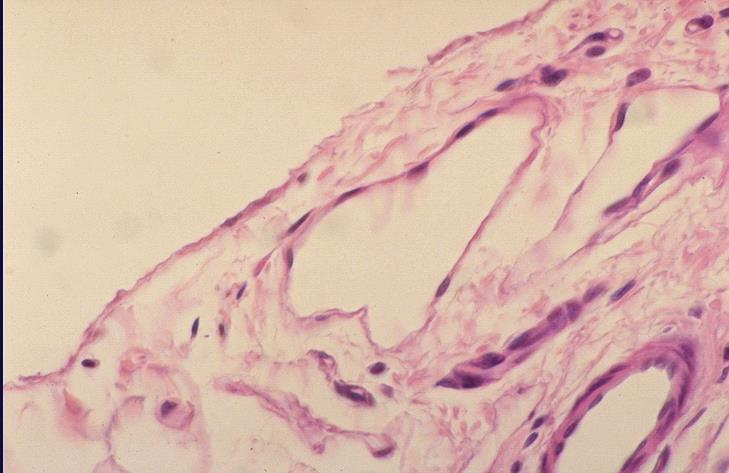
blood vessel in the tunica serous of small intestine
what is the specimen shown
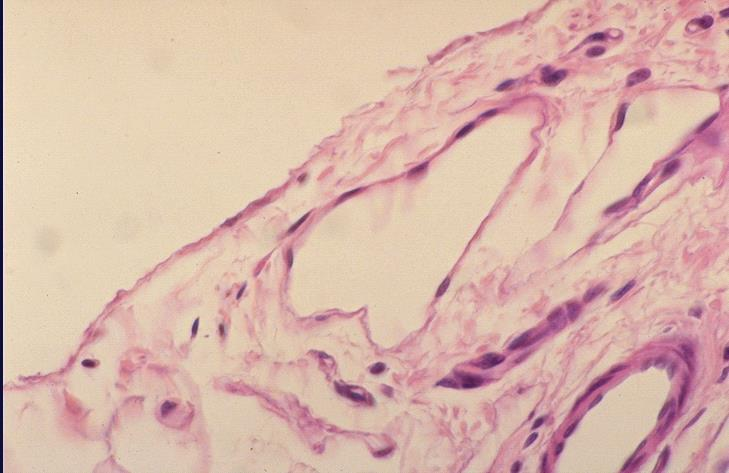
small vein
endothelium
small artery
identify the specific parts
cross section of kidney; simple cuboidal epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
cortex
medulla
identify the specific parts
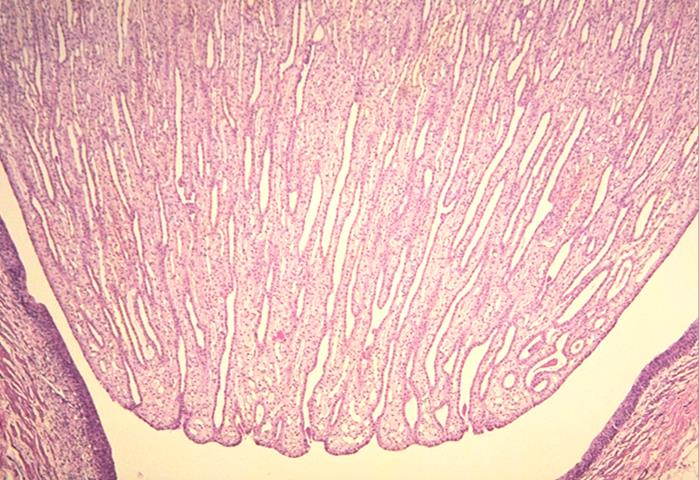
inner medulla of the kidney with collecting ducts
identify the specific part
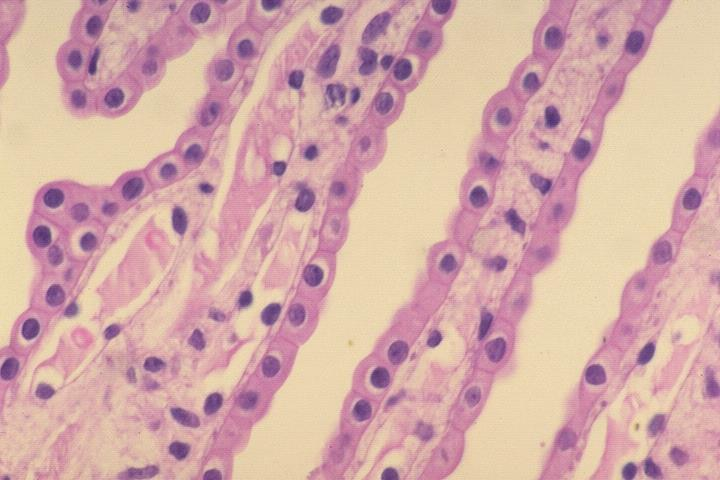
lumen of collecting ducts
simple cuboidal epithelium
what are the white spaces between the collecting ducts
what epithelial tissue is present
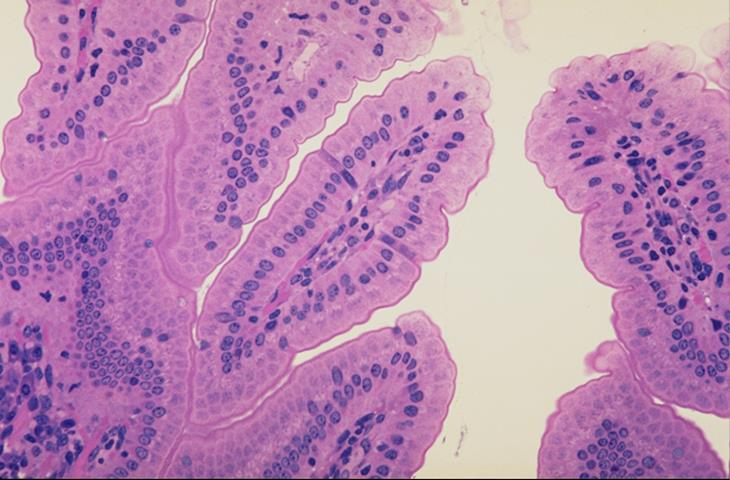
wall of the small intestine of mouse; simple columnar epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
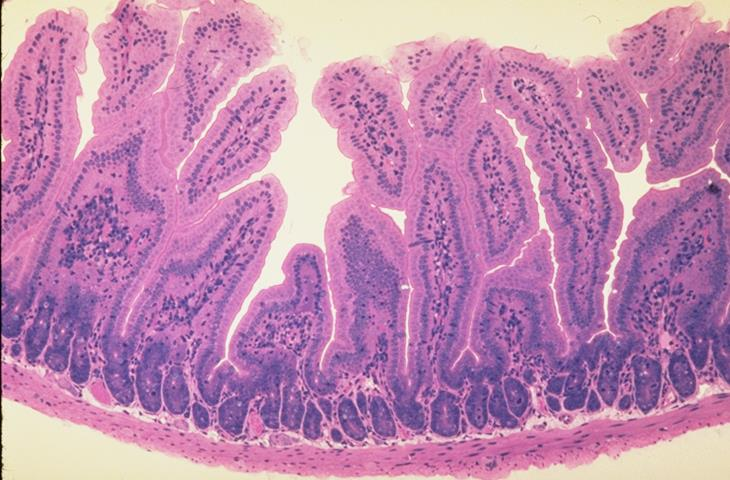
villi of small intestine
what is the specimen shown
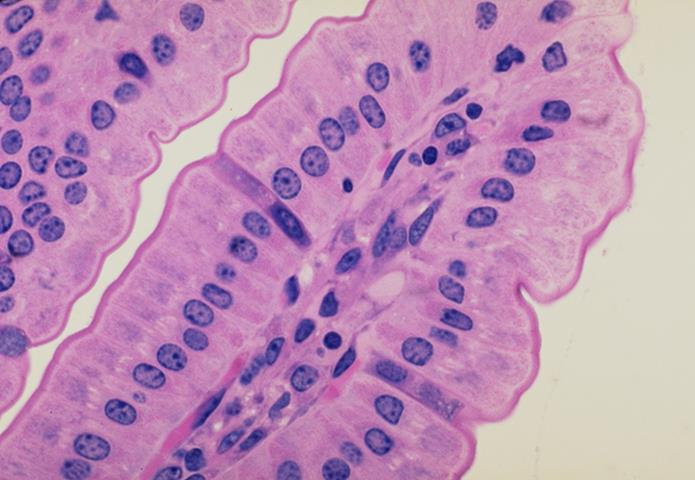
striated border
basement membrane
what are the borders present in the apical surface of the epithelial cells
what do you call the membrane in the inner surface of the villi
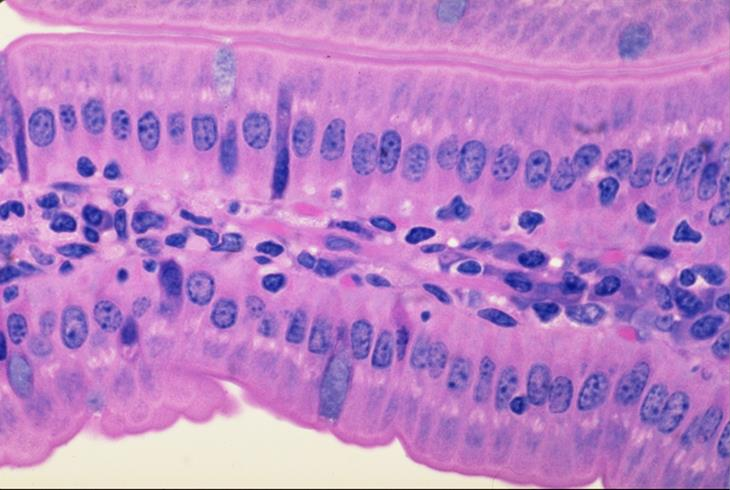
striated border
made up of numerous microvilli on the apical surface of the epithelial cells. these microvilli increase the surface area for absorption by the epithelial cells
apical border
basal border
what are the borders present in the slide
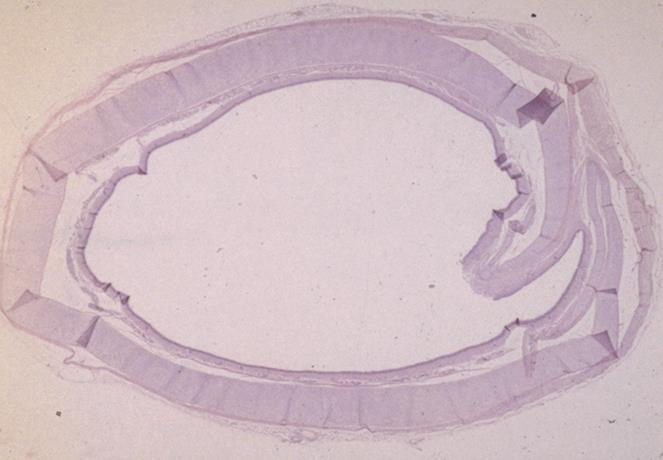
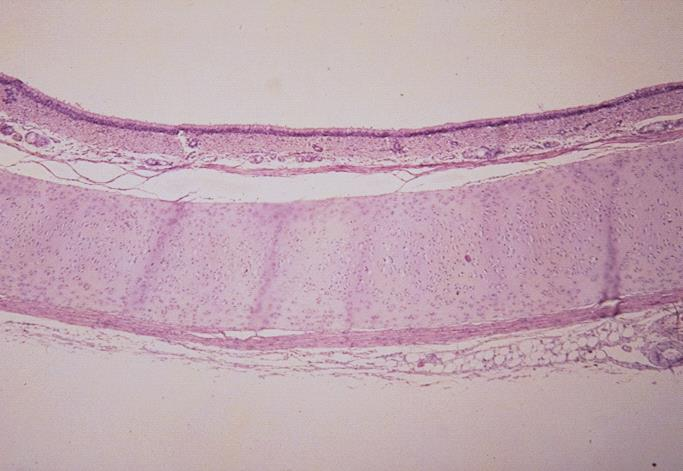
cross section of a canine trachea; pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
wall of a canine trachea
membrane
cartilage
identify the specimen and its specific parts
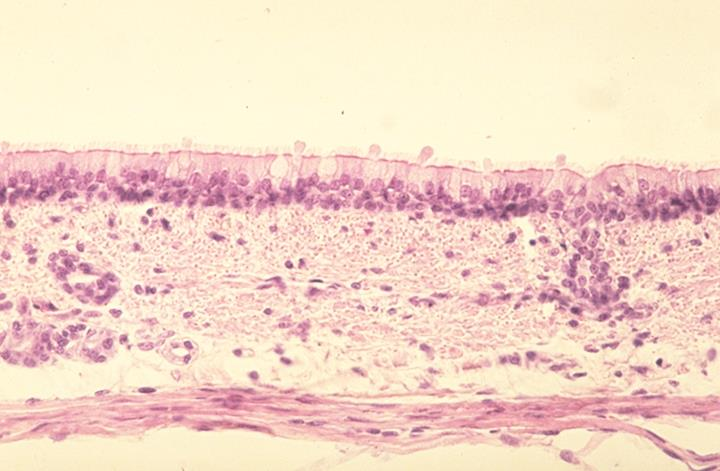
mucous membrane of a canine trachea
epithelium
identify the specimen and its specific parts
cilia
goblet cells
basement membrane
identify the specific parts
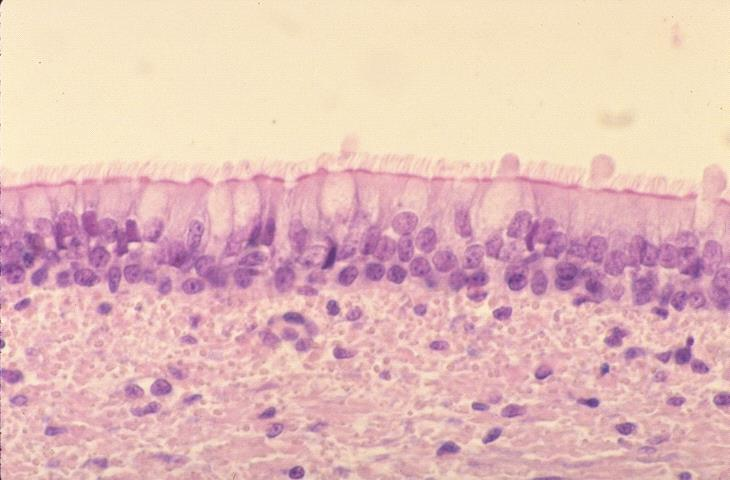
goblet cells
secrete mucus which trap particulate matter in the inhaled air
ciliary movement
produce a current that moves mucus and trapped particulate matter toward the outside
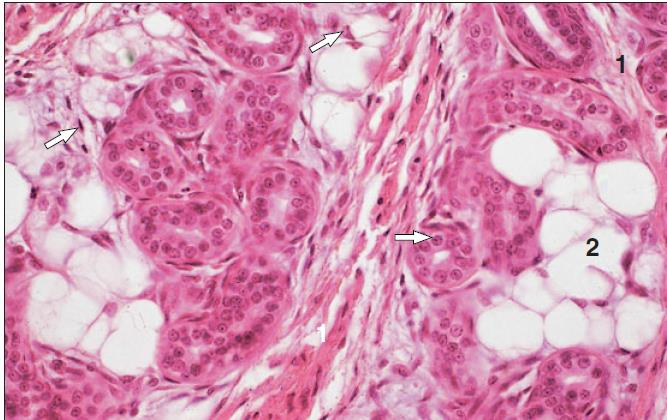
non-lactating mammary gland of a bovine; stratified cuboidal epithelium
lactiferous duct
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
what is the white area shown in the slide
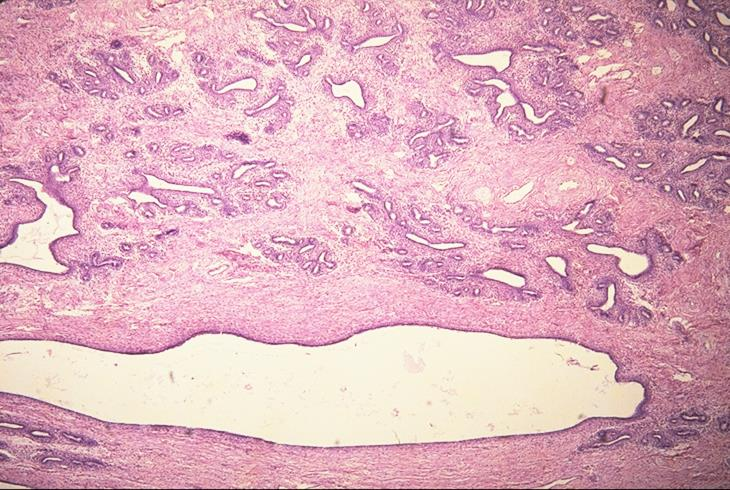
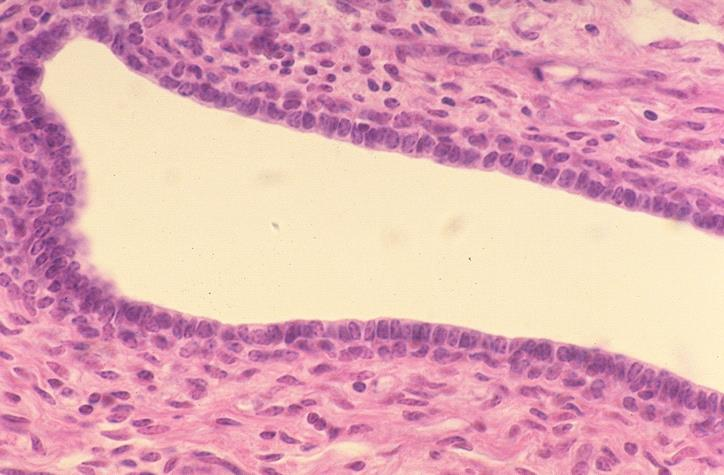
wall of a lactiferous ducts of a non-lactating mammary gland of a bovine; stratified cuboidal epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
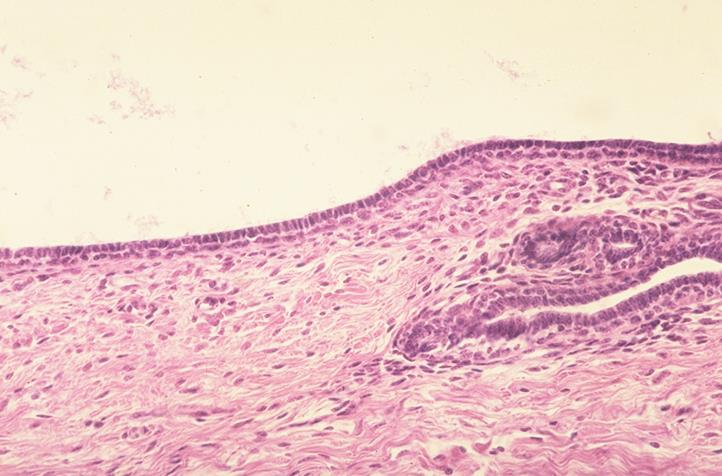
lactiferous duct
basement membrane
identify the middle white part
what membrane surrounds that part
sagittal section of the canine lip; stratified squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
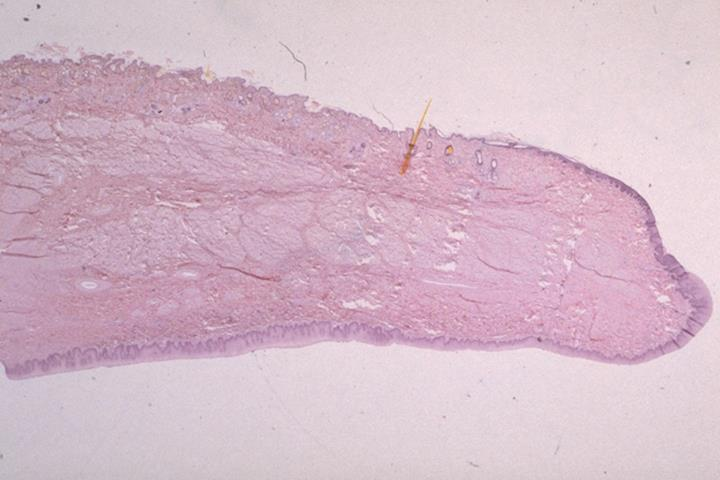
mucous membrane on the inside, lower layer of the lips
skin on the outside upper layer of the lips
identify the specific parts
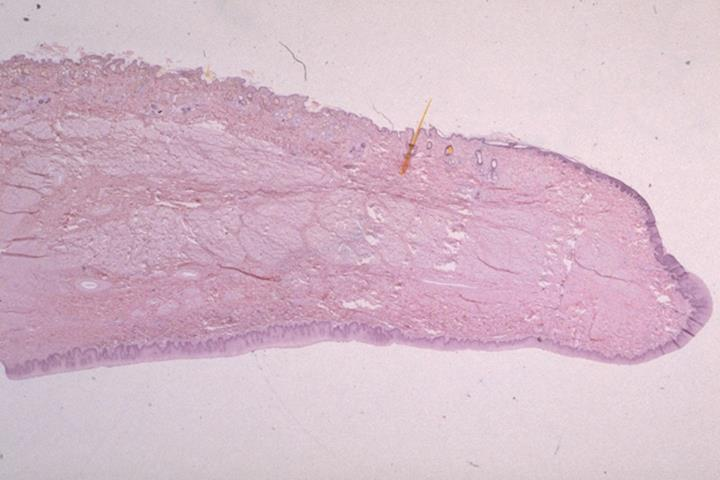
keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what type of stratified squamous epithelium lines the skin of the canine lip
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what type of stratified squamous epithelium lines the mucous membrane of the canine lip
at the edge of the lip
where can you find the gradual transition from keratinized to non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium in a canine lip
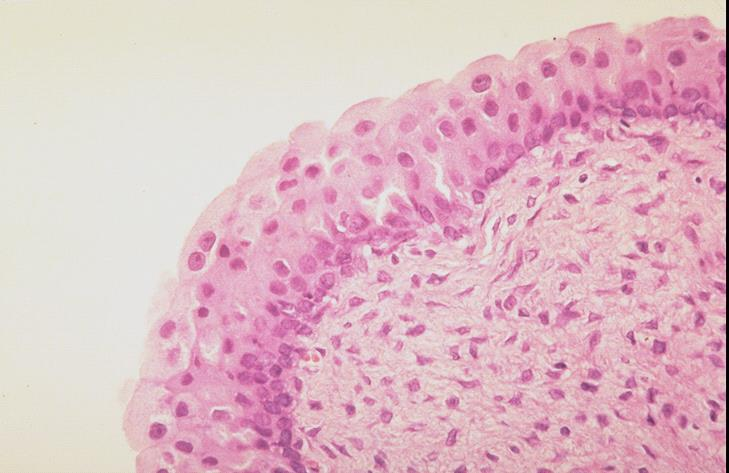
mucous membrane of the canine lip; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
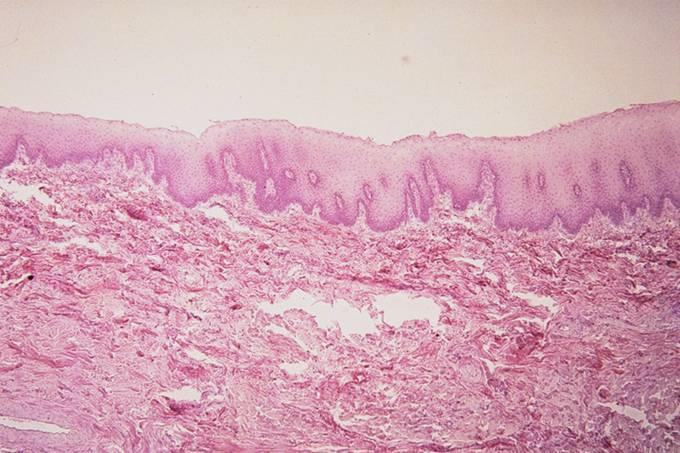
basement membrane
what is the wavy part shown in the slide
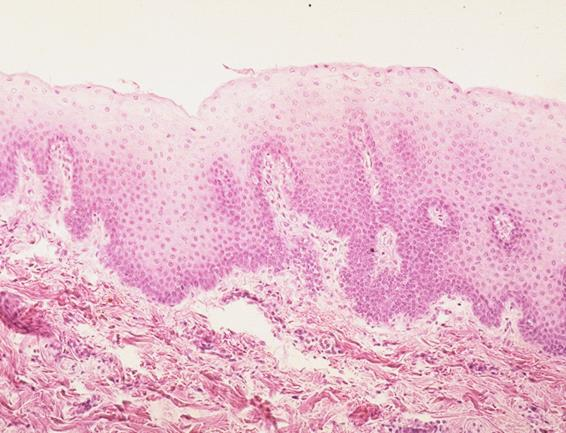
skin of the canine lip; keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
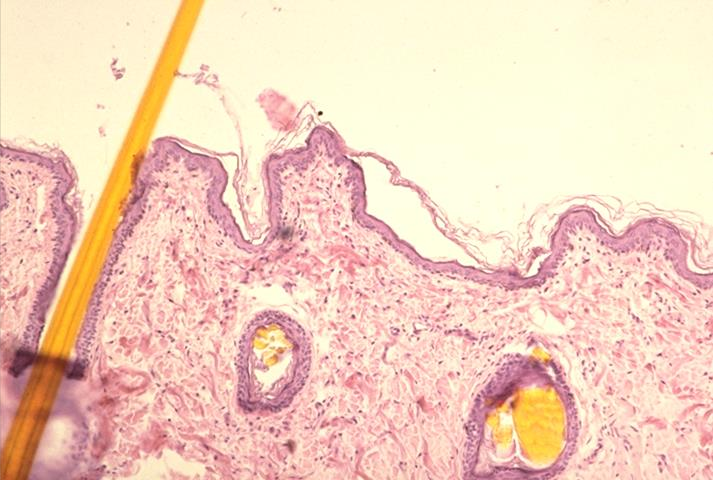
skin of the canine lip; keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
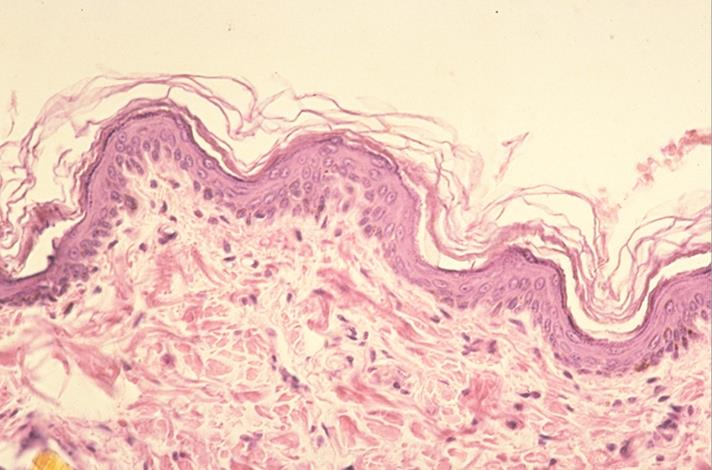
tunica mucosa of an esophagus of a feline; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
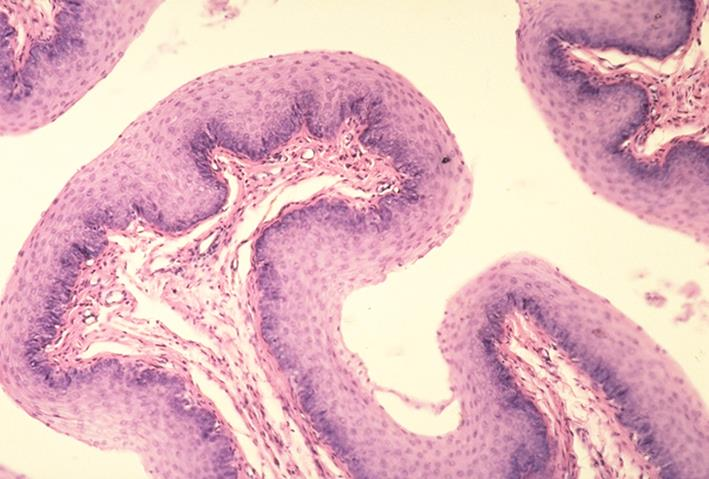
skin of a foot pad of a canine
highly keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
keratin layer (stratum corneum) composed of dead cells
what is the specimen shown
what is the epithelial tissue present
what layer is present in the middle part of the epithelium and what it is composed of
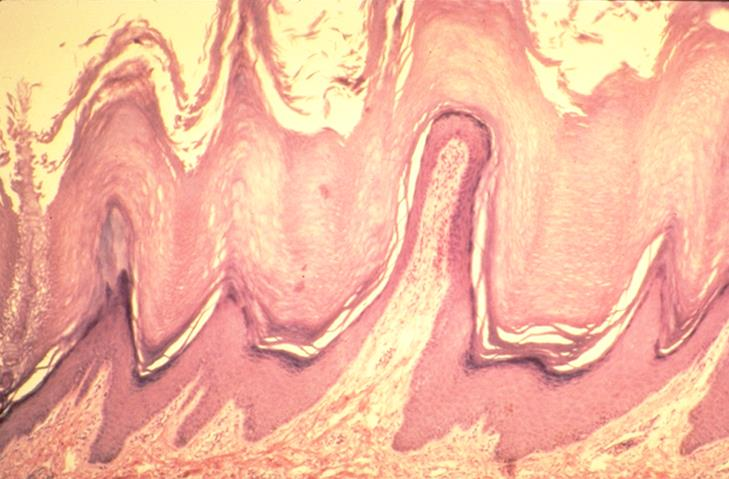
basal layer of the epithelium
where do mitoses for cell replacement occur in stratified squamous epithelium
protective function
with what function is stratified squamous epithelium associated
cross section of the urinary bladder; transitional epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
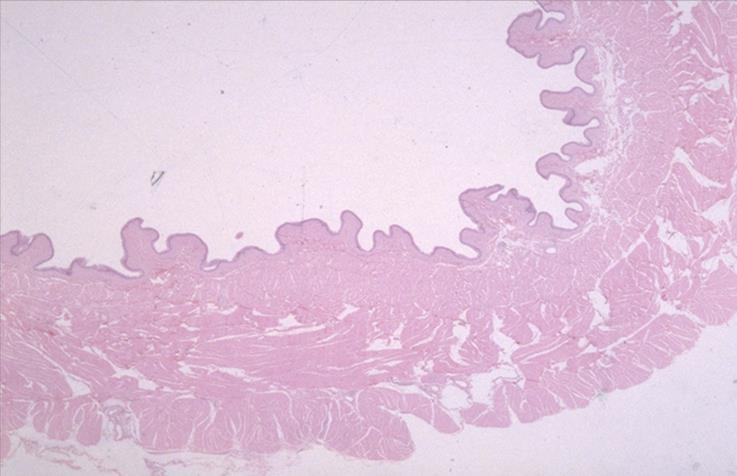
mucous membrane of the urinary bladder; transitional epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
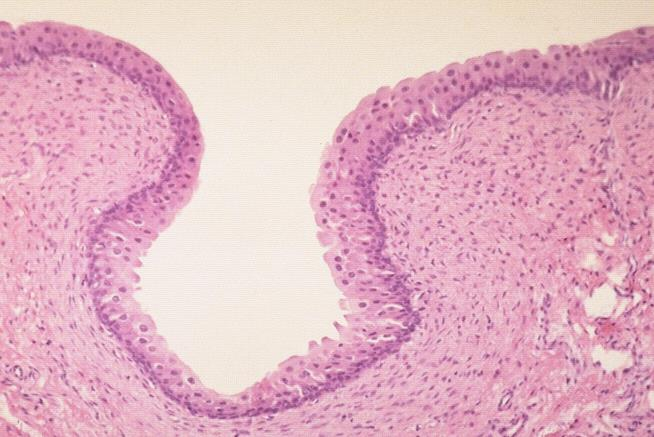
urinary bladder; transitional epithelium
what is the specimen and epithelial tissue shown
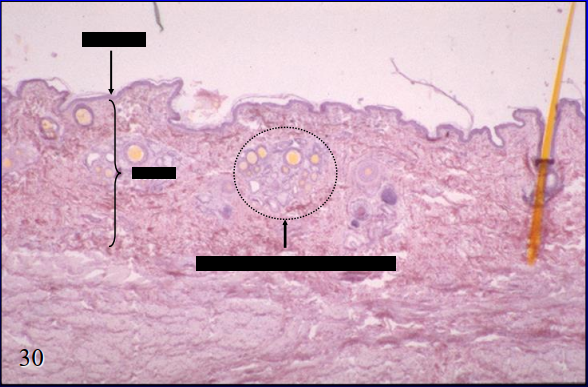
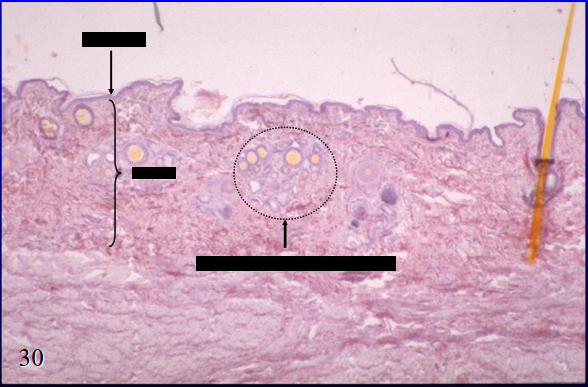
skin side of canine lip
arrow - epidermis
bracket - dermis
circle - skin glands
what is the specimen shown and its specific parts
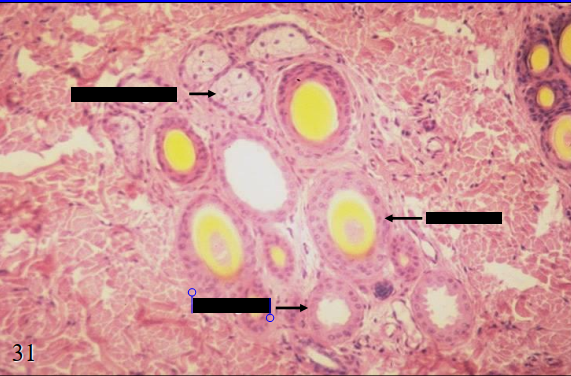
skin glands of the skin side of the canine lip
sebaceous gland
hair follicle
sweat gland
what is the specimen shown and identify the parts
left - sebaceous gland
right - sweat gland
identify the left and right part
sebaceous gland
which gland secrete by the holocrine method
sweat gland
which gland secrete by the apocrine method
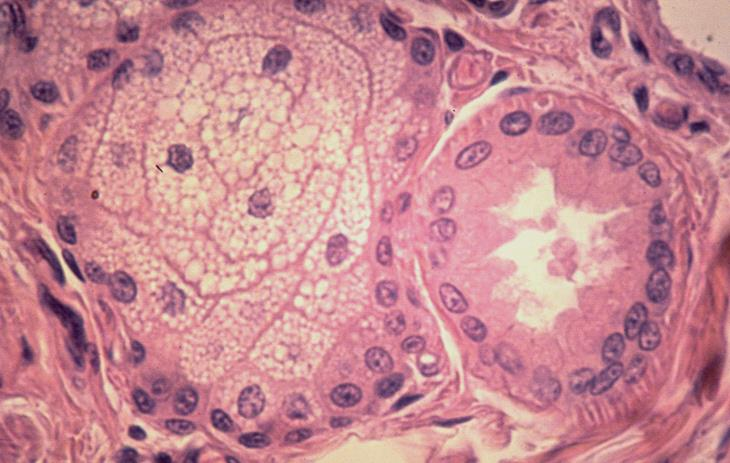
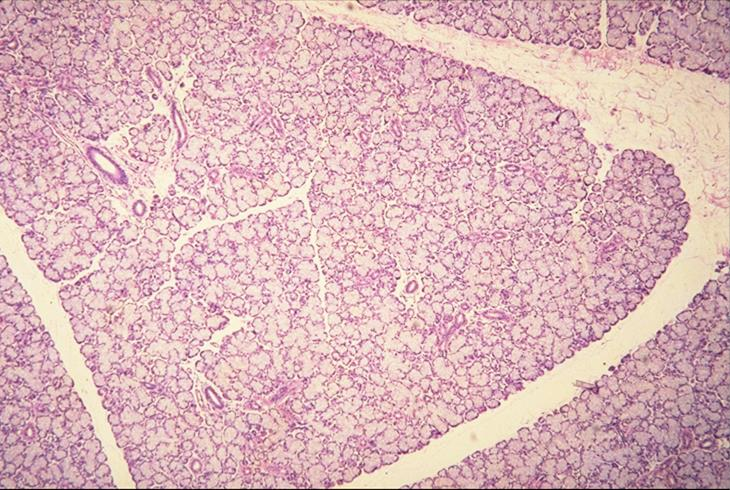
mandibular salivary gland
what is the specimen shown
secretory acini of the mandibular salivary gland
what are the parts surrounded by the black dots
upper - mucous cells
lower - serous cells
right - mucoserous acini
what are the parts surrounded by the white dots
merocrine method of secretion
what method of secretion does mucous and serous secrete by
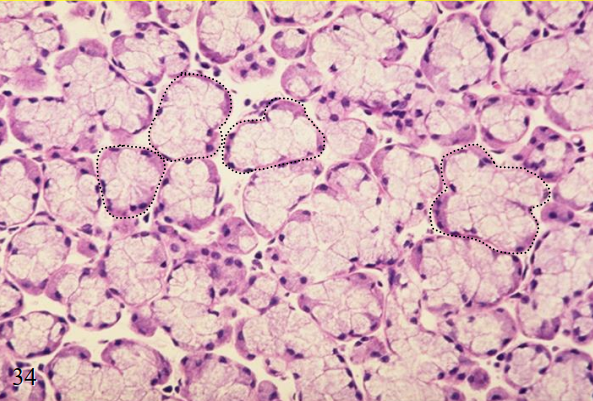
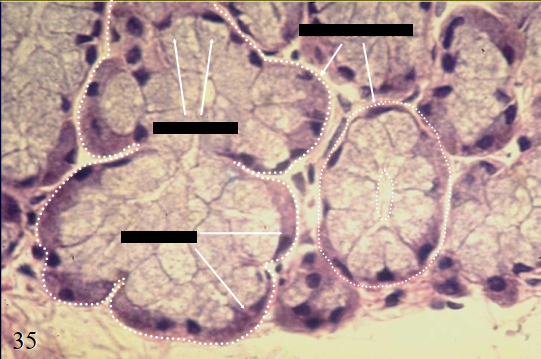
secretory acini of the pancreas
what is the specimen shown
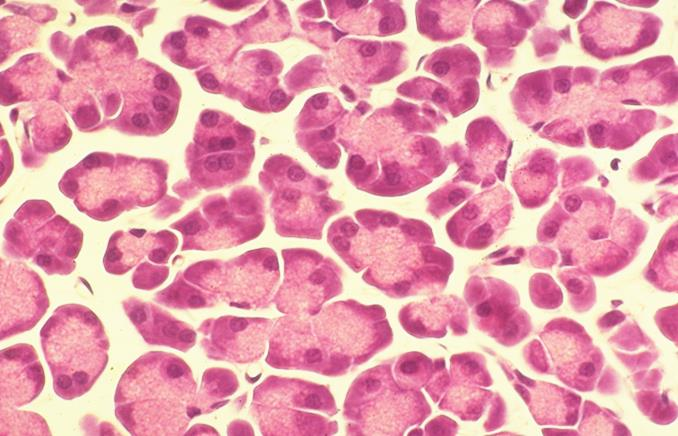
serous types of secretion
merocrine method of secretion
the pancreatic acini produce 1. what type of secretion and 2. secrete through what method
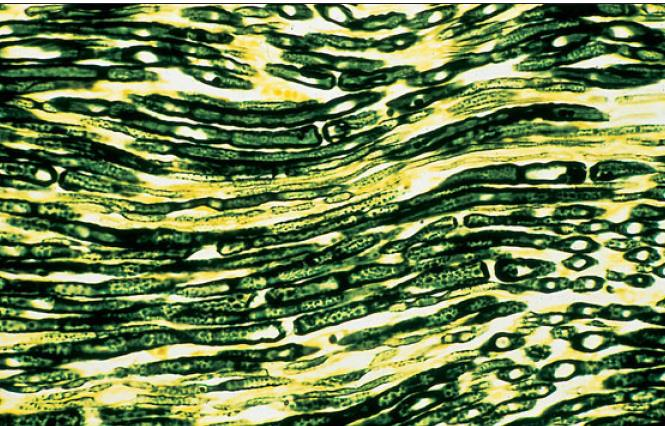
teased loose connective tissue
upper - vein
lower - artery
what is the specimen shown and its parts
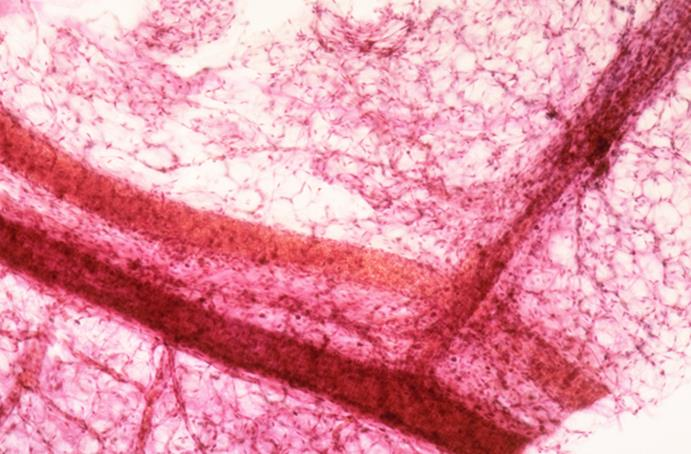
teased loose connective tissue
what is the specimen shown
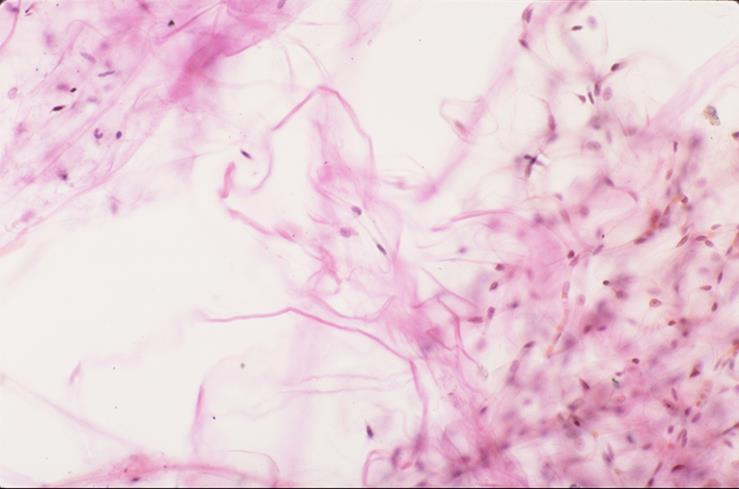
teased loose connective tissue:
macrophage
fibroblast
collagen fiber
what is the specimen shown and its parts
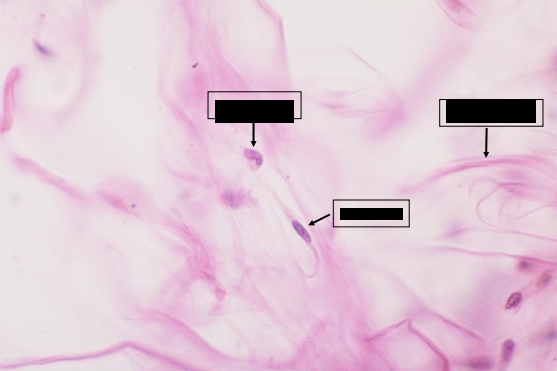
fibroblast
responsible for the synthesis of the extracellular matrix of connective tissue (fibers, ground substance)
primarily responsible for the regenerative capacity of many tissues, ex. healing of surgical incisions
main cell type involve in the repair when spaces left after injury to tissues, whose cells do not divide, are filled by connective tissue which forms a scar
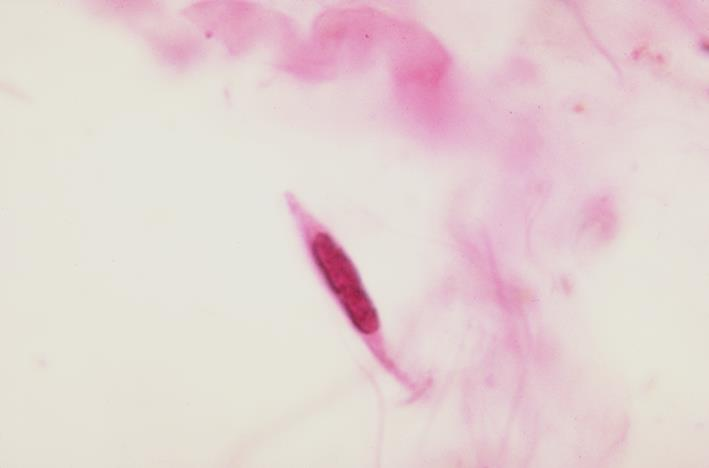
fibroblast
identify the specimen shown
it is responsible for the synthesis of the extracellular matrix of connective tissue (fibers, ground substance)
what is the function of fibroblast
they are primarily responsible for the regenerative capacity of many tissues, ex. healing of surgical incisions. spaces left after injury to tissues whose cells do not divide are filled by connective tissue, which forms a scar. the main cell type involved in this repair is the fibroblast
what purpose do fibroblast serve in wound healing?
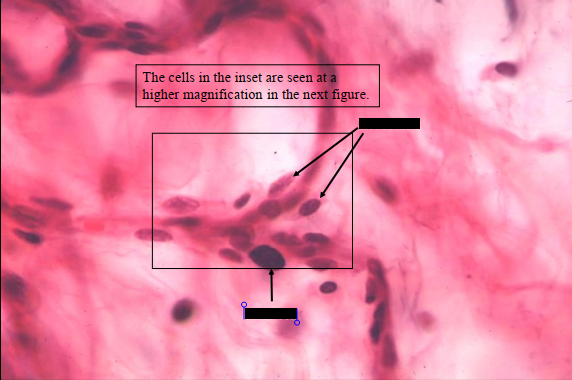
fibroblasts
mast cells
identify the parts of the specimen shown in the slide
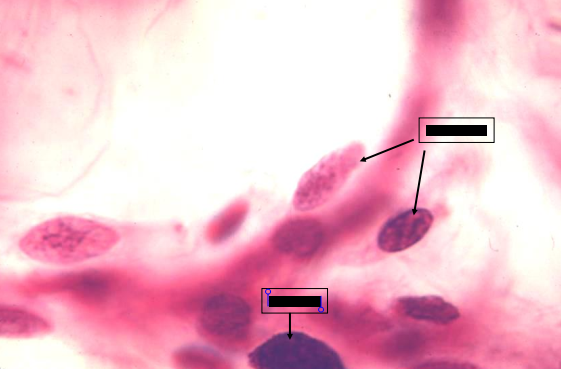
fibroblasts
mast cells
identify the parts of the specimen shown in the slide
fibroblast
have oval nuclei and pale cytoplasm
nucleus may appear euchromatic (pale) or heterochromatic (dark)
mast cells
what is the specimen shown
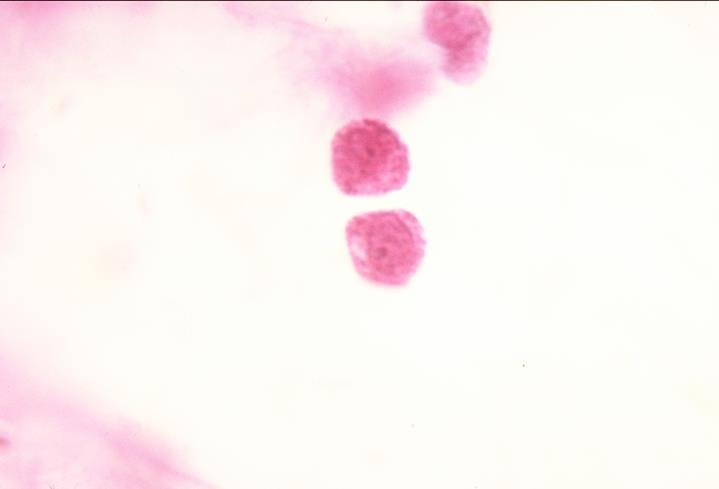
mast cells
the cells contain dark basophilic granules which also stain metachromatically
the granules contain the chemical mediators of the inflammatory response:
histamine
heparin
eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis
what do mast cells granules contain
upper - small artery
lower - blood vessels
mast cells
identify the parts of the specimen shown, what are the cells present?
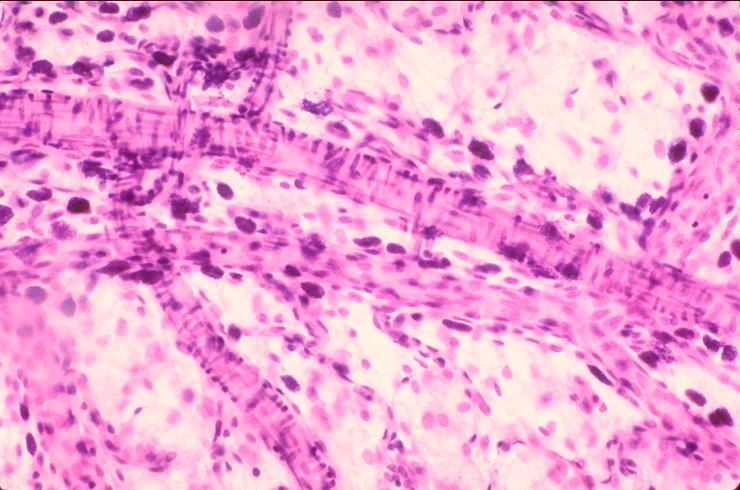
mast cells in the perivascular connective tissue
what is the specimen shown
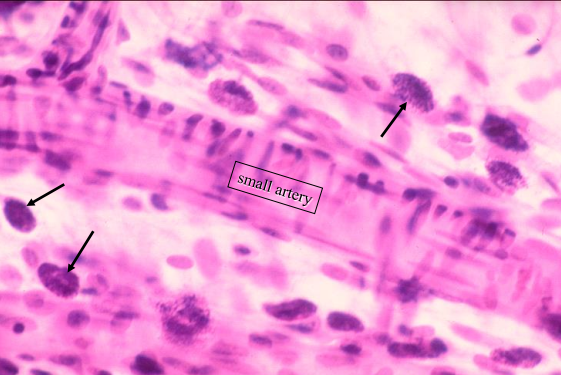
left - blood vessel
arrows - mast cells
upper and lower right - adipose cells
identify the parts of the specimen shown
adipose cells
large cells that appear empty and contain large lipid droplets which were extracted during tissue preparation leaving a large vacuole
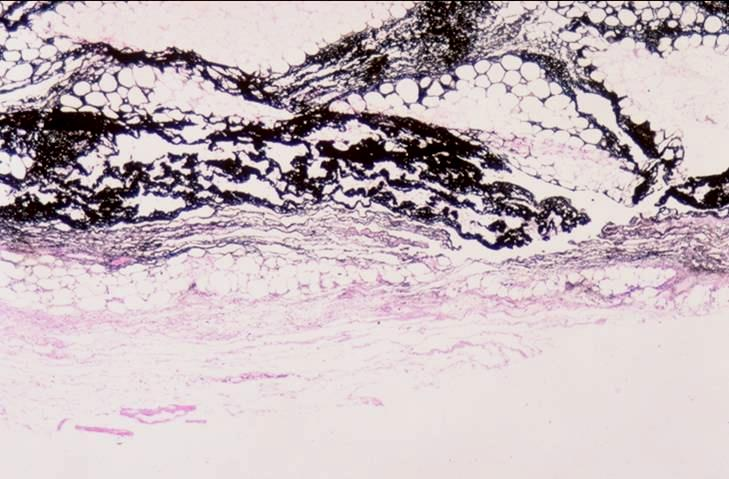
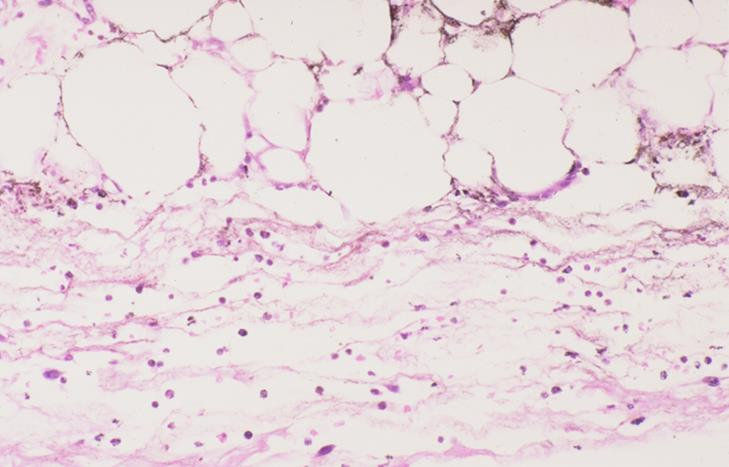
loose areolar connective tissue of canine inguinal region; india ink
what is the specimen shown and staining technique used
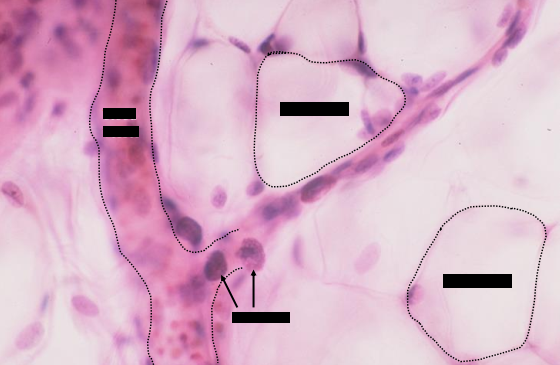
upper - adipose cells
lower - connective tissue cells (mostly inflammatory)
identify the parts of the loose connective tissue
neutrophils
macrophages
identify the inflammatory cells present in the loose connective tissue
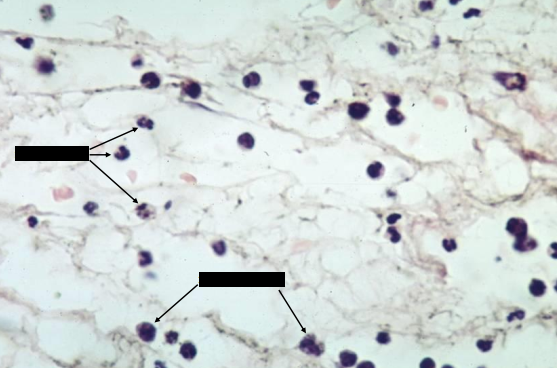
neutrophil
macrophages
identify the inflammatory cells present in the loose connective tissue
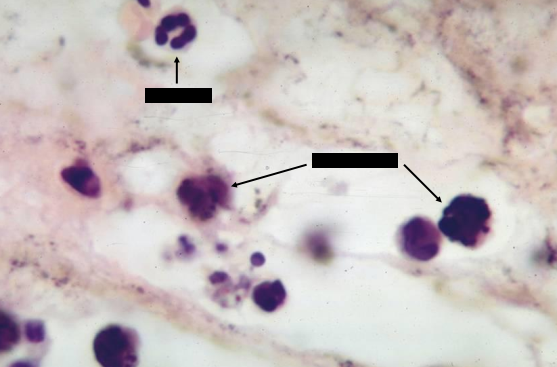
macrophages
have phagocytosed carbon particles (of india ink), thus, their cytoplasm are filled with black granules
neutrophils
cells with lobated nuclei
first to migrate into an inflammatory site
also phagocytic
macrophafe
neutrophils
identify the inflammatory cells present in the loose connective tissue
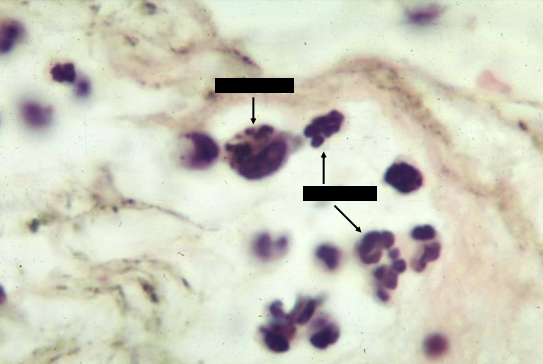
lymphocytes
identify the inflammatory cells present in the loose connective tissue
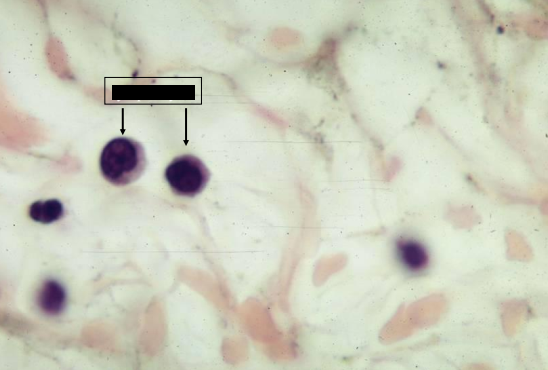
lymphoid cells
also appear in an inflammatory site but at a later time
can be identified by a dark round nucleus, which may be indented, surrounded by a scary amount of cytoplasm
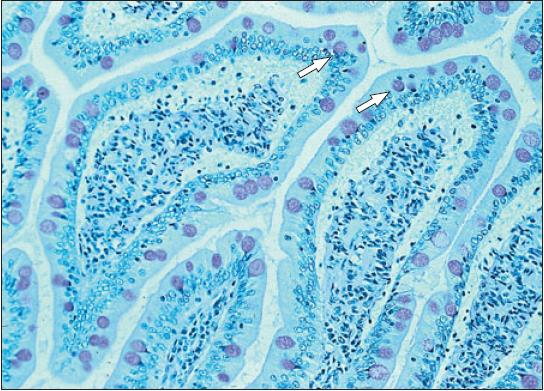
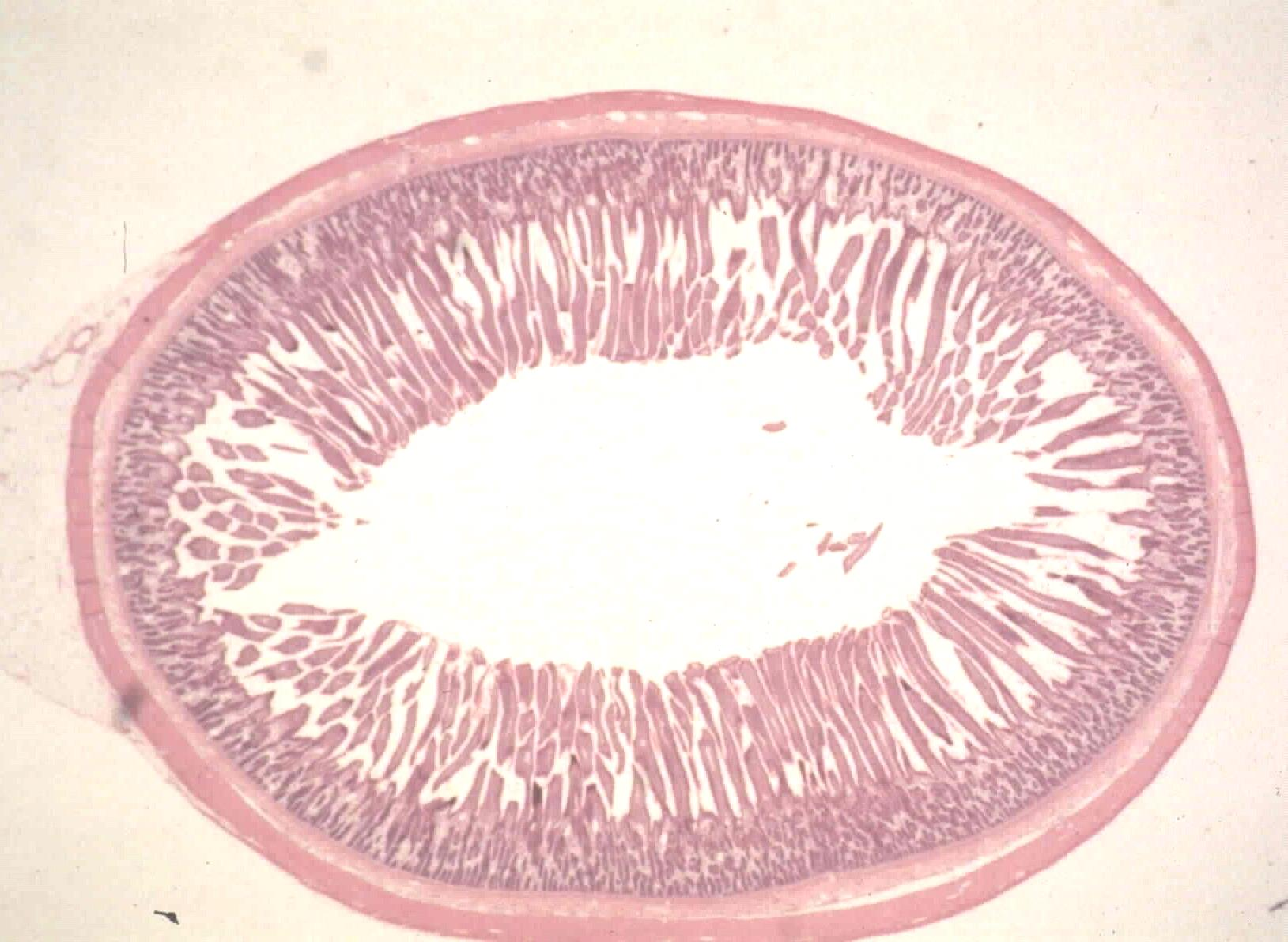
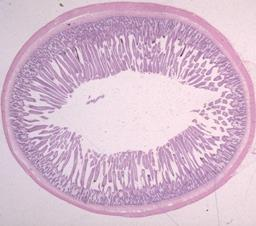
jejunum of canine
what is the specimen shown
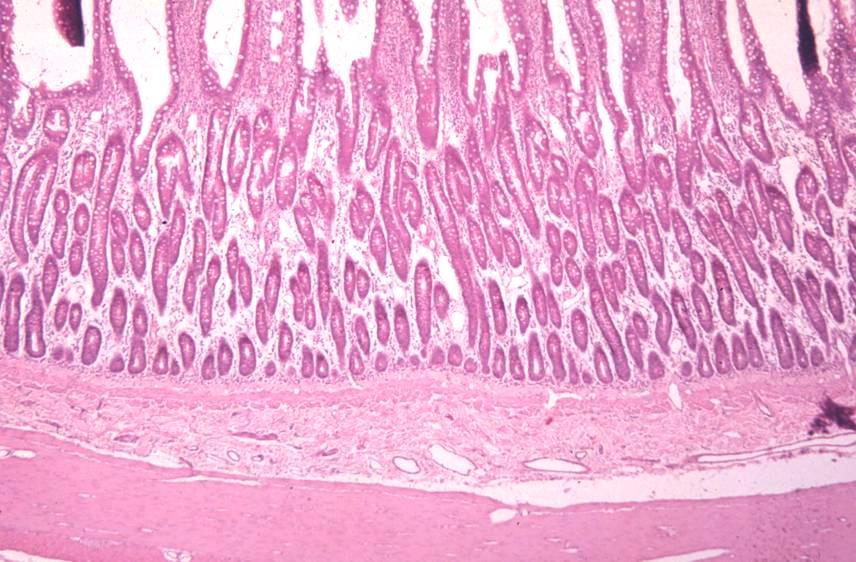
core of the villi of the small intestine of a canine
what is the specimen shown
tunica mucosa of the small intestine of a canine
lamina propria
crypts of lieberkuhn
what is the specimen shown and its parts
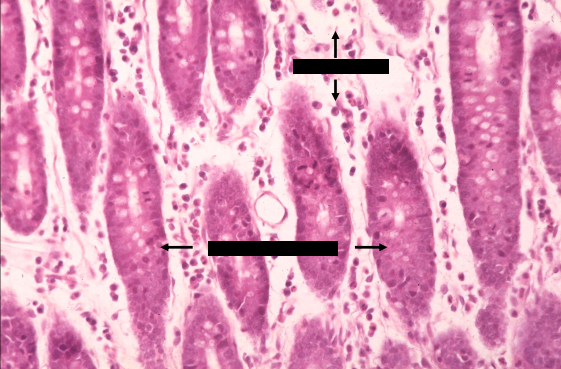
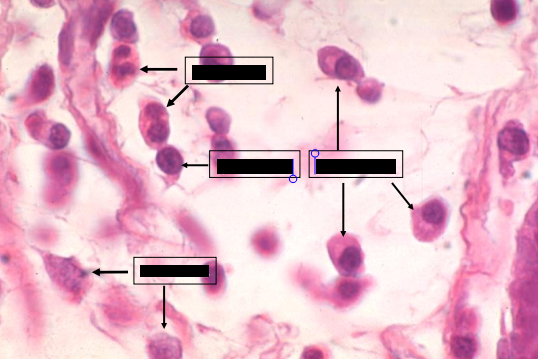
upper arrows - eosinophils
lower arrows - plasma cells
brackets - lamina propria
left and right - crypts of lieberkuhn
identify the parts
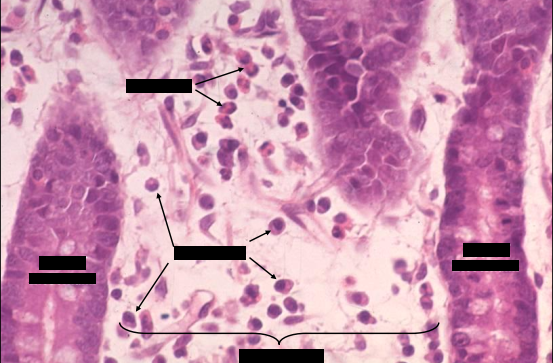
upper - eosinophils
middle left - lymphocyte
middle right - plasma cells
lower - fibroblast
identify the parts