BU288 Final
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
Five bases of individual power
legitimate power
reward power
coercive power
referent power
expert power
Legitimate power
Power derived from a person's position or job in an organization
based on level in organizations hiearchy
Reward power
Power derived from the ability to provide positive outcomes and prevent negative outcomes
Corresponds with positive reinforcement
Coercive power
Power derived from the use of punishment and threat
Generally ineffective and can provoke considerable employee resistance
Referent power
Power derived from being well liked by others (results in commitment)
Available to anyone in an organization who is well liked
Expert power
Power derived from having special information or expertise that is valued by an organization
(results in commitment)
Of all the bases of power, it is most consistently associated with employee effectiveness
Employee responses to the bases of power
Coercive power -> resistance
Reward power -> compliance
Legitimate power -> compliance
Expert power -> commitment
Referent power -> commitment
Ways to achieve power - activities to do
Extraordinary activities
Visible activities
Relevant activities
Ways to achieve power - cultivating the right people
Right people can include:
-Outsiders
-Subordinates (backed by cohesive team)
-Peers (favours can be asked from former associates)
-Superiors (mentors provide special info_
Empowerment
Giving people the authority, opportunity, and motivation to take initiative to solve organizational problems
Fosters job satisfaction, improved self-efficacy, and org. commitment, OCBs
Needs right amount of power to be effective
Influence tactics
Convert power into actual influence over others
-Assertiveness
-Ingratiation (flattery/polite)
-Rationality
-Exchange (doing/trading favours)
-Self Promotion
Self-promotion and ingratiation effective in job search/interviews
Ingratiation/rationality used for superiors
Need for Power (n Pow)
Need to have strong influence over others - personality characteristics
When it's responsible and controlled, its negative properties are not observed
Institutional Managers
Most effective type of managers, use their power for the good of the organization
-Adopt a participative or "coaching" leadership style
-Relatively unconcerned with how likeable they are
Personal power managers
Use their power for personal gain
Affiliative Managers
More concerned about being liked than with exercising power
Strategic Contingencies
Critical factors affecting organizational effectiveness that are controlled by a key subunit
Conditions:
-Scarcity (secure key scarce resources)
-Uncertainty (coping with it)
-Centrality (influence most subunits)
-Substitutability (not replaceable)
Organizational Politics
The pursuit of self-interest in an organization, whether it corresponds with organizational goals or not
Dimensions of Organizational Politics
Where/when is it most likely to occur:
-Middle and upper management
-Subunits w/ vague goals and complex tasks
-Scarce resources, uncertainty and important issues
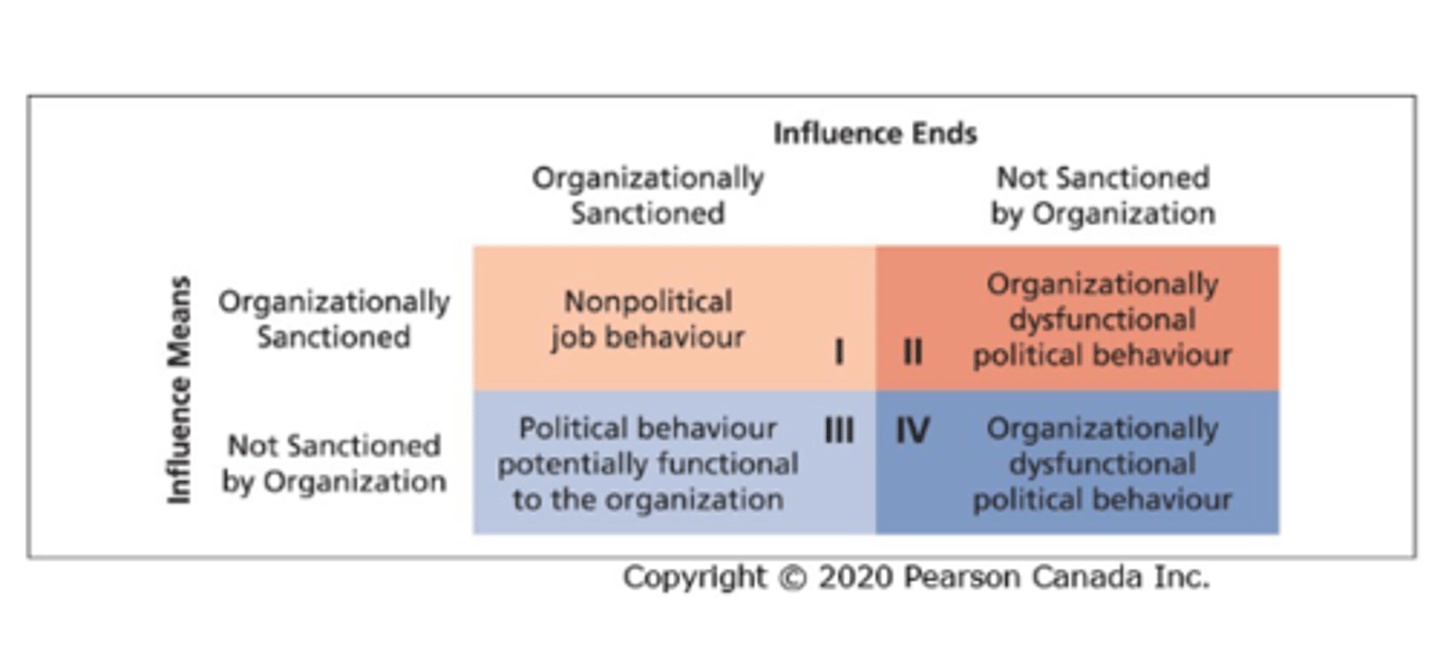
Impacts of Organizational Politics
-Highly political climates result in lowered job satisfaction, commitment, and org. citizenship
-Takes a toll on the performance of older workers compared to younger workers, likely due to stress
Political skill
The ability to understand others at work and to use that knowledge to influence others to act in ways that enhance one's personal or organizational objectives
Four facets of political skill
Social astuteness (ability to "read" others)
Interpersonal influence (put others at ease)
Networking ability
Apparent sincerity
Networking
Developing informal social contacts to get their support when necessary
Methods
- Maintaining contacts (thank-you notes)
-Socializing
- Engaging in professional activities
- Increasing internal visibility (high profile work projects, important committees and task forces)
Networking insights
-Those high in self-esteem and extraversion are more likely to engage in it
-Increased in importance as people are more self-reliant to plot future careers
-Being central in a large network provides power if it is diverse and has many with power
Machiavellianism
A set of cynical beliefs about human nature, morality, and the permissibility of using various tactics to achieve one's ends
High Machs
- More likely to lie or deceit to achieve desired goals (ends justify means)
-Most effective in face-to-face/emotional circumstances
Reactive Politics
Concerns the defence or protection of self-interest
Methods:
-Avoiding actions (buck passing, stalling)
-Avoiding blame (buffing, scapegoating)
Ethics
Code of moral principles and values governing behaviour with respect to what is right and wrong
Common themes of ethical behaviours
Honest communication (advertise honestly)
Fair treatment (equitable pay)
Special consideration (long-term employees)
Fair competition (avoid price fixing)
Responsibility to organization (not acting in self-interest)
CSR
Respect for law (follow labour laws)
Bounded Ethicality
Psychological process by which people come to engage in behaviour that violates their own ethical standards
-People prone to ethical blind spots
-If things are going well, less inclined to be alert for ethical volations
Two main causes of Unethical Behaviours
"bad apple"- personality causes
"bad barrel"- situational causes
Bad Apple - Personality Causes of Unethicality
Personality
- External locus of control
- Strong economic values
Need for power
Machiavellianism
Risk taking
Moral identity
Bad Barrell - Situational Causes of Unethicality
Gain
- Anticipation of reward/bonus
- If underpaid significantly
Extreme performance pressure
- Become self-protective in the face of challenging goals
Role conflict
- Reward system can heighten conflicts of interest
Strong organizational identification
Competition
- Both situations with extreme high/low competition
Organizational and industry culture
- Conduct of peers can influence unethical behaviour
- Corporate codes/cultures can punish or reward unethical behaviour
Deaf ear syndrome
Inaction or complacency of organizations in the face of charges of sexual harassment
Strategies to make better ethical decisions
Identify the impact of the decisions
- Cost/benefit analysis
- Stakeholders
Organizational systems
- Disclosure mechanisms reward ethical actions and punish unethical actions
- Code of ethics/committee
- Training programs
Choices
- What other alternatives
Ethical Behaviour Decision Criteria
Utilitarian
- If delivers the greatest good to the greatest number of people
Rights
- Respects the fundamental rights shared by humans (charter, free speech)
Justice
- If it is fair and impartial in its treatment of people
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ethical Behaviour Decision Criteria
Utalitarian
+ Promotes efficiency, productivity
- Difficult to apply values that aren't easily quantifiable
Rights
+ Protects individuals freedom and privacy
- Creates overly regulated society
Justice
+ Protects interests of under represented and less powerful
- Definition of fairness is ambiguous
Signaling Theory - Ethics
Ethical leaders promote ethical conduct through communication, reinforcement, and decision making
Positively related to:
- Subordinate ethical behaviour
- Job satisfaction
- Organizational commitment
Negatively related to:
- Subordinate work stress
- Turnover
What organizations can change
Goals and strategies
Technology
Job design
Structure
Processes
Culture
People
Three stages of org. change
Unfreezing
Changing
Refreezing
Unfreezing
Recognition that current state of affairs is unsatisfactory
Methods:
-Employee attitude surveys
-Customer surveys
-Accounting data
Change
Implementation of a program/plan to move org. or members to more satisfactory state
People must have capability, opportunity, and motivation to change
Refreezing
Conditions that exist when newly developed behaviours, attitudes, or structures become an enduring part of the organization
Organizational Learning
The process through which an organization acquires, develops, and transfers knowledge throughout the organization
Two methods of organizational learning
Knowledge acquisition
- Acquisition and interpretation of exisiting knowledge external to org.
Knowledge development
- Learning occurs when org. members share experiences and knowledge/when new knowledge is distributed
Learning Organization
Organization that has systems and processes for creating, acquiring, and transferring knowledge to reflect new knowledge and insights
Failure is a more important determinant - stimulates greater information search/acquisition
Four dimensions of a learning organization
Vision/support
- Leaders communicate clear vision of org. strategy and goals
Culture
- Culture for continuous learning
Learning systems/dynamics
- Employees challenged to problem solve
Knowledge management/infrastructure
- Systems to acquire, store, distribute knowledge
Problems that occur in org. change
Diagnosis
Resistance
Evaluation and institutionalization
Causes of resistance
-change is resisted by those at whom it is targeted (both unfreezing and change)
How can organizations deal with resistance
- Good communication if there are misunderstandings
-Involving those impacted by change in the change process
-Transformational leaders are good at overcoming change
Resistance and time
Champions - highly supportive of change
Converts - converted over time
Defectors - defect change over time
Doubters - highly negative of change
Evaluation and Institutionalization
Organizations are notorious for poorly evaluating "soft" change programs (when institutionalized = organizational system)
Possible to do a thorough evaluation with regarding the following outcomes in respect to change:
- Reactions
- Learning
- Behaviour
- Outcomes
Factors contributing to organizational conflict
-Group identification and intergroup bias (in/out group)
-Interdependence
-Differences in power, status, and culture
-Ambiguity (goals, jurisdictions, or performance criteria)
-Scarce resources
Types of Conflcit
Relationship conflict
Task conflict
Process conflict
Relationship conflict
Interpersonal relationships - has nothing to do with the task at hand
(ex. personality clashes)
Task conflict
Disagreements about the nature of work to be done
(ex. differences in goals/technical matters)
Some amounts of task conflict might be beneficial for performance
Process conflict
Disagreements about how work should be organized and accomplished
(ex. disagreements about responsibility, authority, or resource allocation)
Five modes of managing conflict
Avoiding
Accommodating
Competing
Compromise
Collaborating
Adam, Ate, Cheese, Crackers, and Chips
Avoiding
Low assertiveness of one's interests and low cooperation with the other party
-Limited effectiveness: doesn't really change the situation
When to use:
-Opponent is powerful and hostile
-Issue is trivial/lacking information
Accommodating
Low assertiveness of one's interests while cooperating with the other party
-Seen as a sign of weakness
When to use:
-When you are wrong/want to build good will
-When the issue is more important to the other party
Competing
Maximizes assertiveness and minimizes cooperation
-Frame conflict in win-lose terms
When to use:
-You have a lot of power
-You will not have to interact with the other party in the future
Compromise
Combines intermediate levels of assertiveness and cooperation
-Doesn't result in the most creative response to conflict
When to use:
-Conflict stemming from scarce resources
-Good fallback if other strategies fail
Collaborating
Maximizes assertiveness and cooperation
- Integrative (win-win) agreement
When to use:
-When parties share information together
Constructive conflict
Most likely to promote good decisions and positive organizational change
- Parties agree the benefits outweigh the costs
Conflict Simulation
Increasing conflict to motivate change
-Causes can vary however can be manipulated by managers to achieve change
Stressor
Environmental events/conditions with the potential to induce stress
Stress reactions
The behavioral, psychological, and physiological consequences of stress
How to reduce:
Directly dealing with the stressor (decreases chances of reoccurrence)
Stress
Psychological reaction to demands in stressors, makes a person feel tense or anxious
Becomes a problem when it leads to high levels of anxiety and tension
3 Key personality traits impacting stress
Locus on control
-Externals more likely to feel anxious
-Internals are more likely to confront stressors
Type A behaviour pattern
-People who are aggressive/hostile are more likely to exhibit elevated blood pressure and heart rate
-Easily triggered by frustrating, difficult, or competitive events
Negative Affectivity
-People high in NA report more stressors, are more sensitive to existing stressors
-Provoke stress through negativity and gravitate to stressful jobs
Stressors in Organizational Life
Executive/Managerial Stressors
- Role overload, heavy responsibility
Operative-Level Stressors
- Poor physical conditions, poor job design (boring)
Boundary Role Stressors
-Boundary between interaction with organization members and people outside organization (role conflict)
General Stressors
-Conflict, work-family conflict, role ambiguity
Role Overload
When one must perform too many tasks in too short of a time period or work too many hours
Burnout
Syndrome made of emotional exhaustion, cynicism, and low self-efficacy
-Those with high self-esteem, conscientiousness, report less burnout
-Women are more likely to report emotional exhaustion
Consequences:
- Pursue new occupation or job
- Exhibit poor performance/absenteeism
Work Engagement
a positive work-related state of mind that is characterized by vigor, dedication, and absorption
Vigor (Work Enagagement)
High levels of energy/mental resilience at work
Absorption (Work Engagement)
Being fully concentrated and engrossed in your work
Job Demands Resource Model
Specifies how job demands (ex. role conflict, role ambiguity) cause burnout and job resources cause engagement
High job resources = work engagement
High job demands = exhaust employees physically and mentally (burnout)
Job Demands
Physical, physiological, social or organizational features of a job requiring sustained physical or psychological effort
Job resources
Features of a job that help achieve work goals, reduce job demands, and stimulate personal growth, learning, and development
Abusive Supervision
When managers engage in the bullying of subordinates - differential power is most apparent
Damaging to employee well-being - tied to subordinate health problems
Dimensions of techno-stress
Techno-overload
- Too many people have access to us
Techno-invasion
- Work demands have invaded non-work time
Techno-uncertainty
- Technology is changing too often and policy is unclear
Techno-complexity
- Tech brings complication into everyday work
Techno-insecurity
- Others are more adept at using and adapting to new technology
Three reactions to organizational stress
Behavioral reactions
Psychological reactions
Physiological reactions
Behvaioural reactions to stress
Overt activities used to cope with stress
Examples
- Problem solving
- Seeking social support (from others)
-Using addictive substances
-Withdrawal and presenteeism
-Performance changes
Psychological reactions to stress
Reacting with emotions and thought processes rather than overt behaviour
-Common reaction is to use defence mechanisms
Hindrance Stressors
Stressors that damage goal attainment and performance
Presenteeism
The extent that people go to work ill
-Is stress-related in nature
-Depression, bullying, and high job demands are related to presenteeism
Defence mechanisms
Psychological attempts to reduce anxiety associated with stress
-Useful to temporarily reduce anxiety, but not chronically reduce stress
Examples:
Rationalization
Projection
Displacement
Reaction formation
Compensation
Physiological reactions to stress
Work stress is associated with:
-Elevated blood pressure
-Elevated cholesterol
-Elevated pulse
-Onset of various diseases (ill effects on immune system)
Organizational Strategies to Manage Stress
Job redesign
- Enriching operative level jobs
Family friendly human resource policies
-Ex. corporate daycare centres, flexible hours, supportive supervision
Stress management programs
-Ex. meditation, mindfulness practices
Work-life balance, fitness, and wellness programs
-Ex. fitness improves mood, job satisfaction and performance
Three types of communication by strict chain of command
Downward communication (top of org. to bottom)
Upward communication (bottom of org. to top)
Horizontal communication (between depts. or functional units)
Deficiencies in the chain of command
Informal communication
Filtering (tendency for a message to be watered down/stopped)
Slowness (horizontal communication can be especially slow)
The Mum Effect
The tendency to avoid communicating unfavorable news to others
-More likely when the sender is responsible for the bad news
-Applies to both subordinates and managers
Grapevine
An organization's informal communication network
-Cuts across formal lines of communication
-Organizations often have several grapevine systems
Pros
-Keeps employees informed about important org. matters
Cons
-Becomes a problem when it becomes a rumour pipeline
Jargon
Specialized words used by job holders or members of an organization
-Can be a barrier to communication in departments like sales/eng.
-Can also be a barrier to new members/those outside the org. or profession
Non-Verbal Language of Work
Body language
- The extent to which the sender likes and is interested in the receiver (ex. face receiver, maintain eye contact, smiling)
Props, artifacts, and costumes
-Office decor and arrangement
-Clothing
Gender differences in communication
Getting credit
- Men more likely to seek credit for good they have done
Confidence and Boasting
- Men are more boastful about themselves/capabilities
Asking questions
- Men are less likely to ask questions because it can put in one-down position
Apologies
-Avoided by men as it is a sign of weakness
Feedback
- Women buffer criticism with initial praise; men are blunt
Ritual Opposition
-Men use it as a way to exchange ideas
-Men most concerned with power: use it as a way to position in a one-up situation
-Women more concerned with rapport building (avoid putting down others)
Cross Cultural Communication
Language differences
Non-verbal communication (facial expressions/gestures vary across cultures)
Etiquette and politeness
Social conventions (ex. North Americans value directness/privacy)
Cultural context
Cultural Context
Cultural information that surrounds a communication episode
High-context culture: message is strongly influenced by context (literal interpretation is false)
Low context culture: messages are interpreted more literally
Differences in context across cultures
High context cultures
- People want to know about you and your company
- Not a strong desire to get to the point quickly
-Age and seniority are highly valued
Low context cultures
- Favour detailed business contracts
-Meaning is in the message
Information richness
the potential information-carrying capacity of a communication medium
-The degree communication is two-way in real time
-The extent to which parties can receive non-verbal/para-verbal (tone) cues
Less routine communication (important decisions) requires richer networks
Computer Communication/Social Media
Face-to face communication is highest in richness
Slower development of trust using computer-mediated communication
-People are less likely to disclose personal info
-Electronic media is open to misinterpretation (lack of non-verbal cues)
Email is especially prone due to lack of being synchronous
Basic Principles of Effective Communication
Take the time
Be accepting of the other person
Do not confuse the person with the problem
Listen actively
Say what you feel
Give timely and specific feedback
Principles for cross-cultural communication
Assume differences until you know otherwise
Recognize differences within cultures
Watch your language (and theirs)
(ex. speak slowly/clearly if not very fluent in English)